When is surgery required?
Thrombophlebitis is treated by a vascular surgeon or a more highly specialized doctor - a phlebologist who deals exclusively with veins.
In any case, the stages of diagnosis and therapy will be the same. But to get rid of thrombophlebitis, experts do not always recommend surgery, since in most cases it is possible to cope with the disease using conservative methods. In the early stages of development, the disease is characterized by inflammation of the venous wall, as a result of which individual blood cells begin to attach to it. Then a full-fledged thrombus gradually forms, covering part of the lumen of the vessel. As the size of this blood clot increases, blood circulation becomes more and more impaired.
The danger of the pathology is not only the possibility of blockage of the vein in which the thrombus initially began to form, since in some cases collaterals can form. These are spare, bypass pathways for blood flow, ensuring the necessary supply of cells with oxygen and nutrients. The greatest risk occurs when a blood clot breaks away from the inner surface of the vessel and begins to migrate through the bloodstream, creating the possibility of embolism - blockage of the lumen of the vein feeding a vital organ.
Most often, pulmonary embolism occurs, resulting in death without emergency surgery.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in the later stages of the disease, when a blood clot causes complications that interfere with the patient’s normal functioning. Also, surgery may be indicated if one of the deep veins is affected, since this type of thrombophlebitis is the most dangerous. In addition, the surgical method is the only way to prevent embolism when a blood clot breaks off. If the patient's condition is not complicated, but conservative therapy does not produce results for a long time, surgery may also be indicated.
How is the operation performed?
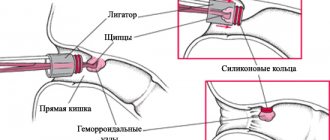
The essence of the surgical intervention is that all blood clots are removed from the hemorrhoid. This is done on an outpatient basis. The type of anesthesia is local.
In order to perform such an operation there is no need to use complex surgical devices. The procedure itself is simple and has a simple implementation technique:
- First, the patient is given anesthesia.
- Next, the doctor makes a small incision on the node that is affected by blood clots.
- The blood clot is removed through this incision. In order to reduce the risk of complications, the doctor injects a saline solution into the wound, which can make the blood clot softer and more pliable.
- Next, the doctor restores the previous condition of the vessel and sutures the wound.
The operation lasts several minutes. After it is over, the patient can go home in about half an hour. The patient does not lose his ability to work and can lead a normal life. Thrombectomy is considered a very low-traumatic operation. Sometimes doctors use laser techniques.
Relief of the patient's condition occurs almost instantly. Acute pain disappears, swelling decreases. Over time, the inflammatory processes completely stop. The final healing of the wound that remains after the operation ends after five days.
Thrombectomy method
Thrombectomy is an operation to directly remove a blood clot from the lumen of a vein. In this case, two types of surgical intervention can be used - traditional (radical) and endovascular - without excision of blood vessels. The first type of thrombectomy is used in most cases only in severe conditions of the patient with thrombophlebitis and deep vein varicose veins.
Restoring the patency of the great veins surgically began to be used since 1965.
Today, endovascular thrombectomy is most often used. It is performed using a catheter, so the blood clot is removed, but the affected vein itself is not excised. This allows you to prevent complications associated with partial or complete removal of the vein, which can be critical in thrombophlebitis.
Contraindications to the procedure:
- chronic diseases in the acute stage;
- severe heart pathologies;
- the presence of a malignant tumor;
- thrombophlebitis complicated by gangrene;
- difficult pregnancy, accompanied by exhaustion of the woman, gestosis or anemia;
- severe venous insufficiency;
- radiation exposure.
Thrombectomy is considered a minimally invasive procedure because a small incision is required. Through it, a Fogerty catheter ending in a latex balloon is brought to the location of the thrombus. During insertion through the incision, it is empty, but when contact with a blood clot is made, it is filled with a drug that promotes the retraction of thrombotic masses. This may require several repetitions of the process if the clot is large. The entire procedure is controlled by an ultrasound machine or x-ray. If it is not possible to remove the blood clot from the vessel, then a catheter is also inserted into the vein, but substances are supplied to the clot that destroy and dissolve it.
During the postoperative period, the patient is required to wear compression garments without removing them for at least three days to prevent relapses. The possibility of re-development of thrombophlebitis is the only disadvantage of endovascular thrombectomy. In addition to slimming knitwear, to consolidate the achieved result, you will need to resort to a course of drug therapy. For this purpose, anticoagulants are most often prescribed - drugs that help reduce blood clotting.
Endovascular thrombectomy
In modern vascular surgery, thromboembolectomy, or endovascular thrombectomy, is gaining popularity. During the operation, the thrombus is removed mechanically, while the vessel is preserved. In preparation for surgery, angiography is used to determine the location of the blood clot.
During surgery, the vessel is incised in the projection of the edge of the clot that has blocked the vessel. An empty catheter balloon is inserted into the incision under the control of an X-ray machine. When it comes into contact with a blood clot, the balloon is filled with saline and removed along with the blood clot. The catheter is inserted and removed several times until the vessel is completely cleansed.
Hemostasis during manipulation is maintained using electrosurgical equipment.
Endovascular thrombectomy restores blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, heart and limbs.
Types of non-radical thrombectomy:
- Thrombolysis
– a highly antigenic procedure that involves long-term administration of drugs that soften the blood clot into the vessel.
- Rheolytic
thrombectomy
is a puncture of vessel segments to remove newly formed blood clots with catheters. - Aspiration
– the blood clot is removed using a syringe placed near the clot. The method is easy to use and quick to perform, but it cannot prevent recurrence of thrombosis.
Crossectomy method
Crossectomy, which was previously called the Troyanov-Trendelenburg operation, involves ligation of the great saphenous vein and its branches. The technique is used only in cases of acute thrombophlebitis, when other methods cannot be effective. The action of crossectomy is aimed at preventing damage to deep arteries by restoring healthy blood flow.
Contraindications to this surgical intervention:
- malignant tumors;
- diabetes mellitus complicated by nephropathy (damage to the renal vessels);
- diabetic foot syndrome – purulent-necrotic processes, ulcers and osteoarticular lesions;
- significant excess weight;
- multiple organ failure syndrome - damage to all organs and tissues with a temporary predominance of symptoms of one or another failure;
- atherosclerosis;
- extreme exhaustion of the body;
- old age.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. After the anesthetic begins to act, the surgical field is treated with a disinfecting solution, then an incision is made in the area of the inguinal fold, and the vein is removed using instruments. A ligation is made at a distance of approximately 1 cm from its confluence with the great saphenous vein. After a similar action, sutures are applied to all appendages of the affected vessel.
Since crossectomy is an emergency operation, which is most often performed urgently without a full examination and preparation, there is an increased likelihood of recurrence. For this reason, in the postoperative period it is necessary to take medications prescribed by your doctor. Most often these are phlebotonics, anticoagulants, disaggregants and wound healing agents. If purulent thrombophlebitis has occurred, powerful antibiotics are prescribed. Painkillers, as a rule, are needed only during the first few days, but dysbiosis often occurs, which requires taking appropriate medications.
The rehabilitation period includes wearing compression garments, adjusting work and rest schedules, giving up bad habits, and performing daily preventive exercises. In this case, the patient will need to be regularly examined by the attending physician, so that at the slightest hint of a relapse, the disease can be stopped in time with medications.
Read also: Thrombus but not a clot
Thrombectomy as one of the methods of treating thrombosed hemorrhoids
If severe symptoms of thrombosed hemorrhoids appear, self-medication is unacceptable. Few people can withstand unbearable pain, so a visit to the doctor is inevitable. If comprehensive measures are not taken in time, the disease will cause serious complications that can only be treated with surgery.
A hemorrhoidal thrombectomy is a surgical operation that is performed to get rid of blood clots and blockage of the blood vessel that feeds the hemorrhoid. This operation makes it possible to restore blood circulation in the area of the affected vein or artery, helping to quickly eliminate the symptoms of hemorrhoids.
Thrombectomy has been used for a relatively long time and has a simple technique. This technique allows you to extract blood clots from almost all vascular structures. The blood clot is removed through a small incision, which is necessary to provide the surgeon with free access to the blocked vessel.
Currently, this technique is the most effective and is used in complex treatment of external hemorrhoids and extraction of blood clots from prolapsed internal formations.
Vascular suturing method
In some cases, doctors are unable to stop the disease either with conservative therapy or minimally invasive surgical methods, and thrombophlebitis returns again even after successful surgery. In this case, the method of suturing the affected areas of the vein can be used. A contraindication to performing a vascular suture is purulent thrombophlebitis, as well as previous radiation exposure.
The material used for suturing is braided or monolithic synthetic threads, which have high strength but minimally injure the vein. In this case, non-absorbable threads made of silk, nylon, nylon and other materials are most often used.
After suturing, blood circulation continues through the vessel, but the blood clot becomes “locked” and is unable to migrate, thereby eliminating the risk of embolism. The only change in blood flow is a decrease in its speed due to the narrowing of the lumen of the vein. This can affect the deterioration of the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the anatomical area.
Removal of hemorrhoids using the radio wave method.
The Surgitron device is used in proctology in the following cases:
- removal of external hemorrhoids;
- treatment of hemorrhoids at different stages;
- excision of fistulas;
- opening of acute subcutaneous paraproctitis;
- treatment of anal fissure;
- excision of anal fimbriae, papillomas, condylomas;
- removal of polyps and benign neoplasms of the rectum.
All stages of the operation using Surgitron correspond to the classical operation, only in this case, instead of a scalpel, the surgeon uses high-frequency radio wave radiation. This reduces surgical trauma because wounds do not need to be sutured.
The radio wave method eliminates the risk of blood loss, since the blood vessels are “sealed” during the operation. This exposure reduces the risk of infection. That is why removal of hemorrhoids using the radio wave method is recommended primarily for elderly and weakened patients who have a reduced ability of tissue to regenerate. The use of the Surgitron device for hemorrhoids makes it possible to facilitate the recovery period for this category of patients.
Do not delay treatment, contact KDS Clinic.
Installation of a vena cava filter
A modern operation is the implantation of a blood clot trap into the vessel. This device is a structure in the form of an umbrella, hourglass or dome. It is designed to retain the blood clot in the vessel, but at the same time allow blood to pass through without interfering with the supply of nutrients to the cells. Depending on the type of vena cava filter, it can retain clots measuring 2-4 mm.
After installing the trap, active drug therapy is carried out aimed at dissolving the blood clot. In this case, there is no likelihood of complications as a result of its migration or embolism of blood vessels leading to vital organs. The vena cava filter can be permanent or temporary; in the second case, it is removed after the thrombus has been completely removed and the consequences of its formation have been eliminated.
Contraindications to the procedure:
- infectious diseases accompanied by high fever that cannot be eliminated with medications;
- the diameter of the inferior vena cava is more than 3 cm;
- childhood and adolescence;
- the inferior vena cava inaccessible for surgery;
- abnormal narrowing of the lumen of the inferior vena cava.
To install a vena cava filter, local anesthesia is used in the form of injections. After the anesthetic has begun to take effect, a catheter is inserted into a pre-selected section of the vein, through which a device is installed into the affected vessel. The entire process is controlled using ultrasound or x-rays, since a small puncture is made and the surgeon does not have the opportunity to directly visualize the actions.
Installation of a vena cava filter is an operation, albeit a minimally invasive one, so after it it is necessary to comply with certain requirements. The patient is prescribed bed rest for up to one week so that the body can recover successfully and the stitches do not come apart. In general, no radical change in your usual lifestyle is required, since the device does not cause physical discomfort. However, to successfully remove a blood clot, the patient will need to reconsider his habits at least for the duration of therapy.
Types of fuel cells
The most common are:
- thrombectomy of hemorrhoidal node;
- surgery to remove blood clots in the brain;
- thrombectomy on areas of the heart;
- thrombectomy operations of the lower and upper extremities.
This type of surgery can be traditional or endovascular. The second method involves no excision of the vessel. Endovascular TE should be considered separately.
Endovascular TE
This technique for operating on the brain, heart, hemorrhoids during pregnancy and other situations has gained increased popularity. A feature of the endovascular thrombectomy operation is the preservation of the vessel while removing the thrombus itself using a catheter. Before starting the procedure, doctors should find the problem area. Computed angiography is used for this. In case of thrombosis, it helps to find those areas where surgery can be performed. Resection of the brachial artery or other area is performed, depending on the location of the identified clot.
During the procedure on the vessels of the heart, brain or hemorrhagic node, the specialist makes an incision along the edge of the tumor (thrombus) and inserts a special balloon-type catheter into it. At the same time, the equipment allows you to monitor the movement of the tool through the monitor. When the catheter reaches the desired point, it fills the vessel with saline and begins to pull it back, attaching the blood clot itself in parallel. This operation is carried out until the node is completely resolved and the lumen is cleared. The non-radical TE method is divided into several subcategories.
- Aspiration TE. To remove a thrombotic formation, a special syringe is used, which is inserted using a catheter and brought to the blood clot. The method is simple and fast, but with its help it is impossible to completely get rid of the entire clot.
- Thrombolysis. Here a substance is injected into the clot, which softens it. The procedure is highly antigenic and takes quite a long time.
- Rheolytic. This TE involves puncture of certain areas in the vascular bed to remove new clots using a catheter.
What surgical technique will be used to treat blood vessels, for example, in the leg, for problems of the brain or heart, is decided only by the attending physician. To decide on treatment methods, the patient must first undergo all the necessary examinations and tests. In addition to direct indications for thrombectomy, there are also contraindications that do not allow the operation to be performed using this method. Then we have to look for alternative methods to solve the problem of thrombosis of the heart, brain, lower and upper extremities, etc.
Features of surgery for thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities
Content
In a pathological process such as thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities, surgery is prescribed to prevent complications such as pulmonary thromboembolism, as well as to restore proper blood flow through the venous bed.
Acute thrombophlebitis is an advanced disease, and the presence of complications identified during examination using instrumental methods leads to the fact that the phlebologist is forced to prescribe treatment using surgical intervention.
After surgery for thrombophlebitis, this disease no longer poses any threat to life.
Preparing for surgery
Patients undergo a comprehensive diagnosis of the vascular network using angiography and X-ray or tomographic monitoring, blood tests for coagulation activity, general clinical examinations, fluorography and ECG. In the presence of concomitant diseases or infections, laboratory tests should confirm recovery or complete compensation of disorders.
Of particular importance is preparation for thrombectomy for thrombosis of hemorrhoids. Three days before the intended operation, patients are prescribed a diet to reduce gas formation in the intestines. To do this, cabbage, legumes, whole milk, brown bread, smoked foods and sweets are excluded from the menu.
It is recommended to drink up to 2 liters of clean water per day, have a first course for lunch, and have a fermented milk drink before bed.
The evening before the operation, you need to take your last meal no later than 12 hours before the scheduled time of thrombectomy; it is recommended to perform a cleansing enema before going to bed using such agents as Norgalax, Microlax, or use Fortrans solution.
Indications and contraindications
In medical practice, there are absolute indications and contraindications for surgical intervention for thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities.
Indications for surgery will be:
- the presence of an ascending process (the formation of blood clots begins to rise up the vein);
- threat of pulmonary thromboembolism;
- development of acute thrombophlebitis.
Contraindications include:
- the presence of inflammation located in the leg area;
- eczema;
- erysipelas;
- late stage of deep vein varicose veins;
- advanced age of the patient;
- pregnancy.
Thrombophlebitis cannot be a safe complication of varicose veins, and detection of an acute process will always be an indication for surgical intervention. The volume of the operation and the timing of its implementation will directly depend on the results of the ultrasound angioscanning and other types of instrumental diagnostics.
A planned operation is indicated for all patients who have been diagnosed with varicose veins with attacks of acute thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities. Attacks have no statute of limitations, since, according to medical statistics, the likelihood of relapse is very high.
Removal of hemorrhoids using radio waves, indications, features of the procedure
In the initial stages of the disease, conservative therapeutic methods are usually used, but when they do not bring the desired result, doctors recommend removing hemorrhoids. Of course, before prescribing an operation, a thorough examination is carried out and only on the basis of the tests a decision is made on further treatment. Radio waves for hemorrhoids are effective in the following cases:
- internal, external form of the disease of 3 and 4 degrees, accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, increased body temperature;
- prolapse or pinching of hemorrhoids;
- concomitant thrombosis.
Despite all the advantages of radio waves, they cannot be used in the following cases:
- concomitant oncological diseases - to avoid the risk of accelerating the growth of malignant tumors;
- a person has a pacemaker - radio waves can cause errors in its operation, which is fraught with negative consequences for the body;
- pregnancy period;
- reduced protective properties of the immune system - wound healing in this case can last up to several months;
- diabetes;
- accompanying acute inflammatory processes in the body.
Like any other methods of treating diseases, the use of high-frequency radio waves has its contraindications. Surgitron cannot be used in the following cases:
- treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy;
- inflammatory diseases in the acute stage have been diagnosed in the body;
- the patient suffers from diabetes or glaucoma;
- the patient has cancer in the body.
If any of these contraindications are present, the attending physician will select and suggest other methods of treating hemorrhoids, but in all other cases, the use of Surgitron is the optimal way to eliminate the disease. By following the doctor’s recommendations and following the rules of the rehabilitation period, you will be able to forget about external hemorrhoids forever.
- internal, external form of the disease of 3 and 4 degrees, accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, increased body temperature;
- prolapse or pinching of hemorrhoids;
- concomitant thrombosis.
Rectal cancer
- concomitant oncological diseases - to avoid the risk of accelerating the growth of malignant tumors;
- a person has a pacemaker - radio waves can cause errors in its operation, which is fraught with negative consequences for the body;
- pregnancy period;
- reduced protective properties of the immune system - wound healing in this case can last up to several months;
- diabetes;
- accompanying acute inflammatory processes in the body.
Main types of surgery
The choice of surgical intervention directly depends on the severity and presence of complications in a given pathological process. There are radical and palliative surgical interventions.
At the same time, ligation or coagulation of the perforators is performed. Carrying out this operation will forever relieve the patient of this vein pathology and destroy the root cause of its development - varicose veins. Since there is no recurrence of the dangerous condition, chronic venous insufficiency of the legs does not progress.
When performing palliative surgery, the patient does not recover completely, and the possibility of relapse remains. The purpose of this operation is to prevent the occurrence of thrombosis in the deep venous system. If this phenomenon has already occurred, the resulting blood clot is removed from the femoral or popliteal vein.
Read also: Thrombosis in women
To reduce rehabilitation time, percutaneous puncture thrombectomy is performed simultaneously with palliative surgery.
In surgical practice, there is an operation for thrombophlebitis, which brings significant relief to the patient’s condition. There are several varieties used in different patient conditions.
These include:
- crossectomy;
- installation of a vena cava filter;
- endovascular method of catheter thrombectomy;
- suturing of the vena cava.
The choice of surgical treatment for thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities remains with the doctor.
Crossectomy
This surgical intervention is the starting point when choosing therapy for this disease. Before starting this treatment, an ultrasound examination of the location of the saphenofemoral anastomosis (the area of the inguinal fold) should always be prescribed. It is at this point that a dissection or puncture is made to intersect the pathological venous vessels.
There are absolute and relative contraindications to this surgical intervention.
The absolute ones include:
- the presence of a high risk of complications after surgery on deep veins;
- identification of advanced somatic pathological conditions in the patient;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- atherosclerosis of the lower extremities.
Installation of a vena cava filter
When an accurate diagnosis of thrombophlebitis is made, surgery to install a vena cava filter is performed according to the following indications:
- there was a possibility of developing pulmonary thromboembolism;
- there is a concomitant pathology that significantly aggravates the current situation;
- the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system: heart failure, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease;
- previous surgical interventions in the area of the heart muscle: stenting, valve replacement.
The device, which is placed in a vein, allows you to catch blood clots that have broken off and can migrate along with the bloodstream. At the moment, the development of surgical technology makes it possible to remove the vena cava filter from the vein after some time.
An important effect of the vena cava filter will be to avoid the occurrence of pulmonary thromboembolism.
Surgery is performed endovascularly, usually through the femoral vein under local anesthesia. The operation takes approximately 60 minutes. The inserted device, which resembles an umbrella, is delivered to the desired location using a catheter, and there it opens.
After the vena cava filter has been installed, a control x-ray is performed. You are advised to stay in bed for the next 24 hours after surgery. On days 5-6, therapy with antibacterial and heparin-containing agents begins.
Endovascular catheter thrombectomy
The operation is performed if veins that are located deep are involved in the disease.
There are the following indications for its use:
- there is a high probability of pulmonary thromboembolism;
- prescribed drug therapy does not have the desired effect;
- there is no possibility to install a vena cava filter;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms.
To carry out this operation, special liquids and/or suction devices are used, with the help of which the lumen of the vessel is cleaned: the blood clot is removed or destroyed directly inside the vein.
A significant disadvantage of this surgical intervention is the possibility of disease relapse.
What is thrombectomy
Thrombosis (phlebothrombosis) can appear in any blood vessels - veins, arteries and capillaries, but most often the deep veins of the lower extremities are affected. Signs of circulatory problems are swelling, changes in skin color, and pain. In severe cases, the pathology leads to muscle atrophy, necrosis or tissue infection.
On a note!
Floating blood clots are especially dangerous. They are washed with blood from all sides, can come off and enter a vital organ along with the bloodstream, which will lead to serious consequences or death.
Thrombectomy involves a set of measures to find and remove a blood clot, restoring normal blood circulation and eliminating signs of thrombosis. This is the safest and most effective method for the treatment of thrombophlebitis, varicose veins and other vascular diseases of the lower extremities. One type of intervention is thromboembolectomy. This is a surgical operation to get rid of blood clots in peripheral arteries and veins.
Possible complications and preventive measures
The very first complication that occurs after surgery for thrombophlebitis will be the occurrence of pain. It is especially pronounced during crossectomy and phlebectomy.
Some time after surgery, a slight increase in body temperature (up to subfebrile levels) may occur. After removing inflamed and diseased veins, blood that gets under the skin during surgery may become inflamed.
Foci of redness may appear on the surface of the skin - this indicates the onset of bacterial inflammation.
Some complications are inevitable accompanying any operation: pain, swelling, areas of inflammation.
They must be treated with patience and understanding.
If you follow all medical instructions, they will go away after a while.
When installing a vena cava filter, it is recommended to use blood thinning drugs in small dosages.
If surgery was performed against the background of venous insufficiency, the patient must be registered with a dispensary at the clinic at the place of residence. You need to visit a doctor every month, take venotonics and wear compression garments.
Possible complications
Removal of thrombosed hemorrhoids using a technique such as thrombectomy, unlike other methods, is characterized by an almost complete absence of complications. In rare cases, patients complain of pain that occurs a couple of days after surgery. Severe discomfort in the anal area is possible.
Similar changes occur at a low pain threshold. Medicines that have an analgesic effect help to cope with this complication.
In order to avoid thrombosis in the future and exclude relapses of the disease, you should perform gymnastic exercises daily, adjust your diet and not sit in one position for a long time. When lifting heavy objects, you should not lean forward, but keep your torso straight.
Thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities: indications, contraindications for surgery
The lifestyle of a modern person, associated with prolonged static loads, inactivity, and obesity, leads to an increase in diseases associated with pathological expansion of the veins in the lower extremities.
Every third woman, every tenth man in the world suffers from varicose veins and, as a result, there is excess pressure on the vascular walls, preconditions for reflux, reverse blood flow, and stagnation in the veins.
In order to avoid the occurrence of complicated forms of venous dysfunction - phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, it is necessary to select therapeutic measures that maintain the blood in a stable liquid state, aimed at creating obstacles to deformations of the veins. Otherwise, such pathological conditions can provoke the penetration of a blood clot into the deep veins of the thigh.
And only surgical treatment, as a result of which the subcutaneous vessel is crossed in the area where it connects with the femoral one, can save the patient. After radical therapy, the blood does not enter the deep main line of the circulatory system, and its reverse flow ceases.
An operation for thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities with the aim of a positive, urgent solution to the issue of formation and spread of a blood clot deeper was proposed by surgeons Troyanov and Trendelenberg, but then the intersection of the vein did not give a complete recovery, and relapses occurred. Now ligation of the vessel is carried out a centimeter from the connection with the deep vein, next to the inguinal fold, the process also affects the venous tributaries.
Carrying out the procedure
Surgitron allows you to convert electric current into high-frequency radio waves and, using special attachments, transmit them to tissue. Radio waves affect cells, transfer energy to them, which practically leads to their evaporation. Due to the lack of pressure, physical contact with the skin and thermal effects, there is no concomitant destruction of surrounding tissue. Small vessels in the affected area are sealed, which prevents bleeding.
When carrying out treatment with Surgitron, the patient takes a position convenient for manipulation. After this, depending on the type of procedure, pain-relieving injections may be used. According to patients, they are the most unpleasant part of the procedure. After this, the doctor selects the appropriate attachment that is more suitable for removing this formation.
Surgitron acts on tissue precisely, pointwise, only on those parts of the formations that are subject to removal. During the procedure itself, the patient only feels warmth at the site of treatment; as a rule, no pain occurs. After completion of the procedure, a bandage with ointment is applied and the patient remains under observation for about an hour.
In what cases is surgery prescribed?
Thrombophlebitis of the great saphenous vein is characterized by rapid spread, when the risk of thrombosis increases many times and the process deepens into the thigh daily at a distance of up to twenty centimeters. And valve insufficiency and stagnation of venous blood only create conditions for accelerating this process. And here, a timely operation within two days can save the patient’s life.
Read also: Injections to strengthen the blood vessels of the legs with varicose veins
The main indications for surgical suppression of the vein may include the following cases:
- The area of the knee joint and the upper third of the thigh is affected by acute thrombophlebitis;
- Purulent inflammation of the walls of blood vessels in the lower extremity is usually combined with the formation of a blood clot, since these processes, supporting each other, are interconnected. Rapidly developing pathological events can lead to the constant growth of a blood clot, when it, attached at one end to the venous wall, is free floating in the clear channel of the affected vessel. Inflammatory processes only further loosen its tissues; with any mechanical impact, it can come off and end up in the vessels of the lungs, which leads to instant death;
- Vascular changes can also be negatively affected by medical actions that are carried out after surgery, the consequences of the procedure of intravenous infusions of concentrated glucose solutions during the treatment of hypertensive pathology, and the placement of catheters in the channels of the circulatory system. And then the development of drug-induced thrombophlebitis occurs against the background of damage to the walls of blood vessels.
The operation will help save a person from life-threatening complications that acute thrombophlebitis is famous for and which can lead to leg amputation.
Technique of the surgical procedure
More recently, to select the site of access to the junction of the superficial vein with the femoral vein, the surgeon was engaged in palpating the pulse in the area of the artery in order to determine the exact location of the vessel affected by thrombosis. Nowadays, more innovative diagnostics are used; thanks to scanning the veins on an ultrasound device followed by dopplerography, it is possible to identify the peculiarities of the localization of the anastomosis in a particular patient.
Most often, its area is located on the leg in the area of the inguinal fold or slightly below it, in rare cases - in the fossa under the knee. Access to the junction is determined depending on the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient, therefore the incision will not be made in the same way for all people.
During the operation, the skin of the leg is cut vertically along a length of no more than five centimeters. After visually identifying the bundle of vessels, the doctor, having treated the tributaries, crosses the trunk of the superficial vein with clamps and then ligates it. To avoid relapses, which include backflow of blood into the vessels of the legs, at least five additional venous tributaries are ligated.
At the end of the manipulations, a drainage is inserted into the wound and it is sutured. Surgical treatment requires special attention and high qualifications of the doctor, because the saphenous vein that needs to be crossed can be confused with the femoral vein, and this will lead to negative consequences.
The next step is to make an incision in the upper part of the leg, a metal probe is inserted into it, and it is advanced to the site of the first entrance. After it reaches its destination, the vein is fixed with a special thread with the upper part of the instrument. A tip pulled through the incision is used to cut off the affected vessel from the tissues surrounding it.
At the last stage of surgery, nodes and tributaries are removed, and perforating veins are ligated. If the vessels are very tortuosity, to remove them it is necessary to make several cuts, removing each section in parts. To extract nodules through tiny, no more than two millimeters, punctures, a Muller hook is used.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia with treatment of the patient’s legs and the use of compression stockings. Complications after radical treatment were not identified, but they can appear in the form of purulent inflammation of the wound surface, leakage or stagnation of lymph only in cases of violations of the surgical technique.
Cases of contraindications to surgery
Conditions in which surgery for acute thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities is absolutely contraindicated include:
- Somatic diseases in the advanced stage can provoke serious complications in the postoperative period;
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding, such methods of treating thrombophlebitis are not recommended;
- Damage to the tissues of the lower extremities of an infectious nature will not allow radical treatment;
- The inability to wear compression garments during the rehabilitation process may result in refusal of surgical intervention;
- Patients with diabetes mellitus and obliterating atherosclerosis are not recommended to undergo surgery of the lower extremities.
Features of the postoperative period
If the surgical removal or intersection of veins in the lower extremities is successful, the patient can get out of bed already on the second day, since his condition should return to normal by this time.
For two months, the patient is prescribed to wear compression hosiery - stockings, bandages, golf - which is selected by the attending physician.
For a complete recovery, the patient needs to constantly move: take walks, perform a complex of physical therapy exercises in the mornings and evenings, but it is not recommended to constantly be in the same position.
For a long time after the illness, indirect anticoagulants are prescribed under the control of the state of the blood and its coagulability. The drugs effectively block the activation of prothrombin. The rehabilitation program should include measures for the patient’s social adaptation and maintaining a full standard of living.
Prevention of such a pathological condition as post-thrombophletic disease will also help maintain the patient’s health. It includes giving up bad habits, adjusting your diet and lifestyle.
Main types of surgical operations
The diagnosis is carried out by a phlebologist. It determines the location of the blood clot, how the clot attaches to the vein, and the damage it will cause to nearby tissue.
The procedure is performed under anesthesia, so thrombectomy does not have any special recommendations during preparation. But patients are recommended:
- Give preference to comfortable shoes that will not interfere with blood circulation;
- Stop taking medications that are incompatible with the operation;
- Before the manipulation, hygiene procedures should be carried out: wash your feet, remove hair in the operated area.
Compression
Before deciding on surgical intervention, the phlebologist will clarify the correct diagnosis. During diagnostic procedures, the exact location of the blood clot, the method of its attachment to the wall of the blood vessel, and the degree of damage caused to tissues as a result of disruption of normal blood flow are established.
The following examination methods are used in diagnosis:
- Ultrasound - duplex scanning of the blood vessels of the lower extremities, as a result of which the site of vein blockage is detected;
- venography - radiography with the introduction of a special contrast agent into the vein, shows the condition of the patient’s veins at the time of examination;
- MRI (if necessary);
- assessment of blood test results.
It is worth noting that surgical treatment of veins in the leg is carried out under local anesthesia, so no special preparatory measures are taken. During this period, the patient is recommended:
- wear comfortable, spacious shoes that do not compress the blood vessels on the legs;
- stop taking medications if they were previously prescribed;
- prepare the leg for surgery: remove hair, carry out hygiene procedures.
Colon cleansing using an enema is not required in this case.
After thrombectomy of the veins of the lower extremities, successfully performed by qualified specialists, the patient will be able to return to everyday life in a few days.
In the postoperative period, conservative treatment is carried out as prescribed by the attending physician:
- blood thinners to prevent the formation of new blood clots (Warfarin);
- drugs to normalize microcirculation and restore venous tone (Pentoxifylline);
- special ointments for blood clots (Hepatrombin);
- antioxidants;
- vitamins, etc.
To avoid various complications, it is necessary to follow some recommendations in the first 6 months after surgery:
- train, but do not load the operated leg;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- use elastic compression: bandages, stockings, knee socks, tights;
- Healthy food;
- apply physical therapy;
- perform light self-massage;
- refrain from visiting the bathhouse, sauna;
- eliminate bad habits.
Thus, if thrombectomy is performed in a timely manner and all prescriptions of the attending physician are followed, the patient will be able to return to normal life within a short time.
After operation
The patient can leave the clinic 10-15 minutes after hemorrhoid thrombectomy. Until the suture is completely healed, careful hygiene of the perineum is recommended:
- washing the perianal area with cool water in the morning and evening;
- washing the perineum after each bowel movement;
- changing sterile dressings after each visit to the toilet;
- treatment of seams with antiseptics 2-3 times a day.
For 3-5 days, mild pain and swelling may be observed in the incision area. To weaken them, the doctor will prescribe local remedies (ointments, gels, solutions for applications and compresses), and oral NSAIDs (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen).
To prevent injury to the sutures during defecation, during the week you should give preference to dishes made from cereals, vegetables and fruits, drink 2 liters of water a day and, if necessary, use laxatives.
It is not recommended to use enemas after thrombectomy of hemorrhoids, as they increase the risk of infection of the postoperative wound.
Until the sutures have completely healed (about 2 weeks), patients are advised to limit heavy physical activity and sports, not lift heavy objects, and walk as much as possible.
Removal of hemorrhoids by radiosurgical method is the essence of the technique
The device produces high frequency radio waves. Their uniqueness lies in the ability to safely cut fabrics without a knife. During the operation, the organ is dissected without contact, and at the same time the vessels are “soldered” together: they are valorized. A burn occurs in the vascular wall, the protein coagulates with the subsequent formation of a blood clot - the bleeding stops. The process is reminiscent of ligating blood vessels during a classic surgical operation. In this case, no infection occurs, everything ends without complications.
The essence of the technique is that the device converts electrical impulses into radio waves of a set frequency. High-frequency energy is concentrated at the tip of the electrode, which provides a cutting effect. When the waves enter the mucous membrane, certain physical processes begin:
- the emergence of resistance in cells;
- release of thermal energy that heats tissue;
- cell death (under the influence of temperature, intracellular fluid evaporates, the membrane is destroyed) and tissue dissection.
Simultaneously with the incision, the proteins of the tissue and vascular walls are coagulated. Thanks to this mechanism, there are no negative consequences in the form of infection and blood loss.
The radioscalpel does not physically affect the tissue, so burns or mechanical damage to the tissue do not develop. Cells quickly regenerate without wasting energy on repairing damage.
Radio waves penetrate to great depths, but do not affect nerve endings or muscle fibers - their contraction may be minimal. This explains the absence of pain during the procedure. In the postoperative period, minor pain may sometimes appear, but it is quickly relieved by taking medications.
Indications for intervention
Treatment using radio waves is indicated for all patients with external hemorrhoids at any stage of its development - from the first to the fourth. Significant advantages compared to other methods make the method most suitable for use in proctological practice for debilitated and elderly patients. This is due to the reduced ability of organisms to repair damaged tissues.
It is especially important when surgical treatment cannot be used. Also used if there are many blood vessels at the site of intended impact
This increases the risk of bleeding.
Indications for use of the Surgitron device are:
- acute proctitis and paraproctitis;
- anal fissures;
- polyps, papillomas, condylomas and other benign neoplasms;
- the presence of fimbriae;
- inflammatory process in the perineal area.
Anal fimbria are formations that appear as a result of enlargement of external hemorrhoidal cones. These are small growths of skin around the anus that resemble folds. In women, their appearance is caused by straining during labor. They do not manifest themselves clinically. But they cause psychological discomfort, so they are removed along with external varicose veins.
It is impossible to independently differentiate what exactly is bothering you - fimbriae, polyp or hemorrhoids at an early stage of development. It is necessary to consult a doctor who, after examination, will recommend a specific treatment method.
Advantages and disadvantages of the operation
The main advantages of surgery to remove a venous thrombus in the leg are:
- minimal risk of injury;
- complete restoration of venous blood flow;
- relieving unpleasant symptoms – pain, fatigue, swelling;
- significant reduction in the rehabilitation period.
The disadvantages of the procedure include the risk of recurrence of thrombophlebitis and infection of the wound surface. But if the manipulation is carried out by a competent phlebologist, no complications should arise.