Fear and anxiety are feelings familiar to every person. They arise under various life circumstances and force the body to mobilize and launch all the necessary processes to overcome difficulties. Sometimes alarm signals entering the brain have no basis. This manifests itself when a person begins to experience feelings of fear and excessive anxiety for no good reason. This reaction of the body is typical during an attack of panic attacks associated with VSD syndrome (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
Some symptoms of a panic attack and a hypertensive crisis overlap, but they need to be distinguished
Why does GC develop?
This dangerous condition can last from several hours to several days, while the patient’s not only neurovegetation is disrupted, but also coronary, renal and cerebral blood flow.
Typically, the development of GC is caused by diseases that occur together with hypertension. But this condition can occur without a prior persistent rise in blood pressure.
The following are susceptible to hypertensive crisis:
- People with arterial hypertension;
- Women in menopause;
- Patients with atherosclerotic pathology of the aorta and its branches;
- People with kidney disease;
- Patients with so-called sudden “withdrawal syndrome” (when they abruptly stop antihypertensive medications).
Such pathologies, when exposed to negative conditions, can create the preconditions for the onset of a hypertensive crisis. Very often, such provocateurs are strong emotional experiences, prolonged stress, and high muscle loads. Alcohol intoxication (one-time and regular) increases the risk of developing a crisis significantly.
Causes of panic attacks: hormones, menopause, postpartum period, PMS, osteochondrosis - video
Fear is a natural reaction of the human body to dangerous situations. She helped our ancestors survive. When a person is in danger, his body prepares to react to it: to fight or run away.
When the brain receives many danger signals, a structure called the amygdala is activated. It takes part in the formation of fear. The body releases large amounts of stress hormones: they increase heart rate and breathing, and increase blood pressure.
The sympathetic department of the autonomic nervous system is activated: it works in relation to the body like a gas pedal, including the stress reaction and defense mechanisms. In some people, during severe fear, the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system predominates, which, on the contrary, works like a brake pedal.
Modern society requires more complex behavioral reactions from people. Many situations cause fear, but at the same time the changes occurring in the body at the physiological level turn out to be unnecessary. A person is afraid of an interview with a new employer, a visit to the dentist, or losing all the money in business. His body is preparing to fight or flee, but there is no need for this.
Modern scientists cannot clearly name the cause of panic attacks. It is believed that several factors may play a role in this:
- Heredity. It is possible that some people's susceptibility to fear is increased genetically.
- Frequent and severe nervous stress. Because of them, the nervous system can begin to react painfully to any trifles.
- Temperament. Some types of temperament make a person more prone to negative emotions and sensitive to stress.
- Disruption of certain areas of the brain. They can arise as a result of various reasons.
- Imbalance in the work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system.
Young people who are neurasthenic, suspicious, and accustomed to listening to their inner state are more susceptible to panic attacks. More often, women turn to specialists for help.
Panic attacks occur unexpectedly, without any reason, but over time, as a rule, a person begins to notice that certain situations provoke them.
Research shows that during a panic attack, the body undergoes approximately the same changes as when faced with mortal danger. But it is not completely clear why such a reaction occurs on its own when there is no real danger.
Panic attacks typically begin in late adolescence or early adulthood. Women suffer from panic attacks more often than men.
It is impossible to predict the risk of panic attacks in a particular person, but it is increased if certain factors are present in life:
- Panic attacks in close relatives: parents, grandparents, sisters, brothers.
- A situation that caused severe stress, for example, the death or illness of a loved one, participation in a disaster, sexual violence.
- Psychotraumatic events in life. It can be anything, a lot depends on how a person perceives the situation. Some people began to experience panic attacks after the birth of a child or divorce.
- Frequent smoking, drinking coffee.
- Physical or sexual abuse that occurred in childhood.
- Spontaneous. They arise without visible, conscious reasons. The person does not understand at all what is happening to him.
- Situationally determined. They often arise as a defense mechanism in response to frequent severe stress and conflicts.
- Mixed. They have a reason, but it should not normally cause panic attacks. The body of a sick person reacts to it excessively.
To date, the culprits of such exacerbations have not yet been fully studied. But thanks to numerous studies, several reasons have been identified that contribute to the development of panic attacks:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance (menopause, abortion, pregnancy);
- frequent stress, psycho-emotional disorders (death of loved ones, divorce, problems at work);
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes, hypothyroidism, etc.);
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system;
- heavy physical activity;
- alcohol syndrome;
- long-term use of potent medications.
It is interesting that psychotherapist scientists have created a general characteristic of the individual who is most susceptible to such unpleasant manifestations. Most often these are women (men are very rare), whose personality is characterized by the following traits:
- artistry;
- instability of thinking;
- tendency to dramatize situations;
- constant anticipation of unpleasant moments, fear of them;
- inadequate response to criticism;
- constant desire to improve your body.
It is in such people that a sudden panic attack may occur, which is accompanied by a feeling of anxiety and a feeling of fear. In this case, somatic symptoms are most pronounced.
The triggering factor for a panic attack is an anxiety disorder. The patient’s psychological constitution is asthenic; he is prone to depression and difficult experiences of the smallest failures in life. Such a patient is a hypochondriac.
He is constantly looking for diseases, which provokes the release of adrenaline and the onset of a pathological condition. In a hypertensive crisis, the pathophysiological mechanism is completely different. Here the provocateur is constant arterial hypertension with high numbers.
If it is treated incorrectly and medications are not taken regularly, it can become complicated in the form of a hypertensive crisis. It is impossible to restore the cardiovascular system once morphological changes occur. Therefore, an inadequate drug regimen ultimately leads to severe complications.
Dangerous symptom
Both occasionally and constantly high blood pressure is a symptom of dangerous diseases. For example, vasoconstriction and, as a result, an increase in blood pressure may be associated with the formation of blood clots, which, if broken off, can lead to a stroke. In general, the higher the pressure, the greater the risk of damage to the heart and blood vessels that support vital organs.
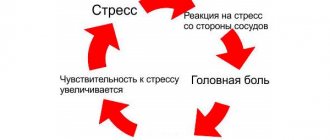
Somatic and mental causes should be distinguished . In the first case, the jumps are due to physical reasons, in the second - psychological. In some cases, people with high blood pressure find themselves in a kind of vicious circle: hypertension provokes disorders, which, in turn, provoke hypertension. These include high blood pressure during panic attacks, which pose a high risk of hypertensive crisis.
In many cases, during a panic attack, the patient's blood pressure rises and the pulse quickens - this is one of the symptoms of a panic attack. At the same time, a person who finds himself in such a situation may not immediately build a cause-and-effect relationship or may not even know about his illness, become afraid of heart problems and thereby aggravate the panic attack. A strong feeling of fear, in turn, again causes an increase in blood pressure.
From a medical point of view, increased blood pressure during panic attacks is due to impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system. Panic attacks are caused by a malnutrition of the brain; the body, trying to prevent them, accelerates the work of the heart muscle to normalize the situation, which causes a jump in blood pressure. However, it is worth remembering that the question of whether blood pressure increases during panic attacks remains open: this is only one of the possible symptoms of this disorder, it occurs quite often, but not everyone is diagnosed.
Taking control of blood pressure during panic attacks is difficult because this disorder leads to surges in blood pressure for both somatic and psychological reasons. Thus, due to strong fear, including for one’s own health, the heart rate increases, which increases the load on the heart muscle. At the same time, panic attacks can be caused by vegetative-vascular dystonia or osteochondrosis - diseases that lead to disruption of the functioning of the cardiovascular system even without panic attacks.
If a person feels an approaching panic attack, a number of rules should be followed that will help shorten the duration of a panic attack and reduce the risk of a sharp rise in blood pressure.
How to distinguish pathological conditions?
Differential diagnosis of panic attacks is carried out with angina pectoris, arrhythmia, mitral valve prolapse, transient ischemic attacks, disorders of pheochromocytomas, thyrotoxicosis and temporal lobe epilepsy. But it is extremely difficult to distinguish them from hypertensive crises.
To do this, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are performed. But the main method here is to competently collect anamnesis from relatives and the patient himself, as well as perform objective studies. During panic attacks, a psychological test plays an important role.
Panic attacks are a type of neurosis that manifests itself as an uncontrollable and irrational attack of anxiety. The existence of this disease became known not so long ago.
Most people experience panic attacks without even knowing what causes them. Every tenth person is susceptible to this type of neurotic disorder.
The medical name of the disease is “autonomic dysfunction.”
How to control your blood pressure when you panic
How to reduce blood pressure during a panic attack? In the case when panic has already begun, doctors recommend taking all possible actions to prevent a further jump in blood pressure. So, what to do when you feel scared:
| Ways to relieve panic | What to do |
| Eliminate the provoking factor | If the pressure is caused by a closed space or a large crowd of people, you need to get out into the open as quickly as possible. |
| Control of breathing (usually an attack of PA is accompanied by shortness of breath, at this moment the person feels as if he is suffocating from lack of air) | It is necessary to try to restore the breathing rhythm using a watch. Watching the time on the dial, observe the duration of inhalations and exhalations. |
| Open the window to let in fresh air. | |
| Remove outer clothing that interferes with breathing. | |
| Try to distract yourself | Looking at foreign elements of the surrounding area helps to get rid of the feeling of fear. For example, observing the flow of water, clouds, or simply counting trees. |
| Meditation Special exercises | Calmness of the mind and physical body during meditation suppresses anxiety. |
| Doing some exercises can also help you stop being afraid and even prevent future panic attacks. For example, you can do an eye massage (circular movements, lightly pressing on closed eyelids). | |
| To take medicine | Corvalol, Valerian, sedative mixture. |
| Rest | Try to rest quietly, lie down for half an hour. |
| Try to distract yourself from obsessive thoughts, convince yourself that everything is fine. |
Following these recommendations will help a person alleviate his condition at a time when blood levels rise due to fear. However, they are not able to help completely get rid of panic attacks; a thorough diagnosis of the body and competent comprehensive treatment are necessary.
Also important is regular monitoring of blood pressure, which is necessary not only when PA manifests itself, but also at rest. Such monitoring will help determine the operating parameters of blood pressure and how many units it rose at the time of alarm.
Which doctor should I contact?
If fear manifests itself frequently, it is necessary to consult a specialist psychotherapist, neurologist, endocrinologist, therapist, or cardiologist. The more accurately the provoking factor is identified, the more effective the treatment will be, the lower the risk of recurrence of attacks in the future.
Treatment of panic attacks with medications
Medications that can normalize the patient’s psycho-emotional background may be prescribed:
- Antidepressants – means their long-term use from 6 to 12 months.
- Tranquilizers - should be taken at the moment of feeling an approaching panic or after an attack.
- Sedatives are used in the initial stages of PA development.
- Neuroleptics - most often used in tandem with other groups of drugs.
- Nootropic drugs improve memory and attention, help the body cope with stress more easily and subsequently resist it.
Hypertensive crisis: classification
You can often hear such combinations - uncomplicated HA, complicated HA. The complicated type is dangerous precisely because of its consequences - heart attack, stroke, and heart failure. It is also possible to develop renal failure. Uncomplicated is not accompanied by the development of such complications.
Also, the Civil Code can be:
- Hyperkinetic. The onset is abrupt, acute with rapid heart rate and high systolic pressure. This type of crisis is not uncommon for the onset of hypertension.
- Hypokinetic. This crisis has a smooth development and is quite difficult. It is typical for patients with stages 2 and 3 hypertension.
- Systolic. It is the systolic blood pressure readings that predominantly increase.
- Diastolic. There is an increase in diastolic pressure readings.
- Systole-diastolic. At one moment, both indicators on the tonometer increase.
- Sympathetic-adrenal. The pressure increases greatly, often systolic. Increased heart rate, pale skin, trembling, increased blood glucose levels. There are no precursors to the development of such a crisis.
- Cerebral. In this case, the pressure increases during cardiac diastole, but the basal metabolic parameters do not change. No abrupt start. Lasts longer and more severe, lasting 5 or more days. A crisis is characterized by severe drowsiness, a feeling of stupor, painful headaches, and sometimes disturbances of consciousness.
It is important to recognize what kind of crisis has overtaken the patient. Treatment should be adequate, symptomatic, under the supervision of doctors.
Depending on the number of manifestations:
- Large (full-scale) attack - four or more symptoms.
- Minor attack – less than four symptoms.
Depending on the prevailing manifestations:
- Typical (vegetative). Symptoms such as increased pulse and heart contractions, spasms, nausea, and fainting prevail.
- Hyperventilation. Main manifestations: increased breathing, reflex cessation of breathing. In different parts of the body, unusual sensations arise in the form of tingling, “crawling”, muscle pain associated with changes in blood pH as a result of respiratory disorders.
- Phobic. Among the symptoms, phobias (obsessive fears) predominate. Fear arises in situations that, according to the patient, are dangerous and can provoke a panic attack.
- Affective. They manifest themselves in the form of depression, obsessive thoughts, constant internal tension, melancholy and angry states, and aggressiveness.
- Depersonalization-derealization. The main symptom is detachment, a feeling of unreality of what is happening.
A panic attack is an extreme form of manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), characterized by disorders of the nervous system. According to the international classification system of pathologies (ICD), this disease is assigned code F 41.0 - panic disorder or, in other words, episodic paroxysmal anxiety.
Vegetative crises are divided into several types depending on the severity of the disease and the combination of symptoms that appear. According to severity they are distinguished:
- mild attacks lasting no more than 30 minutes, accompanied by minor but characteristic disorders;
- conditions of moderate severity, lasting up to an hour, characterized by multiple somatic abnormalities followed by asthenia (neuropsychic weakness), lasting 24 hours, day and night;
- severe attacks with various disorders that do not subside for more than an hour, accompanied by all kinds of paroxysms and subsequent asthenia for up to several days.
Modern medicine identifies four types of panic attacks. Each variety differs from the other in different symptoms of vegetative crisis. For a general idea of such conditions, it is worth considering them in a little more detail. Depending on the symptoms that appear, the following are distinguished:
- a sympathetic-adrenal crisis is accompanied by the appearance of severe anxiety, discomfort in the heart area, increased heart rate and hypertension (increased blood pressure);
- vagoinsular crisis begins with a feeling of cardiac arrest, weakness occurs, a feeling of lack of air appears, and blood pressure decreases;
- vegetative-vestibular crisis is manifested by dizziness and vomiting that occurs as a result of sudden changes in body position: turning the head, tilting and other movements;
- a hyperventilation crisis is accompanied by increased breathing, hypertension, dizziness, and muscle tone also appear.
Any panic attack manifests itself acutely and unexpectedly for the patient. In some cases, the development of a crisis at night during sleep was noted. However, this condition is not considered dangerous and does not pose a threat to human life. Despite the seemingly scary clinical picture, the attack will stop in any case and you should not be afraid of it.
Stages, duration, exacerbation and severity of panic attacks. Panic attacks without panic - video
Over time, the manifestations of the disease change. This can happen at different rates, sometimes over months or even years, and sometimes over weeks. Typically, panic disorder goes through the following stages:
- “Poor” attacks, in which the symptoms are not very pronounced.
- Full-blown panic attacks.
- Hypochondria. Unable to find a logical explanation for his condition, the patient believes that he has a serious pathology and begins to visit therapists, neurologists, cardiologists and other specialists.
- Limited phobic avoidance. The patient identifies situations that, in his opinion, provoke attacks, and tries to avoid them. At this and later stages, many patients see a psychiatrist or psychotherapist for the first time.
- Extensive phobic avoidance (secondary agoraphobia). Symptoms that appeared in the previous stage become more pronounced.
- Secondary depression. A person becomes more and more convinced that he is not in control of the situation and does not know how to get rid of his illness. Attacks can happen anywhere, at any time, they destroy your personal life and career. All this leads to depression.
First aid
People who have panic attacks regularly know what to do at this time in order to experience the inconvenience as comfortably as possible. When feelings appear, the attack begins, there is no need to panic, fuss, or complain to others about your fears. You need to try to relax, take a comfortable position, protect yourself from all irritants, and make sure that fresh air flows into the room.
Self-massage increases the chances of faster removal of a seizure. Exercises are performed alternately until the condition improves:
- The middle finger slowly presses the temples and massages for 30 seconds.
- Go to the eyeball and do the same work for 30 seconds.
Those around you need to calm down and try to help the person who is having a panic attack. First you need to talk to the victim, convince him that nothing bad will happen. If you manage to distract a person having an attack, the panic will stop without the use of medications.
If a person often suffers from panic attacks, it is worth knowing what to do during this period in order to survive it as comfortably as possible. First of all, if you have a feeling that an attack is beginning, you should not panic, fuss and bother others with far-fetched fear. You need to relax as much as possible, take a comfortable position, remove all irritants (bright light, loud sound), and provide a flow of fresh air into the room.
Algorithm of actions
- If your blood pressure has already increased, try to calm down by adjusting your breathing. To do this, you should slowly inhale air, hold your lungs full for 1-2 seconds, and exhale slowly, trying to concentrate on the process.
- Increases the chances of quickly eliminating an attack and self-massage of the temples and eyeballs. Perform the exercises alternately until the condition improves and the tension can be reduced:
- With the middle finger of your hand, first press a little on your temples and massage them for 30 seconds;
- go to the eyeballs and do the same action for 30 seconds.
If a person witnesses another person developing a panic attack and increased heart rate, you should calm down yourself and help the patient cope with the problem. First of all, the victim needs to be reassured, explained that nothing terrible happened and that he will not die. If the patient can be relaxed and distracted, the attack will subside on its own, without the help of medications.
Right now, delete all your accounts in various forums and groups dedicated to panic attacks and vegetative-vascular dystonia. Why? Everything is very simple. The fact is that people who experience panic attacks and try to get rid of them on their own are the owners of a certain psychotype.
These are people with imaginative thinking: they think in pictures, have certain properties, desires and certain character traits. They are more likely to have panic attacks. Therefore, when they go to a forum or group and start reading something like “I was walking on the subway, some woman passed by and pushed me” and other similar stories of the same people, they experience a panic attack, which they can’t cope with on their own They can’t, although they go to a specialized website or forum for this purpose.
With a 90% probability we can say that the next time a person prone to panic attacks is on the subway and some woman pushes him, a picture of the story he read on the Internet will immediately pop up in his head, and sooner In all, he will also experience a panic attack.
Therefore, experts strongly recommend that people who are trying to find an effective way to treat panic attacks on their own completely stop visiting forums and various groups on social networks where similar topics are discussed. The reason is simple: mostly negative people communicate there. They constantly complain, cry to each other, but do nothing to get out of this state. They feel comfortable in it.
For those who have decided to get rid of their problem forever. This advice must be applied 100%: there is no point in collecting other people’s negativity, thereby aggravating your condition.
Second tip
This is the most important advice for those who decide to eliminate panic attacks on their own, as well as preventive information for those who are not susceptible to unreasonable panic anxiety. The phrase that you definitely need to remember is this: avoid avoidance.
READ MORE: What to do to normalize blood pressure
Algorithm of actions
Panic attacks in children: causes, symptoms, treatment - video
In childhood, panic attacks are most often situational. Children are especially susceptible to insults, humiliation, pain, and insult. Emotional upheavals in childhood leave a deep imprint on a person’s entire subsequent life.
The child cannot explain what is happening to him, but changes in his behavior can be noticed. He avoids certain places and situations, withdraws, and it is clear that in certain situations he experiences discomfort. In order to notice violations in time, parents and close relatives must be sensitive.
Measures to combat panic attacks in childhood:
- Creating a favorable atmosphere in the family. Parents should show their child their love.
- Play therapy: they try to switch the child’s attention to those activities that he likes.
- You need to support the child and try to reveal his creative talent.
- Sports activities.
- The child needs to be placed in an environment where he will not be judged and will be perceived as he is.
- Protection from traumatic situations.
- As your child gets older, you need to start learning how to cope with difficult situations.
How to recognize a hypertensive crisis
Hypertensive crisis has the following symptoms:
- A sharp rise in pressure in the walls of the arteries, which manifests itself in increased renal and cerebral
- Blood circulation;
- Nervous breakdown;
- Anxiety;
- Excitement;
- Palpitations;
- Feeling of lack of air;
- Cold clammy sweat;
- Hand tremors;
- Reddened facial skin;
- The so-called goose bumps.
Nausea and vomiting, dizziness are a consequence of defects in cerebral circulation. To these signs are added pathological processes in the visual analyzer. Headache with ringing in the ears and dizziness occurs most often. This pain often intensifies when sneezing, when turning the head, or when straining. It is usually accompanied by unpleasant sensations when moving the eyeballs and photophobia.
Dizziness is one of the common signs of a hypertensive crisis. A characteristic sensation is that all objects are spinning. Sometimes this is dizziness, which increases only with changed positions of the head, and sometimes it does not depend on this, and the feeling of moving does not arise.
Symptoms
A panic attack occurs unexpectedly, suddenly. This can happen in any situation: when a person is at home, in a store, visiting, or driving a car.
Depending on the time of occurrence, there are three types of panic attacks:
- Morning - immediately after waking up.
- Daytime – during the day, most often, attacks are situationally determined and occur under the influence of certain stimuli.
- Nocturnal - the most severe experiences, appear during sleep, usually from 2:00 to 4:00 at night. The fear of sleep gradually develops. Often the patient spends the rest of the night awake, asking one of his relatives to be nearby.
Attacks may occur more frequently or less frequently (from once a day to once for several months). For most patients - 2-4 times a week.
After a panic attack, you feel tired. The patient experiences strong fear that the attack may recur. He begins to avoid situations that can provoke fear.
Panic attacks have three stages:
- Initial (stage of harbingers, aura). The patient feels restless, experiences inexplicable internal tension, and an incomprehensible heaviness in the head.
- Expanded stage. Anxiety and fear are growing. The main symptoms appear. The culmination of the attack is the development of panic.
- Ultimate. A state of lethargy, fatigue, and depression develops. A person can remain in this state for up to a day.
Fatigue, frequent stress, various diseases and negative events can lead to exacerbation of the disease, intensification and frequency of attacks.
Often the patient experiences great fear for his condition and believes that he has a serious illness. He constantly visits doctors and undergoes examinations that show that he is healthy. This further intensifies the fear. A person loses confidence in doctors and medicine in general.
Doctors whom the patient visits often cannot suspect panic disorder, do not understand and are unable to explain to the patient what is happening to him.
There is an atypical form of the disease - the so-called “panic attacks without panic”. During an attack, the patient does not experience fear, he does not experience symptoms from the cardiovascular system. Possible manifestations: loss of voice, “veil before the eyes,” loss of taste, smell, conditions resembling paralysis.
The very first sign of an incipient panic attack is a feeling of intense fear that appears suddenly for no apparent reason. It is impossible to guess what will cause the next attack, so a person is overcome by a constant feeling of anxiety.
When an attack of vegetative crisis occurs, there is a sharp release of adrenaline into the blood. As a result, the following symptoms develop:
- increased heart rate;
- feeling of lack of oxygen;
- acute headache;
- tremor of the limbs;
- chills, increased sweating;
- discomfort in the left side of the chest;
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- fainting state;
- fear of death.
A vegetative crisis and its symptoms appear unexpectedly for the patient. It may be accompanied by several of the above symptoms or all of them at once. The peak of a panic attack occurs after 10 minutes; at the end of the attack, the person feels general weakness and drowsiness, after which everything returns to normal without any consequences.
During a panic attack, a person experiences very severe stress. He is afraid of a repetition of such a condition, thereby provoking its occurrence against the backdrop of the smallest unfavorable factors. A new panic attack may begin due to being in an unfamiliar environment, while staying in a closed space, or with the threat of physical violence or some kind of punishment.
Often a person who has suffered a panic attack (PA) has no idea about its causes.
The symptoms of neurosis, in addition to an inexplicable attack of poor health, are accompanied by a fear of dying or losing their minds.
A panic attack triggers a sharp production of adrenaline by the body, that is, it prepares the body for danger: the heart works in an increased mode, breathing quickens.
A person regards these sensations as a manifestation of serious diseases of the body (somatic), although in fact they do not exist. In the vast majority of cases, the symptoms of PA are similar to a heart attack, so the patient believes that he has developed a cardiac pathology.
In fact, this is just the result of a malfunction in the nervous system. Patients often experience nocturnal panic attacks with increased blood pressure.
The disease is characterized by the presence of phobic anxiety, manifested by various bodily (or somatic) symptoms:
- rapid heart rate (tachycardia);
- chills and sweating;
- muscle tremors;
- tremor;
- hot flashes;
- lack of oxygen;
- spread of pain in the heart area;
- stomach upsets (constipation or diarrhea);
- gagging;
- there is a lump (spasm) in the throat;
- abdominal pain;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- the tips of the arms and legs “tingle”;
- unsteady gait;
- fussiness;
- fainting state;
- weakened hearing and (or) vision;
- increased blood pressure.
In addition, the symptoms of panic attacks are complemented by psychological disorders:
- a feeling of foreignness and unreality of the surrounding world (derealization);
- violation of self-awareness, when a person sees himself from the position of an outside observer (depersonalization);
- phobic fears of death and loss of mind;
- confusion;
- loss of sleep or scary dreams.
Being in such a difficult state, a person realizes that he cannot concentrate on anything. Anxiety increases, and at this moment vomiting and uncontrollable bowel movements may appear. The patient wants to run and hide.
The attack usually lasts several minutes, maximum half an hour. Then the state of health returns to normal. But a feeling of worthlessness comes. A person thinks that in the eyes of others he looks like a coward. These thoughts haunt him and provoke a new round of panic.
The expectation of a recurrence of the attack forms a model of a defensive reaction in the mind - “avoidance behavior.” In this case, the person deliberately limits his stay in situations and places where PA occurred.
This obsessive state ultimately develops into phobias, which are also accompanied by depressive disorder.
The duration of the attack is individual and lasts from several minutes to half an hour. The frequency of the disorder varies from 1-3 times a day to once a month.
Any situation can provoke a crisis: being in a confined space or in crowded places, the need to speak in front of an audience, or traveling by transport.
Panic attacks are divided into 3 types:
- spontaneous. Characterized by a sudden appearance for no apparent reason;
- situational. It is discovered when a person again finds himself in a traumatic environment or waits for its appearance (for example, in anticipation of a quarrel);
- conditional-situational. Here the “trigger” is a biochemical component that excites the nervous system (for example, alcohol or drugs).
It is also worth noting that panic occurs when measuring blood pressure and other medical procedures. It is very important to know how to calm down before measuring blood pressure so as not to distort the readings.
The occurrence of PA can be caused by one or more reasons:
- bad genetics (relatives have mental illnesses);
- excessive demands on the child from the parents;
- stress;
- unfavorable family environment (alcoholic parents or frequent quarrels);
- characteristics of temperament;
- personal character traits: impulsiveness and vulnerability, low self-esteem, suspiciousness and excessive emotionality;
- chronic illness, disability or recent surgery;
- alcohol or drug abuse;
- adolescence;
- pregnancy or menopause.
Autonomic dysfunction is diagnosed after examination and examination by a number of specialists: a cardiologist, an endocrinologist and others.
Examinations by specialists to exclude pathologies such as:
- heart diseases;
- phobias and schizophrenia;
- hypoglycemia;
- hyperthyroidism (high concentration of hormones in the blood plasma);
- mental exhaustion.
Side effects of medications taken should also be excluded.
Medicine has all the means to completely cure this alarming condition.
The essence of the method is a therapeutic effect on the psyche of a patient immersed in a hypnotic sleep. The doctor forms in the patient a different attitude towards the manifestation of the crisis.
While in a hypnotic state, a person cannot consciously build a defense and, with the help of verbal and non-verbal influence, receives the necessary information.
Cognitive behavioral therapy aims to become aware of and break the behavioral habits that trigger an attack.
During the treatment process, the patient develops a new attitude: “Anxiety will not harm me.” As a result, PA no longer seems like a disaster to a person, the fear of death disappears.
For autonomic dysfunction, drugs such as:
- benzodiazepine tranquilizers. They quickly stop the attack (30-60 minutes), but are used for a short time because they have an addictive effect;
- antidepressants that do not stimulate the nervous system. The effect occurs after 2 weeks. And the course of treatment is 6 months. These medications should be taken regularly, not just during an attack;
- Vitamin B supplements. They strengthen the central nervous system.
People often begin treatment for PA with a visit to a psychologist. This is not entirely true, since such a specialist is not a doctor. He is not competent to determine the cause of the crisis and has no right to prescribe medications. And it is possible to cure neurosis only through the joint efforts of a psychotherapist and a neurologist.
So, in order to completely get rid of PA, you must comply with the following conditions:
- find competent specialists and personally contact them for help;
- The prescribed therapy must be strictly followed. As much as you might like, do not violate time limits;
- Only a responsible attitude to treatment will give the desired result.
Treatment methods
Panic attacks are divided into 3 types:
- Spontaneous. They appear for no reason. It is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis to identify diseases that can provoke such attacks. If there are no diseases, then a psychotherapist can help.
- Situational. They arise in a certain situation; you don’t need to conduct a full examination, but go straight to a psychotherapist, because there is a specific fear that needs to be gotten rid of.
- Conditional-situational. Need a stimulus: alcohol, drugs, hormonal imbalance. In this case, you need the help of a specialized specialist.
Panic attacks should be treated by a psychotherapist. The attending physician may prescribe medications or psychotherapeutic methods. Currently, neurolinguistic programming, cognitive-behavioral and behavioral therapy, relaxation, the method of suggestion, and auto-training are popular.
As for medications, selective inhibitors are used - Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft, Fevarin, benzodiazepines - Clonazepam, monoamine oxidase inhibitors - Aurorix. Taking medications is usually long-term - from six months to a year. To stop attacks, you can use Anaprilin or Atenolol, as they are able to block the effects of adrenaline. However, these drugs are unable to prevent subsequent attacks.
A panic attack is a very difficult condition for patients to tolerate, however, it does not threaten a person’s life at all. With an integrated approach to treatment and with the understanding and support of loved ones who accept the condition as a disease, there is hope for a return to a full life and recovery.
In medicine, panic attacks with hypertension are a complex symptom that is difficult to diagnose the first time. Basically, increased anxiety is observed in vegetative-vascular dystonia, hypertension and other vascular and cardiac diseases as one of the symptoms of these pathologies.
To avoid the development of such a phenomenon, it is necessary to know the mechanism of its occurrence, what causes contribute to its development, what symptoms it manifests, and what actions should be taken to relieve panic, thereby preventing its worsening.
According to medical statistics, approximately 5% of people have a predisposition to this pathological condition, and it is more often observed in patients 20-30 years of age, and in most cases in women.
Almost every person has experienced panic to one degree or another, which is a completely normal situation under stress. At this moment, a certain mechanism is launched in the body:
- A sharp release of excessive amounts of adrenaline (stress hormone), which is directly responsible for the safety of the body, thereby turning on a signal that you need to save yourself.
- Due to the increased presence of adrenaline, the heart rate increases, and the respiratory organs begin to work intensively.
- Increased ventilation of the lungs and a decrease in the level of carbon monoxide in the blood fluid causes unpleasant symptoms, such as dizziness, numbness of the arms and legs, tingling of the skin and stuffy ears.
Doctors consider such a reaction to danger to be a normal phenomenon, since a panic attack is just a disturbance in some functions of the body, so it turns on the “emergency” mode.
Experts call three types of panic attacks.
| View | Peculiarities |
| Spontaneous | It occurs unexpectedly and without any reason. |
| Situational | It appears as a result of a stimulus - a specific negative situation or in anticipation of it. |
| Conditionally situational | It develops under the influence of some irritant, for example, coffee, alcohol, drugs, hormonal imbalance. |
Reasons for development
| Deviations in the body | Diseases |
| The cardiovascular system | Angina pectoris. VSD. Hypotension. Hypertension. Mitral valve prolapse. |
| Physiology of the body | Pregnancy. Postpartum period. Determined interval of the menstrual cycle. Hormonal surge in teenagers. |
| Endocrine system | Hypothyroidism. Pancreatitis. Hyperthyroidism. Diabetes. |
| Heredity factor | Genetic abnormalities. |
| Taking certain medications | CNS stimulants. |
The situation is complicated by the fact that it is quite difficult to control attacks of fear, and not every person is able to adequately assess the situation when they arise, because at the moment they are driven by fear for their health.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Chills.
- Dizziness
- Flushing to the head.
- Freezing of the heart.
- Increased heart rate.
- Feeling cold.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
- Discomfort in the heart.
- Sweating.
- Heaviness in the chest.
- Dyspnea.
- Ringing in the ear.
- Loss of orientation.
- Frequent heartbeat.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Increased tearfulness.
- All-consuming fear.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Unreasonable aggression.
- Pale skin.
- Frequent urination.
It should be emphasized that the occurrence of pain in the heart during panic attacks is already a serious situation, indicating a possible complication of the pathological process.
Many patients are interested in how long such seizures last and how often? The duration of attacks is usually 15-30 minutes, but they can last several hours, and their frequency of occurrence is several times a day to 1-2 times a month.
In some episodes, anxiety attacks appear exclusively under certain conditions, for example, only on the street or indoors, before leaving the house or while driving a car, in a crowd or alone, etc. As soon as the person leaves the uncomfortable zone and calms down, the PA will stop.
However, a completely different situation is observed when a panic attack occurs in a patient prone to hypertension. In this situation, the pressure begins to jump much higher than in a person without hypertension.
For a very long time, panic anxiety was considered one of the symptoms of VSD, and was defined as a “vegetative crisis.”
However, today medicine is inclined to believe that the occurrence of panic is not a symptomatic phenomenon, but is of a psychological nature with quite serious consequences.
Experts have proven that a jump in blood pressure does not provoke panic attacks, but is one of the symptoms of hypertension. On the other hand, frequent fluctuations in pressure can lead to more frequent and intensified panic attacks.
So, why does fear raise blood pressure, what factors provoke it? Increased blood pressure occurs for two main reasons:
- Physical.
- Psychological.
The occurrence of a panic attack can be caused by many reasons, however, as mentioned above, stress comes first, from which no one is immune.
Among other reasons, doctors name:
- Smoking.
- Drug addict.
- Presence of depressive disorders.
- Unpleasant deafening sounds.
- Systematic intake of alcohol in large doses.
- Intolerance to bright flickering lighting.
- Inability to do great physical activity.
- Long-term traumatic effects on the psyche.
In addition, there are also factors of an unreasonable nature:
- Depression.
- Tension.
- Nervousness.
- Apathy.
- Insomnia.
- Excessive sleepiness.
According to medicine, a jump in pressure during a panic attack is often a consequence of deviations in the performance of the cardiovascular structure when a malfunction occurs in the nutrition of the brain. In this case, the body seeks to eliminate brain starvation and begins to speed up the heart’s work in order to normalize the situation. As a result, pressure begins to rise.
Often, hypertensive patients find themselves in a hopeless situation when hypertension causes a rush of panic, which in turn also provokes an increase in blood pressure. For example, the emergence of irresistible fear entails a jump in blood counts, which significantly increases the risk of developing a hypertensive crisis.
READ MORE: Panic attacks with cervical osteochondrosis
During panic attacks, the blood pressure rises, the pulse beats faster, and if the patient does not know about the presence of hypertension, he may be afraid of such symptomatic manifestations, which further aggravates the fear syndrome, which leads to an even greater increase in blood pressure.
It follows that a person provokes a jump in blood pressure with his negative thoughts. People who tend to see the negative in everything should clearly understand the mechanism of the body’s processes at the moment of fear, learn to cope with panic attacks and competently respond to their occurrence.
First of all, anxiety attacks are accompanied by the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms of a psycho-emotional and physiological nature. In addition, at the moment of panic, a person feels strong anxiety not only for his health, but also for his loved ones. Under the influence of negative thoughts, he develops an obsessive fear of losing his mind or dying.
Many patients prone to such manifestations would like to know how serious such a situation can be? Experts answer this question as follows:
- During panic attacks, painful physical symptoms appear, to eliminate which the patient begins to take various medications without thinking about their compatibility. Such actions can cause significant harm to the body.
- During initial attacks of fear, when its symptoms are very pronounced, frightened by his condition, a person calls for medical help and demands an injection to eliminate pain in the chest, shortness of breath, believing that he is having a heart attack. However, many cardiological medications have a strong effect, so their use in the absence of cardiac diseases is fraught with harm.
- Manifestations of panic often provoke the development of various phobias (agoraphobia - fear of people, autophobia - fear of loneliness, claustrophobia - fear of limited space, etc.). Such disorders can lead to the development of other mental disorders.
- The presence of fear can be dangerous not only for the patient himself, but also for those around him, because in the event of an unexpected attack of fear, a person loses control over his behavior.
- Symptoms of panic disorder can aggravate the course of chronic diseases, for example, heart disease, gastrointestinal pathologies, etc.
- The occurrence of uncontrollable anxiety is an extremely harmful phenomenon for pregnant women and women with small children, since a child, even an unborn one, feels the psychological mood of the mother.
- The occurrence of unexpected panic against the background of the presence of other mental disorders can push a person to suicide.
If your blood pressure increases significantly during an attack, your doctor will prescribe antidepressants.