Abdominal aorta examination
The purpose of ultrasound screening of the abdominal aorta is to diagnose an aneurysm. The change consists of a dilation of this large artery, which may be local or general. This pathology becomes a consequence of weakening of the vascular walls and accumulation of blood in some parts. The aorta itself is the main arterial vessel in the human body, which passes through many areas, including the abdominal cavity. The latter performs the important function of supplying blood to the lower torso and legs. Indications for abdominal ultrasound are described below.
Indications for ultrasound
The first factor in which the abdominal aorta is subjected to ultrasound is the presence of abdominal pain in the patient, which radiates to the lumbar region. The sensations are similar to renal colic, i.e. strong and aching. As for the localization of pain, it is felt on the left side and near the navel, but can radiate to the lower limbs and groin area. If a person is thin, then the pulsation of the aneurysm can even be felt. All these symptoms are accompanied by complaints of abdominal heaviness and bloating.
In addition to the obvious signs that require an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, there are other indications for this procedure:
- headache and dizziness of a regular nature, pulsation in the area of the back of the head and temples;
- when you turn your head, “spots” flash before your eyes;
- persistent arterial hypertension or hypotension;
- previous stroke, ischemia, hypertensive crisis or abdominal trauma;
- smoking for a long time;
- age from 60 years;
- epilepsy;
- memory impairment.
Preparation for ultrasound of internal organs
In order for a specialist to freely examine the aorta and its branches, the patient must properly prepare for the procedure. To do this, the following simple rules must be followed:
- 2 days before the proposed examination, exclude from the diet all food, the consumption of which can cause increased gas formation and flatulence. This includes legumes, potatoes, cabbage, melon, dairy products, soda and all foods high in carbohydrates.
- Take medications for a couple of days to improve bowel function. Espumisan is an effective remedy. An alternative to it can be regular activated carbon.
- You should completely abstain from food and liquid 8 hours before the procedure.
- For chronic constipation, in the evening before the study, you need to do 2 cleansing enemas with saline solution.
Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta
Timely detection of pathology of the carotid arteries and abdominal aorta allows timely and correct treatment and prevention of the development of cerebral stroke, thrombosis and rupture of blood vessels and other serious diseases.
The examination of the carotid arteries does not require special preparation, and to conduct effective ultrasound diagnosis of the abdominal aorta, high-quality preparation of the patient’s colon is necessary.
Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta is recommended in all patients over 40 years of age as a screening for atherosclerotic lesions of the aorta and its branches, aneurysms (true aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms and aneurysms with dissection), narrowings (stenoses) of the aorta and its branches, the presence of blood clots and anomalies of its development.
Why is it important to do an ultrasound of the abdominal aorta and its branches?
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the carotid arteries in the following situations:
- If the patient complains of frequent headaches, dizziness, loss of consciousness. And also if there is a feeling of “fullness” and pulsation in the temples or the back of the head.
- With a frequent feeling of “darkening” in the eyes or the presence of “ripples” and “floaters” before the eyes with a sudden change in body position or when turning the head.
- With memory loss.
- In individuals with both high (with arterial hypertension) and low blood pressure (with arterial hypotension).
- In persons with a history of various cerebrovascular accidents (stroke, transient ischemic attack, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, etc.).
- In the presence of epileptic seizures.
- Male smokers aged 65 years and older are recommended to undergo an annual ultrasound examination of the carotid arteries for early detection of pathological changes and implementation of preventive measures.
For what symptoms is an ultrasound of the abdominal aorta and its branches performed?
Indications for ultrasound of the abdominal aorta:
- All persons with arterial hypertension over 40 years of age.
- If you have vague pain in the abdomen, pulsating in nature.
- In the presence of intermittent claudication and pain in the lower extremities.
- With the development of impotence.
How is an abdominal ultrasound performed?
Those patients who do not know how to do an abdominal ultrasound often feel fear before the procedure, but this is in vain. The examination is not dangerous and does not cause any pain or discomfort. The ultrasound process itself includes only a few steps:
- The patient comes for an appointment and sits comfortably on the couch, to the right of the doctor. The head is located at the level of the screen, so a person can observe what is happening.
- Next, the doctor lubricates a special sensor and the patient’s abdomen with a transparent gel, which reduces tissue resistance and helps the ultrasound wave penetrate inside.
- The specialist then slowly moves the sensor along the abdominal wall and records the results of the observations.
Dopplerography of blood vessels
The ultrasound procedure lasts about 15-20 minutes. After the examination, you can immediately return to your usual daily schedule. Next, it is worth distinguishing between the terms Doppler ultrasound and ultrasound of internal organs. Ultrasound examination is a broader concept. It can be carried out using the following methods:
- color Doppler scanning (CDS);
- ultrasound duplex scanning (USDS);
- Doppler ultrasound (USDG).
The latest ultrasound method of the abdominal aorta is based on the Doppler effect, which consists of recording changes that occur when sound waves are reflected from blood cells. The Doppler ultrasound method is used for the initial examination, since it allows one to determine only the main characteristics of the current state of the aorta in the abdominal region and, additionally, the parameters of blood flow in it. The ultrasound specialist receives a protocol of high-resolution graphic images. The data is sent to the dashboard of the ultrasound machine. Using these pictures, you can decipher the study.
During an ultrasound, the abdominal aorta is examined in cross section. This gives the doctor the opportunity to check the numerical characteristics of the vessel for compliance with normal values. The value is taken from the maximum internal diameter in cross section. Normally, in an adult, it should not exceed 3 cm. For the iliac branches, this figure is slightly lower and the maximum is 1.5 cm. If during the study the doctor received values less than the above, then an aortic aneurysm is excluded.
Interpretation of ultrasound results
When performing an ultrasound of the abdominal aorta, the doctor examines this vessel along its entire length. An anomaly is any increase in diameter. The result of the study is a transcript of the ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Its quality depends on the qualifications of the specialist. Based on the decoding, the following pathologies or diseases can be identified:
- Atherosclerosis. Its development is a consequence of damage to the walls of blood vessels by cholesterol and its accumulation in the form of plaques.
- Aneurysm. Its sign is an increase in the diameter of the aorta.
- Stenosis of the celiac trunk. Characterized by a too narrow diameter of the main branches of the aorta.
- Occlusion. A sharp narrowing of the aorta to the point of complete obstruction.
- Tortuosity of the aortic arch. It is caused by a hereditary factor and is manifested by elongation, tortuosity, kinks and looping of blood vessels.
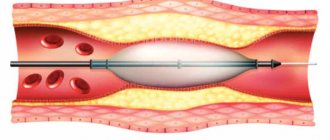
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
An aneurysm means a significant increase in the diameter of the aorta, and in sections located lower towards the pelvis. Inflated indicators may be as follows:
- 3-3.5 cm - in this case, the patient should regularly come for examinations to monitor changes;
- 4-5 cm – with this diameter of the aorta, its dissection is possible within a year;
- 5 cm and above - for an aneurysm of this magnitude, only surgical intervention is indicated.
Wall sealing
Such a pathological process can occur in any part of the aorta - the root, a certain section, or its entire length. In addition to ultrasound, compaction is detected using x-ray examination. Of all the pathologies, this is especially dangerous. Due to high blood pressure or playing sports, there is a risk of wall dissection, as a result of which blood flows in and the vessel ruptures.
Atherosclerosis of the aortic arch
Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta reveals the nature of blood flow in this vessel and its possible pathologies. When cholesterol levels are high, plaque forms on the walls of the arteries. They interfere with normal blood supply to tissues. This pathology is called atherosclerosis of the aortic arch. Its danger is that in the early stages there are practically no symptoms. Only ultrasound can detect even small atherosclerotic plaques. Along with it, if such a disease is suspected, other studies are prescribed:
- X-ray;
- Dopplerography of the veins of the lower extremities;
- cholesterol tests.
Impaired blood flow through the abdominal vessels causes acute organ ischemia. These conditions are considered life-threatening. Ultrasound of large vessels of the abdominal cavity detects narrowings, blood clots, and cholesterol plaques. Thanks to this, the doctor can provide timely treatment.
What does the examination show?
Duplex scanning of the aorta allows us to identify the following pathologies:
- obliterating atherosclerosis is a common pathology affecting the vessels of the lower extremities.
- aneurysm of the abdominal aorta - during diagnosis, this disease is recognized by pathologically dilated vessel walls.
- aortic occlusion.
- aortic thrombosis - which, without timely diagnosis, can lead to death, and non-fatal, but very serious cardiovascular events - heart attacks, strokes.
- congenital anomalies, such as aortic tortuosity.
Indications for examination
Dopplerography of the vessels of the abdominal cavity is carried out if a person has signs of the disease. The following symptoms require diagnosis:
- prolonged increasing abdominal pain;
- chronic headache;
- unstable blood pressure;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- constant swelling of the legs;
- rumbling stomach, constipation.
When prescribing an examination of the abdominal vessels, diseases previously suffered by the person are taken into account. These include heart attacks and strokes, penetrating abdominal wounds, and diabetes mellitus.
When examining a person, a doctor may notice excessive pulsation of the abdominal aorta. This is also a reason to prescribe an ultrasound.
The doctor will tell you about the ultrasound examination of the abdominal vessels and the indications for the procedure in the video:
Sign up for duplex scanning of the aorta in Moscow
If you have alarming symptoms or as prescribed by a doctor, you can sign up for a double “duplex” ultrasound scan at Clinic No. 1 in Khimki. Call or fill out an online form on the medical institution’s website. Timely accurate diagnosis using modern equipment is the key to proper treatment and quick recovery!
Prices for services
| Name | Time | Price |
| Color duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta | 1650 | |
| Color duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta, iliac arteries | 2145 |
Features of preparation
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal vessels is necessary so that nothing complicates the examination. Gases and feces in the intestines interfere with the passage of ultrasound. Therefore, patients are prescribed a three-day diet and medication as preparation.
The diet involves the exclusion of foods that contribute to gas formation:
- fatty food;
- cabbage;
- black bread;
- dairy products;
- legumes
It is recommended to eat stewed vegetables, buckwheat porridge, and crackers. Carbonated drinks are excluded.
For severe flatulence and constipation, two days before the procedure the patient is given medications:
- laxatives - Duphalac or Forlax;
- carminatives - “Espumizan”, “Unienzym”;
- enzymes - “Mezim”, “Pancreatin”.
You must come to the ultrasound on an empty stomach; in the morning you are allowed to drink only a glass of water. You will need to take a disposable sheet and towel with you.
Research technique
To examine blood vessels, a special ultrasound technique is used - Dopplerography. This method is based on the ability of ultrasound to be reflected from red blood cells moving through a vessel. On the computer screen, the doctor sees an image of the blood flow and can measure its speed and uniformity.
The second option for ultrasound is color Doppler mapping (CDC). If Dopplerography provides information about blood flow in dynamics, then ultrasound of the abdominal vessels with color circulation is a static image. It captures a certain period of time and displays it on the computer screen in the form of a still image. This way you can look at the blood flow in more detail.
The manipulation technique is simple. The patient is placed on the couch and asked to expose his stomach. The doctor applies a gel to the skin that improves the conductivity of ultrasonic waves. Next, he examines the projection areas of the abdominal vessels using a sensor. To view some parts of the aorta, he asks the patient to turn on his side.
Ultrasound is not accompanied by pain or discomfort. The entire examination takes no more than 20 minutes. The remaining gel is removed from the skin with a towel, and the person can be free.
In the video, see how a vascular ultrasound looks on the monitor. Below you will see a short video and a more thorough story about the anatomy of the abdominal vessels.
What does an ultrasound show?
Using ultrasound, it is possible to identify defects in the structure of the abdominal aorta and its branches, and disturbances in blood flow. In addition to the abdominal arteries, ultrasound evaluates the condition of the veins. They are less visible because the blood flow in them is slower.
The permissible value of the aorta diameter is up to 3 cm. Its largest branches should normally not be more than 1.5 cm in diameter. The vascular wall is smooth, without protrusions or thickenings. The aorta, celiac trunk, and iliac arteries are smooth throughout, without loops or bends.
Using ultrasound diagnostics, various pathologies of the abdominal vessels are detected.
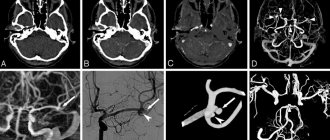
- An aortic aneurysm is an expansion of its wall in the form of a sac. The disease is dangerous due to rupture of the vascular wall and massive bleeding. The image shows a deviation of the blood flow towards the protrusion of the vascular wall.
- Stenosis of the aorta or its branches is a narrowing of the diameter. May be congenital or acquired after injury. The image shows a decrease in the volume of flowing blood and a slowdown in its speed in the narrowed area.
- Atherosclerosis is the formation of fatty plaques in the vascular wall. During the examination, a deviation of the blood flow and its slowdown at the location of the plaque are visible.
- Thrombosis is the blocking of the lumen of an artery or vein by a blood clot. Leads to malnutrition of organs and their death. When performing an ultrasound scan in a vessel of the abdominal cavity, an interruption of blood flow in the blocked area is clearly visible.
- Angiopathy. In diabetes mellitus, a change in the structure of the vascular wall occurs. It becomes thicker and loses elasticity. The image shows slow blood flow.
The doctor performing the ultrasound makes a description of the changes seen. The final diagnosis is made by the attending physician, taking into account other examination methods.
Video of an abdominal aortic aneurysm:
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and its visceral branches
During the examination of patients with abdominal pain, the question constantly arises about its cause. Intestinal ultrasound is a useful and fast screening method that allows you to recognize infiltrative and exophytic intestinal lesions, inflammatory changes, intussusception, inflammation of the mesenteric lymph nodes and much more. However, often an ultrasound of the intestines leaves questions without revealing any significant deviations in the ultrasound picture. Meanwhile, ultrasound duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and its branches: the celiac trunk, the superior mesenteric artery and the inferior mesenteric artery has very useful information regarding the occurrence of abdominal pain, bloating, alternating constipation and diarrhea, weight loss, the development of hydronephrosis and other symptoms. arteries.
Possible contraindications
Ultrasound is the safest diagnostic procedure. It has no medical contraindications, as it does not have a negative effect on human health. But there are still conditions in which it is undesirable to do an examination, because the result will be unreliable.
These conditions are considered:
- patient's alcohol or drug intoxication;
- acute psychosis;
- pronounced flatulence;
- injuries and inflammation of the abdominal wall.
Contraindications are not taken into account when emergency examination of the abdominal vessels is necessary.
Duplex/Triplex scanning of blood vessels
Duplex/Triplex scanning of vessels (synonyms - duplex/triplex vessels, ultrasound duplex angioscanning (USAS)) is a non-invasive study of the arterial and venous systems, aimed at obtaining information about the condition of the vessel. During the examination, the following is assessed:
- condition of the vessel wall (its integrity, structure, thickness),
- patency of the vessel (presence, localization and extent of intraluminal formations - blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques) and the degree of patency impairment,
- its geometry, the anatomical course of the vessel (tortuosity, bending of vessels).
- measure the diameters of blood vessels,
- assess the speed and nature of venous and arterial blood flow.
- The method allows you to diagnose congenital and acquired changes in blood vessels (narrowing, local dilatation, abnormal development of the vessel).
Vascular examination using duplex (triplex) scanning is prescribed for a number of diseases:
- Atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries.
- Diabetic angiopathy of leg vessels.
- Aneurysm (local dilatation) of an artery.
- Identify and evaluate varicose veins.
- Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels)
- Vascular disease of the neck and brain
- When monitoring operations performed on various vessels.
- If vascular thrombosis is suspected.
- For postthrombophlebitic venous disease.
- With compression syndrome (external compression) of the vessel
preparation is required for the examination , except for examination of the vessels of the pelvis and abdominal cavity, where preparation similar to that for an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity is required.
The method is completely safe and has no contraindications.
The result is released immediately upon completion of the procedure
Advantages and disadvantages
The method has many advantages:
- non-invasiveness
- high information content and efficiency;
- painless, no anesthesia required;
- harmlessness due to the absence of radiation;
- there are practically no contraindications due to the fact that ultrasound does not have a negative effect on the body;
- carried out in real time.
There are some disadvantages:
- difficulties in examining small vessels;
- the result depends on the professionalism of the doctor;
- cholesterol plaques can make it difficult for ultrasound to pass through, which reduces the quality of the study.
- when studying cerebral vessels (transcranial duplex scanning - TCD), due to the impossibility of adequate visualization of the vascular wall and lumen of the vessel due to the technical features of modern ultrasound scanners, qualitative information about the state of the lumen of the vessel and its anatomical course is assessed by the nature of the change in blood flow (velocity indicators, nature of the spectrum and blood flow).
Cost of examination
Ultrasound can be done free of charge in municipal institutions at your place of residence. To do this, there must be evidence; often you have to wait in line for a long time. A faster option is a paid examination at a private center. The cost depends on the region of residence and the type of diagnosis.
Cost table for ultrasound examination of abdominal vessels:
| City | Price, rubles |
| Moscow | 1000-5600 |
| Saint Petersburg | 900-5000 |
| Novosibirsk | 1000-5500 |
| Ekaterinburg | 1000-6000 |
| average cost | 975-5525 |
Ultrasound diagnostics is widely used to detect vascular diseases. Special techniques allow you to assess the state of blood flow and identify even minor changes. Diagnosis is simple and available in most medical institutions.
Leave comments and share the article with friends on social networks. All the best and stay healthy.
Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta is a highly informative diagnostic method based on the ability of organs to reflect an ultrasound wave; when supplemented with Doppler, it is possible to obtain data not only on the structure of blood vessels, but also to measure blood flow and identify areas of disturbance in its movement.
The study of the abdominal aorta and its branches allows us to identify many pathologies even at the earliest stages of development: vascular stenosis, atherosclerosis, disturbances in the structure of blood vessels, including compression in lesions of the cervical spine.
Doppler ultrasound of the aorta and its branches is prescribed in the following situations:
- with severe headaches of unknown origin;
- frequent dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- if the patient complains of a feeling of pulsation or fullness in the back of the head or temples that occurs constantly;
- flashing of spots before the eyes when suddenly changing body position or turning the head;
- if the patient complains of decreased memory and attention;
- patients with altered blood pressure: high or low;
- having a history of acute circulatory disorders, this may be a stroke, transient attacks and other manifestations of pathology;
- manifestation of epileptic seizures for the first time or as an assessment of the condition upon diagnosis.
An indication for ultrasound of the abdominal vessels is also old age, especially in people who abuse tobacco products or have occupational hazards related to cardiovascular diseases.
Why do duplex scanning
This is an excellent alternative to invasive methods of vascular research. In fact, today duplex scanning is recognized as the “gold standard” in the field of diagnosing diseases of the veins and arteries.
The study is prescribed if the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- dizziness
- lack of coordination
- drowsiness
- frequent headaches
- loss of consciousness
- swelling of the arms and legs
- convulsions
- high blood pressure
You may also need testing even if you have no symptoms to:
- assessment of blood flow in the postoperative period
- assessment of blood flow before surgery, including on the heart
- timely detection of blood clots (hematomas), identification of any complications blocking blood flow
- assessing the width of blood vessels
Duplex scanning reveals the following vascular diseases:
- abdominal aneurysm
- arterial occlusion (obstruction)
- thrombosis
- obstruction of the aorta and iliac arteries
- kidney diseases
- varicose veins
- venous insufficiency
What will an ultrasound scan of the abdominal aorta show?
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and its branches allows you to assess the body’s blood flow, as well as identify foci of pathology that impede normal nutrition of the organs.
- Obliterating atherosclerosis is a systemic disease characterized by the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- An aneurysm is an expansion of the walls of large vessels, accompanied by thinning, which is a threat to the patient’s life.
- Ultrasound of the celiac trunk determines its stenosis, leading to disruption of the blood supply to the liver and stomach.
- Occlusion is the blockage of a vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque, determined by duplex scanning of the aorta.
- Thrombosis on ultrasound of the abdominal aorta is defined as partial blockage of a vessel by a thrombus, which, with further development, leads to occlusion.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the abdominal aorta can be expressed in lengthening and narrowing, as well as pathological branching of the vascular network. This pathology reduces the level of nutrition of the organ due to obstruction of blood flow.
- Aneurysm dissection is diagnosed in a process localized in the middle layer of the vessel, without damage to the external or internal layers, and requires surgical treatment.
In case of pathology of the vascular system, increased load can give rise to rupture of the aorta, which puts the patient’s life at risk; the slightest suspicion of such disorders serves as the basis for prescribing an ultrasound scan of the branches of the aortic arch.
Duplex scanning of the aorta and its branches allows you to determine the degree of danger to the health of the person being examined in case of aortic valve insufficiency. Visualization of the processes occurring in the vascular network in real time allows you to assess the state not only at rest, but also under load.
Diagnosed pathologies
Thanks to the use of this method, it has become possible to identify various vascular pathologies:
- Atherosclerotic plaques.
- Narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and its causes.
- Dissection of arterial walls.
- True and false aneurysms of the aorta and its branches.
Serious pathologies, manifested by severe symptoms, develop if several vessels are affected simultaneously. This is due to the fact that the branches of the aorta can take over the functions of each other. To make an accurate diagnosis, the entire vascular system is studied.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal aorta
High-quality preparation for the diagnosis of the abdominal aorta will allow you to obtain reliable results and more accurately assess the slightest change in the structure or functioning of the vascular network.
- 3-4 days before the examination, the patient must exclude from the diet foods that contribute to increased flatulence: bread, legumes, fermented milk, fatty foods.
- The day before the diagnosis, take activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight.
- The last meal should not be taken earlier than 8 hours before the ultrasound of the abdominal vessels; drinking water is also excluded for at least 2 hours.
The general principles of preparation are described here; if a more serious approach to the matter is necessary, the doctor will tell you in detail what each person needs to do to improve the quality of the study.
Duplex scanning of abdominal vessels
Advantages of ultrasound research: harmlessness, accessibility, high information content, absence of contraindications, possibility of dynamic observation.
Main indications for diagnostics:
- complaints of abdominal pain of various localizations, swelling, increased blood pressure, dyspeptic disorders, flatulence, heaviness in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region, etc.;
- previously diagnosed: splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity; varicose veins of the esophagus, stomach, rectum, umbilical region, lower extremities;
- increased cholesterol levels in the blood;
— patient age over 50 years;
- history of abdominal trauma;
Contraindications : none.
Preparation for diagnosis : a prerequisite is the last meal 7-8 hours before the examination. Two days before the test, it is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that cause increased gas formation (vegetables, fruits, flour and dairy products, carbonated drinks). For patients with a tendency to flatulence, it is advisable to take enterosorbent drugs (activated carbon, espumizan, etc.) 1-2 days before diagnosis.
Study time : 30-40 minutes.
Research methodology:
- The study is carried out polypositionally. The patient is alternately placed on his back, left and right sides and on his stomach.
- To improve the conduction of ultrasonic waves and improve the quality of the echo picture, a specialized gel is applied to the skin of the areas under study;
- Diagnostics of the vessels of internal organs is carried out: liver, spleen, kidneys, pancreas; the celiac trunk, mesenteric arteries, abdominal aorta, iliac arteries, inferior vena cava basin are examined; Using Doppler diagnostic modes and additional functional tests, the spectral characteristics of blood flow are measured.
Commonly detected pathologies:
- stenosing atherosclerosis of the arteries;
- blood clots in the lumens of veins and arteries;
- signs of portal hypertension;
— diagnosis of the condition after installation of a vena cava filter in the inferior vena cava;
— aneurysm of the abdominal aorta;
- extravasal compression of blood vessels;
— hemodynamic disorders in the abdominal organs;
— abnormalities in the development of renal vessels;
— diagnosis of conditions after angioplasty and vascular stenting, etc.;
Recommended consultations with specialists: therapists, surgeons, gastroenterologists, cardiovascular surgeons, hepatologists.
Progress of the procedure
Ultrasound scanning of abdominal vessels is a highly informative, painless and harmless manipulation. Lasts no more than 20-30 minutes.
- The patient comes to the diagnostic room after completing the preparation at the time prescribed by the doctor.
- Having undressed to the waist, he takes a comfortable position on the couch (the position during the study allows you to observe what is happening on the screen).
- The specialist applies contact gel to the abdomen to improve the penetration of ultrawaves deep into the tissues and eliminate slipping difficulties.
- Using a special sensor, the ultrasound specialist studies the structure of blood vessels and measures the speed of blood flow, while simultaneously recording the data obtained in the study protocol.
At the end of the procedure, the patient receives a ready-made diagnostic result in his hands, with which he must go to an appointment with the attending physician to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Everyone can decipher some indicators on their own, without waiting for an appointment with a specialist.