The most common problem that contributes to visual impairment is damage to the fundus of the eye. It is responsible for the perception of the surrounding image. Deterioration of blood flow in the area of the visual organ provokes atherosclerosis of the retinal vessels, the treatment of which requires a particularly responsible approach. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of a veil and floating spots before the eyes. Since the capillary system of the eye is quite small, even microscopic damage causes the development of serious visual impairments.
Causes of atherosclerosis of the ocular vessels
Complete or partial blockage of blood vessels leads to poor circulation
Atherosclerosis of the eye occurs as a result of systemic damage to blood vessels. The development of the disease is associated with disruption of metabolic processes in the body. The pathology contributes to the accumulation of cholesterol in the blood with the subsequent formation of plaques. Complete or partial blockage of blood vessels leads to poor circulation. The result of this process is disruption of the functioning of the organ of vision. The main causes of atherosclerosis of the ocular vessels include:
- long-term smoking;
- diabetes;
- excessive amounts of stressful situations;
- increased blood clotting;
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased cholesterol in the blood as a result of poor nutrition;
- congenital pathologies of vascular structure;
- age-related changes in the retina of the visual organ.
According to statistics, age-related changes are the main trigger for the development of atherosclerosis. But under certain circumstances, the disease appears at a young age. Obese people who lead a sedentary lifestyle are at risk. Sometimes retinal atherosclerosis is provoked not by an increase in cholesterol, but by concomitant diseases. These include impaired blood circulation and cardiovascular pathologies.
In rare cases, the disease appears after undergoing surgery on the spinal cord or brain. With a hereditary predisposition, atherosclerosis may not progress if the person has taken preventive measures.
Drug treatment
After making an accurate diagnosis and determining the cause of atherosclerosis of the eye, the ophthalmologist selects a comprehensive treatment aimed at achieving the following goals:
- blood thinning;
- restoration of vascular elasticity;
- normalization of cholesterol levels in the blood;
- relieving vascular spasms;
- activation of metabolic processes;
- improvement of microcirculation.
The main method of treating atherosclerosis is drug therapy, selected depending on the root cause of the disease. The following groups of drugs are usually prescribed:
- Angioprotectors (Actovegin, Tivortin). Prevents vascular ruptures.
- Vasodilators (No-Shpa, Eufillin). Relieves arterial spasms, improves blood circulation.
- Disaggregants (Curantil, Aspirin). Improves blood properties, prevents the formation of blood clots.
- Anti-sclerotic drugs (Fenofibrate, Parmidine). They reduce the manifestation of atherosclerosis and prevent the formation of new pathological foci.
- Hypolipidemic (Atoris, Zocor). Normalize blood cholesterol levels.
Symptoms of the disease
Sometimes the pathology is accompanied by swelling in the nasal passages and ears
The symptoms of retinal atherosclerosis become more pronounced as the pathology develops. Due to the accumulation of fatty deposits in the vascular walls, their lumen narrows. Blood does not flow to the organs of vision in the proper way. This provokes atrophy of their individual areas. The main symptoms of the disease include:
- frequent dizziness;
- recurrent headaches;
- pain in one or both eyes;
- temporary or permanent decrease in vision function.
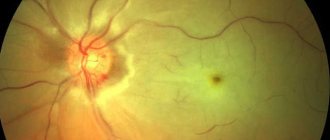
Most patients ignore the first signs of the disease. This leads to active progression of atherosclerosis. In this case, the risk of hemorrhage in the eye area, the formation of glaucoma and optic nerve atrophy increases. Sometimes the pathology is accompanied by swelling in the nasal passages and ears. Small vessels, yellow spots and areas of hemorrhage are clearly visible on the eyeball.
Main manifestations
Atherosclerosis with damage to the ophthalmic arteries leads to their gradual narrowing due to the growth of atherosclerotic plaques. In this case, ischemia of the retinal tissue occurs, slowly progressive atrophy and visual impairment associated with these processes.
Atherosclerosis of the retina can lead to poor vision
At an early stage of the development of the disease, the following symptoms are noted:
- Feeling of discomfort and pain in the eyeballs or in the area near them.
- Short attacks of dizziness and headache.
- Rapid eye fatigue when reading, drawing and other activities that require active vision.
- Temporary or permanent visual impairment in the form of loss of fields, the appearance of flickering spots, etc.
In severe forms of the disease, patients may experience glaucoma, complete atrophy of the retina and nerves, leading to a significant decrease in vision, including blindness. Also, against the background of significant narrowing of the arteries, their rupture can occur with the onset of hemorrhage and retinal detachment, which requires immediate surgical treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
Retinal atherosclerosis is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist. Initially, a detailed study of the clinical picture of the disease is carried out. At this stage, it is necessary to notify the doctor about the existing symptoms and concomitant diseases. Using clinical and instrumental techniques, it is possible to obtain the following data:
- presence of hemorrhage and blood clots;
- the nature of changes in the thickness of the vascular walls of the eye;
- configuration and structure of arteries;
- volumes of lumens in blood vessels.
Modern ophthalmological methods are used to determine the condition of the visual organs. The fundus is studied using the following procedures:
- MRI of the eye allows you to see structural changes and their location.
- Visometry determines the degree of damage and gives an idea of the condition of the retina.
- Computer perimetry is needed for a detailed study of individual areas of the organ.
- Ophthalmoscopy is performed to assess the number of damaged vessels.
The patient’s lifestyle plays an important role in the therapy process.
Initially, it is necessary to determine at what stage the atherosclerosis of the retinal vessels is. Treatment is carried out after establishing the cause of the pathology. An integrated approach involves the use of surgical, medicinal and traditional methods of combating the disease. Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, including magnetic therapy, exposure to laser beams and acupuncture.
The patient’s lifestyle during therapy is of no small importance. Doctors recommend reducing the load on your visual organs. To do this, it is advisable to at least temporarily stop watching TV, playing on the computer and reading books.
Drug therapy
After receiving the examination results, a treatment regimen is selected. Medical therapy includes taking the following groups of medications:
- vasodilators (Eufillin, Nitroglycerin);
- vitamin complexes and antioxidants (Anthocyan forte, Tanakan, Lutein forte and Okyuvit);
- drugs that block the process of blood clot formation (Curantil, Aspirin, Tirofiban, Plavix and Tiklid);
- lipid-lowering drugs that reduce the amount of certain lipid fractions (Crestor, Zocor and Atoris);
- angioprotectors (Detralex, Ilomedin, Tivortin and Actovegin).
Additionally, eye drops are prescribed that have a targeted effect on the lesion. They enhance the effectiveness of the main therapy and alleviate the patient’s condition.
Surgical approach
In case of extensive hemorrhages and retinal rupture, vitrectomy or complete removal of the scloid body is performed
Retinal atherosclerosis is treated surgically if serious complications of the disease have developed. These include glaucoma, optic atrophy and retinal detachment. The most common and effective method of treatment is laser coagulation. In case of extensive hemorrhages and retinal rupture, vitrectomy or complete removal of the scloid body is performed. In order to expand the vascular lumens, scleral ballooning is performed.
Treatment with folk remedies
Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the eye is not recommended to be treated exclusively with folk remedies. They are not effective enough for extensive retinal lesions. The most suitable traditional medicines include the following:
- To prepare the decoction, mix 100 g of chamomile, immortelle and St. John's wort. The herbal mixture is poured with 500 ml of hot water. After 2 hours of infusion, the drink is taken in small sips throughout the day.
- For 1 glass of hot water you need 20 g of lemon balm and valerian rhizomes. The herbs are poured with boiling water and infused for several hours. The total duration of treatment is 20 days.
- A spoonful of dill seeds is poured into a glass of hot water. After prolonged infusion, the finished product is taken 1 tbsp. l. up to 4 times a day.
- An effective tincture based on lemon and garlic helps strengthen blood vessels. The head of garlic should be crushed in a blender along with 1 lemon (with peel). The resulting mixture is poured with 500 ml of alcohol or vodka. After 4 days the drink will be ready. It should be taken 2 tablespoons, once a day.
- Honey is mixed in equal proportions with vegetable oil and lemon juice. The resulting product should be taken on an empty stomach, 1 tsp. every day.
- If the patient does not have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, a folk remedy made from potatoes is used. The vegetable is crushed to a pulp. Potato juice must be taken on an empty stomach for 30 days.
Experts recommend introducing regular consumption of tea with various berries into your diet. Particular attention should be paid to red currants and rowan. It is also advisable to drink vegetable juices and eat fruit purees. Parsley and dill have a positive effect on the condition of blood vessels.
Read also: Atherosclerosis ICD
What are the symptoms of the disease?
The essence of the disease of the blood vessels of the eye is their narrowing, most often due to fatty deposits appearing on the walls, which in turn leads to impaired blood flow.
The patient complains of pain in the eyes, frequent dizziness, and headaches. The eyes get tired much faster. At times, visual disturbances occur. Usually people do not pay attention to such phenomena and attribute them to manifestations of other diseases. Incipient eye problems can only be detected randomly, for example, during an annual medical examination, since all the initial symptoms are characteristic of many diseases.
But the disease is most often identified in later stages, when serious problems with the blood vessels of the eye begin. This ophthalmological pathology can develop to such an extent that it can manifest itself as atrophy of the optic nerve, the appearance of glaucoma, and hemorrhages in the eye tissue.
When a patient with suspected atherosclerosis of the vessels of the eye sees a doctor, first of all a survey is carried out and the presence of chronic diseases is revealed. An ophthalmologist treats this disease. Its task is to assess the condition of the retinal vessels.
The criteria by which the assessment is carried out are as follows:
- The thickness of the vascular wall of the eye is determined.
- The degree of their narrowing is determined.
- The structure and configuration of blood vessels is studied.
The presence of hemorrhages and blood clots is determined.
- The condition of the lumens is assessed.
Diagnosis is carried out as follows:
- As part of the examination, the patient is prescribed visometry, which makes it possible to identify the degree of visual impairment and at the same time determine the condition of the retina.
- Ophthalmoscopy. This type of examination allows you to determine how much damage has affected the arteries and how many of them are damaged.
- Computer perimetry. This test looks for problems in the peripheral retina.
- The traditional examination carried out for all eye pathologies is an examination of the fundus.
- And finally, an MRI of the eye, which is performed to identify abnormalities in all tissues of the eye.
What to watch out for
With early detection, the likelihood of coping with the manifestation of the disease is much higher
Patients with high cholesterol levels should have blood tests periodically to monitor the situation. If the amount of a harmful substance in the body increases, measures are taken to reduce it. Atherosclerosis of retinal vessels requires constant monitoring. Otherwise, the following complications develop:
- optic nerve atrophy;
- complete loss of vision;
- thrombus formation;
- development of glaucoma;
- recurrent hemophthalmosis;
- heart attack
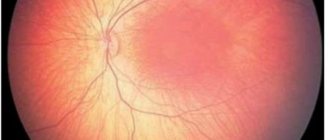
Changes in the fundus of the eye during atherosclerosis lead to loss of visual function. Ophthalmological pathologies are often accompanied by the assignment of disability. The patient completely loses his legal capacity. This has a significant impact on his quality of life. Atherosclerotic prognosis depends on the effectiveness and timeliness of treatment in conjunction with nutrition. With early detection, the likelihood of coping with the manifestation of the disease is much higher.
Atherosclerosis poses a serious threat to visual function. Therefore, treatment should not be neglected. In advanced cases, the risk of death increases as a result of blood clot rupture or the development of an aneurysm. At the initial stages of the disease, it is possible to avoid unwanted complications.
Conclusion
Atherosclerosis poses a serious threat to visual function. Therefore, treatment should not be neglected. In advanced cases, the risk of death increases as a result of blood clot rupture or the development of an aneurysm. At the initial stages of the disease, it is possible to avoid unwanted complications.
Over the past 10-15 years, pathologies of the vascular system of the eye have taken first place among the causes of low vision and blindness. There is a tendency towards rejuvenation of the disease. If previously circulatory disorders were observed mainly in older people, now the average age of patients has decreased significantly. Atherosclerosis of retinal vessels, as well as hypertensive retinopathy, are called the main reasons for this pattern.
Atherosclerosis of the retina, what is it?
The sensitive tissue layer located on the inner back of the eye is the retina. Its function is to convert light signals into nerve signals, and they already serve as a signal for the brain.
This is the basis, consisting of nervous tissue, which provides vision. Its structure consists of ten layers, where there are cellular tissue, nerve cells, and many blood arteries, which ensure metabolic processes and normal functioning of the retina.
Numerous studies of the fundus have confirmed that atherosclerosis of this part of the eye in ophthalmology is the most common problem associated with vascular pathology and causing serious problems with visual impairment. This disease occurs against the background of atherosclerotic manifestations of cerebral vessels, but this can occur in any part of the human body.
Increased pressure in the arteries, metabolic disorders, disruptions in the functioning of the heart, all this can cause changes in the walls of blood vessels, their narrowing and, as a result, a decrease in blood flow.
One of the most serious and common pathologies is retinal detachment. This is caused by malnutrition. This complication requires immediate surgical intervention, as it can lead to loss of vision.
Causes of atherosclerosis of the ocular vessels
Among the most common causes of the disease, pathological changes are observed in the form of:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Generalized atherosclerosis.
With high blood pressure, the vascular walls throughout the body are first affected.
Ophthalmologists are among the first to detect hypertension by changes in the circulatory network of the eye, since one of the accessible places to recognize these changes is the fundus of the eye.
Having discovered vasospasm or atherosclerosis in the vessels of the nerve membrane of the eye, they firmly confirm hypertension.
The cause of hypertension and other diseases associated with disorders of the vascular system is elevated plasma cholesterol over a long period. The causes of retinal atherosclerosis are fatty deposits in the vessels, which interferes with normal blood circulation.
This can happen for several reasons:
- Due to sleep disturbances, constant overwork or being under stress;
- Lack of physical activity and, as a rule, a decrease in metabolic processes in the body;
- The cause may be excess weight, fat accumulation and metabolic disorders;
- Smoking and alcohol, which are provocateurs of vascular spasms and their damage;
- Wrong foods that contribute to the development of vascular plaques due to “bad” cholesterol in large quantities.
With atherosclerotic lesions, plaques form that interfere with normal blood circulation, and oxygen ceases to flow sufficiently. And this is a direct path leading to the formation of blood clots, poor coagulation and serious pathology of the vascular system. As a result of these negative manifestations, the fundus of the eye, its stem branches and the central vein become easily vulnerable.
Sometimes the disease is not detected for years, since the signs of the disease are often concomitant. The clinical picture is often expressed by spasms in the circulatory system of the eye, blockage in thin arteries and their rupture. Therefore, often, the disease can only be identified during a crisis period, with a sharp drop in vision and the formation of edema.
Atherosclerotic angiopathy of the retina occurs in the same way as lesions of other organs, the only difference is in its microscopic formation, since the arterial and venous networks in the fundus of the eye are much smaller than elsewhere.
With this disease of the eye capillaries, complications may arise in the form of:
- Ischemic damage to the optic nerve, often resulting from impaired blood flow in the eyeball;
- The presence of thrombosis in the main vein of the fundus;
- swelling or optic nerve;
- Dangers of vitreous hemorrhage.
Such negative manifestations are fraught with noticeable deterioration or loss of vision. The disease most often affects older people, but it is constantly getting younger, and cases of this disease have become more frequent among the younger generation.
Causes of retinal angiosclerosis
Retinal angiosclerosis – thickening and increased density of the fundus vessels. At the same time, their structure and functional abilities are disrupted. The changes usually affect both eyes. There are just a few main reasons:
- arterial hypertension,
- atherosclerosis.
Depending on the cause, the disease can occur as a hypertensive or atherosclerotic type. Symptoms, developmental features and other parameters will depend on this.
Hypertensive retinopathy
Hypertensive retinopathy is a pathology of the retina and/or blood vessels with prolonged high blood pressure. The cause can be either essential (primary) arterial hypertension or symptomatic (renal, endocrine, etc.).
Initially, this is manifested by spasm of the arteries, and then by hardening of their walls and loss of elasticity (similar changes occur in the vessels of the kidneys). In 80% of patients, the pathology is asymptomatic, especially in the early stages.
Forms of hypertensive retinopathy:
| Form | Features of development |
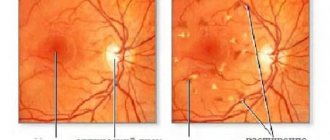
| Hypertensive angiopathy | The veins are wide and branched, the arterial vessels are narrowed. There may be single point hemorrhages, the optic nerve nipple is moderately hyperemic (red). Gwist's sign is observed - tortuosity of small veins near the macula (macula). This form is reversible; when normal blood pressure is established, the manifestations disappear |
| Hypertensive angiosclerosis | The arterial walls become thicker, due to their obliteration (overgrowth) and the accumulation of lipid inclusions in the intima (inner lining) of the arteries, specific symptoms of “copper” or “silver” wire are visible |
| Hypertensive retinopathy | It manifests itself as damage to the retina itself, and not just its arteries and veins. There are plasmatic impregnation, lesions in the area of the macula, white or yellowish in color, plasmorrhagia of a star-shaped or ring-shaped form. The development of retinal edema is possible. Most often observed in the most severe stage III of hypertension |
| Hypertensive neuroretinopathy | Changes in the area of the optic nerve nipple - it is swollen, enlarged, with hemorrhages. Vision decreases, visual fields narrow. Probable outcome: optic nerve atrophy |
The symptom of intersection of arteries and veins (Salus) is specific for angiosclerosis of the hypertensive type:
- 1. 1st degree - the vein is narrowed, compressed by the artery, has a conical shape before and after the intersection.
- 2. 2nd degree - the vein is arched and becomes significantly thinner under the arterial trunk.
- 3. 3rd degree - the vein 'disappears', looks like a broken line. It is observed with a steady increase in blood pressure in stages II A and B of hypertension.
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the form and severity of the pathological process after a comprehensive examination and detailed examination of the fundus using special equipment.
Atherosclerotic retinopathy
Manifestations in the fundus of this pathology are similar to the picture of hypertensive retinopathy. This type is characterized by hemorrhages - on the retina, under the conjunctiva, in the vitreous body, and crystalline deposits along the vessels.
For the development of the atherosclerotic type of angiosclerosis, more provoking factors are required. Among the main ones are: psycho-emotional instability, vitamin deficiencies, hormonal imbalance, lipid metabolism disorders and others.
Symptoms of the disease
Bearing in mind that the causes of the disease are systemic in nature, atherosclerosis is usually observed in both eyes. At an early stage, symptoms are quite difficult to identify. If you identify the disease at an early stage, you can quickly and efficiently stop its development. To do this, you should understand and be able to distinguish its main features.
Its symptoms are very similar to the main symptoms associated with atherosclerotic lesions:
- Dizziness and frequent headaches;
- Pain and pain in the eye sockets;
- Deterioration of vision;
- General poor health and eye fatigue;
- At a later stage, double vision, fogginess, and loss of fields from the view appear.
Due to the slow blood flow in the capillary system of the eye, oxygen starvation occurs, the structure is disrupted and becomes tortuous, this can be seen when diagnosing the disease.
There are other reasons that contribute to the development of retinal atherosclerosis, these are concomitant ailments and various injuries, among them:
- Diseases of the vertebral thoracic and cervical regions;
- Surgeries on the brain and spinal cord;
- Extensive vascular lesion of a sclerotic nature;
- Endocrine system disorders;
- Various injuries and disruptions in blood flow;
- Heart pathologies.
Treatment of retinal atherosclerosis
With the development of atherosclerosis of the retina, treatment should always be selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the individual patient’s body. Concomitant diseases and existing complications must be taken into account.
Treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist, who may choose medication or surgery, or a combination of both.
Self-medication is not recommended due to the risk of developing side effects of therapy or progression of the underlying disease.
Drug therapy
The use of medications is especially effective in the early stages of the disease.
The drug Rosuvastatin
In such treatment regimens, the following groups of medications are used:
- Lipid-lowering drugs, primarily statins (Rosuvastatin, Lovastatin, etc.), which reduce the level of cholesterol and LDL in the blood plasma, thereby stopping the development of the atherosclerotic process in the retinal vessels.
- Antiplatelet agents (Acetylsalicylic acid, Clopidogrel) prevent the formation of blood clots in areas of vasoconstriction and prevent the development of thrombosis and critical ischemia.
- The use of antioxidants (Tocopherol, Dihydroquercetin) can reduce the level of damage to retinal cells.
Taking medications should always be under the supervision of the attending physician in the dosages prescribed by him.
The drug Lovastatin
Surgical approach
The use of surgical treatment methods is indicated in patients with complications of retinal atherosclerosis. The most serious of them is its detachment with the development of hemorrhage into the eyeball. In this case, doctors can use laser coagulation, balloon methods and vitrectomy.
Retinal atherosclerosis is a serious disease characterized by constant progression and a decrease in the level of vision to blindness. In this regard, every person should remember about risk factors that can be eliminated from their lives from a very young age. Such primary prevention is the key to the absence of disease in the future and significantly improves the quality of life in old age.
Diagnosis of the disease
First of all, the general picture of the disease and its symptoms are studied. An ophthalmologist deals with this problem. He conducts basic examinations and, through blood tests, determines the presence of cholesterol levels. Then it collects information about past complications, genetic predisposition and chronic manifestations.
To determine the stage of the disease, a specialist performs fundus ophthalmoscopy and fluorescein angiography of the vascular system. With the help of medications, such as tropicamine, atrophin, the pupils dilate, this allows for a high-quality examination, but vision may deteriorate for some time and the light sensitivity of the eyes will increase.
Read also: Atherosclerosis folk recipes
Ophthalmoscopy or fundoscopy is an examination that allows one to penetrate into the back of the eye and detect various pathologies of the retina, blood arteries, optic nerve head, and choroid.
In addition, the examination is carried out by:
- Visometry - determination of vision in the area affected by atherosclerosis, the condition of the entire fundus of the eye;
- Computer perimetry – examination of the periphery;
- Electrophysiological diagnostics - finding out how cells are able to survive;
- Tonometry - measuring eye pressure;
- MRI, CTM, ultrasound.
Using numerous diagnostic methods, through a serious examination, the following pathologies can be identified:
- The presence of narrowing of the lumen in the blood arteries, the thickness of their walls;
- Changes in arteriovenous junctions;
- Tortuosity of the structure of blood vessels;
- Hemorrhages, blood clots and swelling of the optic nerve;
- Location of changes.
When treating atherosclerosis of the retina, the entire problem of the disease is solved, with the participation of an ophthalmologist and other specialists: a neurologist, a cardiologist and a therapist . The main focus of treatment should be thinning the blood flow, increasing the elasticity of capillary walls, with a mandatory reduction in cholesterol levels.
The nature of the pathology may be different, but the main thing in successful treatment is an integrated approach.
- Medications aimed at increasing blood supply to all structural parts of the eye. It provides treatment courses such as: mildronate, vasonite, solcoseryl, arbiflex. Due to the plasticity of red blood cells acquired under the influence of drugs, they quickly move through the narrowed capillaries. Medicines should be selected on a personal basis, taking into account the characteristics of each patient’s body, chronic and concomitant diseases. Often, medications are taken by instillation into the eyes. With conventional drug therapy, the following are prescribed: angioprotectors, vasodilators, antiplatelet agents and anti-sclerotic agents.
- Taking vitamin complexes necessary to maintain health.
- A diet based on the prohibition of eating foods high in calories and carbohydrates, and limiting salt. With strict adherence to the correct diet, the effectiveness of treatment increases several times.
- Physical activity that promotes the flow of energy into muscle tissue and accelerates metabolic processes, removing toxins and salts from the body.
- Quitting bad habits, such as alcohol and smoking.
- Physiotherapeutic methods such as laser, magnetic therapy or acupuncture.
- Reducing the load on the eye organs is also an important part of treatment. During the therapeutic period, it is worth stopping sitting in front of the TV, computer and limiting reading books.
- Folk remedies that help enhance the healing effect. There are many recipes and recommendations based on many years of experience and cases of successful and quick recovery from illness.
Treatment with folk remedies
Helpful inclusions in your diet include:
- Juices of fresh vegetables and fruits, especially parsley;
- Infusion of dill seeds;
- Tea using red rowan berries and black currant leaves.
Herbal mixtures from medicinal herbs and plants:
Recipe No. 1
Infuse with half a liter of hot water and drink throughout the day.
Recipe No. 2
- Valerian rhizome - 20 g;
- Melissa-20
A glass of hot boiling water. Drink for 20 days in small portions before meals.
It should be noted that consultation with a specialist regarding the use of any folk remedies is mandatory, as there may be contraindications and side effects.
To prevent the disease, such remedies as chokeberry fruits, red currant juice, and olive oil drunk on an empty stomach are successfully used. All these natural natural remedies contribute to excellent results.
What to watch out for
Patients suffering from high cholesterol levels should monitor their levels, reduce them in time, and do this for life.
You should constantly take medications that contribute to the normal maintenance of the ocular circulatory system, anti-sclerotic agents and vitamins, since an advanced stage of the disease can lead to dire consequences, such as:
- Glaucoma;
- Eye infarction;
- Nerve atrophy;
- Thrombosis;
- Recurrent hemophthalmosis;
- Loss of vision;
- Irreversible blindness.
Adjust your diet, do as much physical activity as possible, take homeopathic remedies and vitamins, monitor your cholesterol levels, quit bad habits once and for all, and check your eyes periodically. With timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment, your eyes will remain the mirror of your soul for a long time!
What it is?
This is a severe pathological situation, manifested in blockage of the peripheral vascular network in the area of the eyeball. The mechanism of action consists of several long stages that can take years:
- When a carbohydrate enters the body, regardless of whether it is “simple” or “complex,” the carbohydrate is broken down into glucose. This makes it easier for the body to process and absorb it. When the lipid profile of the blood is disturbed, due to a malfunction of the liver or kidneys, glucose accumulates in clusters and clings to the deformed walls of the vessel. This is how the basis for the plaque is formed.
- Any free fractions traveling in the bloodstream may be attracted to the site of plaque formation, increasing its size.
- The capacity of the vessel decreases, and the specific area of passage of the blood composition decreases.
- When blood thickens, which goes hand in hand with atherosclerosis, blood cells stick together, forming a blood clot.
- The presence of an obstruction causes swelling and fluid accumulation at the site of the rhombus, loss of sensitivity, and tissue death due to insufficient blood supply.
- Under severe stress or anxiety, when the speed of blood circulation increases, the blood clot displaces and is carried away by the blood flow, and if it enters the ventricle of the heart, it can disrupt its functioning and lead to a heart attack.
Causes and risk factors
Atherosclerosis of the optic blood canals occurs in patients who are predisposed to increased levels of “bad” cholesterol in the blood .
For a long time, scientists believed that the disease only affected older people. However, modern research has revealed a pathological and long-term nature of development. Now it seems possible for doctors to identify the primary stages of the pathological process at a young age, in order to prevent the development of the disease at a more mature age.
The formation of lipid plaques on the walls of blood vessels is promoted by:
- Genetic and hereditary factors.
- Excess weight and metabolic disorders.
- Poor lifestyle, lack of physical activity.
- Unbalanced nutrition, when the daily diet is dominated by carbohydrates, refined foods, rich in sugar.
- Unhealthy habits such as using tobacco and alcohol products.
- Mechanical and thermal injuries.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Malfunctions of the central nervous system.
Reasons for development
Atherosclerosis of the ocular vessels occurs in people who are prone to increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
For a long time it was believed that the disease only affects older patients, but thanks to modern diagnostic methods, doctors are able to identify the initial forms of the pathological process among young people.
The deposition of fatty deposits on the inner wall of blood vessels is promoted by:
- genetic predisposition;
- excess weight and metabolic disorders in the body;
- lifestyle devoid of physical activity;
- poor nutrition, when the daily diet is dominated by fatty, fried foods rich in cholesterol;
- bad human habits, in particular smoking;
- injuries;
- disturbance in the functioning of the nervous system, frequent stress, chronic fatigue.
Very often, atherosclerotic retinal angiopathy and associated poor vision occur against the background of chronic spasm of the ocular vessels. A similar phenomenon is observed in diseases of other organs and systems of the human body, such as diseases of the cervical spine, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and the like.
Retina of the eye with hypertensive angiopathy
hypertensive angiopathy
What diseases can cause?
- Diabetes.
- Tuberculosis.
- Hepatitis.
- HIV and AIDS.
Vascular atherosclerosis of the retina causes a narrowing of the lumen of the eye capillaries due to the accumulation of lipid-glucoid formations on their walls. There is a slowdown in blood circulation in the retinal tissue, dystrophy and atrophy, loss of vision (partial or complete), bleeding.
Symptoms of the initial stage:
- pain in the eye area;
- dizziness;
- headaches, migraine;
- chronic eye fatigue;
- blurred vision.
Diagnostics
with the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerotic formations of the retina . During diagnostics, he uses modern clinical and instrumental techniques, which make it possible to identify disorders such as:
- changes in the size of the walls of the eye vessels;
- the measure of narrowing of the arteries and veins of the retina;
- structure and structure of blood vessels;
- the presence of blood clots and hemorrhages;
- the scale and nature of the gaps.
Additional Methods
- Ophthalmoscopy . Determines the number and basic characteristics of damaged vessels.
- Visometry . Makes it possible to assess the stage of vision loss and provides information about the condition of the retina.
- Computer perimetry , with the help of which local parts of the retina are studied.
- Ultrasound examination of the fundus and a conclusion about the condition of its veins and arteries.
- MRI of the eye , which will reveal the presence of disorders in the structural components of the organ, their location and features.
Treatment - specific tips and recommendations
The choice of treatment strategy for atherosclerotic lesions will depend on the results of the study, the presence of accompanying diseases and complications.
Therapeutic relief of the pathological condition is carried out by ophthalmologists, who, after a detailed study of each individual clinical case, decide on the choice of medications and treatment procedures or the urgency of surgical intervention.
Drugs used in the initial stages
Angioprotectors , protecting the weakened and lost elasticity of the vessel wall from ruptures.
- Vasodilators that prevent spasms and improve blood circulation in damaged areas.
- Anti-sclerotic complexes for the direct elimination of fatty plaques.
- Antiplatelet agents , which help improve the rheological properties of blood and prevent the formation of blood clots.
To obtain the maximum effect from the drugs, patients are recommended dosage forms in the form of eye drops , as they go directly to the site of damage, providing an accelerated therapeutic effect. If there are diseases occurring simultaneously with this one, they are also treated to eliminate the chance of complications.
Surgical treatment is used for patients in whom atherosclerosis has caused the development of a critical complication of retinal detachment. Among the most popular surgical interventions today are:
- laser coagulation of the retina;
- scleral ballooning;
- vitrectomy or removal of the vitreous.
Used in practice
- Mildronate , stimulant of central and local circulation. Price – 250 rubles.
- Vazonit , Peripheral vasodilator. Price 340 rubles.
- Solcoseryl , ointment for disinfection. Price 350 rubles.
- Arbiflex , anti-inflammatory drug. Price 480 rubles.
Laser therapy
A modern painless procedure that involves destroying deposits using a laser beam of variable wavelength.
The entire procedure takes no more than 20 minutes and has no contraindications. Because the procedure is expensive, it is optional and serves as an alternative to traditional surgery. After the procedure, the patient must also undergo consultations and be observed by an ophthalmologist for 2 months to monitor health and eliminate possible complications.
Consequences and complications
Increased blood pressure primarily damages the walls of blood vessels throughout the body. Examination of the fundus is one of the mandatory procedures when diagnosing hypertension and its consequences. With hypertensive angiopathy, arterial vasospasms, dilatation and inversion of the retinal veins are observed.
The thickness of the arteries, in relation to the size of the veins, decreases. The veins in the area of intersection with the arteries bend and move into the retina. Sometimes there is a loss of veins at the intersection with the arteries, swelling of the retina occurs, and hemorrhages may develop.
Hypertensive angiosclerosis
Since the causes are systemic in nature, angiosclerosis of both eyes is observed. In the early stages, there are no obvious external symptoms. As retinal damage progresses, double vision, blurred vision, or loss of vision may occur. Angiosclerosis is diagnosed using fundus ophthalmoscopy and fluorescein angiography.
Treatment
The treatment tactics for the disease are developed by the doctor, taking into account the cause and nature of vascular changes, the severity of the pathological processes, concomitant diseases and other individual characteristics of the patient.
If the disease develops against the background of arterial hypertension, the patient is prescribed:
- drugs to strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- antihypertensive drugs (normalize blood pressure);
- diuretics (remove excess fluid, helping to reduce high blood pressure);
- medications to improve blood circulation and normalize capillary permeability;
- anticoagulants (thin the blood);
- metabolic agents (activate metabolic processes in tissues);
- miotics (reduce intraocular pressure, prescribed according to indications);
- vitamins in the form of eye drops and tablets for oral administration (improves metabolism in the retina).
For generalized angiosclerosis, it is recommended to take statins (Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin) - drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels. If you have diabetes, it is important to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
Drug treatment of retinal angiosclerosis is complemented by physiotherapeutic procedures:
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- acupuncture.
Nutrition also affects the condition of blood vessels. Therefore, it is important for patients with angiosclerosis, especially hypertensive patients, to adhere to a dietary diet - eat foods rich in vitamins and fiber. It is better to exclude sugar, salt and animal fats from the menu.
Prevention and prevention of disease
Proper nutrition is the most important factor that will help cure an illness or alleviate its course. Excessive consumption of sugars and carbohydrates leads to metabolic disorders. The body has no need to spend fat deposits, and it has plenty of prerequisites for fat accumulation.
Consume more healthy fats Omega-3 and Omega-6, natural proteins of animal origin, exclude carbohydrates (porridge, bread, fruits, vegetables), starch, sugar from food. To normalize digestion, consume enough fiber, which is found in cabbage, green vegetables, parsley, and dill.
Eye gymnastics and exercises will also be useful. In addition to preventing vascular disorders, this method allows you to avoid deterioration of vision. The doctor will recommend you a list of exercises that you will need to perform at least once a day.
It is especially important to engage in eye exercises when working with monitors and other activities that cause strain on the visual organs. If your professional activity involves such stress, then eye gymnastics is simply necessary.
Limiting exposure to screens is very important in preventing illness. Try not to spend a lot of time in front of monitors and displays unless you clearly need them. Read newspapers, books, preferably on paper, in natural light.
However, prolonged reading can also negatively affect eye health, so you should limit your reading sessions by time.
Walking in the fresh air and exercising outside are also a good means of prevention. It will keep the entire body in good shape, which naturally reduces the risk of developing vascular pathologies.
Maintaining proper eye hygiene is also encouraged. Do not overuse makeup and neglect washing your face during the day.