Patent foramen ovale is a congenital heart defect.
Congenital heart murmurs in infants indicate congenital heart pathologies and diseases, that is, they mean that the baby’s heart is not formed correctly. Of course, what matters is not the fact of their presence, this is just a symptom, but the fact that they impair blood circulation to varying degrees. Such children have a slightly bluish tint to their skin, they do not gain weight well, and they experience shortness of breath. Children with congenital heart murmurs are always carefully examined, and especially serious cases are eliminated through surgery. It can be:
- Ventricular septal defect (one or more holes between the right and left ventricles of the heart) and mitral valve prolapse;
- Stenosis (narrowing) of the pulmonary artery;
- Non-overgrowing botal duct;
- Other congenital heart defects.
In some newborns, noises are detected in the maternity ward, in others they become noticeable a month or two after birth, when the little person’s circulatory system is reconstructed. When the noise gets worse over time, doctors begin to decide how to treat the baby. It is impossible to develop uniform recommendations common to all babies - the child grows, his body “matures” every month.
Some children are recommended to be constantly monitored by a cardiologist, while others are recommended to be monitored several times a year. If necessary, infants are prescribed several courses of cardiotrophic therapy; in other cases, non-drug methods of health support are sufficient. If the degree of the defect is severe, then the only method of correcting it will be surgery.
everything is within normal limits.
We also have had murmurs in the heart area since 8 months, and they are caused by the presence of an additional chord, and the fact that the child is growing quickly, the heart cannot keep up with it. Go to a rheumatologist (cardiologist). And even if a sleeping child has a heart rate, it should be 110 somewhere. The doctor should tell you about this, I measured it.
21-11-2008, 22:24
So we need to do a cardiogram and see. but still experiencing it. Okay, let’s say these are functional noises, but since they manifest themselves more strongly, it means we need to be more careful. Imagine today I called the regiment to make an appointment for an ECG, they made an appointment for me on DECEMBER 19th. I think it can be done.
As I was told, if the nasolabial triangle does not turn blue, the child screams and eats well, all these noises will go away before the age of 3, M.b. additional chord, oval window is open. It’s not scary, but to calm down, do an ultrasound!
Observation, principles of treatment
It would be ideal if mother and baby could be constantly monitored by one doctor. This way, it will be easier to track and record: timbre, dynamics, nature of the disease. And it will be easier to decide on further treatment tactics.
If the noise is not dangerous, periodic monitoring will be required once a year: consultation and echocardiography. Children can eventually lead a normal lifestyle: dancing, sports, swimming, etc.
In particularly serious cases, therapeutic techniques are selected individually for each baby. Choose one of two treatment methods:
Conservative is:
- the autoimmune reaction is suppressed by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- heart failure is eliminated - neurotrophic drugs;
- pathogenic bacteria are killed by antibiotics;
- strengthen blood vessels - angio protectors.
Surgical - if the disease progresses rapidly, surgical intervention is indicated.
Is a heart murmur dangerous? Let's try to figure it out.
Not all noises are dangerous, but only those that cause serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart. If the examination does not reveal any serious health problems, then there is no cause for concern.
But when the noise is accompanied by accompanying symptoms: bluish skin, lack of body weight, poor appetite, etc., it will clearly indicate a disease. Without timely treatment, everything can end sadly.
Important:
- visit a cardiologist on time;
- undergo examinations to monitor the baby’s condition;
- strictly follow all doctor's instructions.
If surgery is required, do it immediately. Because it is prescribed in exceptional cases, life depends on it.
Causes at different ages
Infants
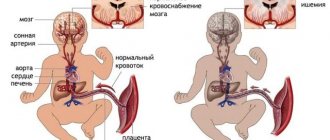
If a pediatrician listens to a murmur in the heart of a newborn, he must first rule out congenital pathologies, because heart defects are quite common and are second in frequency only to defects of the nervous system. They are provoked by various negative effects on the pregnant woman in the first months of gestation, when the fetus’s heart and great vessels are formed.
In the first or second month of life, a murmur in the baby’s heart may be associated with the active ductus arteriosus. Such a vessel also participated in intrauterine blood circulation, and after childbirth it normally closes in the first days of life, although in babies born prematurely, for example, after a cesarean section, the normal period for its closure is 2 months.
Children over one year old
In children aged from 12 months to 6-7 years, both innocent noises caused by physiological and non-hazardous reasons, for example, the presence of MARS or the thinness of the child, and pathological noises indicating quite serious pathologies can occur.
If, at the age of up to 3 years, the pediatrician listens to a systolic murmur, which occurs at the moment of heart contraction, changes in character when changing body position, is inconsistent and rather quiet, such a murmur is often functional.
Pupils
Quite often, the causes of functional murmurs in school-age children are an unbalanced diet or excess physical activity, as a result of which the myocardium does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen necessary for work. In addition, quite active growth at the age of 6-10 years causes a discrepancy in the size of the heart sac, which can also manifest as murmur.
Teenagers
Functional noises that arise in adolescence are often associated with the innervation of the heart, when the child has an imbalance in the influence of one of the parts of the nervous system (vegetative or sympathetic). Over time, this imbalance is leveled out and the noise disappears. However, organic murmurs that appear due to inflammatory myocardial disease or other cardiac pathology are also common in adolescents.
Actions after the test
The causes of heart murmurs in a child influence the diagnosis. Only a complete examination will show the whole picture of the disease. In addition to all of the above diagnostic methods, there is another one - magnetic resonance imaging. This method is not cheap and is used quite rarely. Sometimes it is combined with the introduction of an intravenous dye. Thanks to this method, you can see the work of several body systems.
After the examination has been carried out and a diagnosis has been made, you must listen carefully to the doctor. The frequency of visits to a specialist, recommendations for physical activity, and treatment of the child will depend on the verdict he makes.
Parents of a sick baby should gain strength and patience. Follow all the measures prescribed by the cardiologist.
If a heart murmur is detected in a child, Komarovsky advises going to the doctor as soon as possible and always listening to his advice. Sometimes these sounds are completely harmless and will go away over time. Let the baby run, play, swim, do not prohibit him from moving.
Why does a child have trouble falling asleep and what to do about it?
To determine whether a heart murmur is caused by age-related changes in the baby’s body or whether it is a manifestation of a serious illness, you need to contact a pediatric cardiologist and undergo an instrumental examination. This will determine the exact cause of the noise and confirm or rule out the diagnosis. Depending on the results, the child will be assigned to one of the following groups:
- Children who are practically healthy.
- Children who require supervision.
- Children who should be treated electively or urgently.
One of the most important conditions for the full development of any baby is sound, deep and restful sleep. However, sometimes parents encounter certain difficulties in the process of putting their child to sleep. They cannot understand why the child has trouble falling asleep in the evening. It can be especially difficult to get very young children into bed.
If a child has trouble falling asleep at night, this happens for certain reasons. They are usually divided into physiological, psychological and everyday. Physiological reasons reflect the baby’s health status. But everyday and psychological problems are the result of incorrect actions of adult family members. True, in preschoolers they may appear due to the peculiarities of mental development in a given period. So, let's look at what prevents a child from falling asleep quickly.
Reasons for appearance
Let's find out the causes of heart murmurs in a child. Most often they are of an anatomical direction.
- Incorrect location of chords in the left ventricle. They have several other names: false chords, pseudochords. The intensity of abnormal sounds in the heart depends on their location and quantity. These chordae are harmless and do not affect blood flow.
- Heart murmurs are more common in newborns than in older children. This phenomenon is caused by a change in the shape of the left ventricle. Over time, this pathology passes; the sound can cause the mitral or aortic valve to bend.
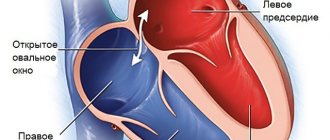
- Heart murmurs in a three-year-old child appear due to an unclosed oval window. It should usually be gone by two months.
The reasons for the appearance of sounds in the heart muscle in newborns include:
- rickets;
- anemia;
- infectious diseases.
Experts do not rule out that the symptom may appear due to the emotional state and physical activity. And let's talk a little more about that...
Symptoms and signs
In most cases, there are no symptoms of a patent oval window. The child looks and behaves like other children, without showing any complaints or showing concern. Pathology is often detected by ultrasound, prescribed as a preventive study. However, an experienced pediatrician, and even more so a pediatric cardiologist, can note some signs that are alarming regarding cardiac pathology: 1.
Bluish, even slight, staining of the nasolabial triangle, which appears when coughing, crying or physical activity. 2. Repeated cases of colds or other infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the respiratory system. 3. Delay in physical development, difficulty performing physical exercises. 4.
Pathological phenomena that are benign in origin, except for the characteristic picture, do not manifest themselves in any way during the examination. There are no negative consequences associated with functional noise in children. They carry organic changes that occur in the heart. They are characterized by the following symptoms:
- accelerated breathing;
- confusion;
- blue discoloration of fingertips, lips, earlobes;
- development slowdown;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- fast fatiguability.
Auscultation makes it possible to hear the main symptom of the disease - pathological sound effects. Normally they should not be in cavities. Over time they can grow. When they become severe, careful diagnosis and treatment are recommended.
Dr. Komarovsky advises that if the symptoms mentioned above appear, contact a pediatric cardiologist. Instrumental and laboratory tests will help to understand the problem. If the condition is functional, then the noise will disappear on its own without therapy.
Komarovsky's opinion
The opinion of doctors regarding an open oval window is very ambiguous. Some experts consider this pathology to be temporary and not life-threatening. Proponents of this theory insist on the absence of hemodynamic disturbances. Therefore, the child does not require any treatment or observation for this matter. Other doctors insist that there is a danger in the presence of an open oval window.
They note an increased risk of pathologies such as embolism. However, medical statistics say that completely healthy children have the same chance of developing an embolism as children with a patent foramen ovale. The only restriction that is relevant for children with an open oval window is professional sports.
Psycho-emotional and physical stress during training, activities and performances play a negative role in the development of the disease. In addition, an anomaly accompanying the open foramen ovale called an aneurysm of the interatrial septum also aggravates the course. An aneurysm increases the likelihood of complications by almost 2 times.
A well-known pediatrician confirms that heart murmurs are detected in many children, and the doctor’s task should be a competent differential diagnosis, after which it will be clear whether such a symptom is a short-term age-related phenomenon or appeared due to illness.
Prognosis for the disease
Doctors diagnose congenital heart disease in 8 babies per thousand newborns. Only the most difficult situations result in death in 20% of cases.
Timely consultation with a doctor and surgical intervention will significantly minimize the danger, avoid serious problems, and allow the baby to live a long time. The only limitation may be a ban on significant physical activity.
Diagnosis and further actions
After a thorough examination of the child, the diagnosis was confirmed. What to do next? Typically, the doctor will recommend following the following course of action. The child is placed under the strict supervision of a pediatric cardiologist. Parents should establish contact with this doctor, since the observation is long. It is necessary to notify the doctor of any changes in the child’s condition.
Every year you need to undergo a routine examination, the purpose of which is to find out the size of the oval window. Based on the data obtained, we can draw a conclusion about the dynamics in the condition of the little patient. If the oval window decreases, then further wait-and-see tactics are fully justified. In such cases, there is reason to believe that the hole will close sooner or later.
Patent foramen ovale is a common condition in newborns.
In the first 48 hours after the birth of the baby, a neonatologist examines the child, auscultates the lungs and valves. Some children have murmurs, in most cases functional, that is, not provoked by serious organic damage to the valve apparatus or congenital defects. However, sometimes heart murmurs in a newborn are pathological and indicate a congenital disease.
In older children, swirls may appear after an illness. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the cause of cardiac murmurs from the first day of a child’s life. To do this, a cardiologist or pediatrician conducts a full diagnostic examination and, if a pathological noise is detected, prescribes the necessary treatment.
If you or your child are diagnosed with a systolic murmur, this means that it is necessary to undergo additional examinations in order to identify the specific cause of this phenomenon.
The following diagnostic procedures are used:
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- Holter 24-hour ECG monitoring;
- chest x-ray;
- echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the heart);
- functional load tests (bicycle ergometry, step test);
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
They do appropriate laboratory tests, which include general and biochemical blood and urine tests, rheumatic tests, coagulogram and other specific studies.
In addition, the patient will need to consult a rheumatologist, allergist, and endocrinologist. If no organic changes are detected, then the person is simply put under control. This means that he needs to periodically come to the hospital for preventive examinations. General restoratives (physical therapy or physiotherapy) are also prescribed. If serious pathologies are detected, the patient is prescribed treatment.
Systolic murmurs appear due to disruption of normal blood flow in the cavities of the heart, changes in blood composition, or the presence of obstructions and abnormal structures. Such sounds are heard at the moment of contraction of the ventricular myocardium.
Functional (innocent) murmurs occur in pathological conditions not associated with a violation of the internal architecture of the heart, and usually disappear over time. Organic ones develop during structural changes and signal serious diseases. To establish the exact cause, additional examinations are prescribed.
How to make a diagnosis
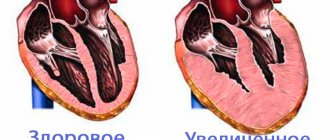
We recommend reading: Causes of cardiomegaly
The diagnosis takes into account:
- clinical symptoms - cyanosis of the child’s lips and face, shortness of breath when moving, changes in rhythm, trembling of the chest when palpating the heart area, the presence of a visible venous network under the skin, pulsating vessels;
- phonocardiography and ECG - clarify the localization of damage to the heart chambers;
- Ultrasound and Dopplerography - allow you to establish blood flow in different phases of myocardial contraction, direction, volume of return, degree of adaptability of the ventricles and atria.
What is a heart murmur and how does it happen?
Thanks to the work of the cardiovascular system, tissues and organs receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen. After birth, a significant restructuring of blood circulation in the pulmonary vessels occurs in the child’s body, the dominant of the right ventricle is replaced by the left, physiological closure of the ductus arteriosus is observed, and the pressure in the pulmonary trunk increases to facilitate the work of the left ventricle. Such changes cause cardiac murmurs.
During the examination, the doctor conducts auscultation using a phonendoscope, listening to the heart valves in turn:
- mitral;
- aortic;
- pulmonary valve;
- tricuspid valve.
The auscultation method helps to assess the frequency and rhythm of tones, their melody and timbre.
Why do extraneous sounds appear?
Parents, having heard the diagnosis (heart murmur), begin to look for the cause of its occurrence. Many of them were described above, and we will talk about some now.
- There has been a narrowing of the large vessels that come from the heart.
- The valves of the heart itself are also narrowed.
- The valve flaps do not close tightly. As a result, the blood returns back.
- The presence of holes in the septum of the heart.
- There is a gap between the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
- The surface of the heart chamber has a rough appearance, there are depressions and bulges.
Heart murmurs in a 2-year-old child appear due to the maturation of the cardiovascular system. This process is associated with an increase in blood pressure. This figure is gradually approaching that of an adult. In this regard, the intensity of blood flow in the cardiac cavities increases. All ducts should be closed by this age. Most likely, the appearance of sounds occurs due to congenital valve pathologies.
The first examination of the baby's heart is carried out immediately after birth. Pathology during this period cannot always be detected. Every month the pediatrician listens to the baby, and if he suddenly suspects heart problems, parents should not immediately panic. During the consultation, the doctor will tell you why heart murmurs in a child are dangerous. As mentioned above, there are dangerous and non-dangerous heart sounds. Let's talk about the first ones, they are the ones who indicate that the body is sick.
- Metabolic processes are disrupted, anemia. The brain compensates for the lack of oxygen by increasing blood pumping. And this leads to heart murmurs.
- Excess thyroid hormones, which leads to changes in blood viscosity and extraneous sounds in the main organ of the circulatory system.
- Heart defects, including stenosis, heart attack, mitral insufficiency and others. It is possible to identify which of them is causing the noise only after a full examination has been carried out.
- Enlargement of the chambers of the heart. The cause of the disease is muscle inflammation, high blood pressure, and disruption of the thyroid gland.
- Endocarditis is inflammation of the inner lining of the heart.
These are the causes of heart murmurs in a child, which are dangerous.
Open oval window (hole) in the heart: causes, closure, prognosis
When there is no hemodynamic disturbance, treatment is not required.
Unlike pathological noise, functional noise is always heard during systole, it is less intense. In newborns, auscultation reveals a greater spread of vortices beyond the boundaries of the heart. If the child does not have a rapid heartbeat, cyanosis or signs of heart failure, then such a noise is not dangerous, but requires observation. It is enough to have an assessment of functional noise over time, recording cardiogram data, and ultrasound of the heart.
What is recommended for parents
Listening to a heart murmur in a child should cause concern for parents. It is necessary to bring the diagnosis to full confidence in the causes. If necessary, consult with a cardiac surgeon several times.
Only a specialist can recommend the correct observation and treatment, and plan a specific date for the operation. If the risk of surgical treatment in terms of complications exceeds the possibility of the expected development of decompensation, then parents are informed about this.
The child must be registered at the dispensary and examined at least once a quarter. The baby needs to be protected from infections, colds, and the sufficiency of vitamins in the diet must be monitored. If necessary, the doctor prescribes supportive therapy and exempts the student from physical education.
Functional noise does not require significant restrictions. You should talk to your pediatrician about the possibility of playing sports. Regular physical exercise is not contraindicated.
How healthy a child grows up depends on the adults. Given the current widespread trend towards a reduction in specialized healthcare services, parents should be prepared for paid consultations.
The Right Action
The basis for the prevention of heart disease in children is compliance with regular medical examinations by a neonatologist and pediatrician according to the following algorithm:
- The primary examination is carried out by a neonatologist in the maternity hospital, when he evaluates cardiac activity using auscultation.
- Screening to diagnose congenital heart defects is done if murmurs are observed in the organ.
- Based on saturation data and ultrasound of the heart, the doctor confirms or removes the diagnosis.
- After discharge from the maternity hospital, the child is supervised at home by a general practitioner for up to a month. Normally, after the third or fourth week, the venous duct closes and the circulatory system begins to fully function. A medical examination helps to identify the slightest deviation from the norm, diagnosing murmurs in newborns.
- Particularly important is the child's infancy (infant up to one year), when the complete restructuring of blood circulation is completed and the doctor makes a conclusion about the nature of the noise.
- Blueness of the skin is the main symptom of hemodynamic disturbances. In combination with severe weakness, dizziness and low hemoglobin - these are indications for examination.
- In addition to auscultation, all children with signs of a heart murmur should be referred for phonocardiography, echocardiography, ultrasound of the heart and great vessels.
- Refusal to examine and treat a child with a heart murmur leads to serious hemodynamic disturbances and heart failure. Regular examinations with a pediatrician help prevent the development of organ pathology.
Most heart murmurs are functional, but without proper detail of complaints and observation, it is impossible to determine the nature of the blood flow disturbance. Neonatologists and cardiologists examine and treat newborns up to 28 days, and later pediatricians.
One of the primary types of examination in cardiology is auscultation, that is, listening.
Prevention
There is no direct prevention of heart murmurs in a child. It is necessary to prevent defects and diseases accompanied by noise.
- Prevention of birth defects begins already in the first trimester of pregnancy. It involves identifying a TORCH infection. Heart formation occurs during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. And such microorganisms and protozoa as toxoplasma, herpes viruses, rubella, hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, as well as treponema pallidum, can cause congenital defects.
- A scheduled visit to your local pediatrician will ensure early detection of heart pathology.
- Improving the child’s health and strengthening his immunity are preventive measures against various infections. Particularly dangerous are frequent sore throats, leading to the formation of autoantibodies. The latter damage the inner lining of the heart, which leads to acquired defects.
- Compliance with all doctor’s recommendations if the child is ill. Thus, bed rest for infections and intoxications is prescribed specifically to relieve the heart muscle. Even if the presence of myocarditis (toxic or infectious) has not been confirmed. This is done to prevent heart failure.
- Special physical exercises will strengthen the heart muscle. But if a child complains of fatigue, you should not force him to exercise. After all, this may be the first signal of heart pathology.
When does systolic heart murmur occur?
The pathogenesis of the phenomenon is simple. Systolic murmur at the apex of the heart occurs due to disruption of the linear flow of blood during contraction of the ventricles, resulting in turbulence that creates additional sounds. This is observed with narrowing, abnormal formations, regurgitation (pathological return), acceleration of blood flow (due to changes in composition, as in anemia).
If normal tones sound like clear beats, then pathological noises resemble buzzing, hissing, and rustling. They are accompanied by additional phenomena - “cat purring” (diastolic tremors), conduction to the axillary region (scapula area), rapid heartbeat.
Depending on the etiology of this auscultatory phenomenon, functional (also called innocent) and organic noises are distinguished. The first category includes everything with a transient nature. And under certain conditions, the normal state is restored. The second type occurs during structural changes in cardiac tissue. In this case, the process is considered non-negotiable, and treatment becomes more difficult.
Functional (innocent) noises appear in the following cases:
- physical stress;
- nervous excitement and neuroses;
- fever, infectious diseases;
- hyperthyroidism;
- anemic syndrome;
- asthenic constitution;
- pregnancy;
- relative valve insufficiency.
Organic noises are characteristic of the following pathologies:
- coarctation (narrowing) of the aorta or pulmonary arteries;
- dilatation of the aorta or other vessels;
- aortic valve insufficiency;
- additional abnormal chords;
- mitral or tricuspid insufficiency;
- valve stenosis;
- combined defects.
In a 17-18 year old teenager with an asthenic physique, in some cases a physiological systolic murmur is detected during examination, but it is considered a variant of the norm.
Getting rid of illness
If suddenly you see that your baby:
- gets tired quickly;
- he has shortness of breath;
- sometimes complains of headache and dizziness;
- the skin has a bluish color;
- looks younger than his peers.
Go to your pediatrician right away. He will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. The following methods are used for these purposes.
- Visual. The skin is bluish, the fingertips and nails are deformed.
- The doctor listens to the chest. Some heart diseases can be diagnosed this way.
- Electrocardiography is a graphic representation of heart rhythms. In this way, disturbances in rhythms and deviations in the main organ of the hematopoietic system are determined.
- Phonocardiography. The graph shows the sounds that accompany the work of the heart muscle.
- Echocardiography is an ultrasound examination with which you can not only see a picture of the heart, but also hear its work, including murmurs.
If a murmur is detected in the child’s heart, the doctor prescribes treatment. There are three main directions.
- Follow-up with a cardiologist. It is carried out depending on the severity of circulatory disorders. During observation, the specialist may prescribe diuretics or supportive medications to the child. If the disease develops rapidly, surgery is prescribed.
- Supportive therapy. Consists of long-term medication if surgery is undesirable.
- Surgical intervention. It is prescribed if congenital defects and noises are identified and their rapid elimination is necessary in order to avoid serious complications. After the operation, medication, rehabilitation procedures and suitable physical activity are prescribed.
It is best if the child is observed by one cardiologist throughout the entire period of treatment. A specialist, knowing the features of the course of the disease, will see in which direction changes are occurring.
What does noise in a child mean?
Detection of systolic heart murmurs in a child does not indicate dangerous diseases. A similar condition is often found in infants, but the reason is the imperfect development of the cardiovascular system and the disproportionality of certain structures. This usually goes away with age.
Another source is the individual congenital features of the structure of the heart (additional chords (strands connecting the papillary muscles and valves)). This is considered normal and does not require any treatment.
Often this phenomenon develops as a result of physical or nervous stress, fever or infectious diseases. When these conditions pass, the systolic murmur disappears.
There are many dangerous diseases in which this diagnostic sign is also detected. These include:
- ventricular septal defect – in this case, blood is discharged from one ventricle to another;
- anomalies of the pulmonary veins and aorta - include dilation or narrowing (coarctation) of blood vessels;
- congenital valve defects (insufficiency or stenosis) - in this case, blood returns to the heart cavities, or has difficulty passing through the narrowed lumen;
- combined pathologies (tetralogy, pentad of Fallot) – combine several developmental anomalies at once.
In this case, the danger is much greater; more often such conditions require surgical intervention. However, with early detection of pathology and proper treatment, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Reasons why a teenager may often bleed from the nose
Why does a teenager often bleed from the nose? Periodic nosebleeds in adolescents can be caused by many reasons, because during puberty the body undergoes restructuring. The transition to adolescence is a rather difficult period. Indeed, in addition to the annually increasing school load and attendance at various sections, attraction to the opposite sex increases and stress resistance decreases. Parents should be sympathetic to the transition period of their child and help him go through this difficult period with them.
Why is this happening
Nosebleeds are common. Children's pediatricians encounter them as one of the causes of various diseases, but most often bleeding in adolescents can occur due to injuries or acute respiratory viral infections.
Let's look at the main reasons that cause this phenomenon:
- The anatomical features of the nose, which consist in the close location of capillaries, influence frequent injuries to blood vessels in this area.
- The presence of neoplasms, vascular defects, and displacement of the nasal septum contribute to frequent bleeding.
- Infectious viral diseases, complicated by sneezing and runny nose, often damage the nasal mucosa.
- In winter, during the heating season or during dry summers, the nasal mucosa dries out, which provokes the formation of a crust that damages the capillaries of the nose.
- Hereditary pathologies of the circulatory system.
- Lack of vitamin C in the body.
- Children often break their noses during noisy games, in the gym and in sports clubs.
- Excessive physical or emotional stress increases blood pressure, which can cause ruptured capillaries in the nasal cavity.
- Bleeding can be caused by various blood diseases (thrombopenia, hemophilia).
- Often liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis) affect blood clotting rates.
- Pathology of the nasopharynx with sinusitis, sinusitis and allergies.
- With long-term use of vasoconstrictor drugs.
- The cause of nosebleeds can be hormonal levels, most often this occurs in girls. In this case, the blood flows down in small drops and quickly stops. This deviation will disappear after the teenager’s body is fully formed.
If a teenager has a nosebleed, you should pay attention to the accompanying signs. Shortness of breath, fatigue, lethargy, redness of the face. Do not forget to inform your doctor about this, this information will help speed up the diagnosis of the disease.
If the nosebleed recurs, you should undergo additional examination:
- of cardio-vascular system;
- spleen, heart and kidneys;
- donate blood for OBC;
- check the nasopharynx for tumors;
- undergo screening for atherosclerosis.
What to do if there is bleeding
The main thing is not to get confused at the right moment. Do not forget that spontaneous bleeding will scare not only the baby, but also the teenager. Additional anxiety contributes to an increase in blood pressure, and as a result, increases blood flow.
The following measures must be taken:
- Calm the teenager.
- Place him on a chair, ensuring that his head is slightly tilted forward so that the blood flows out without obstruction.
- It is forbidden to tilt your head back, otherwise blood will go into the nasopharynx and may cause vomiting.
- If you lose consciousness, you should sniff ammonia, place it on a flat surface and turn your head to the side.
- Do not blow your nose, as this can lead to additional damage to blood vessels.
- Press a cold compress onto the bridge of your nose to constrict the blood vessels.
- It is unacceptable to give your child strong tea and coffee, as they increase blood pressure.
- Insert a gauze swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide into the nostril (you cannot use cotton wool) for a vasoconstrictor effect.
If the bleeding does not stop within five minutes, call an ambulance.
If nosebleeds are caused by the child’s transitional age, then it is worth taking a number of preventive measures:
- ensure additional intake of vitamins C, K, A and calcium supplements into the body;
- regulate indoor air humidity;
- Clean the air conditioner regularly;
- limit exposure to allergens;
- control the physical and emotional stress of a teenager.