A diseased liver causes a number of complications. One of the most dangerous is encephalopathy. If treatment is started in time, the pathology can be stopped and reversed. But to do this, you need to notice the violation in time and seek help. Hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis affects patients with severe organ damage, with clinical signs of obstructive jaundice.
Do you think fatigue could be a sign of hepatic encephalopathy?
Not really
At the initial stage, survival rate reaches 100%. If help is not provided on time, the person falls into a coma, the probability of death is 80%. The disease affects the ability to think clearly; close relatives should know the symptoms and course. Much depends on their timely intervention in the fate of a loved one.
What is the disease
The term hepatic encephalopathy should be understood as a complex of signs of brain damage due to functional liver failure. This condition also occurs due to poisoning of brain cells by various toxic substances. In everyday life, people are poisoned with substances containing industrial alcohol.
Brain damage develops acutely as a result of a viral liver infection or poisoning by chemical toxins used in industry.
With hepatic encephalopathy, symptoms and treatment vary depending on the stage of the disease. Poisoning of the brain manifests itself as mental, intellectual, and personality changes.
Forms of encephalopathy
Depending on the severity, there are 3 types of disease:
- The acute form is a consequence of viral hepatitis, surgical shock, and drug poisoning, which lead to necrosis of liver cells. The rapid appearance of cerebral edema leads to the patient falling into a coma. The acute form ends in death in most cases.
- Portocaval hepatic encephalopathy develops in chronic liver diseases. The cause of brain poisoning is a violation of the outflow of blood from the intestines, bypassing the liver. This happens with infections, bleeding from the stomach or intestines, or excess food high in protein. Brain poisoning in these cases is associated with the accumulation of ammonia. Manifestations of encephalopathy include confusion, spatial disorientation, and mental abnormalities.
- The chronic form of the disease is a consequence of liver diseases, in which toxic factors are the accumulation of manganese in brain cells. This occurs when the excretion of the mineral by the biliary tract is impaired. The chronic form is manifested mainly by mental abnormalities. In severe cases, patients suffer from dementia and lose orientation in space. A person leaving home is unable to find his way back. The patient develops tremors of the limbs until the development of Parkinson's disease.
In some cases, symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy appear without damage to hepatocytes. After eliminating the cause of the disease, the person’s condition returns to normal.
Symptoms of encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis
There are no clear symptoms that can be used to confidently indicate the development of brain damage. If you know a problem with the exocrine gland, pay attention to the state of mental functions. Contact a neurologist or hepatologist as soon as you notice that:
- You have a hard time concentrating.
- They began to make mistakes in their professional activities. The seamstress produces crooked stitches, the Russian language teacher makes spelling mistakes.
- Trembling appeared in my hands.
- You break into screaming with or without reason. The people around you irritate you.
- I constantly want to sleep. Or vice versa, a state of euphoria. The desire to do general cleaning at 3 am is a typical manifestation of this.
The presence of 2 manifestations, in any combination, is a reason to go to the doctor. Not necessarily, after diagnosis a diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy will be made. There are many reasons, but such symptoms cannot be left without attention and correction.
This is interesting: Cryptogenic cirrhosis of the liver: causes, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
Hepatic encephalopathy goes through 4 stages of development. The lower the stage, the greater the chance of recovery.
- The manifestations are similar to overwork, the consequences of prolonged stress. Disturbances in the sleep-wake cycle, mood swings, deterioration of memory and attention. Speech becomes poorer and sometimes confused.
- Symptoms intensify 2–3 times. Irritability turns into aggression. A person stops paying attention to his appearance. Poorly controls behavior. Sometimes he commits unmotivated antisocial actions. The hands are shaky.
- The patient is disoriented. Speech and consciousness are confused. Reflexes characteristic of newborns and children under 1 year of age appear.
- Hepatic coma. Reactions to pain and light gradually disappear. The chance of survival does not exceed 20%
Causes of the disease
In most cases, hepatic encephalopathy is a severe clinical manifestation of liver disease. Depending on the factors that provoke poisoning, there are several types of this condition with an acute or chronic course.
Causes of hepatic encephalopathy:
- Viral hepatitis is accompanied by inflammation of hepatocytes, which are unable to neutralize toxins produced in the body.
- Liver cancer is characterized by tissue degeneration, as a result of which it loses its main function - to neutralize harmful substances.
- Drug intoxication directly turns off the functional ability of the liver.
- Intestinal neurotoxins containing ammonia are poisonous to the brain. Under normal conditions, ammonia is processed in the liver to form urea, which is excreted by the kidneys. If there is an excess of ammonia, most of it does not even enter the hepatic bloodstream. Circulating throughout the body, it reaches the brain, where it damages cells.
- Liver cirrhosis, in which normal hepatocytes are replaced by rough connective tissue.
- Chronic constipation promotes the proliferation of pathogenic microflora that release toxins.
- Alcohol abuse causes the death of liver and brain cells.
- Drug use.
- Surgical shock.
Hepatic encephalopathy is accompanied by changes in blood composition and disturbances in water and electrolyte balance. Processing of substances slows down. As a result, excess ammonia and other toxic metabolic products cause brain swelling.
Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis
The brain is poisoned by toxins that urgently need to be removed from the body. For this purpose, doctors prescribe:
- Cleansing enema.
- Sorbents.
- Preparations containing lactulose. This promotes regular bowel cleansing.
To nourish brain cells, use:
- Glucose. Administered intravenously. The substance nourishes the gray matter. Glucose helps get rid of ammonia and its breakdown products.
- Vitamin complexes.
To normalize the intestinal microflora and stop the growth of pathogenic bacteria, antibacterial drugs are used in combination with probiotics.
Nutrition adjustments involve limiting or eliminating proteins from the diet. This will reduce the amount of ammonia in the blood. Ammonia is a breakdown product of proteins. A healthy liver neutralizes it. In cirrhosis, the function is poorly performed.
The development of encephalopathy indicates ineffective treatment of cirrhosis. The liver needs additional support. Consider a digestive gland transplant.
This is interesting: Nursing care for liver cirrhosis
How does encephalopathy occur?
During the course of the disease, periods are distinguished that are characterized by various clinical changes.
Stages of hepatic encephalopathy:
- in the initial mild period the psyche is not disturbed.
- the second stage is characterized by impaired consciousness, memory, and intelligence.
- at the next stage there are severe mental disorders.
- the next stage is a comatose state in which consciousness is absent and reflexes are not detected.
In hepatic encephalopathy, the stages differ in severity and prognosis. The terminal stage of the condition ends in death in 80% of cases.
General information
Hepatic encephalopathy in liver diseases is not very common, but has a very severe outcome - up to 80% of cases of hepatic coma end in the death of the patient. Hepatologists note an interesting fact: the development of encephalopathy against the background of acute liver failure is almost always a factor that excludes liver cirrhosis in the future. With chronic liver damage, this complication develops much more often than with acute ones; is potentially reversible, but at the same time has a significant impact on the patient’s social activity and ability to work. Pathogenesis and mechanisms of development
Signs of brain poisoning
The symptoms of encephalopathy depend on the nature of the factors that caused the disease. Personality changes are manifested in disturbances of consciousness, speech, intelligence and neuromuscular reflexes.
Signs of hepatic encephalopathy at the first stage:
- At the initial stage, patients are adequate, answer questions correctly, and orient themselves in space and time. Behavior changes towards emotional instability. The rhythm of sleep is shifted - the patient is awake at night and sleeps during the day. His balance is disturbed and his temperature periodically rises. Hemorrhages are noticeable on the skin, and jaundice increases.
- Hepatic encephalopathy of the second stage is characterized by an increase in all signs. Patients suffer from constant sleepiness during the daytime. They experience periodic dizziness and fainting. Speech becomes slurred and slow. When examining the patient, a flapping tremor of the fingers and wrist joint is noted. A significant medical sign of the second stage is a sickly-sweet “liver” odor from the mouth. As symptoms intensify, patients fall into a lethargic state, in which metabolic processes slow down, blood pressure decreases, the pulse is difficult to palpate and the heartbeat is heard. There are no reflexes, and the general state resembles oblivion.
- The third stage is characterized by confused consciousness and mental slowdown. The person is disoriented in space and suffers from a lack of memory. Adding and subtracting prime numbers is a problem for him. Behavior is inappropriate. People in this period are aggressive, commit unconscious actions that they subsequently do not remember. Patients spend most of their time sleeping, have difficulty waking up, and do not make contact. They periodically have seizures. Pain reflexes are preserved. On examination, pronounced jaundice of a dark shade. The liver is reduced in size, lumpy and hard to the touch.
- The final stage is a comatose state in which the person remains unconscious. Patients do not respond to sounds or painful stimuli. The pupils do not react to light. Doctors determine pathological neurological symptoms, stiff neck. Hepatic encephalopathy progresses. On the electroencephalogram, the rhythm slows down and the amplitude of the curve decreases.
Patients in a comatose state die in most cases.
Diagnostic methods
Ultrasound helps determine the extent of liver damage
It is necessary to diagnose hepatic encephalopathy as quickly as possible in order to begin treatment in a timely manner. To do this, you need to determine the cause of this condition, the stage of the disease, and its form.
Before prescribing diagnostic procedures, the doctor will collect anamnesis, clarify all symptoms, their intensity and frequency of occurrence. An anamnesis of the patient’s lifestyle is also of great importance: how often and in what quantities does he drink alcohol, what medications does he take, what chronic diseases does he have. The doctor will also conduct a conversation with the patient’s relatives to find out how much his behavior and condition have changed.
Typically, the following diagnostic methods are recommended for hepatic encephalopathy:
- Blood analysis. A general and biochemical blood test is prescribed. They can identify anemia, inflammation, internal bleeding, and thrombosis. Using biochemical analysis, you can determine the condition of the liver using liver tests (AST, ALT).
- Physical examination. The doctor examines the patient, finds out if he has bad breath, yellowness of the skin, hand tremors, impaired movement, confused speech and other disorders.
- Analysis of urine. A urine test is ordered if there is a suspicion of infection or kidney dysfunction. Bacterial culture may also be prescribed.
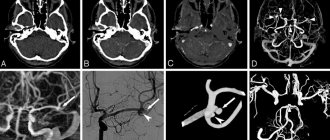
- Ultrasound of the liver. The ultrasound examination procedure is painless and safe. It can be performed on a patient in any condition and at any age. Using ultrasound, you can identify cysts and tumors in the liver, determine its size and structure. As a preparation, a simple diet is prescribed to reduce gas formation in the intestines.
- MRI. MRI can examine both the liver and brain to detect the effects of liver disease. This procedure is also safe, but it costs more than ultrasound and has a number of contraindications. For example, MRI is not performed on people who have metal implanted objects (shunts, crowns).
- Liver biopsy. A biopsy is prescribed if the cause of the disease cannot be determined. The biopsy procedure involves removing a small area of tissue for detailed examination. The information content of such diagnostics is very high.
Hepatic encephalopathy is a serious and dangerous condition. It is impossible to cure it yourself using folk remedies. The patient requires consultation with a therapist, gastroenterologist, or hepatologist.