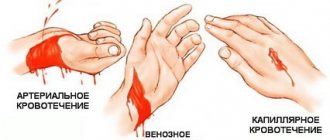
Right ventricular hypertrophy on ECG
Pumped up muscles of the human body are the result of everyday work, during which muscle tissue experiences a certain load.
What happens to the chambers of the heart if the load on their walls exceeds normal? Everything is correct. The muscle cells of the heart also “swing”: they increase in size and thicken. In medical language, this condition of the heart muscle is called hypertrophy. All cardiac chambers can hypertrophy: both the ventricles and the atria. And only some of them can thicken. Let's talk about right ventricular hypertrophy, its causes and clinical manifestations, and also consider the signs of right ventricular hypertrophy on the ECG.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
In a healthy adult heart, the left ventricle has a larger mass than the right. This is understandable, because the left ventricle pushes blood into the aorta, experiencing a heavy load. More often, when it comes to myocardial hypertrophy, doctors primarily mean thickening of the left ventricle. Often, but not always. The right ventricle can also undergo hypertrophy. The pulmonary trunk departs from the right lower cardiac chamber, which gives rise to the pulmonary circulation. In the small circle, the blood is enriched with oxygen in the lungs.
The right ventricle pushes venous blood coming into it from all organs into the vessels going to the lungs. They branch into small capillaries and envelop the alveolar tissue of the lungs, where gas exchange occurs. Carbon dioxide and metabolic products leave the capillaries, and oxygen enters the blood from the lungs. Oxygenated blood flows through the pulmonary veins into the right atrium. This completes the most important function of blood gas exchange and closes the pulmonary circulation. But the right ventricle may experience increased load, resulting in its thickening and hypertrophy.
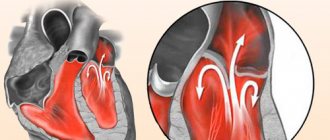
Pulmonary stenosis
What are the reasons for its thickening?
- Heart defects. Heart defects in children are often congenital. The so-called “blue” defects, which are often manifested by cyanosis of the skin in children, shortness of breath, and palpitations. This is Tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect. These are serious defects, often requiring the intervention of cardiac surgeons. Overload of the right ventricle can be caused by pulmonary artery stenosis, when blood from the ventricle cannot flow freely into the vessels, during a heartbeat the ventricle is not completely emptied, and a new volume of blood enters from the atrium, volume overload occurs.
- Lung diseases. Bronchial asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis, tuberculosis - all these diseases lead to an increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery system, and it becomes more difficult for the ventricle to push blood into the vessels, it has to contract with greater force than with normal pressure in the pulmonary vessels.
Thus, the main causes of thickening of the myocardial wall of the right ventricle and an increase in its mass are diseases of the lungs and pulmonary vessels, as well as heart defects, both congenital and acquired.
Diagnosis of prostate cancer
Cardiologists treat and diagnose pathology. If the cause of pancreatic hypertrophy is associated with diseases of the respiratory system, then an additional diagnosis is carried out by a pulmonologist. At the first appointment, the doctor finds out the medical history and symptoms, and conducts a physical examination. From the anamnesis, it reveals risk factors and concomitant pathologies that could lead to prostate cancer. Instrumental diagnostic methods:
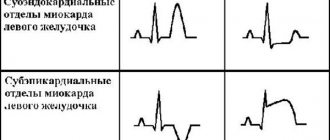
- ECG - shows signs of pronounced enlargement of the ventricle. In the early stages of pathology development, changes in the ECG are insignificant.
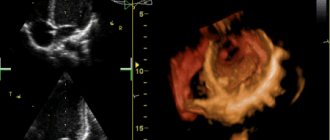
- Ultrasound of the heart - necessary to measure the thickness of the walls of the cavities of the heart and measure the pressure in the cavities.
- Examination with a cardiovisor (dynamic monitoring of heart function).
- Chest X-ray – to determine diseases of the respiratory system and determine the size of the heart.
- Daily monitoring. It is carried out using a special device that is fixed on the arm. It records blood pressure and pulse readings throughout the day.
- Spirography – evaluates respiratory function.
When diagnosing using ultrasound, the most accurate assessment of the condition of the heart can be determined in a combination of echocardiography with Doppler sonography. It provides information about the speed, nature of blood movement through the cavities of the heart, and the presence of defects in the septa and valves.
Right ventricular hypertrophy on ECG
Pumped up muscles of the human body are the result of everyday work, during which muscle tissue experiences a certain load. What happens to the chambers of the heart if the load on their walls exceeds normal? Everything is correct. The muscle cells of the heart also “swing”: they increase in size and thicken.
In medical language, this condition of the heart muscle is called hypertrophy. All cardiac chambers can hypertrophy: both the ventricles and the atria. And only some of them can thicken. Let's talk about right ventricular hypertrophy, its causes and clinical manifestations, and also consider the signs of right ventricular hypertrophy on the ECG.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
In a healthy adult heart, the left ventricle has a larger mass than the right. This is understandable, because the left ventricle pushes blood into the aorta, experiencing a heavy load. More often, when it comes to myocardial hypertrophy, doctors primarily mean thickening of the left ventricle. Often, but not always. The right ventricle can also undergo hypertrophy. The pulmonary trunk departs from the right lower cardiac chamber, which gives rise to the pulmonary circulation. In the small circle, the blood is enriched with oxygen in the lungs.
The right ventricle pushes venous blood coming into it from all organs into the vessels going to the lungs. They branch into small capillaries and envelop the alveolar tissue of the lungs, where gas exchange occurs. Carbon dioxide and metabolic products leave the capillaries, and oxygen enters the blood from the lungs. Oxygenated blood flows through the pulmonary veins into the right atrium. This completes the most important function of blood gas exchange and closes the pulmonary circulation. But the right ventricle may experience increased load, resulting in its thickening and hypertrophy.
Pulmonary stenosis
What are the reasons for its thickening?
- Heart defects. Heart defects in children are often congenital. The so-called “blue” defects, which are often manifested by cyanosis of the skin in children, shortness of breath, and palpitations. This is Tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect. These are serious defects, often requiring the intervention of cardiac surgeons. Overload of the right ventricle can be caused by pulmonary artery stenosis, when blood from the ventricle cannot flow freely into the vessels, during a heartbeat the ventricle is not completely emptied, and a new volume of blood enters from the atrium, volume overload occurs.
- Lung diseases. Bronchial asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis, tuberculosis - all these diseases lead to an increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery system, and it becomes more difficult for the ventricle to push blood into the vessels, it has to contract with greater force than with normal pressure in the pulmonary vessels.
Thus, the main causes of thickening of the myocardial wall of the right ventricle and an increase in its mass are diseases of the lungs and pulmonary vessels, as well as heart defects, both congenital and acquired.
Extrasystolic arrhythmia causes, symptoms and treatment methods
For the reasons for the appearance of such arrhythmia, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
- functional;
- organic;
- toxic.
The functional type of such arrhythmia is the least dangerous, since it is not accompanied by organic disorders in the heart. In this case, the main causes of disorders are severe stress, neurosis, and dystonia. Treatment of extrasystolic arrhythmia of this nature most often does not require hospitalization of the patient. Usually, to cure such a patient, it is enough to streamline their lifestyle and avoid stress. In some cases, sedatives are prescribed.
The organic cause is more serious. As a rule, in this case, extrasystolic arrhythmia is a consequence of more serious heart problems. For example, very often it occurs as a complication after myocardial infarction. In this case, it is necessary to eliminate the main cause of the arrhythmia.
A toxic form of the disease can develop as a reaction to certain medications. Or the main cause may be hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. Here, for effective treatment, it is also necessary to eliminate the underlying causes of the disease.
Depending on the ectopic foci of impulse occurrence, extrasystolic arrhythmia is classified into:
- ventricular (up to 65% of all cases);
- atrial (up to 25%);
- atrioventricular (up to 10%).
The atrial form of arrhythmia is considered the least dangerous.
Diagnosis and treatment with folk remedies
Extrasystolic arrhythmia is usually easily diagnosed. So, during an attack, irregularities in the heart rhythm can be heard even through a regular phonendoscope. But the most accurate picture of the disease can be identified using an ECG. In some cases, the doctor prescribes daily monitoring of electrical impulses of the heart, as well as ultrasound examinations.
An effective method for diagnosing arrhythmia is palpation of the radial artery. During diagnosis in this way, first the doctor feels a kind of wave, and then the pulse “falls out,” which definitely indicates the presence of an arrhythmia.
Treatment is prescribed after identifying the cause that led to irregular heartbeat rhythms. If functional disorders are detected, then it may be enough to eliminate neurosis or stressful circumstances so that the activity of the heart returns to normal. It is also necessary to limit salt intake to a minimum and maintain the correct rest and work schedule. In addition, sanatorium treatment for such patients is recommended.
Treatment with folk remedies for extrasystolic arrhythmia can also be successful, especially if the arrhythmia is not organic in nature. Infusions of cornflower, calendula, valerian, asparagus, lumbago, hawthorn or decoctions of rosehip seeds and hawthorn flowers are perfect here.
For example, you can take a tablespoon of valerian root and add one glass of boiled water, after which you need to leave the tincture for half a day in a sealed container, then strain the solution and drink three times a day. spoon.
Calendula infusion is no less effective. To prepare it, you need to pour 2 tablespoons of the plant with two glasses of boiling water. The medicine is infused for one hour, after which it is filtered. You need to drink half a glass four times a day.
Pharmacological drugs for the treatment of extrasystoles
If extrasystolic arrhythmia progresses and poses a threat to the patient’s life, then pharmacological drugs are used to relieve symptoms.
The most effective and frequently used medicine is quinidine sulfate. It has a good effect on atrial and ventricular extrasystoles. Doctors always recommend starting treatment with this drug.
If the effect of using quinidine sulfate is not observed or there is individual intolerance, then procainamide (novocainamide) is used. This drug is considered the second most effective and has a greater effect on ventricular extrasystoles. If this medicine does not give the expected result, then beta blockers (propranolol, alprenolol) are used for treatment. A good effect is also achieved with the combined use of beta blockers and quinidine in treatment. For organic diseases, another effective remedy is usually used - digitalis glycosides. It is added to quinidine and procainamide if their action is not effective enough.
Right ventricular hypertrophy on ECG
Pumped up muscles of the human body are the result of everyday work, during which muscle tissue experiences a certain load. What happens to the chambers of the heart if the load on their walls exceeds normal? Everything is correct. The muscle cells of the heart also “swing”: they increase in size and thicken.
In medical language, this condition of the heart muscle is called hypertrophy. All cardiac chambers can hypertrophy: both the ventricles and the atria. And only some of them can thicken. Let's talk about right ventricular hypertrophy, its causes and clinical manifestations, and also consider the signs of right ventricular hypertrophy on the ECG.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
In a healthy adult heart, the left ventricle has a larger mass than the right. This is understandable, because the left ventricle pushes blood into the aorta, experiencing a heavy load. More often, when it comes to myocardial hypertrophy, doctors primarily mean thickening of the left ventricle. Often, but not always. The right ventricle can also undergo hypertrophy. The pulmonary trunk departs from the right lower cardiac chamber, which gives rise to the pulmonary circulation. In the small circle, the blood is enriched with oxygen in the lungs.
The right ventricle pushes venous blood coming into it from all organs into the vessels going to the lungs. They branch into small capillaries and envelop the alveolar tissue of the lungs, where gas exchange occurs. Carbon dioxide and metabolic products leave the capillaries, and oxygen enters the blood from the lungs. Oxygenated blood flows through the pulmonary veins into the right atrium. This completes the most important function of blood gas exchange and closes the pulmonary circulation. But the right ventricle may experience increased load, resulting in its thickening and hypertrophy.
Pulmonary stenosis
What are the reasons for its thickening?
- Heart defects. Heart defects in children are often congenital. The so-called “blue” defects, which are often manifested by cyanosis of the skin in children, shortness of breath, and palpitations. This is Tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect. These are serious defects, often requiring the intervention of cardiac surgeons. Overload of the right ventricle can be caused by pulmonary artery stenosis, when blood from the ventricle cannot flow freely into the vessels, during a heartbeat the ventricle is not completely emptied, and a new volume of blood enters from the atrium, volume overload occurs.
- Lung diseases. Bronchial asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis, tuberculosis - all these diseases lead to an increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery system, and it becomes more difficult for the ventricle to push blood into the vessels, it has to contract with greater force than with normal pressure in the pulmonary vessels.
Thus, the main causes of thickening of the myocardial wall of the right ventricle and an increase in its mass are diseases of the lungs and pulmonary vessels, as well as heart defects, both congenital and acquired.