Vagotonia is a pathological condition of the body, provoked by excessive tone of the vagus nerve, which is responsible for the normal functional functioning of internal organs, the process of secretion and the functioning of blood vessels.
This disease is not independent, and the symptoms of vagotonia manifest themselves in dozens of clinical indicators, which greatly complicates diagnosis.
The identical name for vagotonia is parasympathicotonia, or VSD of the vagotonic type. The pathological condition is quite common in children and adolescence.
According to statistics, more than fifty percent of children who are brought to the pediatrician with non-infectious diseases have vagotonia.
Diagnosis of autonomic dysfunction of this type in adults also occurs quite often, when the main factor in the appearance of vagotonia is a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, more stress and heavy physical and psycho-emotional stress in everyday life and at work.
Diagnosis of the disease always occurs using a differential method. Doctors will rule out structural organ damage, according to the patient’s complaints. If hardware tests are normal, but there are further complaints, vagotonia is diagnosed.
A broader concept that includes vagotonia is vegetative-vascular dystonia (vegetative dystonia syndrome, VSD). The concept of vagotonia is a special case, one of the subtypes of VSD. Often the diagnosis may be recorded as autonomic dysfunction of the vagotonic type.
Making such a diagnosis suggests that the dystonia factor is a spasm of the vagus (vagus nerve).
Hypertonicity of the vagus nerve is the cause of vagotonia
Causes that provoke vagotonia
Vagus (from Latin vagus) is the tenth pair of cranial nerves, also called the paired or vagus nerve. It is located in the brain and travels to the chest and abdominal cavity.
The nerve consists of autonomic, motor and sensory fibers that provide contraction of the lungs, digestive tract, glands and heart muscle.
Hypertonicity of the vagus nerve leads to spasms of smooth muscles, increased contractions of the stomach and intestines, and heart contractions also slow down. All these signs indicate progressive vagotonia and require examination by a doctor.
In most cases, the progression of vagotonia is caused by the presence of a number of pathological factors that affect the human body simultaneously. In some cases, a genetic predisposition is possible.
According to statistics, signs of vagotonia are observed in fifty percent of the world's population.
The most common factors that provoke the vagotonic type of autonomic dysfunction are the following:
- Increased pressure inside the skull;
- Psycho-emotional stress, prolonged anxiety states;
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Oxygen starvation of the fetus inside the womb;
- Injuries received during childbirth;
- Weakening of muscles due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- Presence of chronic infectious foci;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Diabetes;
- Hereditary disposition;
- Changes in climate zones;
- Age category – children and women in menopause are more susceptible to damage;
- Disorders of the functional functioning of the digestive tract and respiratory tract.
The progression of vagotonia in childhood is due to incompletely formed individual elements of the nervous system, rapid physiological growth and changes in hormonal levels during puberty.
In the case of females, vagotonia is provoked by the period of gestation, childbirth and menopause.
These conditions are not pathological, but can manifest themselves in various signs of autonomic dysfunction.
Symptoms
Vagotonia is a pathological condition that negatively affects internal organs and systems, therefore the external signs of the disease are divided into several syndromes.
The cardiac group of clinical manifestations includes:
- bradycardia or slow heart rate;
- decreased blood tone or hypotension;
- pain and discomfort in the heart area;
- freezing in the chest.
Symptoms of changes in respiratory function:
- shortness of breath similar to that that begins during asthma attacks;
- weak breathing;
- feeling of suffocation;
- bouts of severe, painful dry cough.
Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system are indicated by:
- lump in the throat;
- violation of the swallowing process;
- loss of appetite, up to complete aversion to food;
- bowel movement disorder;
- belching and heartburn;
- non-localized pain in the abdomen and chest;
- the appearance of a characteristic rumbling in the stomach.
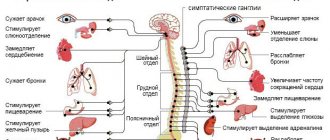
Types of autonomic dysfunction
The nervous system is characterized by a division into two types: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system, which, in a normal state of health, counteract each other, helping to maintain the balance of the body and get it used to new environmental conditions.
If one of the subsystems begins to predominate over the other, then autonomic dysfunctions progress.
To accurately determine the signs of vagotonia, we will consider the signs of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
The predominance of one of the systems over the other is called sympathicotonia (hypersympathicotonia) and vagotonia, respectively.
Prognosis and prevention
Autonomic dysfunction is not considered a serious disease that threatens human life. However, a long course of vagotonia can provoke serious consequences, including a chronic form of the disease. Timely consultation with a doctor and the correct course of treatment for vagotonia provide a favorable prognosis.
Simple preventive measures will help prevent the development of vagotonia in the future:
- observe a sleep and rest regime - normalize the daily routine - sleep at least 8-10 hours a day, take regular walks in the fresh air and relax;
- engage in moderate physical activity - morning exercises, swimming, skiing and skating, yoga are useful;
- harden the body - dousing, rubbing with cold water, contrast shower;
- maintain a proper diet - adhere to a nutritious diet every day with a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins, as well as the correct eating regimen and sufficient drinking;
- give up bad habits, junk food, spending time at the computer and TV;
- take vitamin complexes in the spring and autumn;
- try to avoid stressful situations and recharge with positive emotions - eliminate nervous overload at work, normalize relationships at home;
- engage in intellectual activity;
- prevent the development of chronic forms of diseases - undergo timely examinations by doctors.
Analyze your lifestyle, and if something from our preventive list is not on it, implement it. The results will not keep you waiting!
Symptoms of vagotonia
Signs of vagotonia appear if the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system predominates. Vagotonics have a wide range of clinical signs that prompt the patient to undergo examinations and search for various causes of deviations in the functionality of organs or body systems.
A vagotonic person may suspect serious illnesses or mental disorders. For an accurate diagnosis, you will need to undergo a series of hardware and laboratory examinations, and only after this can a diagnosis be made.
The predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system in children and adults is characterized by the following signs of vagotonia:
- Loss of interest in what is happening around;
- Constant drowsiness;
- Depressive states;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Rare heart contractions (cardiac vagotomy is noted);
- Low blood pressure;
- Lack of appetite while maintaining excessive excess weight;
- Dyspepsia (pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract);
- Nausea, heartburn;
- Constipation;
- Pain in the stomach and intestines;
- Constant feeling of chills and lack of air (pulmonary dystonia);
- Feeling of a “lump in the throat”;
- Dizziness, feeling of loss of consciousness;
- Paleness of the skin;
- Blue skin tone;
- Regular allergic reactions;
- Increased secretion of saliva and sweat;
- A constant urge to urinate that does not relieve swelling.
Many of the above-described signs may not be noted during hardware and laboratory examinations. This indicates that the structural components of the organs are intact, but the functionality is impaired.
The vagotonic type is diagnosed after excluding all possible morphological destruction of organs, and symptoms continue to progress.
A person who has been briefly influenced by a vagotonic effect is not confident in himself, is inclined to question himself, tries to visit all possible doctors, often trying to convince them of the presence of a serious illness.
He describes the complaints that bother such a patient in all colors and details. Fear of a serious pathological condition and the eternal search for a cause lead to psycho-emotional disorders and even suicide.
Quite often, with vagotonia, psycho-emotional changes come to the fore, in addition to other symptoms.
This means that victims cannot normally remember information (especially facts), while thinking in images remains at a normal level. Most of them fail to work both physically and intellectually, as they are plagued by fatigue and drowsiness during the day.
The course of vagotonia can be either chronic, with constantly disturbing symptoms, or in the form of exacerbations (crises), when health rarely worsens.
Exacerbations can be of three degrees of severity:
- Mild degree of vagotonia . Such a crisis continues for fifteen minutes and only one vagotonic reaction manifests itself - increased sweating, slowing of heart contractions, fainting;
- Average degree of vagotonia . This type of exacerbation lasts about twenty minutes and is noted when moderate symptoms appear - pain in the heart, dizziness, drop in blood pressure, slowing of heart contractions and a feeling of sinking in the chest, etc.;
- Severe degree of vagotonia . It means obvious autonomic dysfunctions that affect many organs. In some cases, convulsive states and loss of consciousness are noted. When such a crisis ends with a person feeling general weakness and indifference to what is happening around him for several days.
With the progression of exacerbation of vagotonia against the background of psycho-emotional stress, the following signs may be observed:
- Sympathoadrenal attack - manifests itself in increasing anxiety and fear of death. An increase in the number of heart contractions, high blood pressure and body temperature are often observed. There are chills, trembling of the limbs, an increase in the amount of urine excreted;
- Vagoinsular crisis is characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure and temperature. There is blanching of the skin, nausea, and vomiting. Often accompanied by pain in the abdomen and heart. There is rapid bloating of the intestines. People complain of headaches and difficulty breathing.
Signs of vagotonia in the sympathicotonic type
Since both systems work in opposition to each other, the manifestation of symptoms in sympathicotonia is opposite.
The most pronounced symptoms felt by sympathotonics:
- Rapid excitability;
- Aggressiveness;
- Loss of ability to concentrate on one thing;
- Increased number of heart contractions;
- Increased body temperature;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Strong appetite, but body weight remains small;
- Pale skin tone;
- Poor heat tolerance;
- Cold hands and feet (VSD with agniospasms);
- Frequent constipation with increased urine output;
- Decreased secretion of saliva and sweat.
The course of vagotonia cannot be predicted. For a long time they can proceed to a latent form and manifest themselves in the form of exacerbations, or they can gradually increase symptoms.
Predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system over the sympathetic
How does vagotonia manifest in children?
The main signs that the vagal effect has affected the child are the following:
- Meteor dependence;
- Frequent allergic reactions;
- Increased sweating;
- Swelling;
- Pale skin tone;
- Bluishness of the extremities;
- Hard breath;
- Lack of air;
- General weakness;
- Poor appetite;
- Nausea;
- Pain in the abdomen;
- Narrowing of the esophagus, pharynx;
- Babies are prone to spitting up;
- Diarrhea and constipation.
A separate disease is vagotonia with low blood pressure, manifesting itself by the ninth year of life. With this disease, children complain of pain in the head and chest, and low endurance.
There is loss of alertness, loss of concentration, memory impairment, loss of sleep and anxiety.
Impaired autonomic tone negatively affects the physical and mental development of the child, who has a large amount of excess weight and does not tolerate sports activities well, which causes apathy towards sports.
General fatigue and sleep disturbances affect learning and memory.
Such children are lagging behind the school curriculum.
Symptoms
The patient is worried about bradycardia, digestive function is disrupted, a panic attack and apathy appear. In this case, it is necessary for the doctor to carefully analyze all the patient’s complaints.
Vagotonia can occur in different ways - in mild and severe form. The paroxysmal form is accompanied by chronic infection, stress, constant lack of sleep, and overwork.
The main complexes of disorders can be identified:
- Cardiac – a person is prone to low blood pressure and rare heart contractions. Some people experience a feeling of squeezing and sinking of the heart in the chest.
- Respiratory – shortness of breath appears, which resembles an asthma attack, and respiratory arrhythmia is also a concern. Sometimes a person feels as if there is not enough air in the chest and a dry, painful cough appears.
- Digestive – a lump is felt in the throat, it becomes difficult to swallow food, appetite decreases, the stomach growls, severe heartburn, belching, and in some cases diarrhea or constipation.
- Brain - headache, feeling of heaviness in the back of the head. Then drowsiness increases, weakness appears, and the person is prone to depression, apathy, and hypochondria. Memory also decreases and panic attacks occur.
Diagnostics
At the patient’s first visit, the doctor listens to his complaints and performs an initial examination to determine obvious disorders. After this, the doctor examines the history, not only of the patient, but also of the family. In most cases, autonomic dysfunctions are inherited.
After this, a differential diagnosis is made, which either excludes structural damage to organs and structures of the body, or confirms them.
The doctor may send a patient who is suffering from vegetative dystonia to the following types of examinations:
- Ultrasound examinations (ultrasound);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- General blood and urine analysis;
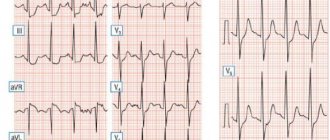
- Electroencephalography (EEG);
- Electrocardiography (ECG study).
- 24-hour blood pressure tracking;
- Fluorography.
The choice of method for examining the body is made by the attending physician, depending on the patient’s complaints and obvious signs.
Causes of vagotonia
The pathogenesis of the development of vegetative dystonia is different for each person. Here we can rather name not the direct causes of the development of pathology, but the factors that provoke its development. These are:
- frequent and severe emotional stress;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetics;
- constant intellectual load;
- increased emotionality;
- frequent viral infections;
- presence of chronic diseases.
Important: In some cases, the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the vagotonic type is detected in people who have changed climate. When moving from one climate zone to another, there is a disruption in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. She cannot cope with the restructuring of the body to the new climate.
Treatment of vagotonia
Vagal disorders (vagus nerves) are treated with both medications and non-drug treatments, and folk remedies. Initially, they try to treat without medications, and if there is no effectiveness, medications are added.
The selection of a course of treatment for vagotonia is carried out individually, and treatment can be long-term and complex. When forming a course of therapy, they are based on the age category, patient complaints and the presence of concomitant diseases.
It is mandatory to note the characteristics of the patient’s mental health and emotionality, as well as the level of mental development.
The main methods of therapy for vagotonia are:
- Restoring normal daily routine;
- Selection of the right diet;
- Increased physical activity;
- Drug support;
- Treatment of concomitant diseases.
What is non-drug treatment?
The first thing you need to do is restore your normal daily routine with proper rest, sleep time of at least ten hours a day and walks in the fresh air for at least two hours. Also, you should avoid watching television and sitting at the computer as much as possible.
Non-heavy physical exercises are selected, which are mandatory for the treatment of vagotonia, both in children and adults. The most beneficial are swimming, gymnastics, walking, and physical therapy.
Children benefit from douches and pine baths, which increase vascular tone.
One of the main factors is the normalization of a healthy diet, with a complete enrichment of vitamins and nutritional components.
With low blood pressure, it is recommended to drink more water, tea, coffee, vegetable cereals, legumes and chocolate. Before going to bed, it is recommended for children to give them honey, juice, compote.
One of the most important points of therapy for vagotonia is psychotherapy. Individual sessions with a psychologist are most effective.
When treating vagotonia without medications, physiotherapy is also used, which consists of electrophoresis with Mezaton, or caffeine, at low pressure and a small number of heart contractions.
Also, massage of the calves, back, cervical region and hands helps against low blood pressure. Acupuncture is quite effective, but it needs to be performed by a qualified specialist.
What medications are used to treat vagotonia?
When the above measures do not have the desired effect, drug therapy for vagotonia is prescribed.
The most common medications are:
- Antidepressants (Diazepam, Noofen, Grandaxin, Medazepam) - used for anxiety, loss of sleep, as well as asthenia with hypotension;
- Nootropic drugs and medications that improve metabolic processes in nerve tissues (Piracetam, Encephabol, Pantogam, Glycine) are used to improve higher processes in the brain;
- Ginseng tincture, Eleutherococcus - increase vascular tone and blood pressure. Can be prescribed to both adult and children's age categories;
- Diuretics (Diacarb, Trental, Cavinton) - used to improve blood circulation in the brain;
- Sedatives (valerian, sage, motherwort) are the safest herbal preparations;
- Vitamin B, antioxidants and other tonic drugs;
- Adaptogens , which are of plant origin, help cope with increasing physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Taking medications without a doctor's prescription can lead to serious complications.
Vagotonia: what is it and how does the disease manifest? Treatment of vagotonia
Children whose severity of autonomic disorder is accompanied by increased fatigue, poor sleep and the presence of other additional problems suffer from such an ailment as vagotonia. Today we will determine what it is and how the disease manifests itself, because it is observed not only in children, but also in adults. We will also find out what the symptoms of this disease are and how to deal with it.
Definition
Surely most people do not know the meaning of the word “vagotonia”, what it is and, in general, what area it comes from. And this is a term from medicine; it means the dominance of the tone of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system over the activity of its sympathetic side. The definition of this word will be deciphered more clearly based on the indicators of this disease.
Symptoms
Signs of vagotonia may be as follows:
- Sweating.
- The skin becomes cold and damp.
- Bradycardia occurs (a type of arrhythmia in which the heart rate becomes less than 60 beats per minute).
- There is a tendency to faint.
- Hypersalivation (increased secretion of the salivary glands).
- Respiratory arrhythmia.
- Patients become slow, indecisive, phlegmatic, have little endurance, and are prone to depression.
- Problems with the digestive system: diarrhea or, conversely, constipation, abdominal pain, swelling under the eyes, allergic reactions of various origins.
- The patient may experience constriction of the pupils.
- Obesity.
- Poor tolerance to cold.
- Strengthening erection.
It also happens that our beloved sons and daughters suffer from this disease. Children with this diagnosis require increased attention from their parents. If they don’t receive it, they can easily become depressed, begin to be capricious, and have problems sleeping.
The memory of such girls and boys is not very good, but imaginative thinking is usually well developed, which allows them to remember not facts, but images.
For example, it is easier for such children to remember a phone number by the order of pressing the buttons on the device’s keyboard than to actually mark the numbers themselves.
Also, children diagnosed with vagotonia are often overweight, but they do not eat well. Such boys and girls suffer from a vestibular disorder. For example, they can get very sick in transport.
In this case, it is important to redirect the child’s attention in another direction. During a long journey, regular mints or, for example, some games (counting cars traveling in the opposite direction, etc.) will come to the rescue.
)
Causes
The most common factors in the appearance of a disease such as vagotonia, the symptoms of which were described above, are:
- Neuroses.
- Minor brain damage.
- Stem and hypothalamic disorders.
- Hereditary abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous system.
- Mental stress, emotional overload.
Vagotonia: treatment of the disease
It is quite difficult to treat this disease, and it must be dealt with by a specialist. But you can reduce the manifestations of the disease using fairly simple methods.
- With a mild degree of damage, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle: do not smoke, do not drink alcohol, sleep at least 8 hours, do morning exercises and exercises, and preferably do this in the fresh air. You should not engage in serious sports, such as weightlifting or football, but a general strengthening set of exercises will benefit the patient.
- Proper nutrition is very important during treatment. To do this, you should exclude fatty, salty, and sweet foods from your diet. But fresh vegetables, fruits, and cereals (especially those with a high content of magnesium and potassium) must be consumed.
- Water procedures will help cope with vagotonia. Activities such as swimming, sauna, and medicinal baths are perfect for this. Salt, pine, radon baths, and rubbing with cold water are recommended for children.
- With this diagnosis, a specialist may prescribe a general massage.
Therapy with drugs
We have already found out how vagotonia manifests itself, what it is and how to treat this disease without the use of drugs. However, in case of serious and severe conditions of the patient, specialists prescribe drug therapy.
Often these are drugs with a sedative effect, antidepressants with vitamin complexes, restoratives and anti-anxiety drugs. Often the doctor prescribes treatment with herbal medicine tablets. Children with increased excitability and anxiety are recommended to drink herbal infusions: sage, hawthorn, valerian, St. John's wort.
This herbal complex has a sedative effect. The course of treatment is usually long - from 3 to 12 months.
In addition to tinctures and extracts, different types of tea can be used.
If the sedative effect is insufficient, anxiolytics and antipsychotics can be used in the treatment of vagotonia.
It is not so easy to completely get rid of this illness, but if a person strictly follows all the doctor’s recommendations, this will significantly alleviate his condition and give him peace of mind.
Now you know about such a disease as vagotonia. We also found out what it is and what its manifestations are.
So, this disease can appear for several reasons, which are mainly associated with emotional overstrain, stress, and neuroses.
Only an experienced specialist can diagnose “vagotonia,” so if the condition of a child or adult worsens, you should definitely see a doctor.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/189905/vagotoniya-chto-eto-takoe-i-kak-proyavlyaetsya-bolezn-lechenie-vagotonii
Prevention
For the treatment and prevention of vagotonia, you should follow a list of actions that will help maintain the normal state of the autonomic nervous system:
- Stick to a daily routine, setting aside time for proper rest and sleep for at least ten hours;
- Allocate at least one hour a day for walking;
- Exercise. Swimming, gymnastics, dancing, athletics, and walking are recommended. Restrictions for athletes with heavy sports;
- Eliminate or minimize psycho-emotional stress;
- Eliminate alcoholic drinks, cigarettes, drugs;
- Proper nutrition. It is necessary to saturate the diet with plenty of vitamins and minerals. Reduce consumption of fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods;
- Maintain water balance by drinking at least 1.5 liters of clean water per day;
- Once a year, undergo a routine examination for early diagnosis of possible diseases.
What is vagotonia
Autonomic dysfunction is a complex of various pathological reactions of the body, which develops as a result of any deviations in the activity of the autonomic nervous system.
Vagotonia in adults is one of the forms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, resulting from increased tone of the vagus nerve. Another type of autonomic dysfunction is expressed in the predominance of the functionality of the sympathetic nervous system.
The vagus nerve is located in the neck and goes from the brain to the organs, thus being responsible for their functioning. Due to the development of vagotonia, the normal proper functioning of internal organs and blood vessels is disrupted, which negatively affects the human condition.
The vagotonic type of autonomic dysfunction is widespread in childhood and adolescence, since they have a growing body, hormonal changes in the body and a fragile, immature nervous system. However, a large percentage of those suffering from vagotonia are also found among the adult population.
The complex rhythm and lifestyle increasingly exposes people to stress and increased emotional stress, which not everyone can cope with.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia - symptoms, types, provoking factors of development
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision ( ICD-10 ), this condition is included in the group: “Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system” and combines vegetative-vascular dystonia, cardioneurosis, neurocirculatory asthenia, vegetative neurosis and other concepts.
Why does VSD occur?
Of course, this is a multi-cause condition that does not develop in a day or even in a month.
The main reason for it is the long-term influence of risk factors on a predisposed organism and the disruption of adaptation of the autonomic nervous system to various stresses.
More and more, scientists around the world are collecting practical observations for this condition, deducing predisposing risk factors, development mechanisms and symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
However, vegetative-vascular dystonia can be a mask for some other diseases and therefore deserves special attention.
How does VSD develop?
Particular attention in the mechanism of development of vegetative-vascular dystonia is given to hereditary and constitutional predisposition, the implementation of which is provoked by the above factors.
As a result, problems occur in the interaction between the nervous and cardiovascular systems and manifest themselves in the form of: functional insufficiency or redundancy in the nervous and hormonal regulation of the cardiovascular system, changes in metabolic characteristics and sensitivity of the receptor apparatus.
How does Vegetative-vascular dystonia manifest?
VSD has a huge number of symptoms, which sometimes tend to constantly change. Moreover, it can have just one symptom or several dozen at the same time.
There are general symptoms for VSD and specific ones that are characteristic of certain types of flow.
Also, the symptoms depend on which part of the autonomic nervous system predominates, the sympathetic ( sympathicotonia
) or parasympathetic (
vagotonia
).
Signs of sympathicotonia:
Signs of vagotonia:
Many people know that disruption of the autonomic nervous system can occur in several clinical types: cardiac, hypertensive, hypotonic and mixed.
What to do if symptoms of VSD appear?
Since this functional disorder may be a mask for another disease, you should seek medical help to conduct an examination and rule out these diseases.
To exclude damage to the heart and other organs, studies are carried out:
ECG, ultrasound of the heart, blood tests, exercise tests, daily ECG monitoring. And usually exclude such diseases as: hypertension, myocarditis, heart defects, myocardial dystrophy, peptic ulcer, bronchial asthma, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, etc.)
If they are not found, then, most likely, the doctor will diagnose vegetative-vascular dystonia according to this type (out of three proposed.
) Prescribe treatment depending on the clinical manifestations, their severity and psychological state.
In treatment there are both general aspects for all types of VSD, and special ones depending on the type of course. More details about them in the article dedicated to this.
Now be sure to watch 2 videos that will help you understand what vegetative-vascular dystonia is and identify its symptoms.
4411
Source: https://bessudnov.com/zabolevaniya-serdechnososudistoj-sistemy/vegetososudistaya-distoniya
Vagotonia: causes, symptoms, treatment of vagotonic type of VSD and dysfunction – Vessels Med
Recent studies confirm the fact that autonomic dysfunction is on the border with mental pathology. The disease develops due to the constant presence of depressive moods, neuroses and stressful situations in life. Dystonia of the vagotonic type is one of the options for the development of this pathology.
Causes of vagotonia
Vagotonia is a condition in which the vagus nerve is characterized by increased tone, as a result of which the functioning of internal organs, glands and blood vessels is disrupted. This type of vegetative-vascular dystonia is not considered to be a separate disease, but rather a condition that requires constant monitoring and observation.
The vagotonic type of VSD is widespread among children and adolescents; adults are not immune from its occurrence. The main reason for the appearance of this condition is infrequent physical activity, as well as the lack of a healthy lifestyle and high levels of stress.
The mechanism of occurrence of the vagotonic type of dystonia looks like this:
- the vagus nerve, running from the brain to the organs located in the peritoneum and chest, supplies them with impulses emanating from the nervous system and regulating the work process;
- when the vessels increase their tone, spasm of smooth muscles occurs, which enhances the motor functions of the intestines and causes a decrease in the heart rate;
- This situation provokes a deterioration in the general condition, which is manifested by sleep disturbances, deterioration of mood and weakness.
Causes of vagotonia:
- previous brain injuries;
- oxygen deficiency experienced by the fetus while in the womb;
- injuries received by the child during the birth process;
- periodic increases in intracranial pressure;
- emotional overload;
- constant stress exposure;
- experiences of strong severity and long duration;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system;
- low physical activity;
- chronic foci of infectious diseases in the body;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- a sharp change in climate zone;
- adolescence and childhood;
- period of menopause in women.
Signs of vagotonia appear under the influence of immaturity of central nervous system regulators, active physical development, and hormonal changes. All these processes are, therefore, they cannot be called a disease, but only disorders of the autonomic part of the central nervous system.
Manifestations of vagotonic syndrome
VSD of the vagotonic type is characterized by a wide variety of symptoms characteristic of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Manifestations of vagotonia can be expressed in several forms:
- Paroxysmal, when disturbing symptoms worsen under the influence of external factors (for example, stress or fatigue).
- Constant, present every day.
- Hidden, with manifestations that do not have an obvious form.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of adolescents, children and adults of the vagotonic type is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The cardiovascular system reacts with the following manifestations: disturbances in heart rhythm, bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, pain in the chest, a feeling that the heart has stopped for several moments.
- The respiratory system produces the following symptoms: shortness of breath, even at rest, a feeling of oxygen deficiency, increased swelling of the larynx, coughing attacks without sputum production, which are difficult to get rid of, as well as other breathing problems.
- From the gastrointestinal tract: a constantly present lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing, decreased or lack of appetite, nausea, heartburn, digestive disorders.
- Brain disorders: fear of speaking, also known as glossophobia, panic attacks, difficulty concentrating, lethargy, depressive moods, difficulty falling asleep at night and daytime sleepiness, hypochondria accompanied by headaches.
- Manifestations from the vestibular apparatus: fainting, dizziness, impaired coordination of movements.
- Complex symptoms: negative reactions of the body to extremely low or high air temperatures, itchy skin, high body weight with lack of appetite, increased sweating, pale skin, lack of initiative, difficulties with learning and work activity.
Ways to combat vagotonia
Therapy for the vagotonic type of dystonia can be carried out using different methods, including changing the usual lifestyle, taking medications, and performing physical procedures.
Treatment of this disorder must necessarily take place in a complex manner, in accordance with the patient’s age and state of health. In order to correct a person’s condition, a specialist can recommend the following directions for correction (which will be an excellent prevention of exacerbations of VSD):
- bringing the daily routine back to normal;
- establishing a balanced diet;
- organization of physical activity;
- supporting the body with medication;
- treatment of somatic pathologies;
- elimination of chronic foci of infection from the body.
In general, to normalize the condition of a person with dystonia, the following principles must be observed:
- sleep at least 10 hours a day;
- take walks outside twice a day;
- limit the time spent at the computer or TV;
- introduce feasible physical activity into your daily routine;
- organize a complete diet, with an increased drinking regimen, including coffee-containing drinks;
- carry out individual work with a psychotherapist or psychologist aimed at normalizing the emotional state;
- undergo a course of physiotherapy (electrophoresis, massage, acupuncture, contrast shower).
If non-drug methods do not bring the expected result, the doctor may recommend taking medications:
- Sedatives (valerian, motherwort, sage, soothing teas).
- Antidepressants and tranquilizers (Diazepam, Noofen, Grandaxin).
- Neuroleptics (Frenolon, Sonapax).
- Nootropics (Encephabol, Pantogam, Glycine).
- Drugs to increase blood pressure (Caffeine, tinctures of Eleutherococcus and ginseng).
- Diuretics and drugs to improve cerebral circulation (Trental, Cavinton, Diacarb).
- Vitamin complexes.
Treatment of the vagotonic type of vegetative-vascular dystonia requires an individual approach, which is determined by the doctor, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient. To get rid of the negative manifestations of dystonia, a calm home environment is important, allowing you to relax and get rid of the influence of stress.
Source:
VSD of the vagotonic type: causes, treatment, prevention
Vagotonia is one of the types of vegetative-vascular dystonia. This is a condition of the body that is caused by excessive tone of the vagus nerve. It is he who regulates the activity of blood vessels, endocrine glands and various internal organs. Therefore, any violation of its functions immediately affects the human condition.
Diagnosis of VSD of the vagotonic type is difficult because it has a large number of symptoms that also apply to other diseases.
Diagnosis is also complicated by the fact that the signs of vagotonia are in many ways similar to serious diseases of the lungs, cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
If the patient is not monitored in a timely manner and regular examinations are not carried out, somatic disorders and mental disorders may develop.
Causes of vagotonia
One of the main causes of vagotonia is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve (paired). The state of smooth muscles, slowing down (accelerating) the heartbeat, and increasing the activity of the digestive organs and stomach depend on it.
It cannot be said that there is one determining reason that causes such a condition in a patient: these are several factors that simultaneously affect the body and cause such a condition in the patient.
Patients diagnosed with vagotonia are mostly children and adolescents, with a growing body and a fragile nervous system.
But now more and more often this diagnosis is given to adults, as the rhythm and lifestyle change. People are increasingly exposed to stress, increased emotional and physical stress.
A sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition also contribute to the development of pathologies.
Important! Vagotonia in adolescents is associated with hormonal changes in the body and immaturity of the nervous system. In women, it can be triggered by pregnancy, the postpartum period, or the body’s preparation for menopause - conditions that also depend on hormone levels.
In most cases, the diagnosis of “vagotonia” is made by exclusion, since examination of the lungs, heart and brain shows no significant abnormalities.
At the same time, the patient continues to complain of dizziness (hypotension), bradycardia, and other dyspeptic disorders.
In such cases, the doctor may suspect dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system and make a preliminary diagnosis of “VVD of the vagotonic type.”
According to statistics, signs of vagotonia are more often observed in women (2 or more times).
The onset is observed closer to adolescence, and at the age of 20-30 years there is a persistent disruption of the autonomic system.
The most likely signs of VSD of the vagotonic type:
- Suffered TBI: concussions, hypoxia, injuries received during childbirth;
- stress, emotional turmoil, overload;
- respiratory function disorders;
- low physical activity;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- sudden climate change;
- hereditary factor;
- diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- hormonal imbalances.
Treatment of VSD according to the vagotonic type
The treatment is initially based on non-drug methods aimed at normalizing well-being. Medicines are resorted to only in cases where all methods turned out to be ineffective and did not lead to the expected result.
Important! Treatment of VSD of the vagotonic type is selected by the doctor individually. Prescriptions depend on age, complaints received, and concomitant diseases.
Source: https://elit30.ru/profilaktika/vagotoniya-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie-vagotonicheskogo-tipa-vsd-i-disfunktsii.html