Lymphocytosis is an increase in the level of white blood cells and lymphocytes above normal. This phenomenon occurs in adults and children of any age. A change in the number of formed elements in a clinical blood test indicates the development of a disease of infectious or some other etiology.
In fact, there are dozens of causes of lymphocytosis, and an accurate diagnosis is made not only by the concentration of the lymphocytes themselves, but also by the level of other formed elements. Initially, the pathology is assigned a code according to the ICD classification D72.8, then it is clarified as the patient is examined.
What are lymphocytes and their role in the immune system.
Blood is the only tissue of its kind in the human body. It consists of a liquid part, plasma, which contains several types of cells. These are red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Their number and ratio are different for men and women, and also depend on age.
Each of these groups performs its own specific functions. Red blood cells contain a special protein, hemoglobin. In the lungs it combines with oxygen, carries it to the tissues, “exchanges” it for carbon dioxide, which is returned to the lungs. Platelets are the main element of the blood coagulation system. They maintain the integrity of the vascular wall and help stop bleeding.
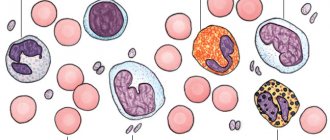
Leukocytes represent the body's defense system. By their number, you can not only identify the acute or chronic course of the disease, but also the state of the human immune system as a whole. This name combines a group of cells that differ in appearance and mechanism of response to stimuli. The fact is that viruses, bacteria, fungi, and allergens are different from each other, therefore the immune bodies must also be structured differently to fight them. This:
- neutrophils, thanks to the function of phagocytosis, absorb and digest viruses and bacteria;
- eosinophils are involved in the formation of allergic reactions;
- basophils, their functions are not fully understood;
- lymphocytes ensure the normal functioning of all parts of the immune system. Up to 80% of their number are T lymphocytes. Killer T cells react to foreign cells and destroy them. Helper T cells recognize pathogenic microorganisms and initiate a protective response. Suppressor T cells suppress the body's autoimmune reactions. B lymphocytes produce immunoglobulins that neutralize bacteria. NK lymphocytes react to their own cells when they degenerate during malignant processes or the introduction of a virus;
- monocytes accelerate wound regeneration and participate in the development and inhibition of inflammation.
The synthesis of “young” lymphocytes occurs in the bone marrow. They finally “mature” in the spleen, lymph nodes and thymus. The function of this organ in the immune system was discovered by scientist Jackie Miller. The lifespan of these cells is about three months. They are found in the general bloodstream and, if necessary, are delivered to the site of localization of the infectious process.
What is relative lymphocytosis?
What are lymphocytes?
Before explaining what relative lymphocytosis is, let's remember what lymphocytes actually are. As you know, they are the main elements that make up the human immune system. They are formed in the bone marrow and “work” in lymphoid tissue. Their main task is to identify a foreign antigen that has entered the human body and facilitate its immediate destruction. In children under six years of age, more lymphocytes are found in the total number of leukocytes - in principle, this is completely normal. This situation is referred to in medicine as “absolute lymphocytosis.” As a rule, as the baby gets older, everything changes - there are more neutrophils. This is called relative lymphocytosis.
Functions
Lymphocytes are rightfully considered one of the most important elements in the pathogenesis of immunodeficiency states, as well as many allergic, oncological, infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Absolute lymphocytosis
In this case, the level of lymphocytes in the blood exceeds the established norm. Doctors note that in clinical practice one can often encounter lymphatic-type leukemoid reactions. They are characterized mainly by the fact that the general blood picture is similar to acute or chronic leukemia. By the way, leukemoid reactions are mainly observed in infectious mononucleosis. It should be noted, however, that in some cases they occur against the background of diseases such as syphilis and tuberculosis. Lymphocytosis in children is usually diagnosed with a viral infection, and lymphocytes differ in morphological diversity. A huge number of atypical lymphocytes are formed in the patient’s blood - they are characterized by nuclear dysplasia and an increase in cytoplasm and in general their properties resemble monocytes.
Possible diseases
So, what does relative lymphocytosis indicate? First, about some infectious diseases: whooping cough, measles, chicken pox (this is especially common in children), malaria, toxoplasmosis, hepatitis, tuberculosis and secondary syphilis. Secondly, about drug-induced hypersensitivity. Thirdly, about all kinds of diseases of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis, myxedema, ovarian hypofunction, acromegaly, panhypopituitarism). Finally, relative lymphocytosis is often observed during prolonged fasting.
Absolute lymphopenia
It is characterized by a reduced level of lymphocytes in the blood and is observed mainly against the background of acute infections. For example, low lymphocytes often indicate the presence of AIDS, as well as purulent and septic processes. The human body also reacts to chemotherapy and radiation therapy with a decrease in lymphocytes.
Therapy
If your doctor diagnoses you with lymphocytosis, treatment should begin immediately. Naturally, first you need to establish its cause, since it usually develops against the background of another disease. Most likely, you will have to take all the tests - this is necessary in order to eliminate errors. The duration of treatment is directly dependent on the existing disease.
The mechanism of development of lymphocytosis
What is lymphocytosis and what causes it? Blood “works” as transport for lymphocytes. The main amount is concentrated in organs - depots. These are the spleen, bronchial vessels, lymph nodes. This determines their relatively low number in normal clinical analysis data. However, when any infectious agent enters through damage to the skin, mucous membrane of the genital organs, mouth, and nose, an immune response develops.
The release of various types of lymphocytes begins from the depot, which causes an increase in their concentration in the total number of leukocytes. It can be absolute or relative. If the symptoms of increased lymphocytosis consist in the percentage predominance of this type of formed elements without changing their total amount in the blood, they speak of a relative increase. If the analysis notes an increase in their overall value, then this is absolute T lymphocytosis (although it is worth noting that all types of these cells are released).
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for lymphocytosis, since it is not a disease, but a symptom. Treatment of the underlying pathology is prescribed by a specialist doctor who will give the patient information about what lymphocytosis is and why it appeared.
- For malignant blood diseases, radiation and chemotherapy, cytostatic drugs, bone marrow transplantation and other methods are prescribed.
- To treat infections of viral etiology, M2 channel blockers, neuroamindase inhibitors, and interferon are used. Bacterial infections are destroyed with antibiotics, fungal infections with antimycotics. Before their appointment, blood cultures are performed to determine the type of microorganisms.
- Symptoms of inflammation are relieved with hormonal, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory or combination drugs.
- A symptom such as body temperature above 38 degrees requires the use of anilides, but long-term use of these drugs is hepatotoxic.
To treat lymphocytosis, a tincture of catharanthus leaves is used as a folk remedy. It helps reduce the level of inflammation in the body and reduce the intensity of symptoms. To prepare, take 10 g of plant leaves and infuse it for a week in 200 ml of vodka. Then the tincture is filtered and taken 10 drops diluted in a glass of water for 3 weeks. It should be remembered that catharanthus is a poisonous plant, therefore, before taking the infusion, consultation with a doctor is required, and the dose should not exceed the permitted volume.
Clinical blood test and its interpretation
Lymphocytosis is shown by a general blood test, which is done in the laboratory within 1 to 2 hours. Based on the number of other formed elements and their ratio, the doctor suggests the cause and nature of the disease. The blood test form is a table that lists the indicators, how many of them actually exist in a particular patient and the norm for adults and children. Let us dwell on them, since this is part of the diagnosis of lymphocytosis.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) – up to 15 mm/hour. During an inflammatory reaction, special substances appear in the blood that increase the adhesion of such cells.
- Leukocytes (4.0 – 9.0 × 109 cells/liter) are no less important indicator than lymphocytes. An increase in their concentration (leukocytosis), especially in combination with an acceleration of ESR, indicates a severe bacterial infection. Lymphocytosis with leukopenia (decreased amount) means a viral disease.
- Red blood cells (3.7 – 5.0 × 109 cells/l). When the blood thickens, which often accompanies dehydration, their number increases; a decrease is usually noted after massive bleeding.
- Hemoglobin (120 – 160 g/l) shows the ability of blood to be saturated with oxygen and carry it. A number below normal means the appearance of symptoms of anemia.
- Hematocrit, color index, mean erythrocyte volume, and platelet count play a role in the diagnosis of specific rare blood diseases and are not usually associated with lymphocytosis.
- Lymphocytes. The form has two values - absolute (1.32 - 3.57 × 109 cells/l) and relative (19 - 37%). It is by these indicators that the type of lymphocytosis is determined.
- Monocytes (0.24 – 0.82×109 cells/l and 3 – 10%). An increase (monocytosis) indicates a protracted course of some diseases of a bacterial nature (for example, tuberculosis). This is also a specific symptom of infectious mononucleosis.
- Eosinophils (0.04 – 0.54×109 cells/l and 0.5 – 5.0%). Exceeding the norm is called eosinophilia. This means allergies, parasitic infestations. This phenomenon is also observed during recovery.
The number of neutrophils is indicative when deciphering the leukocyte formula. Pay attention to their ratio in terms of maturity. Doctors call this a left or right shift. Neutropenia or granulopenia (content below normal) simultaneously with lymphocytosis more often indicates an acute severe viral disease.
Lymphocytosis: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Lymphocytosis is a disease characterized by an increase in the level of white blood cells in the blood. Let's look at what lymphocytosis is, the causes of its occurrence, symptoms and treatment methods.
What are leukocytes needed for?
Leukocytes play a huge role in the body, as they participate in the destruction of harmful bacteria and microorganisms that enter the body, saturate the blood with oxygen, prevent the proliferation of cancer cells, and destroy allergy pathogens and a number of infectious diseases.
Lymphocytosis: causes
Doctors note that the causes of the disease can be very diverse and they are updated in connection with the characteristics of the patient’s body and, as a rule, under the influence of another serious illness. But despite this, the most frequent and obvious are the following:
1) infectious diseases that occur when the body’s immunity decreases under the influence of both external factors (syphilis, allergies) and internal ones (tuberculosis, whooping cough, etc.);
2) transfusion or restoration of blood composition, as well as in case of large blood losses;
3) taking certain medications that lead to changes in blood composition;
4) nervous disorders and mental illnesses;
5) lack of vitamin B-12 in the body;
6) the presence of bad habits such as drug addiction, binge drinking, and smoking;
7) prolonged refusal of food or irregular nutrition, which entails a lack of elements in the body necessary for the formation of a sufficient level of leukocytes;


Lymphocytosis: symptoms
Often, the symptoms of a disease directly depend on the causes that cause it. In general, there are no symptoms that are specific to this disease, since it occurs with a complete absence of symptoms or they are insignificant. Sometimes lymphocytosis manifests itself in the form of infections of the upper respiratory tract and mucous membranes of the oral and nasal cavities, as well as inflammatory processes of the cerebral cortex. In case of AIDS or hepatitis C, lymphocytosis can be detected when the body is severely depleted, and there is also an enlargement of the lymph nodes and spleen, a sharp increase or decrease in temperature, accompanied by chills. And, naturally, this is an increase in the level of leukocytes in the tests.
Leukocytosis: treatment
Since in most cases lymphocytosis occurs against the background of another disease, first of all, it is necessary to diagnose it, and if detected, direct all efforts to eliminate it. In the most ideal scenario, lymphocytosis, the causes of which have already been identified, is treated together with the underlying disease by bed rest, and in the absolute stage, by taking antibiotics. As for prevention, perhaps the only thing that can be recommended is isolation of the patient during treatment. Thus, lymphocytosis, the causes of which are very difficult to determine, is diagnosed in the presence of acute infectious diseases, and it is also recommended to treat it, since, despite the favorable prognosis of doctors, complications such as hemorrhage or poor coagulation may occur against the background of an increase in blood cells.
Causes of lymphocytosis and its types
Lymphocytosis in adults is diagnosed when the number of these blood cells exceeds 3.74 × 109 cells per liter (absolute form) or 37% (relative type). First of all, it is worth noting that sometimes such a symptom occurs for completely physiological reasons. This could be stress, lack of sleep, or in women the first days of menstruation. In addition, there are several types of increases in the number of leukocytes in the blood. Reactive or benign lymphocytosis develops against the background of:
- viral respiratory infections, influenza, mononucleosis (an atypical type of monocytes also appears - mononuclear cells), chickenpox, cytomegalovirus;
- initial stages of HIV;
- such severe acute or chronic bacterial diseases as tuberculosis, typhoid fever, syphilis, tonsillitis;
- parasitic infections (toxoplasmosis);
- autoimmune pathologies;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- food poisoning, ingestion of chemical toxins, overdose of drugs or medications;
- bronchial asthma, eczema, psoriasis.
The causes of lymphocytosis ((in Latin lymphocytosis), as lymphocytosis is called in other words, can also be side effects of certain medications, these are antibiotics, sulfonamides, anti-inflammatory drugs. Immunosuppressants (for example, like Azathioprine), steroids and cytostatics, on the contrary, lead to deficiency neutrophil cells, leukopenia and anemia.The simultaneous combination of a constant relative and absolute increase in the number of lymphocytes indicates oncology (acute or chronic lymphocytic leukemia, thymoma, etc.).It should be emphasized that such a condition requires immediate treatment.
Infectious lymphocytosis deserves special attention. This disease is caused by a lymphotropic virus. The routes of transmission and the mechanism of its development have not been fully studied to date. Its feature is simultaneous leukocytosis.
Norm
The norm of lymphocytes can be expressed in absolute numbers (LYM#), obtained by counting cells in 109/L of blood, or in relative values (LYM%) - the percentage of lymphocytes among all leukocytes. The norm in adults is constant, 19-39% or 1.0-3.6 x 109/l. The number of lymphocytes in children varies and depends on age:
- 22-25% from birth to 4 days;
- 40-76% up to 1 month;
- 38-72% up to 1 year;
- 26-60% from 1 to 6 years;
- 24-54% up to 12 years;
- 22-50% in 12-15 years.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of lymphocytosis are different and are determined by the disease, which provoked deviations from the norm in blood test parameters. Typically, clinical manifestations develop gradually. Those who develop the pathology complain of decreased ability to work, drowsiness, and a feeling of constant fatigue. Then the following may appear:
- increase in temperature, specific numbers are determined by the type of pathology and individual characteristics, usually this value ranges from 37.3 to 38°;
- catarrhal phenomena, this is pain and redness of the throat, hoarseness, possibly cough, nasal congestion;
- lacrimation;
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes (this is especially pronounced in acute mononucleosis);
- a rash may appear;
- reluctance to eat.
With a common ARVI, these symptoms disappear after 7–9 days, even in the absence of treatment. If the temperature persists (or rises) and the patient's condition worsens, this may indicate bacterial complications. In this case, you need to repeat a general clinical blood test. Symptoms of acute malignant lesions of the hematopoietic system develop quickly. Note:
- weakness;
- pallor;
- attacks of dizziness;
- nausea or vomiting;
- constant, successive respiratory infections.
Autoimmune diseases manifest themselves in different ways. A rash that looks like bruises or reddened spots may appear on the body or face. The temperature persists for a long time, although there are no other symptoms characteristic of ARVI. Then morning stiffness of movements, swelling of the joints, and nodular rash on the skin appear.
Symptoms
Relative lymphocytosis is common, as many factors can influence the reduction of other white blood cells. This symptom occurs more often in adults and children under two years of age.
The reasons for such a blood test can characterize various diseases:
- viral infections;
- inflammation with pus;
- rheumatism;
- typhoid fever;
- brucellosis;
- Addison's disease;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
If relative lymphocytosis is detected, then in order to bring the number of cells back to normal, it is necessary to identify the main causes of this phenomenon. Therefore, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination. To confirm the results, you need to take a blood test again and compare the clinical picture. After all, laboratory results often come back false.
Typically, lymphocytosis does not manifest itself in any way, and it is diagnosed during a blood test, but sometimes symptoms of the underlying disease may appear. These signs are often complained to the doctor.
The infection is characterized by fever, enlarged tonsils and lymph nodes, and weakness and nausea. A rash and redness of the skin may appear on the patient's skin. Fever, chills, and rapid weight loss often occur. Sometimes the liver or spleen becomes enlarged.
Therefore, it is important, in addition to the main symptoms, to check all indicators and conduct additional examinations to make the correct diagnosis. In this case, the treatment will be effective and the lymphocyte parameters will return to normal.
Differential diagnosis
As doctors emphasize, it is not tests that need to be treated, but a specific disease. Before starting therapy, the exact cause of lymphocytosis should be established. For this purpose, one general blood test is not enough. To diagnose a respiratory infection, a thorough examination of the patient is necessary, listening to wheezing in the bronchi or lungs to exclude pneumonia.
Measles, rubella, and chickenpox are accompanied by the appearance of a characteristic rash. Mononucleosis occurs in the form of a sore throat, accompanied by severe enlargement of the lymph nodes. Although, to clarify the type of virus, additional tests for lymphocytosis, such as PCR, should be done. This is a way to detect the DNA of the pathogen.
In terms of diagnostics, autoimmune diseases are difficult, especially if there are no other symptoms other than lymphocytosis. A specific marker for such pathologies is an increase in antibody titer in the ANA analysis. Then, if the result is positive, the presence of a number of interleukins, peptides and other protein compounds is checked. They are specific and are produced for any one type of autoimmune disease.
Oncology is diagnosed in a similar way. Additionally, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the internal organs. Long-term chronic lymphocytosis is characterized by hepato- and splenomegaly (an increase in the size of the liver and spleen, respectively). Hearts and joints are also checked. It is necessary to emphasize that lymphocytosis is a condition that persists for several weeks after recovery (this form is called post-infectious).
Lymphocytosis - etiology
Types of childhood lymphocytosis:
- absolute type;
- relative type
The causes of the disease are as follows:
- viruses;
- infectious diseases;
- signs of hepatitis;
- stress;
- increased physical activity
In the presence of a virus, relative lymphocytosis. The reason for the frequent development of the disease in a child is a predisposition to infections.
Additional causes of the disease in children:
- drugs;
- poisonous substances;
A small number of lymphocytes is typical for children of a younger age category. Causes of the disease in an adult:
- infections;
- tuberculosis;
- allergy;
- sexual infection;
- blood transfusion;
- medicines;
- mental disorders;
- lack of vitamin B12;
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- hepatitis C;
- purulent processes
The consequences of this disease are:
- mononucleosis;
- Chagas disease;
- rheumatic pathologies;
- thyroid disease;
Reasons for elevated lymphocyte levels:
- metastases;
- signs of leukemia;
- Crohn's disease
The localization of immature lymphocytes is as follows:
- internal organs;
- circulatory system
The consequences are as follows:
- anemia;
- infectious process;
- presence of bleeding
go to top
Treatment methods for lymphocytosis
Treatment of lymphocytosis consists of eliminating its cause. ARVI can be dealt with using folk remedies. This includes drinking plenty of water (it is better to use rosehip decoction, tea with raspberry or currant jam, fruit drinks for this purpose), mustard plasters, warm compresses on the chest (however, the area of the lymph nodes should be avoided). It is also necessary to rinse the nose with saline solutions and gargle with calendula tincture.
Drug treatment consists of the use of herbal or chemical-based antiviral drugs. Also shown are nasal drops, solutions for treating the oral cavity, palatine arches and tonsil areas. If lymphocytosis is caused by bacterial infections, a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary. When autoimmune or oncological diseases are detected, treatment should begin as early as possible, this increases the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
It will take more than one year to take the drugs. Cytostatics, steroids, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed. As for infectious lymphocytosis, it does not require any treatment and goes away on its own. Despite numerous reviews on forums dedicated to traditional or folk medicine, only a doctor should diagnose the cause of lymphocytosis and prescribe medications.
Any deviations from the norm in a clinical blood test require a mandatory consultation with a doctor. In most cases, an elevated lymphocyte count indicates a viral infection, which is easily treatable. However, this can also serve as a sign of the hidden course of serious diseases. Therefore, to prevent them, you need to undergo such examination regularly, once every 4–5 months.
Source: kakiebolezni.ru
Treatment methods
There is no special therapy for relative and absolute lymphocytosis, since such a phenomenon implies a symptom of a disease. It is necessary to identify the causes, and then prescribe appropriate treatment for the underlying disease.
Blood cancer requires radiation and chemotherapy, cytostatic drugs, and in some cases a bone marrow transplant is required. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are used. If viruses are the cause of the increase in lymphocytes, then antiviral drugs and interferons are prescribed. If the disease is accompanied by elevated body temperature, then take antipyretics.
An important task in relative lymphocytosis is to relieve the underlying inflammatory process. Therefore, symptoms are eliminated with hormonal, anti-inflammatory and mixed drugs.
Thus, specific treatment of relative lymphocytosis is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause, which influenced the significant increase in the parameters of protective cells.
The role of lymphocytes and the norm in the blood
To protect the body, the immune system produces certain cells - lymphocytes. These white blood cells recognize alien cells that have entered the human body.
By synthesizing antibodies to fight them, they help destroy the danger. T-lymphocytes are assigned the role of implementing cellular immunity. B cells are engaged in the production of antibodies and are just waiting for a command to begin their activities.
Cells have different lifespans. Some die within a month, while others store information, providing long-term immune protection.
Normally, the blood contains from 18 to 40 percent lymphocytes, based on the total number of leukocytes. In women, their number changes as a result of pregnancy or menstruation. Therefore, for them, 50-55 percent is not considered a deviation from the norm.
The number of lymphocytes depends on the psycho-emotional state a person is in, how he eats, and what the ambient temperature is . The occurrence of lymphocytosis is determined if white blood cells rise by 15 percent.
In children, the rates are higher, since both the spleen and the thymus gland, which produce blood cells, work more actively. From the day of birth, the child’s body develops its immunity, and therefore the number of lymphocytes reaches from 30 to 70 percent.
Functions of lymphocytes and determination of lymphocytosis
Lymphocytes are immunological defense cells of the human body, which are formed as a result of differentiation during the functioning of bone marrow cells.
Lymphatic cells are responsible for performing the most important functions of immune defense - recognizing all kinds of pathogenic microorganisms and guaranteeing an adequate immune response of the human body to an irritant, that is, foreign microorganisms.
Types of protective blood cells:
- T-lymphocytes, which are formed in the thymus, are responsible for identifying bacterial infections that enter the body. Lymphocytes are also responsible for creating the necessary immunological response to ingestion of pathological microorganisms;
- B lymphocytes make up approximately 15 - 17% of the total cell concentration. Produced in lymphatic and almond tissues. Lymphocytes generate special proteins - antibodies, which guarantee the search for pathogenic microorganisms that have entered the body, as well as malignant cells and their neutralization;
- HK lymphocytes – prevent the invasion of foreign microorganisms into the body and eliminate tumor cells.
Video:
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the concentration of white blood cells in the blood, which flows in the peripheral bloodstream outside the organs.
In a healthy state, the body contains up to 37% of lymphatic cells from the total concentration of blood cells.
With the appearance of pathological microorganisms, toxoplasmosis, hemolytic diseases, and with the aggressive effects of certain medications, lymphocytosis develops.
To accurately determine changes in the composition of the blood, it is necessary to take into account the coefficient between blood cells and the indicator, which is expressed in the weight of blood cells per liter of blood.
READ Is it normal or pathological when leukocytes in the blood are elevated in men?
When the number of neutrophils in the blood changes, both the total concentration of leukocytes and the proportions between monocytes change, the number of which increases. Developing lymphocytosis is divided into relative and absolute.
Relative lymphocytosis is an increase in the number of lymphocytes with a stable total number of white blood cells. Develops due to a decrease in the total number of blood cells regarding lymphocytes.
The process occurs due to inflammatory diseases, due to human infection with viruses or bacteria.
Absolute lymphocytosis is a complete excess of the number of lymphocytes. It mainly develops during acute infectious processes and infection with tuberculosis bacillus.
With the development of a chronic inflammatory process, penetration of lymphocytes into the site of inflammation is observed, that is, lymphocytosis occurs, which inhibits the formation of blood cells.
Blood cells that are not fully mature are called blasts. Immature bodies provoke the development of pathological conditions - anemia, blood loss and others.
The difference between relative and absolute lymphocytosis
A general blood test gives an idea of whether the patient has a relative or absolute increase in lymphocytes.
The latter determines the number of lymphocytes per liter of blood. In adults it is no more than 4x10 to the ninth power. For children, the meaning depends on age. For infants, the norm is 9.00 units, for children over six years old – 8.00.
The relative indicator of lymphocytes is determined as a percentage, taking into account other categories of blood cells - eosinophils, basophils, monocytes. And the norm is considered to be from 18 to 40 percent.
Absolute lymphocytosis is a sign of acute forms of measles, whooping cough, tuberculosis, hepatitis, and AIDS. With these diseases, there are many more white cells in the blood than red cells.
Interestingly, relative lymphocytosis is more common than absolute lymphocytosis. It is clear that this is a state of blood when there are more lymphocytes in it than other leukocyte cells.
Lymphocytosis in children is accompanied by granulopenia, in which the total number of leukocytes decreases. This condition is typical for children from birth to two years old; it is considered a physiological norm and goes away as the baby grows up.
Leukocyte function
It is these white cells that are the “cleaners” of the body; they recognize and destroy pathogenic flora:
- fungi;
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- altered cells that begin the pathological separation process.
There should be about 40% of these white blood cells in the bloodstream. To assess the condition, the non-absolute content of leukocytes is considered, but also the percentage of their various types. Each type of white blood cell fights a specific type of infection.
Their deficiency or excess is classified as relative and absolute lymphocytosis. Relative lymphocytosis syndrome is more common. It is characterized by an increase in the percentage of white blood cells relative to other types of blood cells. During this period, white blood cells may be normal or decrease slightly.
The causes of relative lymphocytosis in children and adults are diseases caused by pathogenic flora, which invade the body when immunity declines.
As an example, the following diseases can be cited:
- Brucellosis;
- Flu or seasonal ARVI;
- Typhoid fever.
Absolute lymphocytosis is diagnosed in acute infections. These are conventionally “childhood” diseases: measles, rubella, whooping cough, scarlet fever. As well as diseases that children suffer along with adults: cytomegalovirus, mononucleosis, hepatitis, sarcoma, tuberculosis and others. During these diseases, the level of lymphocytes in the blood is increased to an absolute value.
Causes and symptoms of lymphocytosis in infants
If the baby’s analysis reveals an increased content of lymphocytes, the specialist does not pay attention to this. After all, this phenomenon is natural for a child. But if accompanying symptoms appear, treatment is prescribed.
Signs of relative lymphocytosis in newborns may appear:
- symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections;
- inflammatory processes in the cerebral cortex;
- chills and fever;
- an increase in the size of the spleen;
- nausea, lack of appetite;
- lethargy, tearfulness;
- rarely skin rashes.
The causes of the pathology lie in the fact that the child’s body has entered the virus of typhoid fever, brucellosis, and influenza.
Lymphocytosis in young children is characterized by a favorable outcome. Treatment is aimed at fighting viruses, bacteria, and relieving inflammation in the body. Continuing breastfeeding will protect the child's body from infections.
Types of lymphocytosis
Lymphocytes are one of the cells of the human immune system. They are formed in the bone marrow and protect the body from foreign microorganisms such as bacteria and infections, and also participate in the process of their destruction. Thanks to the number of lymphocytes, you can find out about your health status and the presence of any disease.
Lymphocytosis in adults is characterized by an increased number of lymphocytes compared to the normal value.
Deviation of indicators from the norm can be caused by the following reasons:
- viral infections (chickenpox, whooping cough, ARVI, hepatitis);
- bacteria (syphilis, tuberculosis);
- blood transfusion after surgery;
- burns and injuries;
- breakdown;
- smoking;
- oncological tumors;
- lack of vitamin B12 in the body.
In addition, the indicator can be affected by poor nutrition or fasting, drinking alcoholic beverages, and taking certain medications. In women, this phenomenon can be triggered by heavy menstruation or the postpartum period, when severe blood loss is observed. As a rule, relative lymphocytosis goes away on its own after all pathological causes have been eliminated.
In children, lymphocytosis usually does not indicate the development of serious illnesses, since their immune system is unstable. Despite this, the doctor must additionally examine the child and rule out dangerous pathological processes.
The lymphocytosis indicator is divided into two types:
- Absolute.
- Relative.
Relative lymphocytosis occurs in patients with pathologies that are characterized by a decrease in the total number of white blood cells in relation to lymphocytes. Viral and infectious diseases usually develop at this stage.
The relative size of lymphocytes is indicated in the leukocyte formula of the blood. It calculates the percentage ratio to other indicators. When such a symptom is confirmed, the level of lymphocytes reaches more than 40%.
Types of lymphocytosis in adults, causes and symptoms
Any deviation in the composition of the blood is a sign that the pathology in the body is caused by acute and chronic infections of viral or bacterial etiology.
In addition to the response to the action of pathogenic microorganisms, the leukocyte formula changes due to:
- leukemia;
- lymphomas;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- Addison's disease;
- liver damage;
- chronic stress;
- intense physical activity in athletes.
Reactive lymphocytosis is determined when the body responds to the occurrence of pathology with an increase in blood cells. After treatment, lymphocytes return to normal .
The malignant form is diagnosed if the patient is diagnosed with chronic or acute leukemia. And only additional tests will be able to give an accurate picture of what is happening in the body of a patient with lymphocytosis. The sooner his cancer is detected, the more successful the treatment will be.
Lymphocytosis in children
Often, lymphocytosis in children is a consequence of the body’s not fully developed immune defense system, but diseases can also provoke this phenomenon.
You need to react calmly to an increase in the level of lymphocytes in a child under 6 years of age - in most cases this is a variant of the norm. There is a clear dependence - the younger the child, the more lymphocytes in his blood. Therefore, before taking any action, it is better to get examined by a doctor to determine the causes of the problem.
Both absolute and relative forms of lymphocytosis can occur in children. Redistribution of the number of immune cells in children is often associated with stressful situations: parental divorce, family quarrels, going to school, etc. To adults, many problems seem insignificant, but a child perceives everything differently and sometimes reacts more sharply. The development of lymphocytosis in childhood is also associated with a predisposition to a number of infectious diseases and their frequent occurrence (acute respiratory infections, measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever and others).
The following factors can affect the child’s blood condition:
- unfavorable home environment;
- significant physical activity;
- poor diet and insufficient time spent outdoors;
- sunburn (the active influence of ultraviolet radiation weakens the body's barriers, which creates favorable soil for the development of pathogenic microorganisms).
It is not difficult to prevent lymphocytosis in a child. Experts recommend hardening the baby from an early age (first with air baths, gradually moving to water procedures), spending a lot of time with him in the fresh air, ensuring the required amount of vitamins and minerals, and protecting him from nervous overstrain.
Diagnostic methods
Even if a blood test shows lymphocytosis, additional examination methods are necessary:
- Analysis of biological fluids will show the presence of antibodies, the appearance of which is associated with an allergic reaction of the body. A bacterial infection is determined in the same way.
- The bone marrow is examined using the myelogram method. Hematopoietic data are compared with the clinical picture of blood from peripheral vessels.
- To identify the structure of blood cells and distinguish deviations from the norm, immunophenotyping of lymphocytes is necessary. Identification of lymphoblasts will indicate pathologies in the body.
- Cytological examination of lymph node tissue will help diagnose malignant tumors.
Since the symptoms of lymphocytosis are similar to many diseases, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the disease that caused an increase in lymphocytes in the blood.
Accurate diagnosis of abnormalities in the blood will allow us to develop a set of therapeutic measures.
Absolute and relative lymphocytosis
Looking at the results of a general blood test, you can pay attention to the fact that the lymphocyte indicator appears in two forms: relative and absolute lymphocytosis.
The absolute value characterizes the number of lymphatic cells per liter of blood. With absolute lymphocytosis, the values exceed 3.6*10 9 /l. The relative indicator is the percentage of lymphocytes in the blood, if the total number of leukocytes is taken as 100 percent. In addition to lymphocytes, these include neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils. The norm of the relative indicator is 19-37%.
It also happens that the absolute content of lymphocytes is within the normal range, but the relative content is not, and vice versa. Relative lymphocytosis in adults is more common than absolute lymphocytosis. In this case, the absolute indicator may even be reduced.
Relative lymphocytosis is observed in diseases during which the number of other types of leukocytes listed above decreases: for example, neutropenia and relative lymphocytosis are quite combined as a result of a general blood test. This means that for some reason there are much more lymphocytes than other leukocyte cells, that is, relative lymphocytosis is observed. What is granulopenia? This is another option for reducing the number of white blood cells and can also be seen with lymphocytosis. Such deviations from the norm are typical for children under 6 years of age.
Diseases that occur with relative lymphocytosis are usually caused by viruses, infections and a decrease in the body's protective function: typhoid fever, leishmaniasis, brucellosis, etc. Other causes of relative lymphocytosis in adults:
- Presence of autoimmune disorders;
- Addison's disease;
- Splenomegaly;
- Hyperthyroidism.
Children under two years of age are especially susceptible to relative lymphocytosis.
Absolute lymphocytosis is a symptom characteristic of acute infections: measles, rubella, whooping cough, chickenpox, scarlet fever, as well as tuberculosis, hepatitis C, hyperthyroidism, AIDS, lymphosarcoma, etc.
In any case, when making a diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account other factors: individual characteristics, genetic predisposition to diseases, general leukocyte formula, results of more specific tests and a comprehensive examination of the body.
Basic treatment methods
Lymphocytosis is a symptom of many diseases, so it is necessary to eliminate the causes of this pathology using traditional and folk medicine.
For identified therapy:
- for malignant tumors, radiation and chemical therapy, cytostatics are used;
- for a viral infection, medications based on interferon and M2 channel blockers are prescribed;
- bacterial disease - antibiotics;
- for inflammatory pathology, non-steroidal and corticosteroid drugs are taken.
In the treatment of children, sulfonamide drugs are used, the action of which is aimed at destroying pathogenic microbes. ACTH is used as a hormonal agent.
Lymphocytosis of non-malignant etiology is treated with traditional medicine:
- Taking echinacea tincture will improve immunity. Take it 20-30 drops three times a day. The product will not only cope with the infection, but will also have a detrimental effect on the cells of pathogenic microorganisms such as a virus or bacteria.
- An infusion of dandelion root will help cope with liver disorders and improve defenses. Prepare the medicine from two tablespoons of raw materials per 250 ml of boiling water. Drink three glasses a day, divided into doses before meals.
- Rosemary will strengthen the child's immune system. A tablespoon of leaves is poured into two glasses of boiling water and left for two hours. After straining, give half a glass to drink before meals. You can add a little honey to your tea.
- Stinging nettle is known as a plant that has a beneficial effect on metabolism and normalizes blood composition. To prepare the medicine, take two large spoons of leaves and pour 250 ml of boiling water. You should drink half a glass up to three to five times a day before meals.
- Among those that boost immunity are berries such as viburnum, cranberries, and raspberries. And grapes help normalize the process of hematopoiesis.
Main causes of lymphocytosis in adults
It is important to understand that an increase in the number of lymphocytes is a natural reaction of the human immune system to an object perceived as a foreign body (it can be a tumor, virus, fungus, etc.). Changes in the blood formula without physiological reasons are a separate problem associated with a violation of the functionality of the body’s defenses; a hematologist will help you cope with it. Normally, the phenomenon of an increase in the number of lymphocytes is temporary, which goes away immediately after the pathogen disappears, but if the symptoms do not disappear, this indicates more serious problems.
The formation of problems in adults can be caused by a variety of factors:
- first of all, this is the presence of an infectious disease;
- recent severe blood loss or transfusion procedure;
- nervous disorders, severe stress;
- vitamin B12 deficiency;
- prolonged fasting, unsystematic nutrition;
- taking medications that can affect blood composition;
- massive inflammatory process with separation of purulent masses;
- ardent abuse of bad habits associated with dangerous substances (alcohol, tobacco, drugs);
- leukemia or cancer in the brain;
- autoimmune disease (characterized by the fact that the cells of the immune system begin to perceive absolutely healthy tissues as foreign agents).
Causes of lymphocytosis in adults (photo)
Lymphocytosis can be caused by diseases such as AIDS, hepatitis C, multiple myeloma, tuberculosis, whooping cough, Crohn's disease, cytomegalovirus infection, vasculitis and others.
The cause of the problem can also be judged by its type. Thus, the absolute form of lymphocytosis, which is characterized by an increase in the number of lymphocytes in the general blood picture, may indicate ARVI, hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, tuberculosis, lymphosarcoma. Relative lymphocytosis (in the leukocyte formula the relative number of lymphocytes increases, that is, their percentage relative to other cells) may indicate the presence of a purulent inflammatory process, rheumatic diseases, hyperthyroidism, etc.
There are situations when the body reacts inadequately to an existing threat - this happens with a highly reactive immune system. In such patients, even the slightest cold causes a significant increase in the number of lymphocytes.
Prevention of lymphocytosis
To prevent an increase in the content of lymphocytes in the blood, it is advised to maintain immunity by playing sports and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Nutrition plays an important role in maintaining normal blood composition . Foods rich in vitamins, selenium, magnesium, potassium, zinc help improve the functioning of the entire body. This is especially true for children and the elderly.
Emotional peace and healthy sleep only benefit the immune system, which will protect against pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
Source: prososud.ru
Lymphocytosis - causes
Lymphocytes
- This is a type of leukocyte, white blood cell.
Lymphocytes are one of the main cells of the immune system, as they are responsible for the production of antibodies and cellular immunity. Normally, their content in the blood ranges from 19 to 38% of the total number of leukocytes. An increased level of lymphocytes in the blood is called lymphocytosis. Types of lymphocytosis
It is customary to distinguish between two types of lymphocytosis:
- relative;
- absolute.
With absolute lymphocytosis, the total number of lymphocytes in the blood increases in relation to their normal content. Relative lymphocytosis occurs due to changes in the content of other leukocytes in the blood, and then the percentage of these cells turns out to be higher when their number is normal.
Causes of relative lymphocytosis
In general, relative lymphocytosis is more common in adults. It can be caused by a number of factors that cause a decrease in the level of other leukocytes:
- viral infections (ARVI, influenza);
- brucellosis;
- leishmaniasis;
- purulent-inflammatory diseases;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- rheumatoid diseases.
Causes of absolute lymphocytosis
Absolute lymphocytosis is usually characteristic of acute infectious diseases, such as:
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- whooping cough;
- chickenpox;
- piggy;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- acute viral hepatitis;
- cytomegalovirus infection and others.
In addition, the cause of lymphocytosis can be:
- tuberculosis;
- some autoimmune diseases;
- hemolytic anemia;
- cancer diseases.
Lymphocytosis has its own characteristics of development in leukemia. With this malignant blood disease, white blood cells do not fully mature and therefore cannot perform their functions. As a result, the content of such immature cells in the blood increases sharply, causing anemia, bleeding, increased vulnerability of the body to infections and other symptoms. An increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood by three or more times is almost always a symptom of cancer.
Other causes of lymphocytosis in adults
In addition to diseases, a violation of the level of lymphocytes can be caused by:
- stress or nervous diseases;
- fasting and irregular eating;
- vitamin deficiency, primarily a deficiency of vitamin B12;
- effects on the body of alcohol, nicotine, narcotic substances;
- taking medications that affect blood composition;
- bleeding.
As a rule, such factors provoke relative lymphocytosis in adults, which most often goes away on its own after the disappearance of the cause that caused it.
Causes of lymphocytosis
The causes of lymphocytosis may be the following:
- Stressful conditions, surges in hormone levels in the body. In addition, physical activity and menstrual bleeding in a woman can cause an increase in the level of lymphocytes. This lymphocytosis is temporary and goes away on its own.
- Tobacco smoking for many years. If a person suffers from this addiction, then his lymphocyte level may remain consistently high. In parallel, erythrocytosis is observed.
- Infectious diseases affecting the body by viruses, bacteria or parasites. At the same time, the immune system is quickly activated. If the infection is bacterial in nature, then the level of neutrophils in the blood increases, and with a viral infection the number of lymphocytes increases. Therefore, any viral infection is accompanied by lymphocytosis. This indicates the activation of the body’s defenses and its active resistance to the disease. The level of lymphocytes will remain elevated until recovery occurs. Lymphocytosis can result from mononucleosis, whooping cough, tuberculosis, syphilis and some other chronic bacterial infections.
- Blood cancer: chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. When the bone marrow is damaged, immature lymphoblasts are formed in it, which do not have the ability to become full-fledged lymphocytes. These cells are unable to form normal immunity, so the person begins to suffer from various infections. Moreover, he will be seriously ill and for a long time. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia most often develops in childhood; in adults, the pathology is less common. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the number of mature lymphocytes in the bone marrow increases, but they are unable to perform their functions.
- Thyrotoxicosis. Lymphocytes take part in the body's immune reactions, which occur in a slow manner. Therefore, an increase in their number in the blood may indicate autoimmune processes. Thyrotoxicosis is one of the most striking examples of such a disorder. In addition, other autoimmune processes can be accompanied by lymphocytosis: Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
- Intoxication of the body with lead, arsenic or carbon disulfide. In case of poisoning, relative lymphocytosis is observed, at this time it is important to monitor the level of neutrophils in order to prevent a sharp drop in immunity.
- Treatment with a number of medications. Lymphocytosis can be caused by taking drugs such as: Levomycetin, Levodopa, Phenytoin, Valproic acid, and some analgesics.
- Splenectomy. Removing the spleen is an operation that can be performed in a hospital only for certain indications. Its absence in the body can provoke a temporary increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood. Then the internal systems adapt and blood counts return to normal.
Lymphocytosis - the causes are very diverse
Lymphocytes are necessary for humans to protect the body from external factors such as pathogenic bacteria and other foreign particles that penetrate inside. Lymphocytosis is a disease in which the level of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood is significantly higher than normal. It is quite difficult to understand in detail how these blood cells work in our body, but having a general idea and understanding the importance of the processes taking place is simply necessary.
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell, cells of the immune system that are responsible for acquired immunity. Normally, 1 microliter should contain 1200-3000 of them, but this figure varies somewhat among different age groups. Relative to all leukocytes, the normal percentage of lymphocytes is 19-37%.
There are not only quantitative, but also qualitative changes in lymphocytes. In the first case, primary cell damage is observed for a variety of reasons. In the second, this is the result of the body’s response to inflammatory processes that occur in organs and tissues. It should be noted that changes in the reactivity of the body are always observed, which is explained by the active participation of lymphocytes in processes that occur at the level of cellular and humoral immunity. With a disease such as lymphocytosis, the symptoms can be different, and they mainly depend on the general condition of the human body, including its immune system.
In order to correctly assess the changes that occur in the blood, it is necessary to determine not only the absolute content of leukocytes in it, but also the percentage ratio between their different types. Therefore, absolute and relative lymphocytosis are distinguished. A change in the percentage of any type of leukocytes does not in all cases correspond to their true increase.
Relative lymphocytosis, the cause of which is an increase in the percentage of lymphocytes, but at the same time there is a normal, and in some cases even a reduced, absolute number, is much more common. It often occurs with various purulent-inflammatory pathological changes and viral infections, including influenza. Such a disease can also develop with brucellosis, typhoid fever, leishmaniasis and other pathological processes that significantly reduce the resistance of the human body.
Regardless of whether absolute or relative lymphocytosis has developed, the reasons for its occurrence lie in the infiltration of inflammation by lymphocytes, which occurs during infections and other pathological changes. In this way, the body reacts to the penetration of foreign elements into the body and fights them.
If, according to research data, a diagnosis of lymphocytosis is made, the causes of which lie in an increase in the number of lymphocytes, then it is called absolute. It often occurs during acute infections such as measles, rubella, viral hepatitis, chicken pox, scarlet fever and others. But the development of lymphocytosis is also characteristic of diseases such as tuberculosis, lymphosarcoma, increased function of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism), acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
With such a malignant blood pathology as lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphocytosis is also noted, the reasons for the development of which are that lymphocytes cannot mature, and therefore, fully protect the body from bacteria and viruses. Immature cells, called blasts, fill the entire circulatory system, as well as many internal organs. This causes the development of bleeding, anemia, the emergence of various foci of infections, and disruptions in the functioning of life support organs.
Lymphocytes guard our body, so you should know whether their number is normal, which is easy to do by regularly conducting a not so complicated analysis.
Symptoms of lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis is not an independent pathology, but only a consequence of any disorders or changes in the body. Therefore, the symptoms of an increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood will be determined by the symptoms of the underlying disease.
With viral infections, fever, sore throat, intestinal disorders, skin rashes, etc. come to the fore. In addition to lymphocytosis, the patient will also experience other abnormalities in blood counts.
With tumors of the hematopoietic tissue, patients experience pain in the bones, and the body temperature will remain elevated all the time. Bleeding increases, immunity decreases.
With lymphocytosis and neutropenia, there is a high probability of a viral infection, such as whooping cough, ARVI, diphtheria, sepsis, etc. With lymphocytosis and monocytopenia, it makes sense to suspect measles, chickenpox, mumps. If monocytes and lymphocytes are significantly higher than normal, the patient should be tested for monocytic leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome.
With infectious mononucleosis, the patient experiences an increase in body temperature, a sore throat, lymph nodes increase in size, and increased weakness and sweating, especially at night. The disease is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus.
Serious poisoning and bacterial infections contribute to an increase in the absolute and relative level of lymphocytes. At the same time, the jump can be quite impressive.
Chronic lymphocytosis, which persists in a person over a long period of time, may be a sign of a sluggish infection, immunodeficiency, or a developing cancer. As a rule, the immunity of such patients is reduced, they get sick for a long time and often, and suffer from constant weakness. Body temperature may remain at subfebrile levels.
At the same time, a long-term slight increase in the level of lymphocytes in healthy people is possible. Experts do not rule out that this may be due to the individual characteristics of the body.
Lymphocytosis in a child
After the birth of a child, he will have increased levels of neutrophils in the blood. Around the 10th day of life, the level of lymphocytes begins to increase, their percentage occupies about 60% of all blood cells. A similar picture will be observed until 5-7 years. In the future, the values of lymphocytes will return to normal and approach similar indicators in an adult. Therefore, lymphocytosis in a young child is a normal variant and is not a pathological sign.
Most often, the child’s body reacts to any infection with a significant jump in the level of lymphocytes. Moreover, other blood cells will remain within normal limits. Leukocytosis can be caused by chickenpox, measles, mononucleosis, influenza, rubella and other infectious diseases. After they are eliminated, the level of lymphocytes will return to its age norm. If this does not happen, or lymphocytosis persists for a long time, it makes sense to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Symptoms and root causes
With the development of lymphocytosis, symptoms can be varied and depend on the state of the body, individual characteristics, and immunity.
To reliably interpret changes in the circulatory system, absolute and relative lymphocytosis are distinguished.
Due to the fact that lymphocytosis is not an autonomous disease, but an indicator of pathologies in any part of the body, the symptoms are not isolated, but depend on the cause that provoked the inflammatory process.
If lymphocytosis is caused by the penetration of viruses into the body, then the symptoms will not take long to appear - on the first day, increased body temperature, headache, sore throat, cough, nasal congestion, diarrhea appear.
A blood test will reveal not only an increased concentration of lymphocytes, but also other deviations from the norm.
In a situation where changes in the composition of the blood occur in a person who has suffered a disease, the state of health will be almost normal, and manifestations of the disease will not occur.
READ Possible health problems if red blood cells are low
It happens that due to the discovery of such a relative increase in protective blood cells, a person may undergo repeated diagnostic procedures in order to discover the cause.
If the generalized number of lymphocytes approaches normal, and in the near future the patient has had an infection of viral etiology, then this is not worth unnecessary worry.
It is necessary to repeat the examination after some time and periodically consult with a doctor.
If absolute lymphocytosis develops, complications may arise. If the total concentration of lymphatic cells increases due to the tumor process of hematopoiesis, then signs of the disease will signal the development of neoplasia.
Pain in the joints and bones appears, the liver increases in size, fever and chills become permanent, problems with blood clotting appear, infections occur with complications due to the weakening of the body's immune system.
With changes in lymph cell concentrations, other abnormal blood tests often occur.
Neutropenia and lymphocytosis are often combined during acute respiratory infections, whooping cough, blood poisoning and during recovery from these diseases.
With lymphocytosis of relative origin and acute neutropenia, the risk of repeated infectious complications, which are neither normal nor pathological reactions of the body, increases.
Measles, rubella, and chickenpox are characterized by increased lymphocytes and monocytes. The levels of these blood cells increase significantly with leukemia, dysplasia and other malignant processes of the circulatory system.
Lymphocytosis, which has become chronic, is a sign of a sluggish infection or an emerging malignant neoplasm.
Reasons that provoke the development of lymphocytosis:
- acute viral infections;
- rheumatic diseases;
- development of hyperthyroidism;
- Addison's disease of the adrenal glands;
- increase in the size of the spleen;
- children up to two years of age.
How to diagnose lymphocytosis?
To diagnose lymphocytosis in a person, it is necessary to take a clinical blood test. In past years, laboratory technicians performed all calculations manually, examining a blood smear under a microscope. Modern laboratories are equipped with automated devices that perform this work. Therefore, lymphocyte counts may vary in the same person, depending on how exactly they were counted.
If the doctor has any doubts, he may order another blood test to count the absolute value of lymphocytes. Existing deviations from the norm are compared with specific symptoms that bother the patient. Additional examinations are prescribed as necessary.
Treatment of lymphocytosis
There is no treatment for lymphocytosis, since this condition is not an independent disease. Therapy is determined by the cause that provoked the increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood.
For acute infections, antiviral drugs or antibiotics are prescribed. Antifungal agents may be needed. For a speedy recovery, you need to drink as much fluid as possible; in parallel, symptomatic treatment is carried out aimed at reducing body temperature, eliminating pain, relieving intoxication, etc.
If a malignant tumor is detected, the patient is prescribed cytostatics and immunosuppressants. To prevent complications from occurring, the patient is prescribed fungicides and antibiotics.
To prevent the development of lymphocytosis, it is necessary to direct efforts to strengthen the immune system, lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and harden yourself. During periods of outbreaks of viral infections, you should avoid crowded places, wash your hands with soap, and take vitamin and mineral complexes.
Lymphocytosis is not a reason to panic. Most likely, after getting rid of the disease, the lymphocytes will return to normal on their own. In any case, if unexplained weakness appears, with prolonged low-grade fever and other pathological symptoms, you should consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. The sooner treatment is prescribed, the higher the chances of a speedy recovery.
Source: www.ayzdorov.ru
Lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis is characterized by an increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood that circulates outside the hematopoietic organs.
A healthy person's blood contains from twenty to thirty-five percent lymphocytes or 0.8 - 3.6 g/l.
Lymphocytosis causes . Lymphocytosis occurs as a result of the presence in the body of viral infections such as influenza, viral hepatitis, whooping cough or non-viral infections - malaria, diphtheria, syphilis, typhoid fever, as well as due to blood diseases such as toxoplasmosis, lymphocytic leukemia and lymphosarcoma.
In order to correctly determine changes in the composition of blood occurring at the cellular level, it is necessary to take into account both the percentage of the number of cells and the absolute value, which is expressed in the mass of cells contained in one liter of blood.
With a significant decrease in the number of neutrophils, the total number of leukocytes in the blood also changes, and the percentage of monocytes also increases, although their number remains unchanged.
Lymphocytosis varieties . Lymphocytosis can be absolute and relative. The first type is characterized by an absolute increase in the number of lymphocytes. Often this type occurs in acute infectious diseases - viral rubella, scarlet fever, measles, tuberculosis and lymphosarcoma.
Relative lymphocytosis is manifested by an increase in the proportion of lymphocytes and their unchanged relative number. This form of the disease is diagnosed much more often than absolute lymphocytosis.
Relative lymphocytosis is detected in almost any disease in which there is a decrease in the number of other types of leukocytes. This form of the disease occurs during rubella, brucellosis, typhoid fever, purulent-inflammatory diseases, and leishmaniasis.
Chronic inflammation and infection contribute to the infiltration of the inflammation site by lymphocytes, as a result of which absolute or relative lymphocytosis develops in the blood.
Lymphoblastic leukemia prevents the maturation of lymphocytes. These blood cells are called blasts and cause infections, anemia, bleeding and other reactions.
Lymphocytosis treatment . Treatment of a diagnosis of lymphocytosis by specialists is aimed at eliminating foci of inflammation in the body. The complex therapy program is aimed at the underlying disease, which is accompanied by one or another form of lymphocytosis. With timely and correct treatment, lymphocytosis goes away along with the underlying disease. Timely treatment under the supervision of experienced doctors reduces the likelihood of adverse situations occurring.