Subarachnoid space (SAP)
exists for all people. It is located between the soft and arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes of the brain. Its purpose is the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid.
SAP expansion
occurs when a lot of cerebrospinal fluid is formed, or its outflow is difficult.
Since the brain is placed in a limited cavity of the cranium, as the volume of fluid increases, its structures are subject to compression. There is a general (uniform) expansion and a local one
.
Subarachnoid fissure
- the sheets of the meninges diverge above the recess of the gyrus and connect above its surface; these spaces are called fissures.
The concept of SAP expansion
is only a conclusion obtained from X-ray, ultrasound or tomographic diagnostics. Additional examinations are needed to determine.
Causes of pathology for uniform and local:
increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid;
malabsorption due to inflammation, swelling; obstructions to outflow - tumor, cyst, hemorrhage. They may occur during the period of intrauterine development
. In this case, the baby is born with hydrocephalus (water on the brain). Provoking factors: developmental defects; anomalies in the structure of the skull, its connection with the spine; trauma during childbirth; maternal infectious diseases.
A special form of the disease is atrophy
(reduced volume) of the brain and filling of the formed spaces with fluid. It is typical for elderly patients against the background of atherosclerosis, malignant hypertension, complications of diabetes.
Clinical signs:
- In adults:
headache that does not respond to painkillers;
nausea, vomiting; feeling of pressure on the eyes. Signs appear suddenly or gradually intensify, with periodic subsidence and exacerbation possible. With brain atrophy, expansion of SAP is an incidental finding during examination. Complications due to untimely treatment
: unsteadiness when walking; dizziness; instability when changing position; difficulty coordinating movements; sensation of tinnitus, visual disturbances, even blindness; partial immobility or paralysis; muscle spasms; loss of consciousness, convulsions; mood swings, aggression, psychosis. - In infants:
swollen veins on the surface of thin skin;
spherical head; the large fontanel is tense, motionless (no pulsation); seam divergence; when tapped, a sound appears, like hitting a cracked pot; upward gaze is limited, there is swelling of the optic discs in the fundus. Consequences:
lag in psychomotor development; late acquisition of skills; increased tone of leg muscles; low physical activity, obesity; mental disorders - apathy, no attachment to parents, reduced intelligence.
Examinations for damage to the frontal and parietal lobes:
visual examination, radiography, ultrasound, MRI, consultation with an ophthalmologist, puncture, PCR study.
Treatment of expansion of the subarachnoid space.
Drug therapy is indicated for meningitis, encephalitis, trauma, and stroke.
The complex includes diuretics (Lasix, Diacarb). Indications for surgery
: anomalies of the skull and SAP; benign and malignant neoplasms; intracerebral hemorrhage; brain abscess; adhesive process in arachnoiditis. If it is impossible to radically eliminate the cause of hydrocephalus, then additional outflow pathways from the cranial cavity are created by shunting.
Read more in our article about the expansion of the subarachnoid space, its symptoms, and treatment.
Read in this article
Explanation of terms: subarachnoid space, convexital and cerebrospinal fluid, fissures
The subarachnoid space (SAS) exists in all people. It is located between the soft and arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes of the brain. Its purpose is the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, it is also called the liquor space. Liquor and membranes protect the brain from traumatic damage, deliver necessary microelements and biologically active substances, and remove tissue metabolic products.
Expansion of SAP occurs when a lot of cerebrospinal fluid is formed or its outflow is difficult.
Since the brain is placed in a limited cavity of the cranium, as the volume of fluid increases, its structures are subject to compression. Depending on the type of disease, there is general (uniform) expansion and local expansion. In turn, the latter can cover the frontal, parietal lobes, and convexital surfaces (as all convex parts of the cerebral hemispheres are called).
When describing a tomogram, there is such a thing as a subarachnoid fissure. The sheets of the meninges diverge above the recess of the gyrus and connect above its surface. These spaces are called slits. When they expand, a fairly large amount of liquid accumulates in them.
It should be noted that the concept of expanding SAP is only a conclusion obtained from X-ray, ultrasound or tomographic diagnostics. To determine its cause, a study of symptoms, a history of complaints, and a neurological examination are carried out.
Subarachnoid space: causes, symptoms and diagnosis of its expansion :: SYL.ru
The subarachnoid space (SAS) exists in all people.
It is located between the soft and arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes of the brain. Its purpose is the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid. Expansion of SAP occurs when a lot of cerebrospinal fluid is formed, or its outflow is obstructed. Since the brain is placed in a limited cavity of the cranium, as the volume of fluid increases, its structures are subject to compression.
There is general (uniform) expansion and local.
Subarachnoid fissure - the layers of the meninges diverge above the recess of the gyrus and connect above its surface; these spaces are called fissures. The concept of SAP expansion is only a conclusion obtained from X-ray, ultrasound or tomographic diagnostics. Additional examinations are needed to determine.
Causes of pathology in uniform and local: increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid; malabsorption due to inflammation, swelling; obstructions to outflow - tumor, cyst, hemorrhage.
They may occur during the period of intrauterine development . In this case, the baby is born with hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
Provoking factors: developmental defects; anomalies in the structure of the skull, its connection with the spine; trauma during childbirth; maternal infectious diseases.
A special form of the disease is atrophy (reduced volume) of the brain and filling of the formed spaces with fluid. It is typical for elderly patients against the background of atherosclerosis, malignant hypertension, complications of diabetes.
Clinical signs:
- In adults: headache that does not respond to painkillers; nausea, vomiting; feeling of pressure on the eyes. Signs appear suddenly or gradually intensify, with periodic subsidence and exacerbation possible. With brain atrophy, expansion of SAP is an incidental finding during examination. Complications due to untimely treatment : unsteadiness when walking; dizziness; instability when changing position; difficulty coordinating movements; sensation of tinnitus, visual disturbances, even blindness; partial immobility or paralysis; muscle spasms; loss of consciousness, convulsions; mood swings, aggression, psychosis.
- In infants: swollen veins on the surface of thin skin; spherical head; the large fontanel is tense, motionless (no pulsation); seam divergence; when tapped, a sound appears, like hitting a cracked pot; upward gaze is limited, there is swelling of the optic discs in the fundus. Consequences: lag in psychomotor development; late acquisition of skills; increased tone of leg muscles; low physical activity, obesity; mental disorders - apathy, no attachment to parents, reduced intelligence.
Examinations for damage to the frontal and parietal lobes: visual examination, radiography, ultrasound, MRI, consultation with an ophthalmologist, puncture, PCR study.
Treatment of expansion of the subarachnoid space. Drug therapy is indicated for meningitis, encephalitis, trauma, and stroke. The complex includes diuretics (Lasix, Diacarb).
Indications for surgery : anomalies of the skull and SAP; benign and malignant neoplasms; intracerebral hemorrhage; brain abscess; adhesive process in arachnoiditis.
If it is impossible to radically eliminate the cause of hydrocephalus, then additional outflow pathways from the cranial cavity are created by shunting.
Read more in our article about the expansion of the subarachnoid space, its symptoms, and treatment.
Reasons for expansion of the subarachnoid space
The main cause of the pathology is a malfunction of the cerebrospinal fluid system. The subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid space is a cavity, a kind of brain reservoir for cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid, formed in the lateral ventricles of the brain.
The cavity is localized above the soft membrane of the brain, and under the arachnoid membrane. Above the grooves of the brain, the cavities diverge, forming cisterns of the subarachnoid space filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Cerebrospinal fluid is in a state of continuous circulation, maintaining the constancy of metabolic processes and providing adequate nutrition to the cells of the brain and spinal cord.
If the subarachnoid space is expanded, this indicates a violation of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics, accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and its redistribution along the convexital surface - the convex parts of the cerebral hemispheres. Pathological changes lead to the development of hydrocephalus - dropsy. The increased volume of fluid compresses the structures of the brain, impairing its functionality.
Pathology of the intrathecal space has 2 forms:
- uneven (local) expansion - indicates a violation of cerebrospinal fluid resorption;
- general uniform expansion - indicates excessive secretion of cerebrospinal fluid.
Violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is provoked by dilatation - expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways, or the presence of obstacles in the external cerebrospinal fluid pathways (tumors, cysts, hemorrhages), which close the lumen.
In newborn children, the expanded subarachnoid space is an anomaly of intrauterine development, the causes of which are:
- defects in the formation of brain structures;
- abnormal structure of the skull;
- trauma during childbirth;
- infection of a woman during the perinatal period with syphilis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis.
Reasons for the increase in interthecal space in adults and children over one year of age:
- TBI (traumatic brain injury);
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the brain and its membranes (meningitis, encephalitis);
- autoimmune inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain (arachnoiditis);
- benign, malignant, cystic neoplasms;
- acute cerebrovascular accident, accompanied by rupture of blood vessels and hemorrhage in the brain;
- cerebral edema;
- chronic heavy metal poisoning.
One of the reasons for the increase in interthecal space is traumatic brain injury
Separately, there is brain atrophy in old age (decrease in organ volume). In this case, the resulting local cavities are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Clinical signs
Manifestations of SAP expansion differ in adulthood and in infants.
Source: https://medspina.ru/diagnostika/subarahnoidalnoe-prostranstvo-rashirno.html
Causes of pathology with uniform and local
In order for SAP to expand, an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid is needed.
This occurs for one of the following reasons or a combination of them:
- increased education (uniform expansion);
- malabsorption due to inflammation, swelling (there are usually local and uneven changes);
- obstructions to outflow - tumor, cyst, hemorrhage (both local and general disturbances occur depending on the level of blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation);
These pathological mechanisms can arise during the period of intrauterine development. In this case, the baby is born with hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
Hydrocephalus
The factors of this pathology are:
- malformations (closure of outflow holes, narrowing of the Sylvian aqueduct, defect in the structure of the SAP);
- anomalies in the structure of the skull, its connection with the spine;
- trauma during childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the mother - syphilitic, toxoplasma, cytomegalovirus, rubella.
Older children and adults suffer from hydrocephalus for the following reasons:
- inflammation of the brain tissue (encephalitis) or membranes (meningitis, arachnoiditis);
- skull injuries, concussions;
- hemorrhage – ventricular, intracerebral with transition to the ventricles;
- cyst or tumor of the brain.
A brain tumor is one of the causes of hydrocephalus and expansion of the subarachnoid space.
A special form of the disease is atrophy (reduced volume) of the brain and filling of the formed spaces with fluid.
Such changes are typical for elderly patients against the background of complications of diabetes with widespread arterial damage (macroangiopathy).
What is the subarachnoid space and why does it expand?
The human brain is one of the most complex and poorly understood organs, which is forced to constantly work. For its normal functioning, it needs adequate nutrition and blood supply.
The human brain consists of three membranes: soft, hard and arachnoid. The subarachnoid space is the space between the pia mater and the arachnoid membrane. The arachnoid membrane envelops the brain and is connected to other tissues by the subarachnoid junction.
They form the ventricular system of the spinal cord and brain, consisting of four cisterns in which fluid circulates.
The subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid, which is responsible for nourishing and protecting the brain. A favorable environment is created for the exchange of useful substances between the human blood and brain, the movement of nutrients to the nerve endings and ventricles.
The end products of tissue metabolism are released and excreted into the cerebrospinal fluid. There is a constant circulation in the brain cavity.
Up to 140 million cerebrospinal fluid cells must be present in the subarachnoid space, which flows from the brain through the opening in the fourth ventricle. Its maximum volume is contained in the space cisterns located above the large fissures and grooves of the brain.
Why is the subarachnoid space expanded?
Disruptions in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid are caused by infectious diseases of the central nervous system, chronic diseases, meningitis, encephalitis, tumors or birth trauma. This leads to a decrease in the amount of gray and white matter in the brain, and as a result, expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs.
The expanded subarachnoid space indicates a failure in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, its excessive production occurs and
Source
Clinical signs
Manifestations of SAP expansion differ in adulthood and in infants.
In adults
A large amount of fluid in the space limited by the bones causes an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The symptoms of this pathology consist of the following disorders:
- , which is not affected by painkillers;
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of pressure on the eyes.
These signs appear suddenly or gradually intensify, with periodic subsidence and exacerbation possible. With brain atrophy, the pressure inside the skull may not increase, so the detection of SAP expansion is an incidental finding during instrumental examination.
If hydrocephalus is not recognized in time and treatment is not started, then complications arise from compression and progression of the underlying disease.
These include:
- unsteadiness when walking;
- dizziness;
- instability when changing position;
- difficulty coordinating movements;
- sensation of tinnitus.
Visual disturbances are manifested by decreased acuity, loss of fields, and congestive changes in the fundus. Long-term hydrocephalus leads to blindness due to atrophy of the optic nerves.
The neurological consequences of expansion of the subarachnoid space include:
- decreased motor function of the limbs - paresis (partial immobility) and paralysis;
- increased tendon reflexes and muscle tone;
- muscle spasm, which leads to contractures (limited mobility) of the limbs;
- in severe forms – loss of consciousness, convulsions.
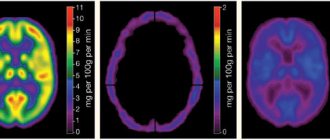
MRI for hydrocephalus
Additional Methods
Patients are advised to consult an ophthalmologist to determine visual acuity, fields and condition of the fundus.
If diagnosis is difficult and there are no signs of brain displacement, a puncture is prescribed. It can alleviate the condition of patients a little, and examination of the cerebrospinal fluid helps in diagnosing inflammation and hemorrhage. In case of congenital infection, a PCR test is performed to determine the pathogen.
Treatment of expansion of the subarachnoid space
Drug therapy is indicated for meningitis, encephalitis, trauma,... The complex includes diuretics (Lasix, Diacarb).
Indications for surgical intervention include:
- anomalies of skull development and SAP;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- brain abscess;
- adhesive process in arachnoiditis.
If it is impossible to radically eliminate the cause of hydrocephalus, then additional outflow pathways from the cranial cavity are created. Such operations are called bypass operations; they can also end with surgical treatment when removing a cyst or tumor, if the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is not restored at the main stage.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs in congenital and acquired hydrocephalus
. Its causes are excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid and/or disruption of its outflow. In adults, it manifests itself as severe headaches and psycho-emotional disorders, while in infants the head becomes enlarged and physical and intellectual development slows down. To find the causes, instrumental diagnostics are carried out. Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Why is the subarachnoid space expanded?
Disruptions in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid are caused by infectious diseases of the central nervous system, chronic diseases, meningitis, encephalitis, tumors or birth trauma. This leads to a decrease in the amount of gray and white matter in the brain, and as a result, expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs.
An expanded subarachnoid space indicates a failure in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, its excessive production occurs and enters the brain cavity, i.e., hydrocephalus or dropsy develops and, as a result, increased intracranial pressure is noted.
If a benign local expansion of the subarachnoid spaces occurs, the ventricles are slightly dilated or are within normal limits, then the disorder goes away on its own after one or two years and does not cause harm to the baby’s health.
But you can’t just hope for a favorable outcome of the disease; you need to contact a neurologist who will prescribe the necessary treatment.
The expansion of the subarachnoid spaces of the brain in adults can be caused by the following reasons:
These factors contribute to the launch of the atrophy process, the amount of white and gray matter decreases, contributing to the expansion of the subarachnoid space.
Structural features of the brain
To understand the essence of this pathology, it is important to know what membranes cover the brain. There are three of them:
The subarachnoid space is located between the arachnoid and soft membranes. The first covers the entire surface of the brain, which in turn is enveloped by the endometrium. To communicate with other tissues, plexuses under the arachnoid membrane are used - membranes. The system of ventricles of the spinal cord and brain consists of the subarachnoid vascular plexuses. It consists of 4 reservoirs in which cerebrospinal fluid constantly circulates.
Subarachnoid spaces are small cavities in the brain filled with a special fluid (CSF). Their job is to nourish and protect the brain. The cerebrospinal fluid contains nutrients that are used to maintain the vital activity of nerve cells and the ventricles of the brain. Tissue waste products are also removed through the cerebrospinal fluid. If the subarachnoid space is expanded, it begins to compress adjacent tissues and blood vessels. Brain cells that do not receive proper nutrition suffer.
Liquor continuously circulates in the cavities of the brain. This is ensured by heart contractions, breathing, and body position. Normally, the volume of liquid filling the cerebrospinal fluid spaces should not exceed 140 ml.
Signs of expansion of the subarachnoid space of the brain and therapeutic actions
To understand the essence of this pathology, it is important to know what membranes cover the brain. There are three of them:
- arachnoid;
- hard;
- soft.
The subarachnoid space is located between the arachnoid and soft membranes. The first covers the entire surface of the brain, which in turn is enveloped by the endometrium. To communicate with other tissues, plexuses under the arachnoid membrane are used - membranes. The system of ventricles of the spinal cord and brain consists of the subarachnoid vascular plexuses. It consists of 4 reservoirs in which cerebrospinal fluid constantly circulates.
Subarachnoid spaces are small cavities in the brain filled with a special fluid (CSF). Their job is to nourish and protect the brain. The cerebrospinal fluid contains nutrients that are used to maintain the vital activity of nerve cells and the ventricles of the brain. Tissue waste products are also removed through the cerebrospinal fluid.
Liquor continuously circulates in the cavities of the brain. This is ensured by heart contractions, breathing, and body position. Normally, the volume of liquid filling the cerebrospinal fluid spaces should not exceed 140 ml.
The human brain is a very complex organ; like the heart, it is forced to constantly work. In this active mode, it requires optimal nutrition and blood supply to function properly. So that in the future you understand what we are talking about, the human brain consists of three membranes:
- arachnoid;
- hard;
- soft.
The space between the arachnoid and pia mater is called the subarachnoid space. The arachnoid membrane itself surrounds the brain and is covered with endometrium on top. It communicates with the other two tissues using subarachnoid connections - membranes. The choroid subarachnoid plexuses form the ventricular system of the brain and spinal cord, consisting of 4 reservoirs. It is in these reservoirs that cerebrospinal fluid circulates.
Subarachnoid spaces, as mentioned above, are cavities in the brain that are filled with a special liquid called cerebrospinal fluid. The cavity filled with fluid serves the function of nourishing and protecting the brain. Liquor is an optimal environment for the exchange of useful substances between the blood and the organ itself - the brain; it also carries nutrients to the nerve cells and ventricles of the brain.
The end products of brain tissue metabolism are isolated and removed in the cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor constantly circulates in the brain cavities, its movement determines the contraction of the heart, body position, breathing, and even the movement of the epithelium on the choroid plexuses. Under normal conditions, the amount of fluid in the subarachnoid space should remain no more than 140 ml.
As a rule, the diagnosis of dilation of subarachnoid convexital spaces does not apply to adults, but is given to young children and, in particular, infants. This could occur due to birth trauma or abnormalities in brain development. If such a phenomenon has occurred, then the baby is prescribed an ultrasound scan of the brain; it is this diagnostic method in children that determines the deviation of the subarachnoid convexital spaces.
The subarachnoid space is the place through which fluid (CSF) circulates. It is located under the arachnoid membrane, which contains blood vessels, between the dura and pia mater. Expansion of the subarachnoid space is a sign of traumatic brain injury, hemorrhage and other serious neurological pathologies.
Reasons for expansion
Expansion of the subarachnoid space in an infant or an adult occurs with pathologies leading to an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, as well as disruption of its outflow due to deformation. Main reasons:
- Neuroinfections: meningitis, encephalitis, tuberculosis.
- Neoplasms that have grown into the space between the meninges.
- Chronic metabolic disorder.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Edema syndrome during fasting, ARVI, heart failure.
- Traumatic brain and birth injuries.
- Birth defects.
- Extensive hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke in an adult.
Infections of the central nervous system, such as syphilis, tuberculosis, meningitis, cause a natural process - inflammation. The immune system responds to pathogens by increasing the permeability of blood vessels in the brain, as well as the arachnoid membrane.
Histamine and enzymes are released that promote the formation of microholes in the capillaries (fenestra). Blood plasma leaks through them, as well as leukocytes. Edema occurs first interstitial, i.e. intercellular.
The amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid spaces increases, resulting in their local or general expansion.
Edema syndrome caused by heart failure can also lead to dropsy of the brain, and, as a consequence, expansion of the interhemispheric fissure and the entire subarachnoid space.
It is useful to know why intracranial hypertension occurs: causes, symptoms, treatment.
A note about the occurrence of nausea and headache: causes of the condition, principles of diagnosis and treatment.
note
Excess fluid in kidney diseases - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis - leads to intracranial hypertension. In this case, moisture is released through the capillaries of the arachnoid membrane, leading to liquorodynamic disturbances. Brain edema provokes compression of the white, gray matter, i.e., neurons and their processes by which they are connected to each other.
Liver diseases lead to an increase in the hormone aldosterone in the blood and a decrease in the content of albumin in the plasma. This creates conditions for the formation of dropsy of the brain. During fasting, protein does not enter the body, so the synthesis of albumin from it, which prevents edema syndrome, stops. This contributes to intracranial hypertension or hydrocephalus.
Craniocerebral and birth injuries deform the cerebrospinal fluid pathways, leading to stagnation of intracerebral fluid.
With intracranial hypertension and dropsy of the brain, the gray and white matter is pushed aside by edema. There is an expansion of the subarachnoid space of the fronto-parietal regions, the cerebellum and other structures. Therefore, symptoms may be as follows:
- Convulsive syndrome similar to epileptic seizures or twitching of the chin and legs.
- Regurgitation in the baby, crying, blueness of the body.
- Restlessness, insomnia or drowsiness (an alarming sign of progression of disorders).
- Increased sensitivity to light, loud sounds, smells, and a sharp increase in headaches.
- Anisocoria (different pupil sizes) with a displacement of the axis of the brain, divergent or convergent strabismus, poor vision.
- Impaired coordination of movement, balance, unsteady gait (with cyst-like expansion of the subarachnoid space of the cerebellum).
- Slow fusion of the fontanelle, increased size at birth.
- Dementia (dementia).
Diagnostics
To establish the presence of pathology, severity and localization, patients undergo:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- EEG.
- Ultrasound examination: echoencephalography, neurosonography (in infants through the fontanel).
- X-ray method of cisternography.
To exclude diseases of the internal organs (kidneys, liver), you should take a biochemical test for transaminases, creatinine, and urea. In case of meningeal signs (tension of the neck muscles), suspicion of encephalitis or other neuroinfections, a spinal puncture is indicated to collect cerebrospinal fluid to determine leukocytes and the presence of microorganisms.
Since the pathology is caused by an increase in the content of cerebrospinal fluid or a violation of its outflow, diuretic therapy is prescribed. Patients use diuretics (Furosemide).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Effective body wraps for weight loss for varicose veins
For cirrhosis, ascites and hydrocephalus in adults, Veroshpiron, an aldosterone antagonist, is indicated. Glucocorticoids also have an anti-edematous effect and reduce the intensity of exudation during the inflammatory process.
To eliminate convulsive syndrome, anticonvulsants are used.
Note to parents! Intracranial pressure in children: causes, symptoms and treatment.
Information about what dilatation of the ventricles of the brain leads to: prognosis of the disease.
For diplococcal and streptococcal meningitis, antibacterial drugs are used, having previously tested the sensitivity of the microflora to them. To treat viral encephalitis, specific immunoglobulin is used.
For anatomical defects caused by congenital pathologies or injuries, surgery is indicated to improve the drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid tract of the brain and spinal cord.
Conclusion
Expansion of the subarachnoid space, especially in early childhood, can lead to dementia, a serious decrease in intellectual functions, and disability. Therefore, urgent surgical resolution or drug therapy aimed at the symptoms and pathogenesis of the disease is necessary.
Loading…
If the subarachnoid space is dilated, what does this mean? Thanks to the media, most people today are well aware of the meaning of doctor's diagnoses. But sometimes the diagnosis can still baffle people, especially when it comes to a small child.
What does this diagnosis mean?
Most often, the diagnosis “Expansion of the subarachnoid space” is made to infants. This pathology can be caused by birth trauma or a deviation in brain development. If an enlarged subarachnoid convexital space is suspected, an ultrasound scan of the brain is performed. This is the main diagnostic method.
If there is an expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain, the cerebrospinal fluid is unevenly distributed and spills out of the subarachnoid space. The result is hydrocephalus (dropsy), increased intracranial pressure, and dilation of the ventricles of the brain. In this case, the cerebrospinal fluid system does not work correctly, which is why brain tissue and internal organs suffer.
The expansion of external liquor spaces leads to various pathologies (asymmetry of the cranium, impaired vision, speech, coordination, some brain functions, mental development, etc.). The degree of development of such pathologies directly depends on how much the subarachnoid space is expanded. Weak and moderate expansion of external liquor spaces is amenable to complex treatment if it is started in a timely manner. If the ventricles are not dilated, then there is a chance that by the age of two the baby’s brain condition will normalize and hydrocephalus will go away.
It is important that parents do not expect everything to go away on its own. You could waste precious time. The bones of the skull will become stronger, but the dropsy may remain. It is imperative to conduct a full diagnosis and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment.
Sometimes expansion of the subarachnoid spaces can be observed with a tumor, cystic formation or inflammatory process. This is extremely dangerous, as it often leads to death. If medical care is provided on time, the prognosis is quite favorable.
During an inflammatory process, such as meningitis, more cerebrospinal fluid is produced than necessary. A large amount of fluid leads to expansion of the space (dilatation). If the problem is a tumor, then it interferes with the proper circulation of fluids inside the brain, creating a physical barrier to it. Other reasons may be an abscess, a hematoma, due to which cerebral edema began.
What it is
The brain contains billions of nerve cells that interact with each other, supporting the functioning of all organs and systems. External protection for the organ is provided by a strong bone frame – the skull. Internal protection is provided by cerebrospinal fluid.
What is cerebrospinal fluid - it is a biological fluid that acts as a shock absorber between the membranes of the brain and spinal cord, protecting the central nervous system from mechanical stress.
Liquor performs many functions:
- Maintains intracranial pressure balance;
- Supports metabolic processes in the central nervous system;
- Maintains oncotic and osmotic pressure at the tissue level;
- Supports cellular immunity;
- Delivers nutrients.
The fluid is formed from glandular cells in the ventricles of the brain and circulates in a closed liquor system, being renewed several times a day (up to 4). The spaces in the central nervous system filled with biological fluid are called liquor spaces.
External expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain in adults refers to neurological pathology. The accumulation of excess secretion occurs in the ventricles of the organ and in the cavity between the soft membrane and the arachnoid. Obstructed outflow leads to compression of the meninges and increased intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics
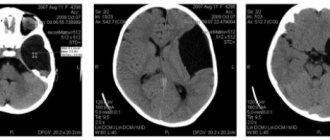
Nowadays, brain pathologies are quite easily diagnosed. For this purpose, hardware methods are used (ultrasound, MRI), and, if necessary, lumbar puncture. The latter allows not only to detect a tumor, but also to examine all its layers and structure. This method allows you to select the treatment regimen for other formations as accurately as possible.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Neurosonography. Duration of the procedure is ~ 15 minutes. It is carried out when it comes to a newborn, and consists of attaching a special ultrasound sensor to the patient’s head. Through the open fontanel, it allows you to collect information about the state of the brain. The advantage of this method is that it can be performed frequently, without any consequences for the baby. Now neurosonography is done in the maternity hospital to exclude pathologies of brain development. The result is deciphered by a pediatrician or neurologist.
- CT, . These methods, although effective, are expensive. They are mainly used to diagnose children over 3 years of age and adults. Now considered the most accurate. To diagnose infants, using CT or MRI is very problematic, since the patient must lie absolutely still during the procedure. If such a diagnosis is indicated for a small patient, it is performed under general anesthesia.
- Cisternography. The purpose of the procedure is to determine how correctly the flow of cerebrospinal fluid is directed. It allows you to accurately determine the type of hydrocephalus in a particular patient.
- Angiography. With this diagnostic method, a special contrast agent is injected into the artery. The goal is to identify deviations in vascular patency.
- Neuropsychological examination. The patient is examined and the doctor interviews him. This examination is carried out in children over 3 years of age and adults. The doctor collects the data from all tests and the results of a visual examination. The goal is to identify disorders in the functioning of the brain.
The results of an ultrasound or MRI should only be deciphered by an experienced doctor. Self-diagnosis is unacceptable and extremely dangerous here. It is very important to accurately establish the cause of the pathology and immediately begin to eliminate it. This directly affects the course of recovery and further functionality of the brain.
A blood test is also carried out, the patient’s behavior, the presence of symptoms, and their severity are assessed.
Alarming symptoms
When the convexital spaces expand, the following symptoms are observed:
- (it appears immediately after waking up);
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- memory impairment (in adults);
- irritability;
- drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- in children, the size of the skull increases;
- high sensitivity to light and sound.
At first, the disease occurs without visible symptoms. Then they make themselves felt, but the intensity may vary. It depends on the degree of brain damage and the amount of cerebrospinal fluid released. If the lesion is local and minor, symptoms may be minimal. This condition responds well to treatment, but it is important to start it at the first sign of pathology, before irreversible structural changes occur. The larger the accumulation of fluid, the more significant these changes are. Over time, the cavities may become larger. External changes may occur in infants - the cranium enlarges (especially its frontal or posterior hemisphere), and basal brain functions suffer.
The causes of pathology at different ages differ. In infants, this is most often birth trauma, meningitis, arachnoiditis, or developmental pathologies (genetic code is disrupted). In adults – mechanical trauma, pseudocyst or tumor.
There are different degrees of uniform expansion of the subarachnoid space:
- light (1-2 mm);
- average (3-4 mm);
- severe (4 mm or more).
Localization also varies (interhemispheric, posterior, anterior, etc.). Different amounts of fluid may accumulate, and the external manifestations will also be different. Sometimes the skull becomes enlarged and there is pronounced asymmetry.
Symptoms of the disease
Of course, like any disease, this pathology has its symptoms. In most cases, as mentioned above, it appears in young children, but sometimes there are older patients who can clearly describe the symptoms. Most often, expanded convexital spaces manifest themselves in the form of signs such as:
- persistent headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- memory impairment (in adults);
- drowsiness;
- irritability;
- fatigue;
- increase in the size of the skull (in young children);
- increased sensitivity to light and auditory stimuli.
In the first stages, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, which significantly complicates timely diagnosis. The intensity of the manifestation of such signs directly depends on the type of deformation. In young children, these symptoms are a consequence of postpartum trauma, arachnoiditis or meningitis, and in adults they are a sign of a tumor in the brain or the result of a mechanical injury.
A mild degree of expansion is a violation of 1-2 mm, a medium degree is 3-4 mm, and a severe degree is more than 4 mm.
When the convexital spaces expand, the following symptoms are observed:
- constant headache (it appears immediately after waking up);
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- memory impairment (in adults);
- irritability;
- drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- in children, the size of the skull increases;
- high sensitivity to light and sound.
At first, the disease occurs without visible symptoms. Then they make themselves felt, but the intensity may vary. It depends on the degree of brain damage and the amount of cerebrospinal fluid released. If the lesion is local and minor, symptoms may be minimal. This condition responds well to treatment, but it is important to start it at the first sign of pathology, before irreversible structural changes occur.
The causes of pathology at different ages differ. In infants, this is most often birth trauma, meningitis, arachnoiditis, or developmental pathologies (genetic code is disrupted). In adults – mechanical trauma, pseudocyst or tumor.
There are different degrees of uniform expansion of the subarachnoid space:
- light (1-2 mm);
- average (3-4 mm);
- severe (4 mm or more).
Localization also varies (interhemispheric, posterior, anterior, etc.). Different amounts of fluid may accumulate, and the external manifestations will also be different. Sometimes the skull becomes enlarged and there is pronounced asymmetry.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space is a disease characterized by stretching of the gap between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain due to impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
More often, the disease is diagnosed in children, but in adults, expansion of the subarachnoid space is also possible under the influence of a number of diseases or injuries.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the stage at which the disease is diagnosed; in general, the prognosis is favorable.
note
The human brain is surrounded by three protective membranes - hard, arachnoid and soft. The latter is directly adjacent to the medulla and provides its nutrition. The arachnoid membrane is connected to other membranes of the brain using connective tissue membranes. In areas where there are no membranes, there are cisterns.
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the 4 ventricles of the brain (third, fourth and two lateral) and the subarachnoid space. Liquor performs the functions of feeding neurons, removing metabolic products, and mechanically protecting the brain.
The normal amount of cerebrospinal fluid in children is 80-120 ml, in adults 120-160 ml. It is updated 3-5 times per day. The rate of circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is affected by the position of the body, the intensity of the heartbeat and breathing.
The expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs due to difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid spaces, dilating the ventricles of the brain. The mechanisms of development of the disorder are different: the tumor mechanically blocks the paths for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, inflammation provokes increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Intracranial pressure may increase.
Expansion rates
The manifestation of symptoms of the disorder depends on the severity of the expansion. There are three degrees of severity of the disease:
- light – gap size 1-2 mm;
- medium – up to 4 mm;
- heavy – over 4 mm.
Typically, expansion of the subarachnoid space is detected in the second or third stage. The first, as a rule, is asymptomatic.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the best treatments for varicose veins
Treatment
In order for treatment of the enlarged arachnoid or subarachnoid space to be as effective as possible and tissue damage to be minimal, you should seek the help of a neurologist as early as possible. His consultation is mandatory if there has been an injury, including a birth injury, there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process, or if the listed symptoms are bothering you.
Please note that this pathology can be asymptomatic for a long time.
For successful treatment, it is important to establish the exact cause and eliminate it. Liquor dynamics must be taken into account. It can express the degree of expansion, show how much the surrounding tissues, vessels, and nerves suffer. Often, sinusitis, intracranial pressure, otitis media, and infectious diseases can provoke expansion in a child. With this development, antibacterial drugs and B vitamins are prescribed. Treatment can be quite long. It is prescribed purely individually, taking into account the nature of the pathology and the age of the patient. The patient must be constantly under the supervision of doctors; in the first stages of treatment, he may be placed in the neurology department.
It is important to limit the spread of cerebrospinal fluid, protect the hemispheres and sulci of the brain from compression, and clear the path for fluid to drain. To do this, it is important to determine exactly which area is affected, which lobe of the brain suffers from compression. This could be the hypothalamus, the cerebellum, several departments at once, etc.
This deviation in children is treated with a complex of drugs:
- means for removing excess cerebrospinal fluid (Asparkam, Veroshpiron, Diakarb);
- agents that improve brain trophism (Pantogam, Cavinton).
For the treatment of children over 3 years of age and adults, slightly different tactics are chosen. They are shown:
- barbiturates;
- diuretics;
- saluretics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- plasma substitutes (solutions);
- painkillers;
- vasoactive agents.
Not all of the listed drugs are included in the treatment regimen. Their selection directly depends on the identified cause. If the problem is hydrocephalus, diuretics are prescribed; when the cause is an infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
It is advisable to supplement treatment with medications with physioneurological procedures. They reduce symptoms, restore the metabolism of cells and brain tissue. The main goal of treatment is to restore blood supply to the brain and normal drainage of cerebrospinal fluid. This will stabilize intracranial pressure and restore the metabolism of cells and tissues.
Subarachnoid space: causes, symptoms and diagnosis of its expansion
The brain is a rather complex structure. It, like the human heart, is constantly working. To function properly, this complex system must have a good blood supply and nutrient supply. This “nutritious” role for the brain is played by its membranes, which not only maintain homeostasis, but also protect against injuries, various bacteria and viruses. There are three membranes of the brain - hard, arachnoid and soft.
Subarachnoid space and its significance
The space between the arachnoid (arachnoid) and soft membranes is called subarachnoid. The arachnoid membrane surrounds the brain and is covered with endothelium. It is connected to the hard and soft membranes by supra- and subarachnoid connective tissue membranes. Its outer surface is not fused with the hard shell, but in some places so-called granulations depart from it, which penetrate deep into the latter and, together with it, onto the inner surface of the cranial bones or into the sinuses, which ensures the resorption of fluid into the venous system. The inner surface of the arachnoid membrane is connected to a soft, thin membrane. In places where such adhesions are absent, expansions are formed - the so-called cisterns.
The environment where cerebrospinal fluid circulates consists of the ventricular system and the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord. The ventricular system is formed from 4 reservoirs - two lateral, third and fourth.
Their choroid plexuses are the main source of cerebrospinal fluid production into the subarachnoid space. The norm for children is on average 80–120 ml, and for adults - from 120 to 160 ml per day, and it is completely renewed 3–5 times.
What is the expansion of the subarachnoid space
The human brain is surrounded by three protective membranes - hard, arachnoid and soft. The latter is directly adjacent to the medulla and provides its nutrition. The arachnoid membrane is connected to other membranes of the brain using connective tissue membranes. In areas where there are no membranes, there are cisterns.
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the 4 ventricles of the brain (third, fourth and two lateral) and the subarachnoid space. Liquor performs the functions of feeding neurons, removing metabolic products, and mechanically protecting the brain.
The normal amount of cerebrospinal fluid in children is 80-120 ml, in adults 120-160 ml. It is updated 3-5 times per day. The rate of circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is affected by the position of the body, the intensity of the heartbeat and breathing.
The expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs due to difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid spaces, dilating the ventricles of the brain. The mechanisms of development of the disorder are different: the tumor mechanically blocks the paths for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, inflammation provokes increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Intracranial pressure may increase.
CSF circulation
The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is a rather complex process.
It constantly flows from the lateral ventricles through the interventricular foramen to the third, and then to the fourth ventricle. From the latter, through the median and lateral openings, the liquor enters the large tank. Then it moves to the basal and washes the subarachnoid convexital spaces of both hemispheres, after which it goes to the spinal cord. Eventually the fluid returns to the brain, where it is absorbed by the dural venous system. In general, the functions of the cerebrospinal fluid are very important. Cerebrospinal fluid performs the function of protecting the brain from injury and regulating internal pressure, and plays an excretory, immunological and transport role.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space and its causes
Changes in size and pressure in the subarachnoid space are often a sign of an inflammatory process or tumor. The mechanism for the development of such changes is quite simple. The inflammatory process (usually arachnoiditis or meningitis) increases the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which gradually stretches the subarachnoid space. During the tumor process, a mechanical barrier is created to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which is a consequence of a local increase in pressure and the formation of expansions in a certain area of the ventricular system of the brain. However, other options are possible that can lead to expansion of the subarachnoid space. In particular, a temporary change in the size of the cerebrospinal fluid circulatory system is possible with reactive cerebral edema and a decrease in intracranial space due to a hematoma or abscess.
Tip 1: What are the consequences of expansion of the subarachnoid space?
Nature has reliably protected the brain and spinal cord. They are surrounded by several shells. Directly adjacent to the brain is a soft membrane of connective tissue. At some distance from it there is another shell, formed by connective tissue and whose structure resembles a fine network, for which it received the name arachnoid (arachnoid). The space between these membranes is called subarachnoid.
The content of the article
The subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The total amount of cerebrospinal fluid ranges from 120 to 140 ml. Above the large grooves and fissures of the brain there are cisterns - areas where the amount of cerebrospinal fluid is especially large.
Liquor comes from the ventricles of the brain, and the outgrowths of the arachnoid membrane absorb it. Impaired circulation leads to expansion of the subarachnoid space.
Reasons for expansion of the subarachnoid space in adults
Poor circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is always associated with some pathological process affecting the brain. This could be a traumatic brain injury, a brain tumor, a stroke, or an infectious brain disease (for example, meningoencephalitis). All these traumatic factors trigger the process of atrophy, the amount of gray and white matter decreases, which leads to an expansion of the subarachnoid space.
Symptoms of expansion of the subarachnoid space
The expansion of the subarachnoid space leads to an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure, which has relatively characteristic symptoms. Patients note a stubborn, persistent headache with symptoms of nausea and fountain-like vomiting, increased sensitivity to visual and auditory stimuli, and dizziness. The degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on the severity of development and on how dilated the subarachnoid space is. In children, expansion of the subarachnoid space is most often observed with hydrocephalus and arachnoiditis. Much less often, birth trauma or developmental defects of the nervous system become the causes of this complication.
In adults, tumors and inflammatory processes of the subarachnoid space are more common. Hydrocephalus is extremely rare and most often develops after a brain injury.
Causes
Causes may be congenital or acquired. Congenital causes of expansion of subarachnoid spaces:
- Injuries to the fetus during the mother's pregnancy.
- Congenital defects in the development of the nervous system.
- Chromosomal abnormalities.
Acquired reasons:
- Trauma to the skull and brain.
- Neuroinfections: meningitis, encephalitis, inflammation of the arachnoid membrane.
- Brain tumors.
- Hemorrhagic stroke and minor hemorrhages.
- Brain swelling.
- Acute intoxication with heavy metals.
- Chronic heart, kidney and liver failure.
Inflammation of the membranes of the brain leads to the formation of adhesions. This impedes the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to increased intracranial pressure and infantile hydrocephalus. Most often this appears after inflammation of a meningococcal, tuberculous and syphilitic nature.
During the period of manifestation of inflammation, the hemodynamics of the blood and blood vessels of the brain changes: the permeability of arteries and veins increases, and plasma enters the intercellular space. This causes swelling, which further increases intracranial pressure.
Tumors, being a voluminous process, compress brain structures and tissues, pinching lymphatic and blood vessels. This complicates the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and blood, the brain becomes congested, the pressure in it increases and diffuse hydrocephalus occurs.
Expand the subarachnoid spaces and chronic diseases of the heart and kidneys. Due to disruption of the functioning of these organs, the outflow of blood from the brain worsens, which leads to a deterioration in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and intracranial hypertension. Less commonly, pathology is caused by poisoning with heavy metals: lead, bromine or mercury.
In newborns, the expansion of spaces is facilitated mainly by congenital malformations of the central nervous system and heart.
People with enlarged subarachnoid spaces may experience disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid: excessive production of fluid and impairment of its utilization. These pathologies are considered as individual characteristics of a person.
Diagnostics
The expansion of the subarachnoid space is easily determined using instrumental examinations, the sequence of which is determined by the underlying disease. Echoencephalography is performed more often in children and makes it possible to see the displacement of the brain relative to the bones of the skull under the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid. CT and magnetic resonance imaging are mostly used for adults. The latest methods make it possible to establish the layer-by-layer structure of the brain and the nature of tumor growth, and, in combination with the results of a lumbar puncture, determine the treatment tactics for inflammatory diseases.
The subarachnoid space is a cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain and spinal cord. This space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid. The fluid is involved in protecting and nourishing the brain.
What is the subarachnoid space? The subarachnoid space contains up to one hundred and forty milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid, which flows from the brain through the openings in the fourth ventricle. Its maximum is contained in the cisterns of space, which are located above the large fissures and grooves of the brain.
The subarachnoid space is divided by the dentate ligaments and the cervical septum, which fix it.
Diagnostic methods
Modern medicine has advanced very far in the study of brain pathologies, so for adults it offers many methods for studying this organ and its abnormalities. For example, magnetic resonance imaging and lumbar puncture make it possible not only to determine the presence of a tumor and pathology, but also to establish the layer-by-layer structure of the brain and the nature of tumor growth.
This allows doctors to accurately understand the necessary tactics for treating inflammatory diseases. The results of ultrasound and MRI diagnostics can only be deciphered by a qualified doctor, so do not engage in self-diagnosis. The duration of recovery directly depends on the timely determination of the cause of the disease.
This aspect is worth dwelling on in more detail. If the expansion of the subarachnoid spaces of the brain has not yet developed into an acute or chronic form, then drug therapy is used to combat the pathology. The following indicators may serve as a reason for prescribing radical treatment methods:
- defects in the development of the structure of the cranium;
- some infectious diseases that occur in acute form;
- oncology;
- hemorrhage;
- focal accumulation of pus;
- spinal arachnoiditis.
If for some reason surgical intervention cannot be performed, then doctors create additional pathways through which the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid will occur. The therapy program is aimed not only at removing fluid, but also at eliminating the very cause that became the catalyst for the onset of the pathological process.
Therefore, very often radical treatment methods are combined with a course of medications, which are selected by doctors individually for each patient depending on his age category, clinical picture and symptoms. In addition, you must strictly adhere to a special diet:
- eat foods rich in vitamins;
- reduce your daily intake of sugar and salt to a minimum;
- completely give up alcohol;
- drink as much fluid as possible every day.
If the patient seeks help from the hospital not too late, then the chances of a full recovery are quite high. But with an advanced form, as a rule, it is impossible to completely get rid of the consequences.
Reason for expansion of the subarachnoid space
Local expansions of the subarachnoid space are a signal of disturbances in the normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. This may be a consequence of injuries, tumors, or infectious diseases of the central nervous system. Undoubtedly, such a condition requires direct consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon and appropriate examinations.
The fact is that quite often the expansion of the subarachnoid space is a symptom of hydrocephalus or increased intracranial pressure.
The set of signs of external benign hydrocephalus in children of the first year of life is an increase in the subarachnoid spaces, which is most noticeable in the zone of the poles of the frontal lobes, while the ventricles of the brain can be only slightly dilated or have normal sizes. Moreover, the contents of these spaces have dense cerebrospinal fluid, which is observed on MRI, CT, and neurosonography. If it is benign hydrocephalus, then in most cases it resolves by two years of age.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space along the convex
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for Joint Treatment: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your joints by taking every day...
Read more "
Many people have probably heard about such a disease as dropsy of the brain, or scientifically called hydrocephalus. Most people and even some doctors believe that such a pathology is characteristic only of childhood. Indeed, it is quite common in newborns, but people after 18 years of age are susceptible to hydrocephalus to no less, and sometimes even to a greater extent. It can be disguised as various diagnoses: in the form of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, mixed dementia, consequences of traumatic brain injury or stroke. And only after a targeted examination is it possible to make the correct conclusion, recognizing dropsy of the brain.
General information
Cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid is contained in the ventricles of the brain and the spinal cord canal in an amount of 125 to 150 ml. It is a kind of derivative of blood plasma and performs a number of important functions:
- Protects the brain from concussions and impacts (shock absorption).
- Nourishes surrounding tissues (trophism).
- Participation in water-salt and protein metabolism (osmotic and oncotic balance).
- Antibody accumulation (immune defense).
- Regulation of intracranial and spinal circulation (hemocirculation).
Liquor is produced by the choroid plexuses located in the lateral and at the bottom of the fourth ventricle of the brain. From the latter, through special openings (Lyushka and Magendie), the liquid penetrates into the subarachnoid space and accumulates in its extensions (cisterns). Washing the cerebral hemispheres, cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed into the venous system through Pachionian granulations and arachnoid cells. The movement of cerebrospinal fluid is also influenced by blood flow, breathing and muscle contractions.
Liquor is extremely important for the normal functioning of the organs of the central nervous system, and its quantity is limited to strict limits.
Causes
The origin of cerebral hydrocephalus in an adult is somewhat different from the mechanisms of hydrocephalus in a child. Basically we are talking about disruption of three processes in the liquor circulation chain:
- Increased production (vascular papilloma).
- Blockage or compression of pathways (tumor, blood clot, adhesions).
- Insufficient absorption (inflammatory process).
Based on the foregoing, hypersecretory, occlusive (closed) and disresorptive (open) hydrocephalus are distinguished, respectively. These are the main factors of acquired hydrocele of the brain. Previously, mixed replacement hydrocephalus was additionally identified, when the expansion of the ventricles and subarachnoid space was combined with atrophic processes in the surrounding structures. However, now it is not considered as true dropsy, because the mechanisms of formation, circulation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid are not impaired, and the increase in internal cavities occurs due to thinning of the brain tissue.
Thanks to the expansion of the diagnostic capabilities of modern medicine, it has become known that hydrocephalus can accompany almost any disease of the central nervous system. In many cases, it becomes a complication of the following pathology:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases (meningitis, encephalitis).
- Intracranial hemorrhages (post-traumatic hematomas, ruptures of aneurysms and vascular malformations).
- Strokes (ischemic and hemorrhagic).
- Tumor processes.
- Encephalopathies (toxic, posthypoxic, etc.).
- Hydromyelia.
Therefore, a complete and timely examination is extremely important for subsequent treatment tactics. And if any symptoms of hydrocephalus appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The cause of hydrocephalus may be hidden at any stage of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation, causing a disruption in the production, excretion or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
Classification
The diagnosis of hydrocephalus is made solely on the basis of the generally accepted clinical classification. In addition to the already mentioned forms of pathology, based on the peculiarities of the development mechanism (pathogenesis), it is necessary to mention other types of dropsy of the brain. According to the rate of development in adults, it is:
- Acute – decompensation for 3 days.
- Subacute – develops over 1 month.
- Chronic – formed over a period of 3 weeks to 6 months.
Hydrocephalus is also divided into groups based on cerebrospinal fluid pressure: hyper-, normo- or hypotensive. These features are important from a clinical perspective, since they largely determine the symptoms of the pathology.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of hydrocephalus is quite varied. The rate of manifestation and increase in symptoms depends on the severity of the pathological process in the central nervous system. With occlusive forms of hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult, the first signs of increased intracranial pressure are:
- Headache.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Congestion in the fundus.
- Dislocation of brain structures.
The headache is bursting in nature, mainly localized in the frontoparietal region and is combined with a feeling of “squeezing out” the eyeballs. It intensifies in the morning, as well as when bending over, coughing, sneezing, and straining.
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
With severe hydrocephalus, signs of dislocation of brain structures are observed. Various degrees of disturbance of consciousness are observed - from drowsiness to coma. Oculomotor disorders occur in the form of nystagmus, displacement of the apples downward and outward (the “setting sun” symptom), and strabismus. With an intracranial hematoma on the side of the injury, pupil dilation (anisocoria) is noted. If compression of the medulla oblongata occurs (herniation into the foramen magnum), then respiratory and cardiovascular disorders are observed, which can lead to death.
Acute hydrocephalus in adults is associated not only with disruption of the central nervous system, but also with a high risk to life.
Chronic accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, in particular replacement hydrocephalus of the brain, has a fundamentally different clinical picture. The first symptoms, as a rule, appear a month after the injury or neurological disease (stroke, meningitis, etc.) and gradually intensify. The main features are psycho-emotional, mental disorders and conduction disorders, manifested by the following conditions:
- Dementia.
- Apraxia of walking - an unsteady gait with legs widely spaced.
- Paresis and paralysis.
- Urinary incontinence.
At first, patients experience daytime drowsiness and nighttime insomnia (the sleep-wake cycle is disrupted). Then the memory for current events gradually deteriorates, the person becomes indifferent, depressed, and answers questions in monosyllables. Over time, intellectual-mnestic disorders worsen, leading to the impossibility of social life and self-care.
Chronic hydrocephalus in adults is accompanied by a complex of psychoneurological disorders that develop after a brain injury or disease.
Diagnostics
Based on the results of a medical examination, one can only assume a violation of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, because similar symptoms can occur in a wide range of pathologies. Therefore, patients are required to undergo additional examination. The diagnostic program for hydrocephalus includes methods for visualizing the internal structures of the brain and determining liquorodynamic parameters. These include the following studies:
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Radiography (cisternography).
- Echoencephalography.
- Angiography.
- Spinal tap.
Based on the results of the examination, a consultation with a neurologist and neurosurgeon is necessary, who will indicate the need for certain treatment methods.
Treatment
Hydrocephalus of the brain in adults is subject to timely correction. The earlier treatment measures are carried out, the lower the risk of neurological complications and the higher the chance of complete restoration of lost functions. But the effectiveness of certain methods depends on the rate of increase in symptoms.
Conservative methods
If the clinical picture of hydrocephalus has not yet reached the advanced stage or is characterized by a gradual increase in symptoms (subacute or chronic), conservative methods can be used. They involve the use of medications that help remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, normalize vascular processes and nourish nervous tissue. The following medications are used for this:
- Diuretics (Diacarb, Mannitol, Lasix).
- Vascular (Actovegin).
- Neurotropic (Cerebrolysin, Cortexin).
- Venotonics (Detralex).
In cases of acute pathology, intensive therapy measures are often required, but without surgical treatment their effectiveness remains quite low. Mixed hydrocephalus of the brain with atrophy is also difficult to correct. Unfortunately, we cannot expect a complete cure, but it is still possible to improve or restore some functions.
Chronic or subacute hydrocephalus can be treated conservatively, in which the patient's condition is at a satisfactory level.
Operation
In case of severe liquorodynamic disturbances, the only option for the patient will be surgery. Treatment of hydrocephalus consists of neurosurgical correction, which is often performed for health reasons. In case of acute dropsy, drainage of the ventricles of the brain is performed using open surgery (trepanation) or endoscopic techniques. The latter are the most acceptable in modern conditions, since they are characterized by low trauma and a low risk of complications.
Treatment of chronic hydrocephalus consists of various shunt operations, the essence of which is to ensure the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into other cavities of the body:
- Right atrium.
- Abdominal cavity.
- Superior vena cava.
- A large tank.
Shunt systems consist of two catheters (ventricular, peripheral) and a valve that regulates the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. This allows you to normalize the pressure in the ventricles of the brain and protect the patient from neurological problems in the future. Surgical treatment is almost 100% effective, which distinguishes it from conservative treatment. Patients experience significant improvement immediately after endoscopic surgery.
The problem of hydrocephalus is widespread not only among children, but also among adult patients. There are many reasons for this, but in any situation you need to seek medical help in a timely manner. After performing diagnostic procedures, the attending physician will recommend the optimal tactics necessary for a complete recovery and rapid social and labor rehabilitation.
The subarachnoid space is the distance between the pia mater and the arachnoid membrane of the brain and spinal cord. The second seems to “cover” its surface. On top it is protected by an additional layer of the endometrium, through which it communicates with other tissues using subarachnoid membranes. They are shaped like vessels and consist of several reservoirs where cerebrospinal fluid circulates.
In the subarachnoid space, the fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid, it is responsible for the following functions:
- Nutrition and brain protection.
- A medium for the exchange of useful substances that come from the blood and must enter the organ.
- A channel of connection between nutrients and nerve cells.
- Promotes the contractile activity of the heart, the functioning of the respiratory system, etc. Allows the human body to maintain the chosen position.
Norm and extension
What is the expansion of subarachnoid convexital spaces? This means that the norm is determined only when the amount of liquid is about 140 ml. If the interhemispheric fissure expands, a pathological condition occurs. The disease does not manifest itself in adults; it is typical for newly born children and older children.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space in an infant can be diagnosed due to injury during childbirth or the formation of abnormalities associated with brain development. This factor in the development of pathology occurs quite often.
In order to understand the nature of such an increase - moderate or significant, children are prescribed an ultrasound examination. This helps to find abnormalities and determine the condition of the subarachnoid convexital spaces.
The expansion comes in several degrees of severity:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
In the first degree, the expansion is small: a maximum of 1-2 mm (the norm is 0). With medium, the gap can reach 4 mm, and with severe, it can go beyond this mark.
If you suspect an enlarged subarachnoid space in an infant, you should consult a neurosurgeon and neurologist. Usually, babies under one year of age are diagnosed with hydrocephalus. In this case, the interhemispheric fissure increases, which can be seen in the frontal lobes.
The likelihood of developing hydrocephalus in children is quite high.
Hydrocele of the brain in a newborn requires timely treatment.
Read about hydrocephalus in adults here.
In this case, the ventricles of the brain have a moderate or slight expansion. Quite often they fully comply with the established norm. The cerebrospinal fluid inside the space is solid, as can be seen based on the results obtained through diagnostic measures.
Hydrocephalus can be benign or malignant. In the first case, it goes away by the second year of the child’s life. Uneven expansion of the space indicates that the cerebrospinal fluid is not distributed correctly in the cavities. Therefore, the gap between the ventricles increases and the pressure inside the skull increases.
If the subarachnoid space is expanded unevenly due to inflammation or tumors, then the cause of the disease is determined more quickly. Pathological processes are provoked by meningitis or infections, which are accompanied by inflammation and increased production of fluid inside the cavity.
Reasons for expansion
Detection of this pathology is aimed at identifying the reasons causing deviations from the norm in the amount of fluid. The main ones include:
- The presence of infectious diseases affecting the central nervous system.
- Formation of a small tumor in the cerebrospinal fluid or cavity.
- Getting injured. Abscesses or hematomas.
- Inflammation of the sinuses.
- Manifestation of intoxications that are chronic. Such substances that can cause such poisoning include: arsenic, alcohol, lead, derivatives of reactive inflammation that accompanies encephalitis.
The disease is characterized by signs of high intracranial pressure or the development of hydrocephalus. Sometimes pathologies such as subarachnoiditis and leptomeningitis are diagnosed, in which the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain become inflamed and the cavities are unevenly expanded.
Signs and diagnosis of pathology
If your baby shows signs of illness, you should not self-medicate. Symptoms for each child are individual, but only a specialist can create a general picture of the development of space expansion.
It was found that the most common manifestations of the disease are signs such as:
- development of irritability to light and auditory factors;
- presence of persistent headache;
- dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- memory impairment (in adults);
- increased drowsiness and fatigue;
- large skull (in children).
At the beginning of its development, the disease may not manifest itself at all, so it is usually detected in the second or later stages. Symptoms arise directly depending on the type and type of skull deformation.
The severity of the pathology can be determined using traditional methods of examining the skull:
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography;
- neurosonography;
- lumbar puncture to exclude the formation of tumors;
- ultrasound examination of the brain.
The results show what a tumor can be like in space, make it possible to see the layers of the brain structure, and trace the dynamics of tumor growth. Based on this, a decision is made regarding the use of one or another therapeutic technique.
Treatment methods
Treatment is carried out by a neurologist, who may invite a neurosurgeon or other brain specialist for consultation. Therapy is aimed at, first of all, removing the cause of inflammation. As a result, the subarachnoid space should return to the parameters provided for by the norm.
First, the doctor prescribes medications that should fight infectious pathologies (sinusitis, otitis, etc.) that can lead to infection of the cavity in the brain. If there is increased pressure inside the skull, then special medications are prescribed to reduce it and normalize the condition.
The therapy is complex, it includes useful substances (vitamin B is the main one) and various antibacterial drugs. All medications are selected based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Children under 3 years of age are usually prescribed the following medications:
- Asparkam or Diarcarb to remove excess fluid in the skull;
- Pantogam or its analogues to improve trophism of the brain and cerebrospinal fluid.
For older children or adults, treatment includes many more medications. These may be drugs that can relieve pain or spasms, as well as various types of barbiturates, saluretics, glucocorticosteroids, vasoactive substances and solutions containing plasma expanders.
Drug treatment is carried out simultaneously with a visit to the physiotherapy office. A set of special exercises is aimed at relieving symptoms, ensuring active metabolism in the body, and normalizing the nutrition of brain tissue. Usually, such methods - medications plus physical therapy - are enough to successfully fight the disease and make a positive prognosis. In some cases, when medications are not effective, surgery may be performed.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space
The expansion of the subarachnoid spaces occurs in conjunction with an increase in head circumference and protrusion of the fontanelles, and a delay in the timing of their closure.
A noticeable expansion of the subarachnoid space may also indicate arachnoiditis or leptomeningitis, in which the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain become inflamed. This may be the result of injury, infection, or a number of other influences. This pathology is detected using ultrasound.
The cause of arachnoiditis can also be chronic intoxication, for example, lead, alcohol, arsenic, reactive inflammation with slowly developing tumors and encephalitis.
General symptoms of arachnoiditis:
- headache that is worse early in the morning, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting,
- dizziness,
- general fatigue
- irritability,
- sleep disturbance.
The main thing in treatment is to eliminate the source of infection, for example, sinusitis or otitis media. For this purpose, antibiotics are prescribed in therapeutic doses.
Regarding the patient's life, the prognosis is usually favorable; only arachnoiditis of the posterior cranial fossa with occlusive hydrocephalus is dangerous.
The meninges play an important role in protecting and nourishing the brain. There are three of them: soft, hard and cobweb. The space between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater is called the subarachnoid space. It constantly circulates cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The functions of cerebrospinal fluid are to provide brain structures with useful substances, remove decay products, and protect the brain from traumatic damage.
As a result of some unfavorable processes, the subarachnoid space expands. This leads to insufficient nutrition of brain structures, which can cause disturbances in its functioning, which in turn will affect the functioning of individual parts of the body.
What processes can lead to expansion of the subarachnoid space? These include the following:
- Birth trauma in infants;
- Deviations in brain development;
- Inflammatory processes in the brain, such as arachnoiditis (inflammation of the arachnoid membrane), meningitis (inflammation of the soft membranes of the brain), encephalitis, etc.;
- The presence of malignant neoplasms, which in this case serve as a physical barrier to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Brain swelling;
- Hematoma or brain abscess, which also contribute to a decrease in intracranial space;
- Sinusitis, otitis and other bacterial and viral lesions of the internal structures of the skull.
- Hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke.
Such disorders often occur in young children. As a result of expansion of the subarachnoid space due to birth trauma, severe hypoxia or congenital pathologies in the development of the brain, uneven formation of fluid occurs, the processes of its outflow are disrupted, which leads to the development of hydrocephalus and hydrocephalus of the brain.
Therefore, if a child (as well as adults) appears the symptoms listed below, it is necessary to undergo a diagnosis. These symptoms include:
- An increase in the size of the skull in children (accompanied by protrusion and slow overgrowth of the fontanel, increased tearfulness, drowsiness, increased intracranial pressure, and constant regurgitation);
- Constant headaches;
- Irritability, apathy;
- Different pupil sizes, squint;
- Loss of coordination in space;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Deterioration of memory and performance;
- Increased sensitivity to irritants (light, sound).
Reasons for expansion
Expansion of the subarachnoid space in an infant or an adult occurs with pathologies leading to an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, as well as disruption of its outflow due to deformation. Main reasons:
- : meningitis, encephalitis, tuberculosis process.
- Neoplasms that have grown into the space between the meninges.
- Chronic metabolic disorder.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Edema syndrome during fasting, ARVI, heart failure.
- Traumatic brain and birth injuries.
- Birth defects.
- Extensive hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke in an adult.
Infections of the central nervous system, such as syphilis, tuberculosis, meningitis, cause a natural process - inflammation. The immune system responds to pathogens by increasing the permeability of blood vessels in the brain, as well as the arachnoid membrane. Histamine and enzymes are released that promote the formation of microholes in the capillaries (fenestra). Blood plasma leaks through them, as well as leukocytes. Edema occurs first interstitial, i.e. intercellular. The amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid spaces increases, resulting in their local or general expansion.
Neoplasms of the central nervous system can disrupt the flow of cerebral fluid, causing its stagnation, as well as dropsy. promotes uneven moderate or sometimes strong expansion of the subarachnoid spaces of the convexital surface of the brain (under the roof of the skull) or the basal, interhemispheric. This depends on the location of the pathological formation, as well as its size.
Edema syndrome caused by heart failure can also lead to dropsy of the brain, and, as a consequence, expansion of the interhemispheric fissure and the entire subarachnoid space.
Excess fluid in kidney diseases - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis - leads to intracranial hypertension. In this case, moisture is released through the capillaries of the arachnoid membrane, leading to liquorodynamic disturbances. Brain edema provokes compression of the white, gray matter, i.e., neurons and their processes by which they are connected to each other.
Liver diseases lead to an increase in the hormone aldosterone in the blood and a decrease in the content of albumin in the plasma. This creates conditions for the formation of dropsy of the brain. During fasting, protein does not enter the body, so the synthesis of albumin from it, which prevents edema syndrome, stops. This contributes to intracranial hypertension or hydrocephalus.
Craniocerebral and birth injuries deform the cerebrospinal fluid pathways, leading to stagnation of intracerebral fluid.
Diagnosis of expansion of the subarachnoid space
If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and exclude such a diagnosis as expansion of the subarachnoid space. There are 3 stages of the process: light, medium and heavy, when the distance between the shells reaches more than 4 cm.
In newborns and children of the first year of life, the method of neurosonography (ultrasound examination through the soft tissue of the fontanel) is used for diagnosis.
For adults, such a diagnosis can be established only through magnetic resonance imaging, which allows one to obtain clear layer-by-layer images of all internal structures of the brain. With their help, you can identify different types of shells and estimate the distance between them, comparing it with the norm. In addition, the tomogram will show focal and diffuse changes caused by lack of nutrition, compression of tissues during expansion of the ventricles of the brain, and in places increased accumulation of fluid.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space in infants
- The subarachnoid convexital spaces in infants expand as the head grows - it increases in circumference. Parents may notice a pathological process by the protrusion of the fontanelles - places of the skull where the bones of the skull converged so that the child could pass through the birth canal without hindrance.
- Also, in infants, expansion of the interhemispheric fissure and subarachnoid space is accompanied by a rapid increase in the skull, which leads to the fact that the child cannot raise his head. In this case, a diagnosis is made of perinatal encephalopathy.
- In addition to the general impairment of the condition, a decrease in reflex function, children become capricious, refuse to eat, lag behind their peers physiologically, and lose weight.
- There is another very indicative symptom - “moon gaze”. The eyelids of sick babies are constantly drooping and part of the white is visible from under the skin - the pupil and iris roll under the eyelids. With minor brain lesions, this look appears periodically; with severe lesions, the iris can be seen for a short time.
- In children, brain atrophy may also occur, in which expansion of the convexital subarachnoid spaces occurs. The furrows in the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital regions increase.
- The ventricular system is also pathologically deformed due to expansion. In this case, serious examinations are carried out only in the second year of life - earlier, diagnostic measures are considered dangerous to the baby’s life.
Not only computer and tomographic studies may be required, but also the extraction of cerebrospinal fluid using a puncture.
At an early age, children undergo neurosonography - the condition of the cranial cavity can be examined using this method only before the fontanelles fusion.
If a significant area is damaged or leukomalacia is diagnosed - this term refers to softening of the brain, a condition when functional abilities are impaired, impulse signals in the required volume are not sent or received - in the future the child will lag behind in development.
But you shouldn't panic. The child’s body has a great chance of recovery; with timely and adequate treatment – when the first symptoms appear – the chances of recovery increase.