- Causes and symptoms
- Forms of 2nd degree hemorrhoids
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
- 2nd degree hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Perhaps everyone has heard about such a delicate problem as hemorrhoids. In this article we will talk about grade 2 hemorrhoids - a minor complication of rectal disease, leading to the formation of tangible nodes. This degree responds quite well to treatment, and this article will tell you what exactly will be treated and how.
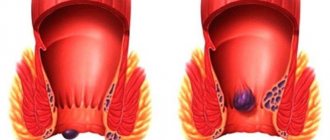
What stage 2 hemorrhoids look like in the photo
When the patient does not receive proper treatment, the incipient hemorrhoids move on to the next phase of development.
At stage 2, hemorrhoids only appear in some patients, while in another group the pain intensifies. The pain syndrome becomes more pronounced with increased pushing during defecation. The disease at this stage is characterized by the presence of an internal node with its independent reduction.
In the photo of stage 2 hemorrhoids, you can see fairly enlarged nodules that protrude into the posterior canal. The muscles and ligaments of the rectum degrade over time. Dystrophic processes occur in the tissue structures, due to which the nodes fall out and the possibility of visual inspection is given (if the disease is external).
The photo shows that nodes extending beyond the intestine can be pinched and subject to injury. The clinical picture of the second degree is bright, manifested by thrombosis, bleeding and loss of painful lumps from the intestine.
Features of symptoms of the second stage of the disease
In addition to the direct release of hemorrhoidal nodules, during the development of stage 2 hemorrhoids, there is an increase in the severity of other symptoms, which are also inherent in the initial stage of the disease.
During bowel movements, bleeding may occur in the form of drops or a small stream.
Despite the fact that this makes many people worried and sends them to the doctor, some patients do not attach serious importance to it.
Bleeding occurs because hemorrhoids are damaged when they prolapse. However, after reduction the bleeding most often stops.
However, this condition requires immediate treatment, as further development of the disease can lead to more serious consequences.
In addition, the second degree of the disease is characterized by increased itching and burning sensation, and the appearance of pain during bowel movements. In cases where the disease is aggravated by the appearance of anal fissures, pain and bleeding become even worse.
Also, the patient often has the feeling that there is a foreign body in his anal canal, and after visiting the toilet it seems to him that the intestines are not completely emptied.
In cases where there is no straining and constipation, hemorrhoids may not fall out even at the second stage of the disease.
However, if any symptoms, even the most minor, appear, you should immediately consult your doctor.
The fact is that many manifestations of hemorrhoids are similar to the manifestations of the development of tumors in the rectum.
Reasons for the transition of the disease to stage 2
At the beginning of their appearance, hemorrhoids may occur without obvious symptoms. Many patients are embarrassed to see a doctor; some assume that the disease can go away without intervention. Hemorrhoids are a disease that develops in stages, and delay in treatment leads to a transition to the next stage of pathology.
The transition of the disease to stage 2 also occurs under the influence of certain factors:
- Regular consumption of hot and spicy foods, deficiency of plant fiber in the body;
- Constant stressful conditions;
- Excessive drinking, smoking;
- Systematic constipation;
- Heavy physical activity.
Chronic form
Hemorrhoids become chronic when the necessary treatment is not applied to it and the pathology gradually progresses. At this stage, there is an active intensification of absolutely all symptoms:
- bowel movement is accompanied by copious bleeding, which stops only after the hemorrhoids are reduced to the rectal area;
- severe itching and burning appear, but this condition is easily tolerated by patients;
- there is a constant sensation of a foreign object in the rectum;
- bowel movements occur with severe pain.
Treatment of chronic pathology can take place at home, as well as in a hospital setting. It is usually based on following a diet, as well as taking preventive measures. The rest of the therapy is prescribed individually after examination by a doctor.
Symptoms
In phase 2 of the disease, hemorrhoids become large. If the formation falls out, it is easy to notice. The cones begin to bleed. You can straighten the nodes using your hand; repeated prolapse occurs only when constipation occurs.
Characteristics of this stage are:
- Feeling of heaviness and fullness in the rectum. The sensation does not go away even after the act of bowel movement.
- Severe pain that intensifies during defecation.
- Itching, burning.
- The appearance of blood during bowel movements, during heavy physical exertion.
- Frequent constipation.
- Prolapse of hemorrhoids due to repeated constipation.
The patient can pinch the nodes and mistake them for a tumor. When damaged, cones can become inflamed, which leads to increased pain and increases the possibility of pathogenic elements entering the body.
Hemorrhoids at stage 2, accompanied by prolapse of nodes, leads to the fact that the patient, avoiding pain, postpones the process of bowel movement, complicating the condition.
The location of the nodes in stage 2 hemorrhoids determines the type of disease:
- Internal hemorrhoids develop when the node is inside, prolapse is rare;
- The external type is observed when the cones are located at the exit from the rectum;
- The combined form is the most severe type. Several nodes are found inside and outside the intestine. During the act of defecation there is a high probability of bleeding and damage.
Symptoms and signs of the chronic stage
Stage 2 chronic hemorrhoids manifest themselves somewhat differently. Its main manifestation, of course, is discomfort in the rectal area. The provoking factor is feces, which, as they progress, irritate the hemorrhoids and injure them. The inflamed mucous membrane of the rectal canal swells and further impedes the movement of digested food to the exit.
The nature of the pain may vary, depending directly on the course of the disease. Thus, stage 2 internal hemorrhoids only sometimes make themselves felt - mild discomfort during bowel movements, a “foreign body” in the anus during the period of remission of the disease. Whereas during an exacerbation, the second stage of hemorrhoids may not be inferior to the acute stage of the pathology:
- itching – intense, exhausting, throughout the day;
- burning – in the anorectal area both when visiting the toilet and outside of it;
- increasing discomfort due to overcrowding of the rectal ampulla;
- traces of blood on paper during defecation;
- less often – an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels;
- cessation of pain after defecation.
External chronic hemorrhoids of the 2nd degree often become aggravated, since varicose nodes fall out of the anus and can be injured or pinched. The nature of the unpleasant sensations intensifies many times over and becomes unbearable. The patient requires urgent medical care - for hemorrhoids of the second stage, treatment is carried out in a surgical hospital. During the period of remission of the disease, the symptoms are practically not expressed - the “clusters” of hemorrhoidal cones are reduced and do not interfere with the release of feces.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing grade 2 hemorrhoids does not require special procedures:
- The specialist discovers the appearance of the disease during the examination;
- Internal and mixed types are revealed by palpation.
- To confirm the diagnosis, the proctologist may prescribe sigmoidoscopy. The study allows you to observe the condition of the rectum using a mini camera. Using the examination, information is obtained about the number and size of nodes and the desired therapeutic course is determined.
Diagnosis of second stage hemorrhoids
Several diagnostic procedures help the doctor identify grade 1 and 2 hemorrhoids:
- At the first consultation with a proctologist - after complaints and anamnesis of pathology have been collected, the doctor conducts a digital examination of the rectal canal. The procedure allows you to feel the hemorrhoidal protrusions in the rectum.
- Anoscopic examination is an examination of the rectal lumen using a special mirror.
- Sigmoidoscopy - examination of the tissues of the rectal canal with a rectoscope. It is a cylinder that the doctor will insert into the anus. Typically, about 25–30 cm of the rectum is examined.
- Coprogram is an analysis of feces for the presence of hidden traces of blood in them, which comes from injured varicose sacs.
- Ultrasound of pelvic structures - identification of tumor formations or cysts that can interfere with the full movement of feces and contribute to the formation of hemorrhoids.
From laboratory tests for clarifying purposes, experts recommend blood tests to diagnose chronic anemia, deviations in the concentrations of glucose, liver transaminases. This allows us to clarify the nature and causes of the development of stage 2 internal hemorrhoids, the treatment of which will be prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment
Surgery for grade 2 hemorrhoids is recommended in exceptional cases. Conservative therapy is generally prescribed. The course of treatment is chosen by the doctor; stopping the medication is not allowed until the symptoms disappear completely.
Use tablets:
- Troxevasin and Detralex. The action of the drugs is aimed at improving vascular tone in order to prevent relapses.
- Diclofenac and Ibuprofen. The medications are painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Used to treat inflammation and suppress pain.
Topical medications are intended to relieve symptoms. In most cases, such drugs are prescribed in combination with tablets.
The following ointments are effective for this phase:
- Heparin;
- Troxevasin;
- Proctosan;
- Relief;
- Levomekol.
Ointments help to quickly relieve inflammation, activate blood flow, and improve the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels. Ointments help ease the act of defecation, prevent damage to nodes and the appearance of cracks.
Treatment of stage 2 hemorrhoids using suppositories is a fairly effective method, especially when the bumps are located inside at a noticeable depth.
Almost all suppositories for hemorrhoids contain anesthetics, which explains their analgesic effect. Suppositories help relieve pain, itching, stop bleeding and prevent possible infection of the nodes.
A specialist prescribes suppositories based on an examination and assessment of the patient’s condition.
The following suppositories are in demand:
- Proctosedyl - reduces pain and swelling;
- Prednisolone – relieves burning sensation and suppresses pain;
- Hepatrombin G - reduces the degree of thrombosis.
Also used:
- Spongostan;
- Adroxon;
- Beriplast;
- Tachycomb.
Adrenaline suppositories are used to stop bleeding. In rare cases, when other drugs do not help relieve pain, a novocaine blockade is performed.
In order to improve the general condition, medications are prescribed to normalize the intestinal microflora and laxatives.
The nature of the development of the disease
Symptoms and treatment of stage 2 hemorrhoids depend on the form of the disease.
Features of the chronic form of the disease
Hemorrhoids of the 2nd degree become chronic in cases where there is no adequate treatment.
All symptoms increase:
- During defecation, large volumes of blood are observed . The more advanced the disease, the more pronounced this symptom appears. Bleeding is not life-threatening and stops after the hemorrhoids are reduced. However, this manifestation cannot be ignored.
- Both the itching and burning sensation become more noticeable , but are easily tolerable.
- The sensation of a foreign object being inside the anal canal may be present all the time.
- Severe pain during defecation.
Treatment of chronic hemorrhoids of the second stage is carried out both at home and in clinical settings.
Most often, it includes strict adherence to a diet and preventive measures. More specific measures can only be prescribed by a qualified doctor.
Acute form - very sharp and painful
This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of acute severe pain in the anal area.
There are three stages of the process:
- thrombosis of hemorrhoidal processes;
- the appearance of an inflammatory process in hemorrhoidal processes;
- transfer of the inflammatory process to surrounding tissues.
In the acute form of hemorrhoids, conservative treatment is first prescribed. Analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, ointments and special enemas are used.
For severe pain, painkillers (on a non-narcotic basis) are used, as well as some mixed drugs.
Also, vascular tonics (phlebotonics) are used for treatment. The most popular of them is Detralex.
To combat bleeding, suppositories containing adrenaline are effectively used. Hemostatic agents (for example, Adroxon) are also used.
Conservative therapy provides only a temporary effect, allowing you to comfortably survive the acute stage of the disease. After the inflammation disappears, it is necessary to begin minimally invasive treatment, and in the most advanced cases, surgery.
Combined hemorrhoids
The combined form of the disease manifests itself in the fact that hemorrhoids only partially fall out of the anal ring, and parts remain inside it.
This condition is dangerous, as it can lead to complications of the disease and the appearance of the third stage of hemorrhoids.
It is almost impossible to independently determine the form of hemorrhoids; the diagnosis is made exclusively by a proctologist.
Operative method of treatment
When drug therapy does not help, stage 2 hemorrhoids are treated with surgery. The bumps need to be eliminated before complications arise. It is customary to use minimally invasive methods:
- Latex rings. A latex ring with a diameter of approximately 1 mm is placed on the leg of the knot. The blood vessel is pinched, as a result of which the hemorrhoidal nodule dies within 7 days. During one procedure, 1-2 lumps are doped. The next procedure is carried out after two weeks
- Sclerosis. A special substance is injected into the hemorrhoidal node, causing the blood vessels to stick together. As a result of the procedure, the tissue masses of the node are replaced by connective tissues.
- Desarterization. It is performed using an anoscope. The essence of the method is to stop the blood supply to the nodes by ligating their blood supply arteries. The method is used in complex and advanced variants of the disease.
- Coagulation with infrared rays. A beam of infrared waves is directed to the base of the hemorrhoid, under the influence of which protein coagulation occurs. The cone is deprived of nutrition and dies. To guarantee, the procedure is performed at several points. One node is removed per session. Subsequent intervention is carried out a week later.
In modern medicine, cryodestructive intervention is also used, when hemorrhoids are treated with liquid nitrogen.
The minimally invasive method of intervention allows the patient to return to normal life in a matter of days. For a certain period of time after surgery, it is recommended to undergo regular follow-up with a doctor in order to avoid possible complications and relapse of the disease.
Treatment options for stage 2 hemorrhoids using minimally invasive techniques
If conservative therapy does not bring the desired results or hemorrhoids are complicated by thrombosis or pinched nodes, proctologists recommend using minimally invasive techniques:
- cutting off the node with a laser beam followed by sealing the wound is used for single large external and internal bumps;
- latex ligation is indicated only for internal hemorrhoids - a special ring is put on the leg of the node, followed by tightening, excluding the varicose cavity from the normal blood flow;
- sclerotherapy - the introduction directly into the node of a special drug that glues the walls of the varicose formation, depriving it of nutrition, followed by sclerosis and death, used for any location of hemorrhoids;
- for small, multiple hemorrhoidal nodules, infrared photocoagulation is used - treatment of the affected area, which causes coagulation of proteins in the walls of the vessels feeding the cavity, followed by drying and disappearance of varicose formations.
Two more methods of gentle operations are rarely used:
- disarterization - ligation of the arteries supplying blood to varicose veins, followed by their death - due to the lack of expensive equipment;
- cryotherapy - freezing the hemorrhoid with liquid nitrogen - due to the risk of necrotization of nearby tissues.
Minimally invasive techniques are performed on an outpatient basis, without the use of anesthesia (maximum local anesthesia). The whole procedure takes no more than half an hour, no rehabilitation is required. The downside is the possibility of relapse of the disease.
Doctor's advice
The therapeutic therapy and minimally invasive intervention carried out will be effective only if the rules and instructions of the specialist are followed.
These recommendations include:
- Healthy lifestyle. Light physical activity, walking, and physical education are required.
- Strict adherence to personal hygiene. If you have hemorrhoids, you should stop using toilet paper, replacing it with a rinsing procedure.
- It is necessary to completely exclude fatty, spicy foods, alcohol from the diet, and it is advisable to give up the bad habit of smoking.
- It is necessary to include fresh vegetables and fruits in your daily diet, providing the body with plant fiber. A properly formulated diet will prevent constipation and exacerbation of the disease.
General recommendations
It should be understood that stage two hemorrhoids occur due to multiple provoking factors. Therefore, his therapy will be largely useless if the patient does not change his lifestyle, thereby eliminating the causes that worsen his health.
There are not many recommendations, but they are significant. Patients should pay attention to several important nuances:
- change in diet. It is necessary to exclude unhealthy dishes from the menu - pickles, smoked foods, marinades, numerous spices and fatty foods. You should also not drink alcohol or coffee drinks. The diet includes fermented milk, vegetables and fruits enriched with fiber. Such a diet will help improve bowel movements and prevent constipation;
- greater mobility. If the “provocateur” of the disease is a sedentary lifestyle, it is necessary to increase physical activity. It is not at all necessary to become an athlete, but walking, swimming, exercise and simply climbing a flight of stairs are desirable - they will eliminate blood stagnation in the pelvic organs;
- hygiene measures. After each bowel movement, it is necessary to wash the anorectal area and perineum with cool water to prevent infection or reduce inflammation.
If the patient follows medical advice, varicose hemorrhoidal veins can be defeated with “little blood.”
Treatment of stage 2 hemorrhoids is carried out comprehensively, preference is given to conservative methods - drug therapy and folk recipes. If medical assistance is provided at this stage of the pathological process, there is a high probability of slowing down the development of the disease and saving the patient from negative symptoms.
It is only important to get rid of your own prejudices and consult a doctor in time.
In medical practice, hemorrhoids mean inflammation of the hemorrhoids. There are four stages of this disease, the most easily treatable are the first two.
Hemorrhoids cause a lot of inconvenience to their owner, so it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor to prevent the situation from worsening. This article will list possible treatment options for this disease.
Treatment methods for varying degrees of disease
All methods of treating internal hemorrhoids can be divided into two large groups: conservative methods and surgical intervention. The choice of a specific treatment regimen depends on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
At the first stage
Treatment at the first stage includes the use of suppositories, ointments and folk remedies.
Folk remedies:
- baths using chamomile and other soothing herbs.
- Decoctions and lotions.
- Candles made from potatoes or soap.
Attention! Folk remedies are used after consultation with your doctor.
Suppositories and ointments are aimed at stopping bleeding, restoring the tone of the veins and preventing further formation of nodes.
Phlebotonics (detralex, horse chestnut extract) are used to increase the elasticity of the vascular wall of the rectum.
Vikasol is a hemostatic drug, but for the first stage suppositories such as Thrombin and suppositories with adrenaline are more relevant.
To prevent thrombosis, Proctosedyl and Hepatrombin are used.
If the patient is bothered by constipation, laxatives help : Guttalax, Bisacodyl and Regulax. However, you should not abuse laxatives, as it may cause difficulties with independent bowel movements. To prevent constipation, you need to eat more vegetables and fruits. The introduction of ready-made fiber or bran into the diet also has an excellent effect.
Second degree of disease
The likelihood of a patient at the second stage seeking help from specialists increases. To completely defeat this delicate disease, long-term conservative treatment is necessary. Sometimes surgical intervention is required when suppositories and ointments do not give the desired result.
The following types of drugs are used for treatment:
- phlebotonics.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Thrombolytics.
- Analgesics.
- Hemostatic medications.
Phlebotonics ensure restoration of elasticity of rectal vessels. They help reduce inflammation and avoid the appearance of new nodes. These include drugs such as Phlebodia, horse chestnut extract, Detralex.
Anti-inflammatory drugs reduce swelling and protect against complications. At the second stage, they are used in the form of suppositories, which contain substances such as Diclofenac, Indomethacin or Hydrocortisone.
Thrombolytics provide prevention of thrombosis. At the second stage, they are applied topically, in the form of suppositories. The most famous thrombolytics are Heparin ointment and Troxevasin suppositories.
Analgesics help a person maintain a normal lifestyle. Candles with belladonna and menthol are excellent for relieving pain. It is also possible to use injections of painkillers.
Hemostatic medications are a preventative measure in the fight against anemia. They can be of general or local effect. The most famous drug for general effects is Vikasol, and Thrombin or suppositories with adrenaline are suitable for topical use.
If conservative treatment methods fail, or if there are complications, minimally invasive or surgical intervention may be required. At the second stage, the following are most often used:
- photocoagulation.
- Sclerotation.
- Ligation of nodes with latex rings.
- Cryotherapy.
The listed types of interventions are considered minimally invasive, as they involve minimal impact on the body. These procedures do not require anesthesia, and the person ends up at home within a short time.
At the third stage
At the third stage, suppositories and tablets are used as an aid. The main treatment is through minimally invasive or surgical intervention.
For the third stage use:
- cryotherapy.
- Ligation with latex rings.
Other methods of minimally invasive interventions at this stage are characterized by low efficiency. If there is the slightest doubt, the specialist recommends a full-fledged operation. To do this, the patient is hospitalized, prepared for the procedure, and then helped through the recovery period.
During the recovery period, hemostatic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs are actively used. They are necessary to relieve inflammation and local swelling.
Also, suppositories and ointments reduce pain and help the wound heal faster. Actively used drugs include Heparin, Relief, Ichthyol and Phenol. To facilitate bowel movements, mild laxatives are prescribed, for example, Regulax.
At the fourth stage When the nodes are constantly on the outside, when it is impossible to straighten them on your own, urgent surgery is required. At this stage, minimally invasive methods of intervention provide only short-term results. Without surgery, the nodes may be pinched or thrombosis may develop, which poses a danger to the patient’s life.
After the operation, the patient remains in the hospital for some time. Recovery takes approximately two weeks, but the specific time frame is determined by the attending physician. For several months, you should not lift heavy objects and avoid constipation and diarrhea. Specific recommendations at the fourth stage are given by the attending physician, taking into account the general condition of the patient and concomitant pathologies.
Internal hemorrhoids are considered a dangerous disease that leads to numerous complications. Because of this, if you have the slightest discomfort in the anal area, you should contact a proctologist to clarify the diagnosis and choose the right treatment.