Maintaining all body systems in good condition is not an easy job, and it is simply unrealistic to monitor this constantly. If any of the organs is damaged, the body lets us know about it through pain. But what if it is not the organ that is damaged, but the blood vessels of the brain? But an aneurysm may not manifest itself. To protect yourself from the consequences, you need to know everything about it.
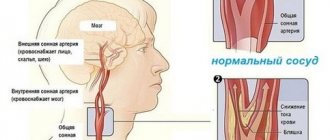
Intracranial aneurysm is a pathology in the form of a formation on the wall of a brain vessel that gradually fills with blood and increases in volume.
As it grows, it begins to put pressure on adjacent nerves, blood vessels and brain tissue, which causes subsequent symptoms. But the worst thing is a rupture of an aneurysm, when there is a huge probability of death.
The main methods of treating cerebral artery aneurysms
Surgical minimally invasive intervention is performed taking into account existing chronic pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, age, general physical condition of the patient, type, number of intracranial aneurysms. The use of non-invasive treatment techniques is indicated:
- patients over 60 years old;
- people with a burdened somatic status;
- for aneurysms with a wide neck and unfavorable neck-to-bottom dimensional parameters;
- anatomically poorly located aneurysms.
All manipulations on the vessels of the brain are carried out under multiple magnification in a specialized operating room. Additionally, constant x-ray monitoring is carried out. Endovascular interventions are performed through a small puncture made near the inguinal ligament. The necessary catheters are inserted into the femoral artery using an introducer. Next, a telescopic microcatheter with an internal lumen of about 1 mm is passed into the desired area of cerebral vessels.
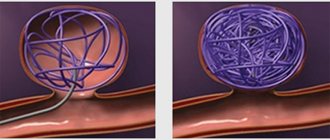
Use of microcoils for embolization
Embolization of aneurysm with microcoils
Interventions of this type are used for aneurysms with a narrowed base (neck). It is especially indicated in the acute period of hemorrhage. The aneurysmal cavity is completely filled from the inside with thin platinum wires that have a soft structure. Due to this, the aneurysm is completely excluded from the blood circulation process. This eliminates the risk of vascular wall rupture and reduces the likelihood of complications.
Application of stent-assistance
Embolization of aneurysm with microcoils with stent-assistance
Aneurysm embolization using axium microcoils with stent-assisted solitaire stent
The method involves the use of microspirals in conjunction with a special cellular stent. The cells support the coils of spirals in the cervical region. Operations of this type are prescribed exclusively in the cold period since they require the mandatory use of antiplatelet agents. Used as an adjuvant in the treatment of complex aneurysms (fusiform, generalized). Prevents the migration of microspirals into the lumen of the supporting vessel. Review by Shapiro et al. in 2020 showed: the percentage of successfully occluded brain aneurysms after stenting is over 61%.
Occlusion with balloon assistance
The essence of the technique is to temporarily inflate a non-detachable balloon in the supporting vessel (at the level of the aneurysm neck). Manipulations are carried out simultaneously with the implantation of platinum spirals. There are several options for embolization: the use of spherical, hyperexpandable elements, and double-lumen balloons. After achieving reliable fixation of the coils in the lumen of the aneurysm, the inflatable elements are removed. Durability and effectiveness of balloon-assisted occlusion according to statistical data from Cekirge S. et al. (check method - control angiography) - 82%.
Application of pCONYS for bifurcation aneurysms
A modified stent-assistance is used to stop intracranial bifuking aneurysms with a wide neck. Stenting is performed using special stents. One of these is pCONYS, a self-expanding natylon matrix stent. The device is intended for correct remodeling of blood vessels in bifurcation-type aneurysms.
The design of the stent ensures optimal positioning in the aneurysmal cavity and suggests the possibility of repositioning the element with complete removal into the delivery microcatheter. According to data published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery for 2013-2014, positive results from the use of cerebral artery endoprostheses are achieved in 97.3% of clinical cases. Modern stent-assisted techniques do not increase the rate of intraoperative complications, are relatively safe, and provide long-term results.
Flow redirection stents
Flow redirecting stent
The technique is effective in the treatment of fusiform aneurysms, aneurysms with cervical recanalization, when there is difficulty in performing coiling (GDC). The method involves the installation of densely woven self-expanding stents, which in a certain way redirect the blood flow in the vascular lumen. This leads to stagnation of blood in the cavity, provoking thrombosis of the aneurysm. The guide stent is selected according to the diameter of the artery (+0.25 millimeters). Its length should exceed the size of the arterial defect by 10-12 mm.
Endovascular operations are currently the method of choice in the treatment of cerebral artery aneurysms.
Embolization
This technique has become widespread in the last 15 years. It allows you to exclude the damaged vessel from the cerebral circulatory system without opening the skull. A special catheter is inserted through one of the veins or arteries. It moves through the circulatory system until it reaches the aneurysm. After this, using special instruments, the vessel is disconnected from blood circulation.
Embolization is the least traumatic way to eliminate aneurysms. That is why it has become widespread.
Efficiency and advantages of treating cerebral aneurysm using modern endovascular techniques
Embolization is a method that has proven to be highly effective.
That is why it is often used to disconnect a cerebral vessel from the circulatory system when:
- Inaccessibility of the aneurysm.
- Risk of serious complications with direct intervention.
- Carrying out operations on elderly people.
- Treatment of patients in serious condition.
Intervention is also prescribed when the aneurysm cannot be clipped.
Over the past few years, a large number of interventions have been performed. Moreover, surgery on cerebral vessels was prescribed even for gigantic aneurysms. The majority of patients did not require a long stay in the intensive care unit and were discharged from the clinic within 2-3 days.
There was no damage to any major healthy cerebral vessel. Thanks to this, patients were able to lead a normal life and did not experience any restrictions.
In some patients, the aneurysm was not completely excluded from the bloodstream during one intervention. In this case, another operation was performed. Repeated intervention on the cerebral vessels did not lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Main advantages of the method
- Low probability of need for repeated interventions. The operation is performed a second time in approximately 1 case out of 300.
- Possibilities for intervention to stop a cerebral vessel in patients who are contraindicated for extensive surgical clipping.
- Short duration of the procedure. Usually the operation takes no more than 2-3 hours.
- Opportunities for full recovery of health. An aneurysm will not bother you.
Life after surgery
Full recovery after open operations takes up to two months; after endovascular operations, patients return to a full life in less time. The duration of recovery depends on the patient’s health status before surgery and postoperative complications.
Aneurysm before and after endovascular surgery
After a craniotomy, the wound may feel painful for several days; as the wound heals, itching may occur and there may be swelling in the area and numbness for several months.
You may experience headaches, fatigue, and anxiety for about two weeks until eight weeks after open surgery. Therefore, a nap in the afternoon is recommended.
The patient should be under the supervision of a neurologist and take the necessary medications and painkillers. During the year, it is necessary to avoid contact sports, lifting weights of more than 2 - 2.5 kg, and prolonged sitting.
If the work does not involve stress, after about 6 weeks you can discuss with your doctor the possibility of starting work.
Despite the fact that the use of MR angiography and CT angiography is limited by the presence of possible image distortions from metal clips, stents and coils, these methods remain quite effective in postoperative monitoring.
Re-examination after open surgery is recommended to be carried out in the period from 6 to 12 months after the intervention.
After endovascular surgery, control digital subtraction angiography is recommended in the period from 6 to 12 months after the intervention.
Feedback from patients after surgical correction of a vascular aneurysm of the brain is positive. Among the adverse reactions that persist in the delayed period after surgery, many note a deterioration in health when the weather changes.
There are many positive reviews about the treatment at the N.N. Burdenko Institute, where over the past ten years more than 400 surgical corrections of unruptured aneurysms have been performed, with positive results from the operations.
For this purpose, it is necessary to submit the relevant medical documents to the selected clinic, and if there are quotas, a “Protocol of Quota Decision” will be issued, the patient is included in the operation plan and waits for his turn.
If the patient comes to the clinic independently, without referral documents, the operation is carried out for a fee.
In the case of paid treatment, the cost of the operation is very individual and depends on the materials used during the operation, the qualifications of the doctor, the time spent in the hospital, etc. On average, the cost of an operation in Moscow clinics for clipping an aneurysm is about 80,000 rubles, for endovascular shutdown aneurysms - approximately 75,000 rubles.
Given the high mortality rate from hemorrhage when an aneurysm ruptures, if indicated, prophylactic surgery to exclude the aneurysm from the bloodstream is recommended.
Symptoms and signs of intracranial aneurysm
An aneurysm is most often asymptomatic, until it reaches a large size or ruptures.
Occasionally, pain may appear in the frontal part of the head.
Symptoms of a growing mass do not appear immediately, and sometimes may subside.
Expressed in:
- pain in the forehead and eyes;
- numbness, a feeling of stiffness or partial paralysis of one side of the face;
- weakness of the facial muscles;
- blurred vision;
- pupil dilation.
Types of surgery
Medical tactics depend on the location of the cerebral aneurysm (carotid, anterior, middle, vertebral artery), the presence or absence of mechanical damage (rupture) of the wall, clinical symptoms, and the general condition of the patient. Surgery is indicated for all patients with an aneurysm identified during a diagnostic examination of vessels located in the brain.
If the pathologically altered vessel has not ruptured, the timing of surgical intervention may be postponed. According to medical statistics, the probability of rupture does not exceed 1-2% annually. If, based on the results of neuroimaging of brain structures, a ruptured aneurysm is detected, surgery to remove the pathologically altered vessels is carried out as soon as possible.
The urgency of the response is associated with a high risk of repeated violation of the integrity of the wall with the development of a new intracranial hemorrhage. The occurrence of repeated foci of hemorrhage associated with rupture of the walls is observed in 15-25% of cases during the first 2 weeks from the moment of the first rupture. Within 6 months - the risk of recurrent hemorrhage increases to 50% with mortality rates of about 60%.
The tactics of surgical intervention are determined under the influence of such established factors as repeated mechanical damage to the walls of the pathological vessel and the development of vasospasm - a significant narrowing of the vascular lumen as a result of prolonged, intense contraction of vascular smooth muscle. The timing of the operation is determined taking into account the form of ischemia resulting from cerebrovascular accident.
With a compensated form of the ischemic process, surgical intervention can be performed immediately. In case of decompensated form, wait-and-see tactics are recommended. There are 2 main types of operations for aneurysms of arteries in the brain: endovascular surgery (minimally invasive intervention without incisions) and open microsurgical intervention.
Endovascular surgical treatment is carried out through small punctures (punctures) with a diameter of 1-4 mm. Medical procedures are carried out under constant monitoring using X-ray equipment. In some cases, tactics involve combining both methods. First, to prevent relapse in the presence of a rupture of the aneurysm wall, endovasal embolization (blockage) is performed, then open surgery (after stabilization of the patient’s condition).
An open operation is performed under general anesthesia using microsurgical instruments, operating equipment and a microscope. During an open operation, in 98% of cases it is possible to completely isolate the damaged area of the vessel from the circulatory system. An open operation involves sequential execution of actions:
- Trepanation (opening) of the skull.
- Dissection of the dura mater.
- Opening of the arachnoid membrane.
- Identification of the main feeding vessels and aneurysm.
- Aneurysm clipping (exclusion from the general blood flow).
- Closing the wound.
A control diagnostic examination is often carried out using intraoperative (occurring during surgery) Doppler ultrasound. Endovasal intervention is performed in cases where clipping through open surgery is not possible. Difficulties are often associated with inaccessible localization (vertebrobasilar area, paraclinoid zone, internal carotid artery, area of the ophthalmic segment) of the pathologically altered vessel, and the patient’s advanced age (more than 75 years).
X-ray endovascular surgery involves placing a catheter balloon or microcoils into the aneurysm cavity. The action of the microspiral is based on the formation of blood clots in the cavity of the affected area of the artery. Blood clots clog the vascular lumen, which leads to the exclusion of the aneurysm from the general blood flow. In 85% of cases, embolization (blockage) of the aneurysm makes it possible to achieve radical exclusion of the pathologically from the cerebral circulatory system.
Classification of intracranial aneurysms
Pathology can be classified according to several criteria, for example:
- form;
- size;
- location;
- nature of occurrence;
- number of cameras.
Forms
The following types of aneurysms are distinguished:
- Saccular or “berry”. The most common form (appears in more than 90% of cases). It is named so because it looks like a bag or a large berry.
- Fusiform or fusiform. Cause of occurrence: expansion of the walls of the vessel in any area. Unlike the berry artery, the artery expands on both sides.
- Lateral. It looks like a tumor. It is located on the side, on the wall of the artery.
Magnitude
The size of the formation is determined by the diameter:
- milliary (up to 3 mm);
- small (3-10 mm);
- normal or medium (11-15 mm);
- large (16-25 mm);
- gigantic (more than 25 mm).
Location
Most often, in 47% of cases, pathology occurs in the anterior cerebral and communicating arteries.
The rest are localized on arteries such as:
- middle cerebral (23%);
- internal carotid (22%);
- vertebrobasilar system (6%);
- on more than one (15%).
Number of cameras
Aneurysms are divided into:
- single-chamber;
- multi-chamber.
Nature of occurrence
According to the nature of its occurrence, the pathology is divided into:
- congenital;
- acquired.
It is important to know that severe symptoms of a transient ischemic attack can last up to 24 hours. Further progress in the clinical picture of the attack is usually attributed to a stroke. You will read about this in the article.
It is very important to distinguish and correctly develop imitative and global synkinesis. You can find out how this happens here.
Features of the postoperative period
Brain surgery always causes consequences for the body. However, with proper rehabilitation and following the doctor’s recommendations, they can be overcome. Here's how the process begins:
- after the surgery department, the person is transferred to the neuro intensive care unit for several days;
- every day the surgeon examines the patient, studies the emerging consequences and prevents complications;
- if adverse symptoms occur, a computed tomography scan is performed;
- the most common consequences are vascular spasms and hypoxia of brain cells, sometimes hemorrhages occur under the arachnoid membrane;
- in the absence of exacerbations, clipping and other operations do not lead to death;
- if a large aneurysm was located near the basilar area, the risks increase;
- Also, the risk of mortality is high in people admitted with hemorrhage.
Disability after embolization of a cerebral aneurysm occurs only in 4% of cases. Statistics show that 8 out of 10 patients return to their normal lives, but only 4 of them begin working.
Consequences of clipping
Complications after artery clipping occur in approximately 10% of cases. This 10% includes consequences such as:
- disturbance of attention, concentration;
- constant headaches;
- minor and significant speech problems;
- ischemia, pulmonary edema - in rare cases.
Mortality occurs only in very difficult situations. If possible, you should not refuse the operation.
Restorative procedures
In the first days after the intervention, to prevent the consequences of the operation, the patient is monitored by medical personnel
It is important to notice bleeding and other symptoms in time
In the first days of recovery, the patient is prescribed nootropics, analgesics, diuretics and neuroprotectors if bleeding occurs.
Open trepanation and operations near brain tissue are complicated by additional consequences:
- repeated hemorrhages;
- infections and inflammations (in very rare cases);
- neurological disorders;
- necrosis of nervous tissue and neurological deficit - vasospasm.
During rehabilitation, the patient uses different methods: physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy. After endoscopic clipping, you can return to your normal life within a week. At the same time, there is no need for complex physiotherapeutic procedures.
Under the constant supervision of specialists, the patient undergoes courses of massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy, and also takes preventive medications.
Diet during rehabilitation
To prevent consequences after surgery, it is also necessary to follow a diet. Doctors recommend sticking to it for the rest of your life:
- You should not eat animal fats, including lard and large amounts of butter;
- sharply limit fatty dairy products: cheeses, ice cream, processed cheeses, condensed milk, cream, cottage cheese and milk with high fat content;
- you cannot eat more than 2-3 yolks per week;
- minimize the consumption of fatty fish, canned food, squid, oysters and caviar;
- It is forbidden to eat a lot of sweets and starchy foods;
- Restrictions include polished rice and semolina;
- It is better to completely exclude peanuts, hazelnuts and pistachios from the diet;
- vegetables cooked with fat, only a little olive oil is allowed;
- store-bought sauces, spices;
- tea and coffee with cream, alcohol and soda.
During the diet, lean meat is consumed, and the skin is removed from fish and chicken. Stewed, boiled and steamed dishes are used. You should also minimize the amount of salt.
Risk group. Danger of aneurysm
An aneurysm is a disease of the arteries of the brain that is found in various people, regardless of age.
The risk group includes:
- smoking,
- alcohol abusers,
- patients with hypertension, hereditary vascular pathologies.
The insidiousness of an aneurysm is that in the early stages the symptoms of brain damage are almost invisible. It is not easy to notice them, especially for a constantly busy person. At the same time, a relatively small number of people undergo comprehensive examinations of the brain and blood vessels.
Many patients do not pay attention to headaches and nausea. Usually these conditions are associated with chronic fatigue and age.
Important! 25% of patients suffering from protrusion of the wall of a cerebral vessel die.
The importance of identifying the disease at an early stage
At the first symptoms of an aneurysm, you should immediately seek qualified help. It should be remembered that over time the formation will only increase, aggravating the course of the disease and increasing the likelihood of death. Ideally, aneurysms should be removed before they rupture, this will preserve all the functions of a healthy body and protect a person from disability
Nowadays, there is no way to prevent the formation of an aneurysm, so it is very important to undergo preventive examinations. If an aneurysm has been identified, there is no need to despair.
Modern medicine offers treatment methods that are highly likely to ensure a complete recovery of the patient.
It is important to choose a medical institution that offers truly qualified care. Before giving consent to the operation, you need to familiarize yourself with the statistics of deaths and complications in this hospital
After the operation, the person will have to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol, and will also be given a list of prohibited medications. Effective rehabilitation methods can minimize the consequences of cerebral hemorrhages. Thus, timely treatment will allow the patient with an aneurysm to lead a full and healthy life after removal of this formation.
And to prevent headaches, you can use orthopedic pillows and mattresses https://www.vegas-md.com, which will allow you to sleep well and feel cheerful.
August 3, 2015
Disability due to aneurysm
Assignment of disability after open surgery occurs after a socio-medical examination. Only in 7-10% of cases the patient is given one of the categories of disability.
The appointment is due to functional imbalance, partial incapacity. Temporary disability is also prescribed if the patient needs long-term rehabilitation.
The disability group is given depending on the symptoms and consequences:
- The first is prescribed if the patient needs outside care and supervision. At the same time, he cannot provide for himself, incapacity is given, and a guardian is assigned to the person.
- The second group is given for partial impairment of functionality. Sometimes they are given partial incapacity.
- The third group is established for moderate dysfunction. This may include partial hearing loss, paralysis or disorientation. At the same time, the possibility of self-service remains 100%.
Surgeries to remove arterial aneurysms of the head
Let's look at how a cerebral aneurysm is removed using different surgical techniques.
Endovascular embolization
It is a minimally invasive operation to introduce artificial embolic substances into the aneurysm. Once the embolisate hardens, blood flow in the aneurysm stops.
Preparation:
- Laboratory examination;
- Consultations with an anesthesiologist and surgeon;
- A day before the procedure - CT or angiography.
Technique:
- Local anesthesia.
- Skin incision over the projection of the femoral artery.
- Insertion of a conductor with a catheter into the artery.
- Passing the catheter to the aneurysm.
- Removing a conductor.
- Injection of a contrast agent into the catheter and visualization of the aneurysm.
- Insertion of an embolisate (balloon or stent containing surgical glue) through a catheter.
- Filling the aneurysm with embolic agent.
- Removing the catheter and suturing the thigh area.
The duration of the operation is 45-60 minutes. Rehabilitation lasts from 2 to 14 days.
Microsurgical technique
It involves shutting off the aneurysm from the bloodstream by installing an artificial clip on its neck.
Preparation:
- Consulting a surgeon, anesthesiologist;
- Laboratory screening;
- Blood pressure correction;
- Shaving hair from the scalp in the area of the surgical field;
- The day before surgery - CT scan or angiography.
Technique:
- General anesthesia.
- Connecting a monitor to monitor the correctness of the operation.
- An incision in the scalp in the area of the surgical field.
- Opening the skull.
- Detection of an aneurysm.
- Applying a surgical clip to the neck of the aneurysm.
- Checking clipping efficiency (monitoring).
- Restoring the tightness of the skull.
- Suturing of soft tissues.
Duration of the operation: 1.5-3.5 hours. Rehabilitation time: from 4 weeks to 6 months.
We talked in more detail about aneurysm clipping in a separate article.
Revascularization intervention
It is an open operation with craniotomy, during which the aneurysm is removed and a new blood flow path is created between the intact arteries.
Preparation:
- Laboratory screening;
- Cerebral angiography, CT (MRI);
- Consultations with a neurosurgeon and anesthesiologist;
- Taking antiplatelet agents (aspirin 75 mg) for a week before surgery.
Kinds:
- EICMA - extra-intracranial microanastomosis - creation of an end-to-end anastomosis between the middle cerebral (MCA) and superficial temporal (STA) arteries. The PVA connects to the MCA through the burr hole, forming a new pathway for intracerebral circulation;
- EICA - extra-intracranial anastomosis - connection of the branches of the external (ECA) and internal (ICA) carotid arteries. A segment of the radial artery is used as a shunt (connecting bridge). The shunt is connected to the ends of the ICA and ECA, having previously brought the ICA to the surface of the skull through a burr hole;
- IICA - intra-intracranial anastomosis - an operation to connect arteries inside the cranial cavity. An anastomosis is created between the anterior or posterior cerebral arteries (ACA, PCA), branches of the MCA. A type of ICA is reimplantation - cutting off a segment of the affected artery coming from the aneurysm and its subsequent suturing into the nearest arterial vessel.
EICMA, EIKA and IIKA are performed according to the same algorithm and differ only in the types of anastomosis.
Technique:
- General anesthesia.
- Hypothermia of the brain.
- Connecting a monitor.
- Trepanation of the skull.
- Isolation of the recipient vessel.
- Removal of the aneurysm.
- Isolation of the donor vessel and its connection to the recipient vessel.
- Creation of anastomosis.
- Restoring the tightness of the skull.
- Suturing of soft tissues.
Time: 3.5-8 hours (depending on equipment, number of surgeons in the team). Rehabilitation time: from 1 month to six months.
How is the treatment carried out?
After local anesthesia, the doctor inserts a hollow plastic tube (catheter) into the femoral artery and advances it, using angiography, to the site of the aneurysm. Using a guide catheter, coils of platinum wire or small latex beads are passed through the catheter and inserted into the aneurysm. They fill the aneurysm sac, cutting it off from circulation, causing the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) that completely seals the aneurysm cavity. The softness of platinum allows the coil to conform to the fancy shape of the bag. To fill it completely, an average of 5-6 spirals are required.
The average duration of the procedure is 1-2 hours.
When the neck of the aneurysm is too wide, it is sometimes necessary to place a stent in the main vessel to hold the coils inside the sac. Because the stent acts as a barrier between the aneurysm and the mother vessel, it is very unlikely that coils will protrude from it.
Benefits and risks of interventions on cerebral vessels
If there is a narrowing of a vessel area that threatens the development of a stroke, restoration of its patency with the help of medical instruments is indicated. For this procedure, the patient is placed under general anesthesia and a contrast agent is injected intravenously.
At this time, he is on the operating table, the puncture site of the femoral vein is specially treated with antiseptic agents and covered with sterile sheets. An infusion catheter is placed in a peripheral vein, most often in the elbow area, so that solutions and anesthesia can be administered.
Vital signs are monitored using special equipment that is connected and records heart rate, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, and degree of blood oxygen saturation.
The coil as a method of treating aneurysms
Endovascular embolization of a cerebral aneurysm has a similar effect, the drugs for which are delivered in the same way, through a catheter. After the site of protrusion or vascular malformation has been reached, a sclerosing substance, for example, alcohol-based, is injected.
Endovascular embolization
A burn occurs on the inner surface of the vessel and the walls stick together. Blood flow through the pathologically altered vessel is stopped, the progression of the growth of the wall defect is stopped, and the likelihood of rupture and the occurrence of massive intracerebral bleeding is prevented.
Use of stereotactic equipment
The patient's head is placed in a special fixing frame. It is secured with special screws. Before installation, the scalp is numbed on the forehead and back of the head. This installation guarantees reliable immobilization of the patient’s head and prevents accidental involuntary twitching. This also improves the accuracy of the gamma rays.
After the manipulation is completed, a series of photographs are taken after a certain time in order to ensure the reliability of the blockage of the vessel. The catheter is carefully removed, and the puncture site is treated and sealed with a bandage, or a pressure bandage is applied. The duration of the operation, depending on the complexity, is about 30-40 minutes. After it, the patient is given bed rest for eight hours.
If there is a need to remove a cerebral aneurysm, then it is better to opt for endovascular techniques. Their most important and undeniable advantage is minimally invasiveness. To insert a catheter, no large access is required; a small incision or even a puncture is sufficient.
At the end of the operation, there is no need for stitches; a small bandage will suffice. The low-traumatic nature of endovascular operations significantly reduces the hospitalization time of patients. Discharge can be planned as early as the next day after the intervention. The risk of unpleasant consequences such as scars and serious complications such as recurrent bleeding and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection is reduced.
The introduction of such treatment methods has made it possible to help people whose disease was previously considered incurable.
In some cases, this operation can be performed under local anesthesia using sedatives. This is especially true for patients whose concomitant diseases are a contraindication to general anesthesia.
It has been clinically proven and confirmed by medical experience that catheter embolization helps to cope with bleeding quickly and effectively. This is especially true in emergency cases.
The procedure has proven to be a good way to treat tumors and modified vessels that have limited access. If, due to the severe course of the patient’s disease, open surgery is not possible, then vascular embolization can achieve stabilization of the condition. Thus, timely closed aneurysms and anastomoses not only help control the symptoms of the disease, but also significantly increase the patient’s life expectancy.
^Top^
Indications and contraindications
The embolization procedure, performed using special devices, prevents the development of the disease. Intravascular occlusion of the aneurysm prevents the subsequent development of complications in the acute period of stroke.
The procedure is carried out in case of development:
- vascular spasm;
- intracranial hematoma.
Before starting the intervention, a list of contraindications is determined for a patient with unstable thrombus formation in the lumen of the aneurysm.
Indications for intravascular treatment are:
- localization of the aneurysm;
- the risk of repeated deformation or rupture of the protrusion;
- patient's refusal to undergo neurosurgical surgery affecting cerebral vessels.
The procedure is contraindicated in the case of the development of such pathological conditions as motor and speech disorders, vascular malformations, vasospasm, increased blood clotting, type 2 diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma.
Aneurysm embolization is performed in the event of the development of such pathologies of internal organs as:
- arteriovenous malformation;
- bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruption of homeostasis in the postpartum period;
- development of hepatocellular carcinoma;
- kidney cancer;
- preparation for liver resection.
Despite the fact that the intervention is a safe procedure, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age and hereditary factors. Contraindications for the operation are pregnancy and incomplete patency of blood vessels.
During full-term pregnancy, tracheal intubation poses a danger, causing blockade of the pressor response during general anesthesia.
Neurosurgical pathology in the expectant mother, its treatment with endovascular blockage can cause premature birth or have a teratogenic effect, although it is not an absolute contraindication for the procedure.
How is the operation performed?
Aneurysm surgery is always performed using general anesthesia.
When clipping, after accessing the brain, the tissue under which the aneurysm is located is exposed. Next, the adjacent tissues are sharply dissected and the carrier artery is exposed. When the neck of the aneurysm is isolated, a clip is applied to it. For small aneurysms, optical instruments are used to increase the scale of the surgical field. Sometimes, during surgery, the patient discovers a complex anatomical structure of the aneurysm and surrounding tissues, as well as a significant size of the aneurysmal protrusion. In this case, temporary application of clips can be used, which are removed after the main stage of the operation - application of the clip to the neck of the aneurysm.
cerebral aneurysm clipping technique
With endovascular intervention, access to the aneurysm is achieved by puncturing the femoral artery and guiding the probe under MRI control to the surgical site. At the end of the probe there is a balloon inserted into the lumen of the aneurysm. Once the balloon is placed and secured in the aneurysm, the aneurysm is embolized (“blocked”) and becomes functionally inactive.
endovascular aneurysm embolization
All stages of the operation are carried out under strict MRI or CT control. After the intervention, the patient spends about five days in the intensive care unit, after which he can be transferred to the neurosurgery department.
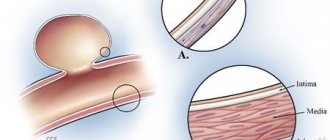
Characteristics of the pathology
A cerebral aneurysm differs from a normal element of the circulatory system in structure - it lacks some layers (muscular wall, elastic membrane) characteristic of normal vessels.
The wall of the aneurysm consists of connective tissue, which has low extensibility, plasticity, and elasticity, and is therefore susceptible to mechanical damage. Rupture of an aneurysm located in the brain is a common (85% of cases) cause of hemorrhage in the subarachnoid (under the arachnoid membrane) space of a non-traumatic nature. As a result of hemorrhage in this localization, blood enters the space under the arachnoid membrane. Such foci of hemorrhage often cause impaired blood circulation in the brain tissue, which occurs in an acute, severe form.
These conditions have a high incidence of adverse outcomes. The prevalence of the pathology is about 13 cases per 100 thousand population annually. The average age of patients is 40-60 years. Rupture of the wall of the affected vessel leads to severe neurological deficit or death.
The main type of treatment is clipping of the aneurysm; during the procedure, it is excluded from the general blood flow of the vascular system supplying the brain. When a pathologically altered vessel ruptures, characteristic neurological symptoms are observed, which often depend on the location of the hemorrhage.