Classifications of Kimmerly anomaly
Anomalies can be divided according to the degree of progression :
(Most common division)
- Incomplete Kimmerly anomaly. An arched growth of bone tissue on a vertebra.
- Kimmerly's complete anomaly. Closed ring on Atlanta.
Types by location :
- Lateral Kimmerly anomaly. It is located between the known transverse and small articular processes.
- Medial Kimmerly anomaly. Connective tissue from the articular process to the posterior arch of the atlas.
Types by distribution :
- Unilateral Kimmerly anomaly.
- Bilateral Kimmerly anomaly.
How to identify and diagnose?
If you have severe headaches, balance problems, or a crunch in the cervical spine, you should immediately make an appointment with a neurologist. After a preliminary examination, the doctor may prescribe an x-ray of the cervical spine in three projections. In principle, this may be enough to see the extra arch of the atlas vertebra.
In the future, diagnostic measures will be aimed at establishing the degree of damage to the vertebral artery and assessing its capacity. For this, Doppler scanning, MRI, and computer diagnostic methods are used. After the data obtained, it is possible to prescribe an adequate treatment method.
Danger of disease
Kimmerly's anomaly is dangerous because the abnormal structure of the vertebra can cause disruptions and disruptions in the blood supply to the brain, the most serious of which is a stroke.
In the presence of the disease, blockage of the arteries is possible. In its advanced stage, Kimmerly's anomaly causes a lot of inconvenience in everyday life. The presence of hum, hissing, tinnitus and visual disturbances cause constant discomfort for the patient.
The appearance of such a symptom as syncope (short loss of consciousness) significantly worsens the quality of life of a sick person and often provokes injuries and bruises. There is a possibility of sleep disturbances if a person turns his head uncontrollably, which causes neck compression.
Kemerli's anomaly: not a disease, but a variant of the norm
Kemerli's anomaly (Kimerli or Kimmerli) is not a disease, but a congenital deviation from the norm. The anomaly is an extra arch, a bony outgrowth located at the top of the first cervical vertebra.
Kemerli's anomaly, the treatment of which is not required for all patients, may not cause any abnormalities. Only in some cases do people with such abnormalities experience health complications.
The brain is nourished by a system of arteries through which blood and nutrients move through the cervical vertebrae to its posterior sections. With a normal structure of the skeleton, in particular the spine, they go into the cranial cavity, bending around the first cervical vertebra.
If a person has Kemerli's anomaly, then there is a semi-ring on the vertebra, which the arteries cannot always go around. Sometimes they are pinched between the vertebra and the neck muscles, which leads to impaired cerebral circulation.
Infringement can be permanent or occur with a certain position of the head or rotation of the neck.
How can a person understand whether he has Kemerli anomaly? Its symptoms are few, inconsistent and different for all people. However, if at least some of the following symptoms are observed, there is a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
People with this disorder may experience:
• Dizziness that occurs when tilting or changing the position of the head
• Noise or buzzing in the ears, especially when tilting or turning the head
• “Sparkle” in the eyes that occurs when turning the body or head
• Loss of balance, sometimes falling due to loss of coordination. Happens when changing position or bending
• Severe muscle weakness caused by tension
If a person has Kemerli’s anomaly, and treatment is not started, then the symptoms can develop into more serious phenomena characteristic of cerebrovascular accidents:
• Severe headaches
• Eye twitching that occurs from time to time
• Decreased sensitivity in the face, arms, legs
• Complete loss of coordination
• Tremor of the arms or legs
• Stroke
In order to establish what caused such a complex condition of the patient, it is necessary to conduct a complete diagnosis.
If there is a suspicion that the cause is Kemerli’s anomaly, then to confirm the diagnosis the following is prescribed:
• Study of blood flow using Doppler scanning. It allows you to see exactly where and in what position of the head the cervical arteries are compressed.
• Digital radiography. A procedure similar to an x-ray. Features higher image quality with less radiation exposure to the body
• Magnetic resonance imaging. With its help, the doctor can examine the structure of the spine, all arteries and blood vessels.
• CT scan. A procedure that clarifies information obtained from magnetic resonance imaging.
There is no specific treatment for the anomaly, which is quite logical.
However, patients benefit from treatment of symptoms, which is tailored to each patient individually. The goal of this treatment is to weaken the tone of the neck muscles and ensure normal blood flow.
Kemerli's anomaly, or more precisely, its symptoms can be eliminated with the help of simple manipulations. The patient is prescribed:
• Massage
• Acupuncture
• Hirudotherapy
• Wearing special collars that secure the neck
• In more severe cases, normalization of blood circulation with the help of medications.
In addition, each person with such a deviation in the structure of the spine receives individual recommendations related to the characteristics of prevention and behavior. Common to all are:
• Limit sudden movements and physical activity, especially in the neck area
• Gymnastic exercises, selected strictly individually
• Constant supervision by a neurologist
• Immediately consult a doctor in case of exacerbation
Treatment methods
It should be noted right away that almost always the disease does not require treatment, because it does not cause any inconvenience and occurs without symptoms.
In other cases, when Kimmerly's anomaly requires intervention, the bone formation is removed surgically.
Treatment of the disease in asymptomatic form consists of maintaining a certain lifestyle and following recommendations. The latter include:

Avoiding excessive stress and heavy lifting;- No sudden movements of the neck and head;
- Comfortable and non-traumatic sleeping position, availability of a suitable pillow;
- Blood pressure control;
- Regular visits to the doctor;
- Prevention of cervical diseases.
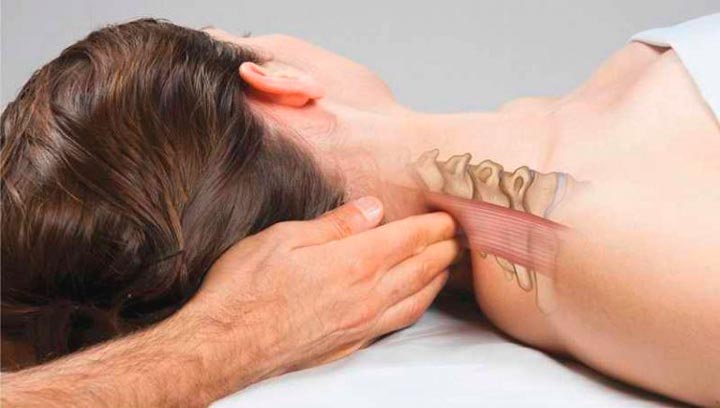
Also, positive dynamics are observed with complex treatment, including:
- Drug therapy;
- Massage;
- Moderate physical activity (health exercises);
- Manual therapy and acupuncture.
Symptoms
Signs of Kimmerly syndrome are caused by a lack of blood flowing to the brain, which is especially pronounced when moving the head, lifting heavy objects with outstretched arms, and certain physical exercises. Possible symptoms include:
- Sensation of audible rustling, noise, crunching in the ears;
- Darkening, “spots”, “veil” before the eyes, discomfort in the eyeballs;
- Clumsiness of movements and uncertainty of gait;
- Muscle weakness;
- Dizziness;
- Fainting conditions.
With significant difficulty in blood circulation through the vessels supplying the brain, cerebellar symptoms appear - trembling in the limbs, loss of coordination, nystagmus. Severe pathology is characterized by intense headaches, sensory pathology and movement disorders.
A critical narrowing of the lumen of the vertebral artery can lead to transient ischemic attacks, when the patient experiences severe pain in the head, short-term disturbances in speech and movement, and may lose consciousness. The most severe manifestation of Kimmerly's anomaly is considered to be cerebral infarction due to complete cessation of blood flow. This condition is more likely if there are other vascular changes - atherosclerosis, hypertensive angiopathy, vasculitis.
As noted above, Kimmerle's anomaly is usually asymptomatic. However, in a quarter of patients the disease has a clear clinical picture.
Posterior cervical syndrome
This symptom complex is associated with the appearance of constant pain in the neck, moving to the back of the head and forehead - like “removing a helmet”. This pain occurs more often in the morning (after a night's sleep in an uncomfortable position), as well as during the day during long walks, trips in shaking vehicles or intense turns of the head.
Migraine
The headache often progresses to a migraine attack. The latter, as a rule, is preceded by a period of precursors (the so-called aura): irritability appears, patients see “flashes of light”, feel tingling in their fingers, etc. After the aura, a severe headache occurs in the back of the head, which is often accompanied by vomiting or fainting.
Balance disorders are characterized by the appearance of dizziness (rotation of the body or the world around), a feeling of instability, nausea (even vomiting) and interruptions in the functioning of the heart. Such symptoms intensify with prolonged stay in a forced position or head movements.
Hearing disorders
Usually there is tinnitus, burning or tingling sensations in the temporal region, hearing loss (difficulty perceiving whispered speech, changes in the audiogram). These manifestations are often associated with dizziness and balance problems. However, hearing impairments are more persistent and long-lasting, and their strength varies according to the position of the head.
Changes in the visual analyzer are characterized by the appearance of bright flashes before the eyes (photopsia), blind spots (scotoma), increased fatigue and decreased visual acuity. Symptoms of conjunctivitis often occur (but without inflammation!): a feeling of “sand in the eyes,” increased vascular patterns on the sclera, lacrimation. Sometimes entire fields of vision may be lost (usually when the cervical spine is stressed).
General violations
Patients often complain of so-called autonomic disorders: the appearance of heat or cold, increased sweating, cold skin and inadequate changes in its color. Sometimes swallowing is difficult and insomnia occurs. Often, such manifestations are combined with migraine and other described symptoms.
Orthopedist: “If your hip joint and knees ache, immediately get rid of the habit...
Transient ischemic attacks
Attacks of ischemia (bleeding) of the brain are accompanied by disorders of sensitivity and balance, dizziness, nausea, as well as disturbances in vision, speech and swallowing. These symptoms disappear within 24 hours.
Syncope
In some cases, attacks of fainting are possible, which are characterized by a sharp lack of blood in the corresponding structures of the brain. As a rule, a person loses consciousness when he moves his head intensely or stays in uncomfortable positions for a long time.
Drop attacks
From English “drop” is translated as “fall”. This is the main manifestation of the attack: when the head is sharply thrown back, pronounced weakness appears in the muscles of the body, as a result of which the person falls (but remains conscious!). At the same time, muscle strength and movement in the limbs are quickly restored.
Kimmerly Anomaly and the Army

For men of military age, the question is whether it is possible to serve with such a disease. You can immediately please everyone who seeks to defend their homeland and upset those who would prefer to evade this state duty - Kimmerly’s anomaly will not be considered a reason for refusal to serve in the army!
Exceptions are those cases when the disease is pronounced and its symptoms do not leave the possibility of full life activity. To obtain a deferment, it is necessary to undergo an examination and record the presence of clinical symptoms by a neurologist.
Therapeutic prevention of Kemmerli syndrome
There are no special treatment and preventive measures for neurological pathology. All prevention is based on compliance with general rules, similar to those for the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Avoiding overload on the cervical vertebrae and muscles.
- Maintaining a balanced diet.
- Active lifestyle.
- Prevention of infectious diseases.
- Preventive examination by a neurologist.
Take care of yourself and always be healthy!
Considering the congenital nature of the pathology, prevention of Kimmerle anomaly consists in creating normal conditions for intrauterine development of the fetus:
- 2 months before conception, mother and father are recommended to take folic acid;
- during pregnancy (especially in the first trimester) avoid stress and infectious diseases;
- conduct a screening ultrasound examination at 11-12, as well as 20-22 weeks to prevent other anomalies.
At a conscious age, it is necessary to prevent provoking diseases that cause circulatory disorders in the vertebral arteries:
- avoid the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, preferring foods low in unsaturated fats (precursors of cholesterol);
- treat inflammatory vascular diseases - vasculitis;
- treat spondyloarthrosis and cervical osteochondrosis;
- correct increases in blood pressure;
- prevent head, neck, or shoulder injuries;
- conduct active surveillance for similar anomalies (Chiari malformation or platybasia).
If the joints of your arms and legs begin to hurt, immediately remove them from your diet...
Orthopedist: “If your knees and lower back start to hurt, remember, never touch...
With pain in the joints, neck or back, the body has a severe lack of...
Kimmerly's anomaly is not a terrible diagnosis, nor is it a chronic disease. This is a deviation from the normal structure of the vertebra, allowing you to live a full life, but following simple rules to avoid exacerbations.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will suffer karma
Pathogenesis
The reasons for the occurrence of this anomaly are not fully known to science. According to some data, the appearance of an “extra” bone arch in the vertebrae in some cases is possible as a result of the development of a dystrophic disease of the spine. This condition is popularly called osteochondrosis. However, this anomaly is not congenital; it is classified as acquired.
↓ Be sure to study the recommended material on the topic ↓
Lumbar radicular syndrome: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
An abnormal bone ring restricts the functioning of the vertebral artery. Often this condition is accompanied by chronic ischemic attacks in the posterior regions of the brain. But the presence of an additional arch does not always provoke the development of problems with blood vessels. Only in 20% of patients with this pathology there is a connection between the development of compartment syndrome and the presence of anomalies of the cervical vertebrae.
Congenital malformation of the atlas is common. In normal condition, the vertebra consists of anterior and posterior arches. There is a small “groove” on the back, over which a bony “canopy” sometimes forms. This developmental defect forms a channel from the “groove”, which interferes with the normal functioning of the artery.

Often, patients with abnormal development of the cervical vertebrae complain of a migraine-like headache and darkening of the eyes.
We recommend studying:
- Degenerative changes in the lumbar spine
- Lumbar radicular syndrome: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Forms of pathology
Kimmerle's anomaly comes in several types. The following forms of the condition are distinguished:
- full and partial;
- one-sided and two-sided;
- congenital and acquired.
An incomplete anomaly is accompanied only by the presence of an extra bone ring. In the case of a complete one, the arch has an intermittent shape, and in the structure of the cervical vertebrae there is a lateral atlanto-occipital ossified ligament, which arises due to the deposition of calcium salts. For this reason, the vertebral artery is compressed even more, which leads to more serious consequences.
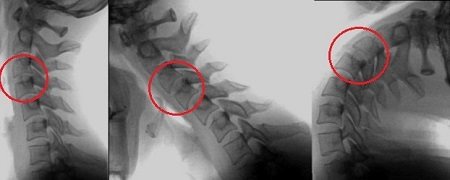
Kimmerly's anomaly comes in several types. The acquired form is more common than the congenital form.
Symptoms and manifestations
Kimmerly's anomaly can occur without specific manifestations and symptoms, but more often it manifests itself in the form of the following signs:
- sudden darkening of the eyes and the appearance of black dots;
- tinnitus and extraneous sounds in one or both ears;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- migraine;
- loss of sensation in the limbs;
- dizziness;
- facial muscle weakness;
- fainting with sudden turns or uncomfortable position of the head.
The anomaly in a more severe form may be accompanied by involuntary oscillation and movement of the eyeballs, impaired coordination of movements, and involuntary trembling of the limbs. Some patients suffer from ischemic attacks. In some cases, Kimmerly's anomaly can cause ischemic stroke.
Symptoms of the pathology most often appear with falls, sudden movements of the head and turns.
In addition we recommend:
- Two forms of spinal dorsalgia, its diagnosis and treatment
- What is the vertebral artery syndrome in cervical osteochondrosis?