For the brain to work correctly, without overstrain and failures, blood circulation must be ideal. Moreover, the most important role is played not only by the influx of oxygen and nutrients, but also by the timely outflow of blood. Recently, doctors are increasingly diagnosing a violation of the venous outflow of the brain - a dangerous pathology that in most cases develops due to an incorrect lifestyle. Whatever form of dyscirculation is identified (congenital or acquired), it in any case indicates the presence of dangerous diseases and in the future can cause pathological changes in brain tissue. That is why, at the first symptoms of a disorder, you should immediately contact the clinic, because at an early stage it is much easier to get rid of the disease and prevent complications.
Dyscirculation of the brain
The main function of the circulatory system is to transport nutrients. When cells and tissues have received vital elements, it is necessary to remove all metabolic products. Veins are responsible for this. The main ones are:
Some pathologies lead to destabilization of blood flow. Venous discirculation of the brain is a deterioration in the outflow of blood from organs and tissues . It is a consequence of another disease.
In medical practice, there are three main stages of the disease:
- Primary changes, clinical picture and symptoms are completely absent.
- Typical disorders are accompanied by paraclinical pathology, allowing the patient to lead normal life activities.
- Encephalopathy. This condition requires urgent medical intervention. The microsymptoms of the disease manifest themselves chronically.
In addition, a violation of the outflow of venous blood can be primary or chronic. Chronic stagnation can cause a cessation of blood supply to the brain and damage to parts of the organ.
Causes of impaired venous outflow
Venous outflow is obstructed, what does this mean, is it dangerous? This pathology has a very adverse effect on the human body. The reasons for its appearance are mainly acquired.
These include:
- Head injuries – any injury can lead to poor circulation. This includes surgical operations and the consequences of difficult childbirth.
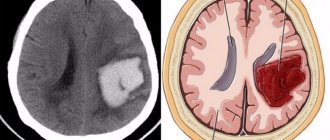
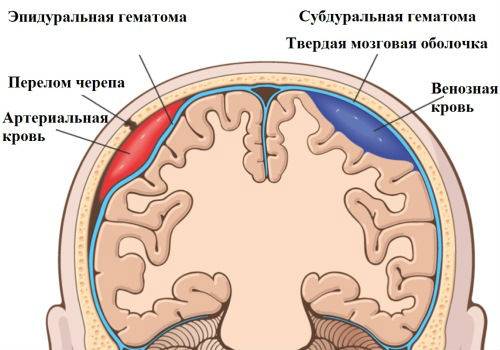
- Internal hematomas - they form after stroke conditions with swelling of the brain of the head.
- Tumors are the most common cause of congestion. As the tumor grows, pressure occurs on various areas of the brain. What causes the venous lumen to be blocked?
- Underdeveloped veins - this may be a consequence of genetic predisposition or secondary factors. But if blood cannot flow normally from the brain to the heart, then discirculation occurs.
- Related diseases - the cause may lie in atherosclerosis, thrombosis or venous insufficiency.
Any therapeutic measures may be temporary if the underlying cause of the disease has not been established.
Main symptoms of the disease
Each stage of the disease has its own symptoms. Initially, the disturbance of venous outflow does not manifest itself in any way. And over time it becomes brighter:
- Meteopathy – sensitivity to changes in atmospheric pressure. When weather conditions change, the head feels tight and weak.
- High intracranial pressure – This is due to impaired blood flow, which makes blood circulation difficult, and the body tries to make up for the lack of nutrients through its own efforts. Over time, this symptom intensifies.
- Neurological symptoms. Children with impaired venous outflow experience mental disorders, seizures, and epilepsy. When the disease is in a severe stage, lowering the head becomes difficult.
- Adults lose consciousness and their vision becomes dark. If at the same time there is thrombosis of the venous sinuses, then the sense of space is lost, temporary stunning, painful sensations, and dizziness.
- In pregnant women, the disease can occur with symptoms similar to toxicosis.
- These manifestations are a signal that requires immediate contact with a specialist.

How dangerous is the disease?
Until recently, brain dyscirculation was considered a minor pathology that did not interfere with human life. But today it has been proven that due to improper blood flow, the soft tissues of the brain begin to atrophy.
Also, do not forget that diagnosing this pathology indicates that another disease is present. Which caused this problem.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of this pathology is carried out by a neurosurgeon or neurologist. Rehabilitation is based on identifying the causes of the disorder and finding the location of the narrowing of the veins. This requires instrumental diagnostics:
- Dopplerography of blood vessels - this technique combines ultrasound and Doppler examination. The method shows the blood circulation rate and pathological changes.
- REG of blood vessels – assesses the general tone and condition of blood vessels. Diagnostics indicates the filling of the veins with blood and the intensity of blood circulation.
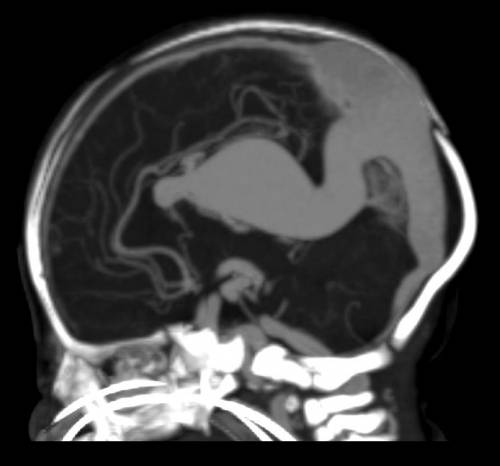
- MRI is a technique that makes it possible to find the pathology and the cause that causes it. The procedure is performed with contrast.
After the study, a course of treatment is prescribed. After which the symptoms, causes and consequences of the disease must be stopped.
Drugs for treatment Venotonics are medications that stabilize blood flow. They increase blood flow, restore the previous tone and functionality of blood vessels. These include Detlarex.
When the disease just begins to manifest itself, vasodilator tablets can be used. But for patients with low blood pressure, patients with thrombosis or atherosclerosis, they are prescribed very carefully.
After injuries that were the result of stagnation, neuroprotectors, vitamins and substances that increase tone are prescribed intramuscularly.
Patients suffering from this disease should not drink alcohol or junk food, or smoke.
You can also use yoga and Pilates as exercise therapy to improve your condition. Classes must be conducted under the guidance of an experienced instructor.
Video: Exercises for cerebral circulation:
Venous cerebral dyshemia (VD, venous discirculation) is a condition when blood circulation on the way from the central nervous system to the heart muscle is impaired. Blood circulation slows down, blood stagnation appears, and the direction of its movement changes.
Violation of the venous outflow of the brain - symptoms and treatment
20.03.2019
The veins of the brain are involved in the outflow of venous blood. From the brain it returns to the heart, where it then goes to the lungs for oxygenation. Venous blood contains predominantly carbon dioxide, a small amount of nutrients and many metabolic products, “waste”, that need to be disposed of.
The veins in the brain are divided into deep and superficial. The latter are located under the arachnoid membrane and are connected to each other by venous anastomoses. These vessels collect blood from the gray and white matter of the cerebral hemispheres. Veins located deep in the brain collect blood from the subcortical and stem structures: the midbrain, cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.
Violation of the venous outflow of the head occurs in two types:
- Venous dystonia. The pathology is based on a functional disorder of the vein walls. By contracting, the unit volume of blood decreases, which disrupts the outflow.
- Mechanical obstruction and difficulty in venous outflow. It is based on pathologies that obstruct the flow of blood through the veins.
A decrease in cerebral venous outflow occurs in three stages:
- Latent. This is a preclinical stage that does not have a detailed clinical picture and is asymptomatic. At this stage, the disorder is not diagnosed due to the lack of signs.
- Cerebral venous dystonia. The first nonspecific symptoms develop, indirectly indicating disturbances in the outflow of venous blood.
- Venous encephalopathy. This is an expanded stage, the stage of manifestation of the clinical picture.
What are the symptoms
There are syndromes that appear when there is a disorder of venous outflow:
Asthenovegetative
This is a sign of the second stage - cerebral venous dystonia. Signs of asthenovegetative syndrome:
- small physical and intellectual stress causes rapid fatigue;
- the functioning of the digestive tract is disrupted: appetite disappears, nausea occurs, and often vomiting; stool becomes upset: diarrhea and constipation become more frequent;
- sleep disturbance;
- hyperhidrosis – excessive sweating;
- headache, mostly dull;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- cold hands, feet and fingers.
Violation of the venous outflow of the brain in children with asthenovegetative syndrome manifests itself as follows:
- emotional lability: laughter quickly gives way to irritability;
- interests disappear;
- memory capacity decreases;
- school performance declines.
The second syndrome is angiodystonic.
Angiodystonic
It appears like this:
- aching headaches in the temples and back of the head;
- sudden changes in blood pressure, sudden coldness of the hands and feet;
- heartache;
- short-term visual impairment.
Psychopathological
The third syndrome is psychopathological.
The activity of cognitive functions and the emotional-volitional sphere is disrupted. This is manifested by the following symptom complexes:
- Affective disorders: mood swings, irritable weakness, depression, dysphoria. Sometimes cyclothymia manifests itself - a cyclical pattern of hypomanic and subdepressive syndromes, which alternate with each other every week (the timing of the shift is individual for each).
- Neurotic disorders: mild obsessive states and fears appear.
- Disorder of worldview and perception of one’s own “I”: Depersonalization and derealization. Patients have a feeling that the world has changed, for example, it has lost all its colors and become gray. This condition is a sign of a psychotic disorder.
Hypertensive
The fourth syndrome is hypertension. Its signs:
- increased nervousness;
- nausea and fatigue;
- palpitations; palpitations;
- bags under the eyes and dark circles with bulging veins;
Violation of the venous outflow of the brain in an infant with hypertension syndrome manifests itself as follows:
- veins protrude from the head;
- fontanelles pulsate;
- the seams on the skull are coming apart;
- Head circumference does not increase in proportion to body growth.
Betholpesia is characteristic of a violation of the venous outflow of the brain. This is a condition characterized by impaired consciousness during a severe coughing attack.
Venous encephalopathy
The last stage of the pathology is venous encephalopathy. It is characterized by specific “venous” complaints:
- Headaches at night.
- Noise in ears.
- When wearing a tie, cephalalgia increases, dizziness appears, and vision is impaired (a symptom of a tight collar).
- In the morning there is a feeling that the eyes are covered with sand.
Causes
The venous outflow of the brain may be disrupted due to the following reasons:
- Pulmonary failure.
- Coronary heart disease, heart failure.
- Neoplasms.
- Ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
- Congenital underdevelopment of the venous network of the brain.
- Spinal hernias in different parts.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- The presence of blood clots in the bloodstream.
Diagnosis and treatment
Pathology is detected using subjective signs (patient complaints) and instrumental research methods, which include:
- Computed angiography of cerebral vessels.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. Examines the state of the venous system of the brain.
- Magnetic resistance tomography. Visualizes tumors and cysts in the brain.
The essence of treatment is to restore normal blood circulation and eliminate the cause. To do this, the following drugs are prescribed for venous outflow of the brain:
- Diuretics: Furosemide, Mannit, Hydrochlorothiazide, Diacarb.
- Venotonics (stabilizing venous tone): Venoruton, Phlebodia.
- To prevent the formation of blood clots, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are prescribed: Varvarin, Aspirin.
Treatment of impaired venous outflow of the brain also involves improving microcirculation in the nervous tissue with the help of Piracetam and Cerebrolysin.
Prevention and exercise
Prevention depends on the type of human activity. For example, if you have a sedentary lifestyle, you should get up from your chair every hour and do a light workout.
In addition, impaired venous outflow manifests itself as a consequence of the underlying disease, so it is this that should be prevented.
For example, to prevent heart failure, you should normalize your diet and quit smoking.
There are exercises that help improve blood flow and drainage to the brain, which should be performed at least once a day:
- Sit on a chair or armchair and straighten your back. Now slowly move and tilt your head back and hold it in this state for 3-4 seconds, then return your head to the reverse position. Repeat 10 times.
- Standing or sitting position. Try to stretch your neck upward. The exercise consists of 10 repetitions.
- Sitting or standing position. Try to mentally imagine an infinity sign and describe it with the top of your head. Repeat 5 to 10 times.
Didn't find a suitable answer? Find a doctor and ask him a question!
Source: https://sortmozg.com/zabolevaniya/venoznyj-ottok-golovnogo-mozga
What is venous discirculation
In the human body there are deep and superficial cerebral veins. Superficial ones are necessary for blood flow from the cerebral cortex, deep ones are necessary for the transfer of hemoglobin, which supplies cells with oxygen. The vessels carry blood to the sinus, after which it passes into the venous artery and leaves the brain through the vertebral arteries.
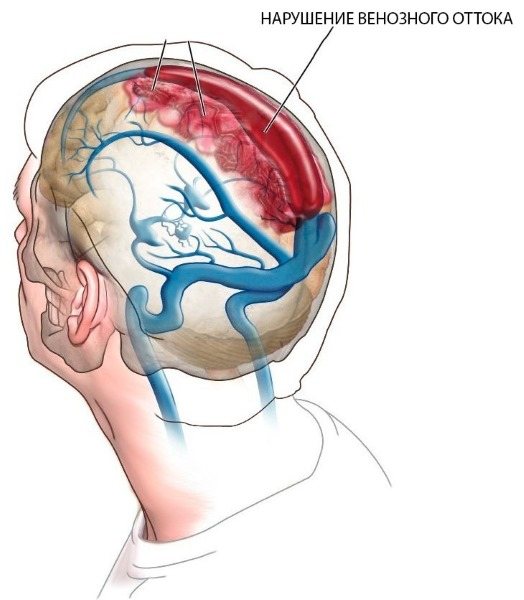
Venous discirculation of the brain is a violation of blood circulation on the way from the central nervous system to the heart muscle.
Venous discirculation of the brain is a condition of the body that is expressed by pathological changes in blood circulation in the cervical spine.
Causes and mechanism of development of venous stagnation
Blood stagnation begins with difficulty in venous outflow from a certain part of the body (tissue, organ). Thanks to the anastomoses, which are well developed in the venous system, hyperemia usually occurs without changes in venous pressure. An excessive increase in pressure is possible only with underdevelopment of collaterals, while the difference in arteriovenous pressure decreases and blood circulation in the capillaries slows down.
Venous stagnation is characterized by expansion of capillaries to the size of venules. The reason for this phenomenon may be a change in the structure of the connective tissue of the bloodstream and internal capillary pressure. The connective tissue membrane ceases to perform its function and no longer serves as a support for the capillaries. It should be noted that only the venous sections of small blood flows change in size, due to this their elasticity is greater than the arterial sections.
Due to the slowdown of processes and blood movement in the stagnant venous area, intensive release of oxygen into the tissue and absorption of carbon dioxide from the tissues into the bloodstream occurs. A sharp imbalance leads to carbon dioxide poisoning or oxygen starvation. Changes in oxidative processes lead to a decrease in heat production, increased heat transfer and hypothermia in the area of venous hyperemia.
Due to increased pressure in the veins and capillaries, increased permeability of the vascular walls, the accumulation of water increases, which leads to edema. Also the cause of swelling is a change in the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood.
The following factors lead to venous stagnation:
- Arteriovenous hypotension.
- Embolism, thrombosis (blockage of venous vessels).
- Decreased elasticity of vein walls.
- Excessive blood thickness, complicating proper circulation.
- Neoplasms and edema, constricting venous blood flow.
- Myocardial dysfunction.
- Accumulation of blood or air in the pleural plane.
Disturbances in the outflow of venous blood in the brain are caused by the following reasons:
- Changes in the elasticity of veins (violation of tone).
- Intracranial hematomas.
- Brain swelling due to stroke.
- Detachment of the network of venous capillaries in the brain.
- Intoxication of the body with alcohol and nicotine.
- Arterial pressure changes.
- Slow venous outflow from the head and neck is explained by the presence of neoplasms, osteochondrosis and other pathologies of the spinal column.
The consequences of the disease are as follows:
- Hypoxia.
- Reduced oxidative processes.
- Swelling caused by congestion, with subsequent liver damage.
- Venous hyperemia is the cause of blood clots, which poses a direct threat to human life.
- A pathological change in venous outflow through the vertebral veins is caused by scoliosis, due to compression of the carotid or vertebral arteries.

Classification
There are 3 stages of the disease:
| Stage | Characteristic |
| Latent | The pathology has a latent form, and there are almost no symptoms |
| Cerebral | The stage has non-dangerous symptoms |
| Venous | Accompanied by organic microsymptoms. The condition requires the help of doctors because it threatens the patient’s life |
It is also customary to classify pathology according to Berdichevsky:
- Primary stage. Vascular tone is altered, which leads to impaired blood flow in the brain.
- Stagnant stage. Mechanical obstructions to cerebral circulation are noted.
Basic therapy
Deterioration of blood flow can occur either independently or in conjunction with other brain diseases. This factor is the main one when choosing a treatment method and its prescription.
Another reason for such disorders may be the formation of thrombophlebitis in the brain, the appearance of blood clots in the sinuses, and also due to congenital anomalies (irregularly sized veins, etc.).
Cases of mechanical compression in the cranial cavity:
- tumor of the neck and brain;
- severe head injury;
- severe swelling and displacement of bones;
- thrombosis at the level of the jugular vein;
- for bronchial asthma;
- due to suffocation.
As is known, venous outflow is associated with arterial circulation. For example, due to increased pressure, there may be an increase in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid inside the skull directly into the sinuses.
To eliminate tension in the venous system in this case, an antihypertensive treatment complex should be used.
In addition, strokes can cause severe swelling of the brain, which will result in impaired blood flow in the veins. Hematomas strongly compress the vessels, which leads to a deterioration in the outflow of blood in the areas of hemorrhage.
- excessive physical activity;
- frequent inversion of the body, tilting the head;
- due to constant holding of breath (in swimmers, divers, musicians and singers);
- tight collars on clothes;
- the child may have worsened venous outflow due to frequent screaming;
- during a strong and frequent cough.
In the early stages, the disease can be easily suppressed with simple treatment. If disturbances increase the lack of blood flow, then more serious actions will have to be taken. Some may require surgery to restore blood supply to the brain. It is prescribed only in the most severe cases, when other methods are not effective enough.
The main drugs for such disorders act on the veins, helping to improve blood flow. At the same time, they strengthen blood vessels, increase their tone and suppress inflammatory processes. You can take them at home without staying in hospital. However, it is important to follow your doctor's orders and get checked regularly.
The best medicines:
- "Excusan";
- "Detralex";
- "Doctor Theiss";
- "Anavenol";
- "Antistax."
During treatment, you should definitely stop eating junk food, alcohol and smoking. After recovery, it is not recommended to return to them, since they can provoke the recurrence of problems, due to which the outflow of blood from the head will again be disrupted.
Causes of obstructed venous outflow
Venous discirculation of the brain is a pathological condition that appears for the following reasons:
- heart pathologies;
- disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system;
- heart attack;
- genetic predisposition;
- heatstroke;
- long-term use of medications;
- development of osteoarthritis, disruption of the spine, serious cranial injuries;
- diseases causing blood clots.
How the disease develops, symptoms
Venous discirculation of the brain is a condition that develops due to impaired blood circulation and is accompanied by various pathological processes.
They are as follows:
- decrease in venous lumen with subsequent manifestation of stagnant-hypoxic effects;
- headache;
- dystonia.

The disease has several stages, differing in symptoms and severity:
- First stage . Main signs: high intracranial pressure; weather dependence; mental disorders, symptoms of epilepsy; copper taste, faintness, darkness in the eyes.
- Second stage . Main symptoms (asthenovegetative syndrome): disruption of the gastrointestinal tract; minor loads quickly cause fatigue; increased sweating; insomnia; sharp pain in the head; cold extremities.
- The third (psychopathological) syndrome is expressed as follows: affective disorders: mood swings, irritability, dysphoria; cyclothymia – subdepressive and hypomanic syndrome; violation of emotional-volitional and cognitive functions; neurotic disorders: fears and obsessive states.
Characteristic signs in children
Venous discirculation of the brain in children is a condition characterized by the following symptoms:
- increase in temperature;
- pain in the area of poor blood supply;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- migraine;
- paralysis;
- involuntary movements;
- nose bleed;
- convulsions;
- metabolic disorder;
- changes in speech;
- chills;
- increase in blood pressure.
Venous dysfunction
Venous dysfunction develops when there is compression of the vein, spasm, or thick blood. The causes include cardiovascular diseases, cough, hormonal disorders, infections, as well as increased pressure in the chest (for example, when singing) and abdominal cavity (when straining), hereditary predisposition, and in children - congenital pathologies.
To identify, ultrasound of blood vessels, tomography, and fundus examination are performed. Without treatment, there are consequences: fainting, convulsions, psychosis, neurosis.
And here is more information about microcirculation disorders.
Venous outflow (dysfunction) is obstructed - what does this mean?
When there is dysfunction of the venous outflow from the cranial cavity, this means:
- mechanical obstacle (for example, muscle compression);
- narrowing of the vein due to reflex spasm;
- a decrease in the speed of blood movement when it thickens.
As a result, there are:
- weakening of blood flow, lack of nutrition and oxygen supply;
- increased venous pressure;
- swelling of brain tissue;
- dysfunction of cells and brain centers.
Clinically, venous dysfunction manifests itself:
- circulatory failure - headaches, heaviness in the head;
- encephalopathy – mental disorders (depression, neurosis, psychosis);
- venous hemorrhage - double vision, facial asymmetry, instability when walking, severe disturbances of movement and sensitivity;
- thrombosis of the veins and venous sinuses, thrombophlebitis - headache with nausea and vomiting, impaired consciousness, fever, decreased vision, nosebleeds.
Reasons for stagnation
The main causes of venous stasis (stopping the outflow) of the brain are shown in the table.
Outside of diseases, cerebral venous dysfunction is enhanced by:
- singing;
- playing a wind instrument;
- scream;
- pregnancy, childbirth;
- lifting weights;
- static loads in sports (strength exercises);
- lack of a pillow when sleeping at night;
- overheating;
- excessive exposure to the open sun;
- compression of the neck by a collar or tie;
- low physical activity;
- traveling with a long stay in one position;
- obesity;
- chronic constipation (straining).
Brain dysfunction in children: causes
Possible causes of dysfunction of the venous outflow of blood from the brain in children include:
- anomalies in the structure of veins;
- compression during early fusion of bone sutures;
- suffocation during childbirth, entanglement of the umbilical cord;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- infections;
- poisoning
Early fusion of bone sutures in children leads to venous dysfunction
How is dysfunction in the venous system diagnosed?
Signs of circulatory disorders in the veins of the brain are detected using:
- examination of the fundus - tortuosity, dilated veins, uneven patency, signs of congestion;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck with Doppler sonography - impaired blood flow;
- CT, MRI with contrast of blood vessels - enhanced vascular pattern, dilation of veins and sinuses of the brain.
It should be taken into account that venous blood flow is more variable than arterial blood flow, therefore for accurate diagnosis it is important:
- normal blood pressure at the time of examination;
- absence of attacks of headaches and heaviness in the head for 3-5 days;
- exclusion of alcohol intake for 5-7 days;
- the first half of the menstrual cycle in women.
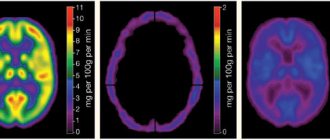
MRI with contrast
Since venous congestion is caused by diseases of different origins, a comprehensive examination is required. First, you need to contact a neurologist, and if necessary, he will recommend a consultation with an ophthalmologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist or other specialists.
Consequences without treatment
For a very long time, venous circulation disorders are compensated, so the appearance of symptoms (headaches, tinnitus, dizziness) is already a sign of depletion of such capabilities. Without treatment there are consequences:
- fainting, especially when coughing;
- convulsions;
- insomnia;
- mental disorders - tearfulness, depressed mood, aggression, agitation, delusional ideas;
- auditory and visual hallucinations;
- suicide attempts;
- unsteadiness when walking;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- muscle stiffness;
- trembling of limbs;
- twitching of eyeballs.
Diagnostics
The disease is diagnosed through subjective signs and instrumental examination methods:
- Complete blood test . Shows: hemoglobin is a blood pigment found in red blood cells. Responsible for transporting oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide. The norm is 135-170 g/l; red blood cells – normal (4.1-5.2)*10 to the 14th power; leukocytes are white blood cells that are found in the lymph nodes and bone marrow. The normal state is (4.1-9.2)*12 to the 10th power.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG). The diagnostic method shows the general tone and condition of the blood vessels, determines the blood supply to the veins and circulatory activity.
- the electroencephalogram may be normal. But the examination is recommended after a stroke. A decrease in alpha rhythm is a sign of circulatory abnormality.
- CT scan (CT). It makes it possible to determine the relationship of veins with structures in cross sections and their diameter, but does not show the characteristics of blood flow.
- CT - angiography . The method makes it possible to identify vascular pathologies at the early stages along with disruption of the arteries, and also to determine their tortuosity and unevenness during congestion.
- Contrast magnetic resonance imaging . Allows you to identify the main cause of the complication. Contrast MRI helps visualize blood flow in the cerebral veins. Used if CT angiography did not help to identify disturbances in the functioning of blood flow in the VBB.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using modern methods, such as:
- Computed tomography of the brain (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (MRI);
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain;
- Angiography;
- X-ray of the skull (if there is injury or suspicion of it).
The same diagnostic methods are used for adults and children.
Depending on the complexity of the disease, one or more methods are used to detect impaired venous outflow in the brain. A referral for examination can be obtained from a general practitioner and neurologist, or you can contact a paid diagnostic center.
The methods used to identify the disease will help to understand what stage the disease is at and what the future treatment prognosis is.
Drugs that improve venous outflow
Venous discirculation of the brain is a pathological condition for which, as a rule, medications containing heparin are used.
They are as follows:
- Warfarin . The medicine affects blood clotting, the effect is observed after 4-5 days. Treatment is unacceptable in acute stages of the disease. The dosage must be monitored by the treating specialist; self-medication is prohibited. The duration of therapy is up to six months.
- Enoxaparin is prescribed to normalize blood flow in people who suffer from allergic reactions. The main advantage of the product is the possibility of intermittent use, which allows for outpatient treatment.
Additional medications taking into account the cause of stagnation:
- To reduce head pressure, use a remedy in the form of Eufillin injections;
- anticoagulants that help thin the blood and prevent the development of thrombosis: Aspirin, Plavik-S, Urokinase, Heparin;
- diuretics – remove excessive amounts of salts: Furasimide, Mannitol. Used with caution, as they have many contraindications;
- venotics - help improve fluidity and help activate muscle tone: Detralex, Phlebodia, Dopelgerts;
- to increase microcirculation the following are used: Phenibut, Betagistin, Stugeron;
- nootropics – activate metabolism: Nootropil, Cortexie, Thiocetam.
Exercises to help improve venous drainage
During circulatory problems, physical exercise often helps. They must be performed three times a day, for 10 minutes.
Exercise 1 - head tilt, execution steps:
- You need to sit down on a chair.
- Relax your muscles.
- Throw your head back.
- Maintain deep and even breathing.
Duration of execution – up to 2 minutes.
Exercise 2 - long neck, performed as follows:
- You need to take a sitting position.
- The muscles need to be relaxed and the head tilted towards the chest.
- The head rises as high as possible during inhalation.
- As you exhale, it lowers again.
Performed up to 10-15 times.
Exercise 3. Drawing eights. You need to make movements with your head, similar to the image of the number 8, while breathing moderately and relaxing your body. Perform the exercise several times, and your eyes must be closed.
Exercise 4 - power tilt, performed as follows:
- A sitting position is assumed.
- Fingers should be crossed near the base of the chin.
- As you exhale, you need to tilt your head and apply pressure with your hands.
- When inhaling, you need to tilt your head back.
How to treat outflow disorder?
Seeing a doctor at the stage of moderate manifestations allows you to prescribe timely therapy and adapt the patient’s life to the altered blood flow in the brain.
In general, the following should be provided:
- refusal of too strenuous work, night shifts;
- limiting physical activity;
- stopping smoking and drinking alcohol;
- inclusion of vegetables and fruits in the daily diet, limitation of heavy and spicy foods, salt, seasonings;
- normalization of sleep with evening walks, tea with mint, herbal sedatives such as valerian, motherwort, lemon balm (ready-made drug Novo-Passit).
Among the choice of drugs, the doctor prescribes a course of use:
- venotonics (Detralex, Venoruton, Aescusan drops, Phlebodia 600);
- diuretics, which are indicated for severe symptoms (Lasix with Eufillin intravenously), for continuous use - Diacarb according to the scheme;
- to prevent thrombosis, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are recommended (Warfarin, Thrombo Ass, Cardiomagnyl);
- Prodectin, Piracetam, Stugeron, Cortexin, Cerebrolysin help improve the functioning of brain cells.
The effect of self-massage
Read the article: Signs of cerebral venous dyshemia
Massage of the collar area helps relieve tension in the muscular corset of the neck. Relaxation improves venous blood flow. A massage course can be carried out with the participation of a specialist 2 times a year. But it is much more useful to learn self-massage and do it several times a day. Several rules must be followed:
- massage each side with the opposite hand;
- maintain a calm breathing rhythm;
- start with light circular movements, gradually pressing harder on the muscles in the suprascapular region;
- lightly clasp your neck with your hand and use your fingers to perform spiral movements from bottom to top along the paravertebral zone to the base of the skull.
Physiotherapeutic techniques in the form of electrophoresis with Eufillin and laser exposure are also prescribed in the “collar” area.
Additional physical activity
Yoga classes are suitable to increase venous outflow. In this practice, there are a large number of asanas that are aimed at restoring blood circulation and strengthening blood capillaries.

Breathing through the larynx during exercise helps pump air, which in turn improves blood circulation.
To improve overall blood circulation, you can use running. Taking into account the fact that running may not be accessible to everyone due to health reasons, you can start with simple long-distance walking. Doctors recommend jogging in parks or forested areas. This creates a more pronounced treatment effect.
Massage
Often, pathologies of venous circulation arise due to compression of the vessels of the head and neck.
Massage in these areas of the body relieves muscle tension, which helps get rid of excessive blood flow to the capillaries:
- It is necessary to massage the neck with gentle movements, first on one side, and then on the other. To avoid possible complications, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
- During the procedure, a person does not have to feel discomfort, otherwise the situation can be complicated.
- If severe pain is felt or tingling is noted, the massage is completed.
Operation
If the disturbances in circulation are very significant, then the specialist recommends surgical intervention. But surgery is used if medications fail to help.
Main types of operations:
- Angioplasty: A catheter is inserted into part of an artery to improve blood circulation and enlarge its walls.
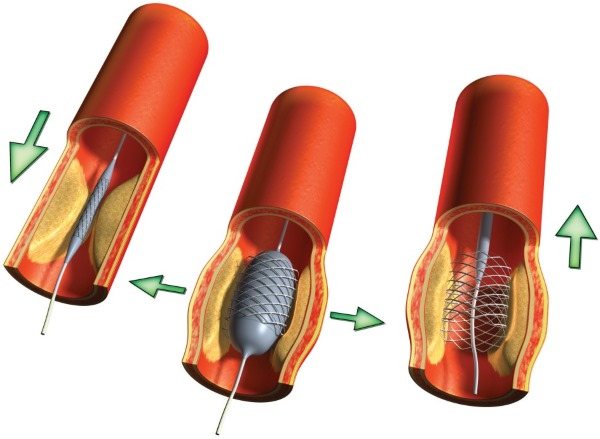
- Bypass surgery : an artificial vessel is placed near the area of narrowing of the vein. This creates a new pathway for the bloodstream to move.
- Endarterectomy is a method of removing the inner part of the affected capillary.
Traditional methods of treatment
All methods are used only as a comprehensive treatment and are selected individually for each patient. It is necessary to take into account intolerance to specific components. It is possible to increase blood circulation using traditional methods only at stages 1 and 2 of the disease.
Plants that help cure venous congestion:
- Grape berries, as well as its juice. They have a positive effect on blood composition, restore the functioning of blood capillaries and artery walls.
- Mix hawthorn berries, meadowsweet and strawberry leaves in equal parts. The collection should be filled with 1 glass of boiled water. After this, let it brew in a thermos for about 5-6 hours. Strain the broth and take 0.5 cups twice a day.
- You need to mix 3 tbsp. l. chamomile and 2 valerian roots. The plants need to be crushed and 1 cup of boiled water added, then drained and cooled. Take 2 glasses morning and evening.
- Nettle. You can consume fresh nettle in unlimited quantities every day. Also, the juice of this plant thins the blood and strengthens the walls of blood vessels.

- Dried leaves and walnut bark can help improve your condition. All components should be allowed to brew for 1 hour. Then you should take 1/3 cup twice a day before meals.
- You will need 2 tbsp. l. rose hips, to which you need to add 0.5 liters of boiling water, then let it brew for about 4 hours. Use the composition half an hour before meals. This method makes it possible to get rid of tinnitus.
- You need to take one 1 tbsp. l. ground onion and mix it with 2 tbsp. l. honey Use the mixture half an hour before meals. The recipe can be used to avoid the likely consequences of the disease.
Traditional methods of treatment can only be used in combination with modern therapy after consultation with a doctor.
Complications
If left untreated, venous insufficiency leads to severe complications.
Among the likely side effects, the main place is occupied by the following pathologies:
- A stroke is the death of tissue on the surface of the brain, which affects coordination of movements and speech abilities. The severity of complications is determined by the amount of dead tissue and the speed of restoration of venous blood flow.
- avoid cerebral hemorrhage : maintain a work and rest schedule; avoid sharp bends; observe restrictions on staying deep under water; avoid places with high temperatures; avoid strong physical stress; Prolonged reading is prohibited.
- Hypoxia. A complication occurs if blocked venous blood flow causes oxygen starvation of the brain. The state of hypoxia can cause partial or complete paralysis, or cause death.

- Discirculatory encephalopathy - a condition that often causes prolonged oxygen starvation or a complete absence of venous blood flow, which leads to the death of brain cells. Encephalopathy is quickly treated after eliminating the original causes of dysgemia.
Video about cerebral venous circulation
What is a violation of the venous outflow of the brain:
Disturbance of the venous outflow of the brain is a condition of the body in which the tone of the veins decreases, resulting in venous stagnation of the vessels of the brain. Changes in cerebral venous drainage can affect people of different genders and ages. Short-term disturbances are caused by coughing, screaming, sudden turning of the head, physical exercise and much more. There are three different types of this type of violation. During the first two stages, many will not even feel the changes occurring in the brain area. The occurrence of disturbances in the venous outflow of the brain can be absolutely anything. The exacerbation of this disease occurs in autumn and spring.
Who needs prevention?
No less than in treatment for already developed pathology, the body also needs to prevent the problem of venous outflow - regular self-diagnosis.
An urgent examination by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist is necessary, with the necessary studies being carried out when:
- dull headache that gets worse with head movements;
- swelling of the lower eyelid;
- cyanosis of the cheeks, lips, nose;
- buzzing in the head with maximum manifestations in the morning;
- pronounced weather dependence;
- fainting, or dizziness, or blurred vision, not to mention mental disorders and epileptic seizures.
Measures to prevent disorders of the venous outflow from the brain also include maintaining an optimal work schedule, sleep and wakefulness, taking care of proper nutrition, and eradicating habitual intoxications and other harmful traditions from your life.

Other valuable methods of influencing the body in order to improve its condition are:
- various relaxation techniques;
- use of herbal medicine;
- taking a contrast shower;
- use of yoga.
The risk group with the greatest likelihood of developing impaired outflow through the veins of the brain includes:
- smokers and alcohol abusers;
- professions associated with constant lifting and carrying loads;
- office workers who sit for a long time at a table with their heads bowed, needing an awkward turn of the head;
- architects and draftsmen;
- people of underwater professions;
- operating surgeons;
- athletes involved in swimming, diving, weight lifting;
- opera singers and wind musicians.
If the doctor has discovered venous congestion in the brain, then treatment must be carried out with the utmost seriousness and advice must be heeded even if the symptoms are not too severe. Traditional methods should be used only after consultation with a doctor. The ability to think rationally and not be a burden to others depends on the outcome of behavior and therapy.
Diseases by symptoms
Any symptom is a signal from the body that any organ, department or entire system is damaged. To find out why there is a violation of the venous outflow of the brain in a child, it is necessary to exclude certain diseases. Make sure that your child undergoes timely diagnosis, check with doctors about the cause of the disturbance in the venous outflow of the brain and how to quickly and effectively improve the child’s condition.
List of diseases in which children have impaired venous outflow of the brain
- tumors
- hydrocephalus
- traumatic brain injuries
- chest and abdominal injuries
- problems with intervertebral discs
- epilepsy
An injury sustained during childbirth can provoke a disturbance in the circulatory system; anomalies in the development of veins, which can be inherited, can also affect the development of a violation of the venous outflow of the brain in a child.
Sports for intracranial pressure
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is an indicator that reflects the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid on the brain. The indicator varies depending on various reasons. It can also rise in healthy people. It often occurs even in newborns after birth trauma. The main causes of increased intracranial pressure:
- cerebrospinal fluid is poorly absorbed;
- excess fluid secretion;
- circulation disturbance.
Factors influencing ICP disorders:
- head injuries;
- osteochondrosis;
- tumor, meningitis.
High blood pressure negatively affects brain function. There is a violation of coordination, memory, and speech. The main signs of the disease: severe headaches, irritability, fatigue, nausea, emotional disorders, increased blood pressure, loss of consciousness, fainting. If you experience these symptoms, consult your doctor immediately for advice. When treating increased intracranial pressure, therapeutic exercises, walks in the fresh air are recommended, and swimming is also effective. Is it possible to play sports with ICP? It depends on the type of sport and load.
Sports activities
Many athletes, after receiving a traumatic brain injury, want to stay in sports and not change their lifestyle. Let's consider whether intracranial pressure and sports are compatible. How are they interconnected? To stabilize ICP, the following recommendations must be followed:
- exclude all activities that contribute to pressure changes;
- refuse baths, saunas;
- take diuretics;
- use a high pillow for sleeping;
- reduce the amount of fluid consumed per day.
Sudden changes in ICP can lead to disruption of the functioning of the brain and cause vascular hemorrhage. Active sports - running, regular jumping, parachute jumping, weight lifting, somersaults, gymnastics - contribute to sudden changes in pressure if you have a problem. If you have elevated ICP, you should avoid active sports. It is not recommended to use the elevator or fly by plane. Flying can provoke an exacerbation of ICP. What sports are allowed for ICP? For treatment and prevention, gymnastic exercises are allowed, which are part of a special complex developed by doctors and help restore blood circulation. Rowing classes are recommended, and you can visit the swimming pool. If you have problems with ICP, doctors do not prohibit cycling, badminton, table tennis, tennis, archery, fencing, and chess. All types of sports activities that do not involve sudden bending, lifting or carrying heavy objects are prohibited.
Gymnastics, hockey, football, running, trampolining, weightlifting, boxing, bodybuilding, all types of wrestling, snowboarding, diving, equestrian sports, handball, basketball, acrobatics should be avoided. Exercise will only intensify the manifestations of ICP and can at some point provoke death associated with vascular rupture.
Physiotherapy
If you have intracranial pressure, you are allowed to visit the gym, where you can do stretching and special exercises for treatment and prevention. It should be remembered that all actions must be agreed upon with a doctor. He will develop an acceptable training program and determine the norms of physical activity. Let's consider acceptable exercises for intracranial disorders associated with pressure changes.
- Exercise 1. It is recommended to take a cylindrical stick, up to 40 cm long. We wrap our hands around it, move it behind the spine and stroke the neck muscles from top to bottom. Duration is 10 minutes. It is recommended to repeat five times a day.
- Exercise 2. Using your thumbs, massage the area at the bottom of the head (vertebrae between the neck and head). Perform three times a day for 15 minutes. Stimulates blood circulation in osteochondrosis. Normalizes venous outflow.
- Exercise 3. We tilt the head from side to side, up and down. Perform five times in each direction, repeat four times a day.
Massages, especially in the collar area, help in the treatment and prevention of ICP. Yoga and stretching that do not require tilting the head down for a long period of time are acceptable.
Contraindications for sports
If you are diagnosed with ICP for any reason, you will have to stop playing active sports. All sports exercises affect blood circulation and require an accelerated rhythm of their implementation. Some of them involve lifting weights, which affects vascular tension. When the rhythm accelerates, the heart begins to eject blood faster, its flow to the brain increases, and ICP rises accordingly. Many athletes after training experience dizziness, weakness, nausea, and may lose consciousness. At the first signs, you should seek help from a doctor. Is it possible to cure the disease and return to sports?
Over a long period of treatment, it was often possible to stabilize the pressure for normal living conditions. But sudden changes in such conditions had a negative impact on patients. Successes have been achieved in diagnosing the disease in the early stages. In medical practice, relapses have been observed in many cases.
Indications for sports
According to doctors, it is not worth completely limiting physical activity. Performing acceptable amounts of physical exercise when diagnosing a disease allows you to improve blood circulation in the body, has a beneficial effect on blood vessels, helping to saturate cells and tissues with oxygen, and helps improve metabolic processes in the body. Take care of your health, consult a doctor on time and you will be healthy.
Treatment and specialists
Treatment of impaired venous outflow of the brain in a child should only be carried out by a qualified specialist. Only a doctor can tell you how to treat a violation of the venous outflow of the brain in a child, how to get rid of the complications of a violation of the venous outflow of the brain and prevent its occurrence in the child in the future. The following doctors can answer the question of what to do if your baby has a cerebral venous outflow disorder:
- pediatrician
- pediatric neurologist
- pediatric surgeon
In order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, in order to accurately determine the violation of the venous outflow of the brain in a child, for this, the doctor prescribes the necessary examinations, and also prescribes a course of drug treatment and measures with the help of which cerebral venous angioma improves.
Arm yourself with knowledge and read a useful informative article about the disease, impaired venous outflow of the brain in children. After all, being parents means studying everything that will help maintain a degree of health in the family on the island.
Find out what can cause the disease and how to recognize it in a timely manner. Find information about the signs that can help you identify illness. And what tests will help identify the disease and make a correct diagnosis.
In the article you will read everything about methods of treating such a disease as impaired venous outflow of the brain in children. Find out what effective first aid should be. How to treat: choose medications or traditional methods?
You will also learn how untimely treatment of a disease that affects the venous outflow of the brain in children can be dangerous, and why it is so important to avoid the consequences. All about how to prevent disruption of the venous outflow of the brain in children and prevent complications.
And caring parents will find on the service pages complete information about the symptoms of the disease, impaired venous outflow of the brain in children. How do the signs of the disease in children aged 1, 2 and 3 differ from the manifestations of the disease in children aged 4, 5, 6 and 7? What is the best way to treat the disorder of cerebral venous outflow in children?
Take care of the health of your loved ones and stay in good shape!
Treatment
Often, when such pathologies appear, patients are found to have varicose veins. In this case, in parallel with the main treatment, drugs and medications that can thin the blood are prescribed.
In some cases, mainly in the early stages of the disease, massage is highly effective in patients. It is carried out in the area of the shoulders and neck. You should not prescribe such procedures on your own, as they are effective only if prescribed by a doctor after a thorough examination and diagnosis.
Quite often, doctors recommend slightly increasing and diversifying physical activity. For example, gymnastics will provide quick improvements, but it is worth setting the dose of exercise correctly. Swimming is also a good way to improve blood flow. Almost all swimming pools have massage therapists and trainers who work with people with similar disorders and diseases.
For successful, and most importantly quick treatment and restoration of venous outflow of blood in the brain, you should eliminate bad habits from your life.
These include smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, eating fatty and heavy foods, and visiting fast food restaurants.
In order to achieve blood thinning, sometimes it is enough to reconsider your diet. For example, in such cases it is recommended to eat more vegetables, fruits and herbs, and drink grape or nettle juice more often.
Nowadays you can find almost any drug in pharmacies. The range of drugs that improve venous blood flow is simply huge.
Drugs for such purposes are in different price categories, so anyone can afford such drugs. For example, venotonics show positive dynamics.
In general, these are drugs that are a preventative measure. They are able to strengthen blood vessels, normalize their permeability, reduce fragility and remove swelling.
Also, taking venotonics leads to strengthening and improving overall venous tone and eliminating inflammation.
Among the most popular and widespread such drugs are the following:
- gel or cream Aescusan, Gerbion or Venoplant. These preparations are made on the basis of horse chestnut. Their cost is moderate and affordable to everyone;
- Antistax capsules or gel. This medicine also contains horse chestnut and grape leaf extract;
- preparations based on Gingobilob extract (Ginkor-fluorine).
Whatever the medications, you should start taking medications only after a doctor’s prescription. Self-treatment can have a detrimental effect on the course of the disease and increase symptoms.
Also, self-medication is sometimes simply ineffective due to incorrect identification of symptoms.