Leukocytes in the blood of men
Leukocytes in the blood of men are a group of white blood cells that are components of the immune system of the human body.
For males, there is their own norm for such substances, which differs slightly depending on the age category. In addition, normal indicators can be increased or decreased, which almost always occurs against the background of some illness. Nevertheless, there are several quite harmless provocateurs.
High and low leukocytes have their own clinical manifestations, but they very often go unnoticed by people or are completely disguised as symptoms of the underlying disorder.
A general clinical blood test will help determine the content of leukocytes, however, it cannot accurately indicate the provoking cause. To identify the provocateur, patients need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Normalization of white blood cells occurs against the background of treatment of the underlying disease, which is of a purely individual nature and can be either conservative or surgical.
What determines the leukocyte count in men?
The main factor that affects the number of these cells is the age of the man. In children their number is much higher.
This condition is called leukocytosis. It persists for about 2-3 weeks after birth. The maximum concentration is observed in the first 3-4 days of life, and with age it gradually decreases to levels characteristic of adults.
Articles on the topic
- Causes of low blood albumin in men, women and children
- The normal level of albumin in the blood of men by age in the table
- The norm of bilirubin in men in deciphering the results of blood or urine tests - reasons for the increase
This is due to the fact that a newborn’s body is much weaker, which is why the child needs a larger number of immune cells. The following factors also influence their level:
- Eating. It is recommended to donate blood on an empty stomach.
- Times of Day. More accurate results are obtained when taken in the first half of the day.
- Psychological state of a person. Nervous tension may affect results.
- Physical exercise. The indicators for a rested and tired man will be different.
- Other factors: bad habits, visiting a bathhouse or steam room, exposure to the sun, uncontrolled use of certain medications.
Norm and reasons for deviation
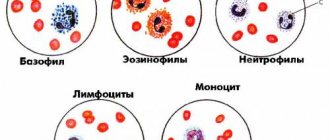
As mentioned above, leukocytes are a whole group of components, each of which has its own normal values.
- neutrophils – 55%;
- lymphocytes – 35%;
- monocytes – 5%;
- basophils – 1%;
- eosinophils – 2.5%.
As for the absolute content of such substances, it will differ slightly depending on the age category of the male representative.
Thus, the norm of leukocytes in the blood of men will be:
Acceptable values (x10 9 ml|l)
Persons over 60 years of age
If elevated values are detected, clinicians talk about leukocytosis, and if they are lower than normal, they talk about leukopenia. In any case, completely different factors will act as provocateurs.
For example, elevated leukocytes in the blood of men most often develop against the background of:
- pyelonephritis or pneumonia;
- pathologies of infectious nature;
- viral and bacterial diseases;
- inflammatory lesion of the appendix;
- heart attack and stroke;
- tonsillitis and otitis;
- fungal diseases;
- leukemia and radiation sickness;
- extensive burns;
- malignant neoplasms;
- bone marrow damage;
- massive blood loss;
- intoxication with chemical and toxic substances;
- chronic renal failure;
- injury to muscles, joint tissues or violation of the integrity of the skin;
- diabetic coma;
- inflammation of the prostate gland;
- allergic reactions;
- autoimmune diseases.
An increase in leukocytes in the blood of males can also be triggered by less dangerous factors, namely:
- poor nutrition;
- excessive physical activity;
- long-term use of medications for medicinal purposes, in particular antibiotics or glucocorticoids;
- psycho-emotional shocks.
The main causes of leukopenia:
- viral hepatitis;
- flu;
- typhoid or typhus;
- malaria;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- infectious pathologies of bacterial nature;
- hypothyroidism;
- autoimmune diseases;
- anemia and dystrophy;
- endocrine disorders;
- inflammation of a purulent-septic nature;
- malignant lesions of the hematopoietic system or bone marrow.
Low white blood cells are also often a consequence of:
- prolonged stress;
- chronic depressive state;
- uncontrolled use of certain groups of drugs, for example, barbiturates, analgesics and cytostatics;
- severe exhaustion of the body;
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of copper and other minerals, as well as vitamins in the body.
Any of the above factors should be eliminated as soon as possible.
White blood cells normal in men by age table
Like a woman » Beauty and health » House doctor » Tests
Leukocytes mean a heterogeneous group of blood cells that differ in appearance and role. They are united by the presence of a nucleus and the absence of independent coloring.
They are important components of the blood, because the main sphere of action of leukocytes is to protect the body from pathogenic agents, internal and external.
They protect the human body from illnesses and help cope with them if the disease does penetrate inside.
Types of leukocytes and their functions
Leukocytes consist of:
- neutrophils (55%);
- lymphocytes (35%);
- monocytes (5%);
- eosinophils (2.5%);
- basophils (0.5%).
In more detail, the functions of leukocytes are as follows:
- destruction of bacterial infection in the blood;
- responsibility for general immunity and the presence of immune memory;
- absorption of foreign agents entering the blood;
- fight against particles that provoke allergies;
- act as scout cells that help detect foreign particles.
Absolutely all leukocytes move briskly and easily seep into the space between the cells. It is there that they find and absorb foreign particles, thereby protecting the body from infections and viruses. They die en masse, which is why it is so important that the body is able to produce new ones in sufficient quantities to replace the lost leukocytes.
Leukocytes in men: normal
In male blood in young years, the concentration of leukocytes depends on age. The norms of white blood cells are as follows:
| Quantity | |
| years | leukocytes (?109) |
| Up to 15 | 4,3–9,5 |
| 15–20 | 4,1–9,3 |
| Over 21 | 4,0–9,0 |
Starting from adolescence, the number of leukocytes in the male body gradually decreases. After twenty-one years, the norm no longer changes. It is the same for representatives of both sexes and is in the following range: 4.0–9.0×109 per liter of blood.
According to some data, in men of advanced age (after seventy years) a further decrease in leukocytes is possible. The norm during this period is in the range from 3.8 to 8.7?109.
When you have a cold, the number of white blood cells rises to the upper limit and is 8.5 or 9 units. Fighting the infection, a huge number of leukocytes die. And when the body is almost healthy, the level of white cells drops to the lower limit of normal. The body's protective functions are significantly weakened, and leukocytes need time to recover.
Leukocytes: influencing factors
In order to control the level of leukocytes, you need to periodically resort to laboratory tests and donate blood for analysis. It is he who determines how effectively the processes of protection and restoration occur in the body.
The average white blood cell count in an adult male ranges from 4.2 to 8.9×109 per liter. However, the specific value depends on some subjective and physiological factors, namely:
- the body is rested or tired after a day of work or physical activity;
- what time of day: afternoon, evening or morning. More accurate analysis results are noted earlier in the day;
- whether a person is full or hungry. The presence or absence of food in the stomach affects the number of leukocytes;
- psychological state: enduring positive and negative stress, emotional outbursts and overloads. Or the man is calm and balanced.
The number of leukocytes can also be affected by:
- exposure to the sun;
- visit to the bathhouse and steam room;
- the presence of unhealthy habits - smoking and addiction to alcoholic beverages;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications.
Therefore, it is recommended to donate blood for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach. The body needs to be adjusted so that it is in a state of rest and relaxation.
Deviations from the norm: reasons
Depending on the content of leukocytes in a man’s blood, the following deviations from the established norm are recorded:
- Exceeding the level of white blood cells is leukocytosis.
- The level of leukocytes is below normal - leukopenia.
In addition, irregularities in the leukocyte formula, which contains information about the types of leukocytes, can be recorded. Their percentage ratio is relatively constant and shows the state of the immune system.
The deviation of leukocytes from the established norm itself is not a disease. This is only a consequence of undesirable processes occurring in the male body.
White blood cells are elevated
The following causes of leukocytosis can be distinguished:
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, namely in: the rectum;
- bladder;
- prostate gland;
- seminal vesicles.
The increase in the number of white blood cells can also be affected by:
- great physical overload;
- poor nutrition;
- absence of the spleen, removed for medical reasons.
Additional tests will help identify which leukocytes are responsible for their excess increase. Depending on this, leukocytosis occurs:
- Eosinophilic - manifests itself along with allergic reactions.
- Basophilic – accompanies gastrointestinal diseases, in particular colitis and gastritis.
- Lymphocytic – acute and chronic infections such as hepatitis and tuberculosis have settled in the body.
- Monocytic - the culprits of leukocytosis are bacterial infections, and sometimes cancer.
White blood cells below normal
A decrease in leukocytes below the established norm is doubly dangerous. Firstly, the body suffers from a disease that causes a decrease in white blood cells. Secondly, resistance decreases, and the threat of contracting an additional disease increases.
Leukopenia is caused by the following reasons:
- excessive use of hormones, analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- acute viral disease;
- weakened immunity;
- certain forms of leukemia;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system.
The level of leukocytes in the male body can change in one direction or another throughout the day. This is influenced by diet, cigarette and alcohol abuse, and psychological state.
A decrease or increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood of men indicates that the immune system is weakened and pathogenic processes are occurring in the body. Therefore, it does not hurt to conduct an additional examination and identify the cause of such phenomena.
Source:
The norm of leukocytes in the blood of men: tables by age, reasons for deviation
Leukocytes are white blood cells that are the basis of the immune system.
They move freely throughout the body, contain a special enzyme that breaks down and binds breakdown products, and gets rid of foreign agents.
You can read about the norm of leukocytes in women here.
Functions of leukocytes
The key functions of leukocytes are:
- Absorption of foreign substances;
- Destroying infection;
- Fight against substances that provoke an allergic reaction;
- Responsible for local immunity;
- Synthesize antibodies;
- They develop memory for foreign agents and pass them on to the next generation;
- Act as “scouts”, helping to recognize foreign particles;
- Remove breakdown products from the body.
Normal blood levels depending on age
In men, the normal number of leukocytes in the blood ranges from 4–9 × 10 to the 9th power, table by age:
| Age | Leukocytes (×109) |
| Up to 15 | 4,3–9,5 |
| 15–20 | 4,1–9,3 |
| Over 21 | 4,0–9,0 |
After the age of 55, especially in the elderly, after 70, the norm of leukocytes in the blood of men decreases to 3.8–8.7 × 10 to the 9th power. This is due to the fact that the viability of leukocytes decreases, as functional and structural changes occur in them.
The bone marrow, which synthesizes leukocytes, also undergoes changes, adipose tissue grows in it, and the production of nucleated cells decreases.
Now you know what the norm of leukocytes in the blood of men is, but what could be the reasons for the deviation?
The level of leukocytes in the blood of men may vary depending on the following situations:
- Physical, emotional stress;
- Staying in the sun, tanning;
- Hungry or full stomach (after eating, the number of white blood cells increases);
- Visiting a bathhouse, steam room;
- Fatigue;
- Stressful situation;
- Uncontrolled use of certain medications (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs);
- Blood transfusion (donation);
- Smoking, drinking alcohol;
- Poor nutrition (leads to an increase in the level of leukocytes);
- Time of day (leukocyte levels increase in the evening).
Changes in the level of leukocytes can be of the following types:
- Primary changes - observed in diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- Secondary - occur depending on the reaction of the circulatory system to various pathological conditions that occur in other systems and organs.
Deviations from the norm
Deviations from normal indicators can be of the following types:
- Leukocytosis - an increase in the level of white cells in the blood against the background of inflammatory processes, in physiological (natural) conditions;
- Leukopenia – a decrease in the number of leukocytes is observed with reduced immunity, purulent-inflammatory processes, bone marrow diseases;
- Disturbances in the composition of the leukocyte formula;
- Extra immature white blood cells.
Leukocytosis
The main reasons for the increase in the number of white blood cells are:
Leukocytosis is divided into the following classes:
- Basophilic – observed in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Monocytic – occurs against the background of a bacterial infection and in the presence of cancerous tumors;
- Eosinophilic – observed in allergic reactions;
- Lymphocytic - occurs in the presence of acute and chronic infections.
The reasons for deviation of the level of leukocytes from the norm can be serious, or can only mean a weakened immune system.
Source: https://krovinushka.ru/analizi/lejkotsity-norma-u-muzhchin-po-vozrastu-tablitsa.html
Symptoms
Leukocytosis and leukopenia have their own clinical picture. However, the problem is that all the signs are nonspecific and weakly expressed, which is why they may go unnoticed.
If white blood cells are elevated, this may be indicated by symptoms such as:
- weakness and fatigue;
- secretion of a large amount of sweat;
- decreased vision;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- aches in muscles and joints;
- attacks of dizziness.
If the norm in men is lowered, then complaints may arise about:
- decreased physical activity;
- headaches of varying severity;
- weight loss;
- heart rate disturbance;
- enlarged spleen and liver;
- muscle and joint pain;
- hyperthermia;
- chills and fever.
The above symptoms will always be supplemented by external manifestations of the underlying disorder.
Diagnostics
The norm of leukocytes in men is determined during a general clinical study of the main biological fluid of the human body. In the vast majority of cases, such a blood test involves taking material from a finger, but sometimes venous blood is used.
In order for the hematologist to correctly assess the level of such substances during the deciphering process, male representatives should undergo simple preparation for such a diagnostic test.
Among the preparatory activities it is worth highlighting:
- complete refusal to eat on the day of the study - the procedure is carried out only on an empty stomach;
- avoiding taking any medications several weeks before the intended visit to a medical facility (if this is not possible, you must inform the clinician about the use of medications);
- For several days, you should limit physical activity and avoid the influence of stressful situations.
It should be noted that to identify a factor that could provoke a deviation from the norm, the data obtained during such a procedure may not be enough, so a comprehensive examination will be required.
Primary diagnosis is common to everyone and combines:
- familiarization with the medical history;
- collection and analysis of life history;
- a thorough physical examination of the patient;
- a detailed survey of the patient for the doctor to compile a complete symptomatic picture.
Treatment
In order for the level of leukocytes in a man’s blood to normalize, first of all it is necessary to begin treatment of the underlying disease. If this is not done, then bringing the values back to normal using conservative methods will not give the desired effect.
To reduce white blood cell counts, clinicians most often prescribe the following medications:
- antibacterial substances;
- antacids;
- corticosteroids.
Along with taking medications, it is necessary to maintain a gentle diet.
During treatment, patients are advised to completely exclude from the menu:
- fermented milk products;
- fatty meats and fish;
- greens and carrots;
- grapes and pomegranate;
- seafood and offal;
- fast food;
- oatmeal, buckwheat and rice.
You may also need leukapheresis - cleansing the body of excess leukocytes.
If the values are low, the content of such components can be increased with the help of specially targeted drugs prescribed by the clinician, as well as by consuming:
- dietary varieties of meat and fish;
- greens and fresh vegetables;
- legumes;
- dairy products;
- buckwheat and rice, oatmeal and corn porridge;
- nuts and dried fruits.
After preliminary consultation with a doctor, you can use traditional medicine recipes at home.
general description
Leukocytes in the blood are white blood cells that have a nucleus and move throughout the body. Lymph nodes and bone marrow are responsible for their production.
Leukocytes can be found in many organs and tissues:
- glands;
- intestines;
- spleen;
- liver;
- lungs;
- mucous
On average, these cells live for about 10 days.
Leukocytes perform several functions at once:
- Protect the body from the “invasion” of foreign bodies. These could be viruses or infections. White blood cells capture a foreign cell and destroy it.
- They attract useful substances, such as amino acids and enzymes, and distribute them throughout the body.
- They take an active part in the process of blood clotting.
- Promote the resorption of tissues that have died as a result of injury.
- Participate in the formation of certain substances, in particular heparin and histamine.
There are several types of leukocytes.
Each of them performs its own special job:
- Neutrophils provide protection against infections. They capture pathogens and destroy them by digestion. Neutrophils accumulate at the site of infection and die after completing their work. Dead cells turn into pus.
- Eosinophils begin to act after infection of the body with worms. They move to the intestines and die there, releasing poison that has a negative effect on worms.
- Basophils are involved in all allergies occurring in the body. A great example is the reaction to an insect or snake bite.
- Lymphocytes. These are the so-called patrol officers. They move around the body, trying to find foreign microorganisms. They also react to their cells, which for some reason have mutated and become part of the tumor. Lymphocytes are divided into 3 groups. T lymphocytes destroy foreign organisms. B lymphocytes are responsible for the formation of antibodies. NK lymphocytes detect and destroy cancer cells.
As you can see, leukocytes occupy far from the last place in the coordinated functioning of the body. That is why it is worth taking fluctuations in their number seriously.
Prevention and prognosis
To ensure that the concentration of leukocytes in men always remains normal, and a general clinical blood test does not show any changes, it is necessary to follow simple preventive measures.
The main recommendations are:
- maintaining a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- avoiding the influence of stressful situations;
- taking medications strictly as prescribed by the attending physician;
- undergoing a full examination at a medical institution - this should be done at least 2 times a year.
The prognosis of leukocytosis or leukopenia always depends on the root cause of a particular disorder. This is due to the fact that each underlying disease has a number of its own complications, which sometimes lead to death.
How to find out your leukocyte level - indications and preparation for analysis
The analysis is performed on an empty stomach early in the morning. It allows you to determine what kind of hemoglobin a man has, the number of red blood cells, the color indicator of the corpuscles, how many reticulocytes are in the blood, the number of platelets, what is the leukocyte formula in a man’s blood.
You can’t even drink tea on an empty stomach, because... it may distort all results or give an incorrect clinical picture. Tests are taken in a special clinical laboratory, after which cells and blood cells are counted under a microscope. In young men under 30 years of age, in mature men (up to 60 years of age) and persons older than this age, the indicators differ.
How to find out your level
To find out the total white blood cell count (WBC), you need to take a finger prick for a general analysis . It allows you to count all blood elements and obtain a detailed leukocyte formula.
Indications
A general blood test is prescribed by a therapist . It is indicated for absolutely all patients seeking medical help or undergoing a preventive examination.
Preparing for analysis
- Let your doctor know if you are taking medications; you may need to stop taking some of them for a few days before the test.
- Keep a gap of 9-10 hours between the last heavy meal and the blood donation procedure so that food leukocytosis does not affect the accuracy of the analysis.
- The optimal dinner should not include spicy, smoked, fried, fatty foods, or alcohol.
- Stop smoking 3 hours before the test.
- The morning before, refrain from drinking too much and drinking strong, sweet tea or coffee.
- On the day preceding the procedure, do not engage in excessive physical labor, do not visit the bathhouse or solarium.
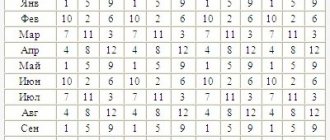
Normal indicators for men of different ages - table
You can find out what the norm of leukocytes in the blood of men up to 40 years of age and older than this age can be from this table.
Table of leukocyte norms:
| Age, years | Norm of leukocytes, billion l |
| 12-18 | 3,5-8 |
| 18-25 | 4-9 |
| 25-40 | 4-7 |
| 40 | 4-7 |
| 40-55 | 3-7 |
| 55-60 | 3-10 |
| 60 and older | 3,9-8,5 |
Normalization of leukocyte levels
In order to normalize the level of white blood cells, the patient is prescribed the following recommendations:
- Eliminate the underlying cause that led to an increase or decrease in the level of leukocytes;
- Normalize your daily routine and rest;
- Do not abuse alcoholic beverages, stop smoking;
- Review your diet, include in your diet foods that contain protein (fermented milk products, legumes, meat, fish, brewer's yeast);
- Eliminate foci of inflammation in the body;
- Relieve intoxication and dehydration of the body;
- Introduce moderate physical activity;
- Stop taking medications to which hypersensitivity has occurred;
- Increase local immunity by taking immunomodulators (Licopid, Immunal, Lysobact), ginseng tincture, Eleutherococcus. Lizobact, 2 tablets three times a day. Eleutherococcus tincture, 20 drops per glass of water, twice a day;
- Multivitamin complexes: Aerovit, Biovital, Gendevit. Gendevit, 1 capsule 1 time per day.
Did you like the article? Share it with your friends on social networks:
The data from a general blood test is the first “flashlight” that illuminates the general condition of a man’s body and helps the doctor suspect which pathology the patient has. Making a diagnosis always begins with deciphering the leukoformula and assessing the level of leukocytes, reflected in the line “WBC”, which means “white blood cells”. Right now we will talk about the norms of leukocytes in the blood of men.
Leukocytosis
For a man, leukocytosis is considered to be an increase in leukocytes in the blood of more than 9-10 billion liters. This phenomenon can be pathological or physiological.
The causes of leukocytosis are as follows:
- Various infectious diseases such as sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia.
- Diseases that cause inflammation in the male body.
- Burns of a large area, when almost the entire body is affected.
- Blood loss.
Sometimes an increase in the number of these blood cells can occur with cancer. An increased number of leukocytes is often observed in men 55 years old in the presence of various pathologies.
Leukopenia
With leukopenia, the number of white blood cells in the body decreases. The causes of leukopenia can be hypoplasia and aplasia of the brain. This disease can occur if the bone marrow is damaged after taking various medications. X-ray irradiation, deficiency of substances (such as folic acid, iron, copper), metastases in oncology, typhus - all this causes leukopenia.
The following symptoms occur with leukopenia:
- weakening of the body;
- temperature increase;
- the person is shivering;
- heart rate decreases;
- there is constant anxiety;
- headaches appear.
Consequences of high and low values
Leukocytosis and leukopenia are not treated separately from the diseases that caused them. A change in the number of white blood cells in the blood is not a disease as such, it is a consequence of pathological processes occurring in the body.
If minor fluctuations occur, then there is no need to worry, this may be a normal reaction to external stimuli.
Exceeding the norm of leukocytes is considered less dangerous than their deficiency.
A high concentration indicates that the body is fighting, resisting, and has strength. There are no specific symptoms of leukocytosis, they are general in nature: weakness, weakness, slight increase in temperature, sweating.
Usually the indicator drops to normal values on its own soon after the cause is eliminated.
Leukopenia is much more dangerous, because it indicates that the body does not have the strength to fight diseases. In this case, the risk increases that a person will quickly catch any infections, a weakened immune system will not be able to resist, illnesses will take a long time and be difficult, and can spread throughout the body.
If treatment is not started, there is a high risk of developing a serious disease. Rapid infection can cause septic shock.
Examination of a blood sample
To determine the number of white blood cells in men, the doctor prescribes a complete blood count or WBC blood test. Since leukocytes are designated “WBC” or “white blood cells”, which means “white blood cells”, this is the indicator that will interest the doctor. In addition, as a result of the analysis, you can find the designation p/box and s/box. These are the band and segmented types of white blood cells, respectively. The total level of leukocytes in the blood has a unit of measurement billion/l or a numerical value multiplied by 109.
- From 18 to 25 years of age, the normal white blood cell count is 4–11×109. At this age, the male body is fully formed, mature and strongest.
- From 26 to 35 years of age, psychologists note a high psycho-emotional load caused by stress at work and the development of family life. The indicator is in the range of 3.5–8.5 × 109.
- After 36 and up to 45 years, there is a slight decrease in hormone activity. Leukocytes are at the level of 3–8×109.
- After 46 years, the amount of hormones produced decreases; the norm is 2.9–7 × 109.
- At the age of sixty, the level of white blood cells is 2.8–8.5 × 109.
The leukocyte formula of blood reflects the balance between different types of leukocytes. The ratio between different types of cells is expressed as a percentage. With an increase in the number of band cells, the leukogram shifts to the left. A decrease in the concentration of band cells means that the leukocyte formula of the blood has shifted to the right.
The breakdown of the analysis, as a rule, is presented in a table and contains both an indicator of the patient’s leukocyte count and the norm corresponding to his age category. On average, for a healthy young man, the concentration of white cells in a blood test should be 4–9 × 109. The leukocyte level depends on some external factors and may be slightly higher or lower than normal. For example, if a guy has recently been in a sauna or spent a long time on the beach, the indicator will increase, but will return to normal over time.
Normal in adults
The level of leukocytes in the blood varies. This indicator is influenced by a number of factors: age, time of day, dietary habits. Therefore, the spread considered normal is quite large. The number of leukocytes is practically not affected by gender, the differences are insignificant.
The distribution of these cells by type in the blood is as follows:
- neutrophils - 55%;
- lymphocytes - 35%;
- monocytes - 5%;
- eosinophils - 2.5%;
- basophils - 1%.
The proportion of a particular type of white cells is calculated relative to the total content of leukocytes. When making a diagnosis, both the overall change in the number of leukocytes and fluctuations in the composition of individual groups are taken into account. It is based on these types and their relationship with each other that the leukocyte formula is deciphered.
The content of protective cells can be determined by a general blood test. The average norm for adults of both sexes is considered to be from 4 to 9 x 109 U/l. Small fluctuations up or down are not critical.
Normal blood levels: table by age
The content of leukocytes in the blood depends to a large extent on the age of the patient; this factor is considered decisive. In children, rates are several times higher than in adults.
Normal leukocyte count (U/l in 109)
Newborns up to 3 days
From 16 to 21 years old
If there is a deviation from the normal age indicator, then we can already talk about increased or decreased values. We need to figure out what caused this condition.
Differences by gender
The composition of blood in terms of leukocytes in men and women is practically no different, the difference is 0.5x109 cells per 1 liter of blood. However, in the former there are practically no fluctuations in the level of leukocytes throughout their lives.
Exceeding the permissible limit
If a general blood test indicates that leukocytes are elevated, leukocytosis occurs. At the same time, there is an increased production of white blood cells to fight pathogenic microorganisms. Leukocytes are the first to detect the “intruder.”
Thanks to the action of the immune system, resistance to viruses and bacteria begins.
In this case, there may be no complaints from the patient or clinical symptoms. The main causes of leukocytosis are as follows:
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases and inflammation.
- Infectious diseases in the acute stage (bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.).
- Elevated leukocytes in the blood are observed during inflammation and diseases in the genitourinary system.
- A reaction to certain medications (analgesics, antibiotics, etc.) may increase the white blood cell count as a result of the analysis.
- Diseases and pathologies of the heart and cardiovascular system (heart attack, stroke, etc.).
- Complete or partial removal of the spleen.
- Extensive blood loss.
- Bone marrow damage.
- Allergic reaction.
- Vaccinations cause a slight increase in white blood cells in the blood to build immunity to a particular disease.
If, during additional clinical tests, urine, like blood, contains a large number of leukocytes, then the possible cause of this condition lies in a disease of the genitourinary system. Before reducing leukocytes in the urine, you should find out the cause of the disease and determine an accurate diagnosis. Decoding a blood test in an adult depends not only on established standards, but also takes into account some external factors. There are also non-medical reasons for a high level of leukocytes in a patient’s blood.
- Heavy physical activity, sports.
- Psycho-emotional stress and severe stress.
- Blood transfusion.
- Damage to the skin and tissues (burns, cuts, etc.).
- Malnutrition.
- Alcohol abuse and other bad habits.
In some cases, leukocytosis is accompanied by corresponding symptoms. Patients complain of shortness of breath, weakness, loss of appetite and other signs characteristic of a weakened state. However, symptoms of elevated white blood cells should not be confused with fatigue caused by heavy stress at work and at home.
Main reasons for low and high values
The content of leukocytes is higher or lower than normal - this is a potentially dangerous condition that may indicate pathological processes occurring in the body. Fluctuations in the indicator in any direction can be caused by the influence of some external factors and physiological reasons.
Leukocytosis is an increased number of white blood cells in the body. It is caused by oncological processes, bleeding, malfunction of the thyroid gland, infectious disease, poisoning, inflammation.
A high level of white blood cells indicates that the body is in a stressful situation and is preparing to protect itself from any negative influences..
The increase in the volume of leukocytes due to diseases and pathological conditions is uneven: there are more representatives of a certain group (basophils, neutrophils, etc.). This allows the doctor to guess what exactly is happening in the body.
An increased level of white blood cells can lead to allergic reactions, general weakness and poor health. However, after the stimulus disappears, leukocytosis usually goes away on its own.
Leukopenia is a low number of white blood cells in the blood. This condition is considered more dangerous, because it indicates that the body does not have enough strength to fight diseases.
Leukopenia is caused by anemia, viral and bacterial infections, malignant tumors, constant exposure to chemical factors, chemotherapy, and radiation. Some medications (antibiotics, anticonvulsants, etc.) can also be the cause.
One of the common causes of leukopenia is a lack of certain substances in the body. In this case, a deficiency of red blood cells and hemoglobin will be observed in the blood test. Therefore, when conducting a blood test, they always look at the accompanying symptoms.
With a physiological increase or decrease in leukocytes, the number of all cell types changes uniformly. Climatic conditions have the strongest influence on this: heat leads to leukocytosis, and cold leads to leukopenia.
Fluctuations can be caused by high physical activity, a special emotional state, stress, food (or lack thereof), and time of day. Typically, the body responds to stimuli with increased production of white blood cells. A decrease in this parameter indicates a general loss of strength and the body’s inability to resist adverse effects.
Reduced rate
In some cases, a complete blood count will indicate a low level of white blood cells in the patient's blood. This is the same as leukocytosis, an alarming sign indicating the development of diseases. Leukopenia is a condition in which the white blood cells in the blood are low.
In the absence of the required number of white blood cells, the body becomes unprotected against pathogens, and immunity decreases.
Often this condition is not the cause of the disease, but one of the symptoms.
- Damage to the body by HIV, in which the immune system suffers. White blood cells are destroyed by pathogenic microorganisms, leaving a person vulnerable to various infections.
- Viral diseases in the acute stage (flu, etc.).
- Development of cancer of the bone marrow and other organs.
- Pathological abnormalities in the process of producing white blood cells in the body.
- Poisoning with toxins of natural or chemical origin.
- Lack of substances necessary for the normal production of blood cells (vitamin B, iron, etc.).
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Reaction to taking medications (hormones, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.).
Symptoms accompanying leukopenia include fatigue, dizziness, headaches, anxiety, palpitations, and fever. The number of white blood cells in men's blood varies throughout the day. Additional stress and lack of sleep, smoking and other factors can affect the result of the analysis. To establish an accurate diagnosis, additional examinations should be performed.
Deviations from the norm
Deviations from normal indicators can be of the following types:
- Leukocytosis - an increase in the level of white cells in the blood against the background of inflammatory processes, in physiological (natural) conditions;
- Leukopenia – a decrease in the number of leukocytes is observed with reduced immunity, purulent-inflammatory processes, bone marrow diseases;
- Disturbances in the composition of the leukocyte formula;
- Extra immature white blood cells.
Leukocytosis
The main reasons for the increase in the number of white blood cells are:
- Burns, injuries;
- Viral, infectious diseases;
- Purulent-inflammatory processes;
- Oncological diseases;
- Allergic reaction;
- Poisoning;
- Damage, injury to internal organs;
- Bleeding;
- Heart pathologies;
- Immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS, HIV);
- Diseases of the lungs, liver;
- Inflammatory process in the pelvic area (rectum, prostate, bladder);
- Kidney pathologies;
- Diseases of the endocrine system (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus);
- Splenectomy.
Leukocytosis is divided into the following classes:
- Basophilic – observed in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Monocytic – occurs against the background of a bacterial infection and in the presence of cancerous tumors;
- Eosinophilic – observed in allergic reactions;
- Lymphocytic - occurs in the presence of acute and chronic infections.
Leukopenia
A decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood in men can be observed under the following conditions:
- Anemia (anemia);
- Vitamin B12 deficiency;
- Chemotherapy;
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system;
- Weakened immunity;
- Hypotension (low blood pressure);
- Radiation;
- Autoimmune pathologies (the body synthesizes killer cells against its own healthy tissues);
- Radiation sickness;
- Hematopoietic diseases (leukemia);
- Exhaustion, intoxication of the body;
- Acute viral disease;
- Bone marrow depletion.