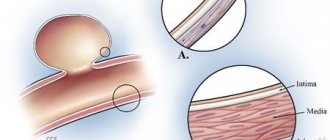
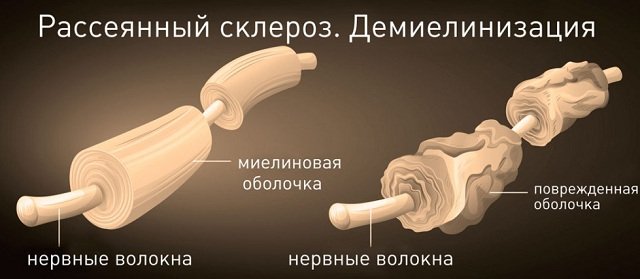
Demyelination is a pathological process when the myelin sheath covering nerve fibers becomes deformed.
Since this sheath performs the function of protecting nerve fibers, maintaining electrical excitation along the fiber without loss, demyelination leads to disruption.
Functionality of nerve fibers and pathologies of the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous system and brain.
When these fibers are damaged, multiple pathological processes can develop, the general name of which is demyelinating brain disease.
The destruction of the membrane can be provoked by certain viral or infectious diseases, as well as allergic processes of the human body.
In most cases, the demyelinating process leads to further disability.
This pathological condition of the body is most often diagnosed in childhood and in people under forty-five years of age. The disease tends to actively progress even in those geographical areas where it was not typical.
In most cases, the process of transmission of demyelinating diseases occurs due to hereditary predisposition.
Mechanism of demyelination development
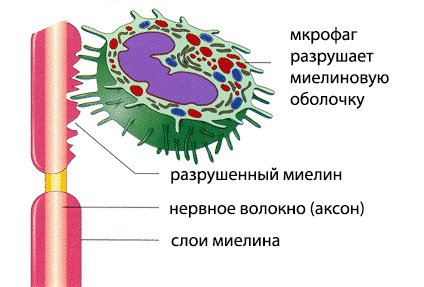
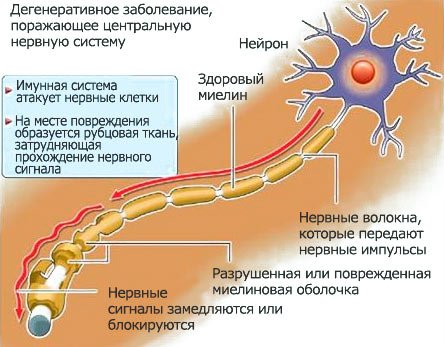
The fundamental mechanism for the development of demyelination is an autoimmune process, when antibodies to nervous tissue cells begin to be synthesized in a healthy body.
As a result, an inflammatory process occurs, leading to irreversible damage to neurons and leading to the destruction of the myelin sheath of the nerve.
This process leads to disruption of the transmission of nerve excitations along nerve fibers, which disrupts the normal processes of the body.
central nervous system
Classification
Classification of demyelination occurs into two types:
- Damage to myelin, a consequence of a gene disorder, called myelinoclasty;
- Deformation of the integrity of the myelin sheaths under the influence of factors that are not related to myelin (myelinopathy).
Also, the classification of the process occurs according to the location of the pathological process.
Among them are:
- Deformation of the membranes in the central nervous system;
- Destruction of myelin sheaths in the peripheral structures of the nervous system.
The final division of demyelination is based on prevalence.
The following subspecies are distinguished:
- Isolated , when disruption of the myelin sheaths occurs in one place;
- Generalized, when the demyelinating disease affects many membranes in different parts of the nervous system.
Causes and mechanisms of demyelination
Causes of demyelination
It is noted that demyelination has a greater number of recorded lesions, according to geographic location and race. The disease is registered predominantly in people of the Caucasian race, rather than in blacks and other racial representatives.
As for geography, demyelination is recorded mainly in Siberia, the central part of the Russian Federation, the central and northern parts of the United States, and Europe.
The most frequently provoked causes of risk are listed below:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Damage to the myelin sheath by autoimmune agents;
- Failure in metabolic processes;
- Strong and prolonged psycho-emotional stress;
- Toxic damage to the body from gasoline, solvent vapors or heavy metals;
- Damage to the body by diseases of viral origin that affect cells that contribute to the formation of the myelin sheath;
- Bacteriological infections;
- Poor ecological state of the environment;
- With high consumption of proteins and animal fats;
- Primary tumor formations of the nervous system and metastases in nerve tissues.
The progression of the autoimmune process can start on its own, under unfavorable environmental conditions. In this case, heredity is the primary factor.
If a person has certain genes, or normal genes are mutated, then a large number of synthesized antibodies can occur, which penetrate the blood-brain barrier and lead to inflammatory processes and deformation of myelin.
If there are infectious agents in the human body, antibodies to the virus are formed, which is a normal reaction of a healthy body. Sometimes parasitic bacteria are similar to the myelin sheath and the body attacks both of them, mistaking them for foreign.
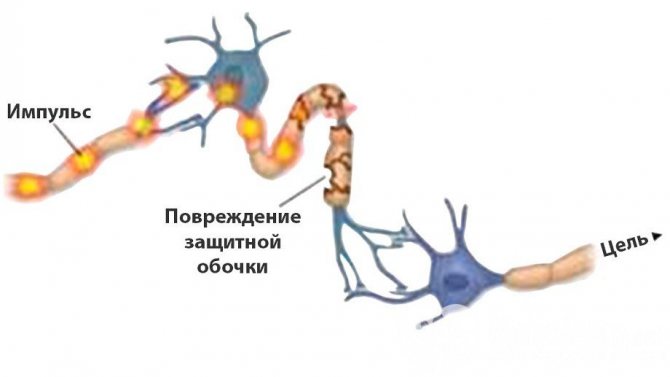
Inflammatory autoimmune diseases lead to disturbances in the conduction of nerve impulses, which can be resumed.
Partial damage to the myelin sheath causes a condition in which impulses are not completely transmitted, but perform part of their functions.
If this condition is left untreated, the lack of myelin will lead to complete destruction of the sheath and the inability of signal transmission along the nerve fibers.
The essence of pathology
Most people don't know what it is, what brain demyelination is. However, demyelinating diseases of the nervous system occur in both children and adults. Interestingly, the frequency of their occurrence is related to geographic location and race: the largest number of patients with this diagnosis are Caucasians and are observed in Europe and America.
Neurons have a specific shape that distinguishes them from all other types of cells. They have very long processes, some of which are covered with a myelin sheath, which allows the transmission of nerve impulses and makes this process faster. If the myelin is destroyed, the process will either not be able to communicate with other neurons through electrophysiological impulses at all, or this process will be extremely difficult.
Subsequently, the structure of the human body whose innervation is connected with the damaged nerve will suffer. This means that the disappearance of the myelin sheath can have a wide variety of symptoms and consequences. Patients with similar diagnoses, but different localization of the pathological focus can live for different amounts of time; the prognosis depends on the importance of the affected structure.
The immune system plays a very important role in the destruction of the membrane, suddenly attacking the living structures of the body.
In many cases, this is explained by the fact that the immune system reacts very violently to infectious pathogens located in the medulla, and at the same time to the structural components of the central nervous system; a so-called autoimmune reaction develops. But there are other, non-infectious reasons for such failures.
Some causes of this central nervous system disease do not depend on lifestyle (for example, heredity), others are associated with a person’s neglectful attitude towards his own health.
Most likely, the demyelinating process of the brain occurs under the influence of several factors simultaneously.
The development of this disease may be associated with the following factors:
- Defects in hereditary information associated with the formation of the myelin sheath.
- Adverse habits that cause poisoning of neurons with smoke, narcotic compounds, and alcohol.
- Long-term exposure to stress.
- Viruses (rubella, herpes, measles)
- Neuroinfections that affect nerve cells.
- Hepatitis vaccination.
- An autoimmune disease that causes destruction of the myelin sheath.
- Metabolism failures.
- A paraneoplastic process that develops due to the growth of neoplasms.
- Intoxication with any potent harmful substances (including those used in everyday life - paints, acetone, drying oil), as well as toxic metabolic products.
Demyelination of the brain - symptoms
The clinical manifestations of demyelination depend on the location of the lesion, the degree of its development, as well as the body’s ability to independently restore the myelin sheath.
Deformation of the myelin sheath in certain local places is determined by partial paralysis. With partial demyelination, there is a loss of sensitivity in the area to which the affected nerve led.
When the myelin sheath of a generalized type is destroyed, the following symptoms are noted:
- Constant fatigue;
- Low physical endurance;
- Drowsiness;
- Deviations in the functioning of the intellect;
- The person has difficulty swallowing;
- Unsteady gait, staggering is possible;
- Decreased vision;
- Hand tremors - trembling with outstretched arms, may indicate the progression of demyelination foci;
- Digestive tract problems – fecal incontinence, uncontrolled urine output;
- Memory impairment;
- Hallucinations may occur;
- Convulsions;
- Unusual sensations in certain parts of the body.
If one of the above symptoms is detected, you should urgently contact a qualified neurologist.
Treatment
Treatment usually involves improving the patient's quality of life. This is achieved by treating symptoms or slowing the rate of demyelination. Treatment may include medications, lifestyle changes (eg, stopping smoking, adjusting daily routine to increase rest periods, changing diet), relaxation, exercise, patient education, and, in some cases, thalamic deep stimulation (for intractable tremor). . Also, depending on the phase and course of the disease, treatment is used that affects the innate immunity.
Treatment is specific to the patient and depends on the symptoms that are present with the disorder, as well as the phase of the disease.
How to stop demyelination?
It is practically impossible to completely stop the demyelination process, but it is possible to prevent the progression of the disease in advance.
Diagnosis and therapy of such pathological conditions, today, is a complex and practically unexplored process. However, great progress has occurred in research in the fields of immunology, biology and molecular genetics, which have been carried out for quite a long time.
The enormous efforts of scientists have made it possible to study the basic mechanisms of progression of demyelinating diseases and the factors that provoke its start.
Thanks to this, new treatment methods were invented.
The main way to diagnose the disease has been to examine the body using MRI, which helps to identify foci of demyelination even at the initial stages of development.
Features of multiple sclerosis
The peculiarity of multiple sclerosis is due to the fact that it is a frequently recorded form of destruction of the myelin sheath. This form of sclerosis is not associated with the usual term “sclerosis,” which is characterized by weakening of memory and intellectual activity.
According to statistics, this disease affects about two million people on the planet. Most of the patients belong to the young group and people of the middle age group (from twenty to forty years), predominantly female.
The main mechanism is the destruction of nerve fibers by antibodies produced by the body.
The consequence of this is the disintegration of the myelin sheaths, with its further replacement by connective tissues. “Scattered” characterizes the fact that demyelination can progress in any part of the nervous system, without tracking a clear dependence of the location of the lesion.
The factors that provoke this disease have not been definitively determined.
Doctors suggest that its development is influenced by a complex of factors, including: hereditary predisposition, external factors, as well as damage to the body by diseases of a viral or bacteriological nature.
It is noted that the dominant registration of multiple sclerosis is greater in countries where there is less sunlight.
Most often, several places in the nervous system are affected at once; processes also develop in the spinal cord and brain. A characteristic feature of multiple sclerosis is the detection of plaques of varying degrees of age during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination.
The detection of young and old plaques indicates progressive inflammation, and explains the difference in signs that change according to the degree of development of the disease.
Patients who are affected by multiple sclerosis with progressive demyelination are characterized by depression, a decrease in emotional background, a tendency toward sadness, or a completely opposite feeling of euphoria.
As the number of lesions and their size increases, changes occur in the motor system and sensitivity, as well as a decline in intellectual activity and thinking.
Prognosis for multiple sclerosis is more favorable if the pathology makes its debut with deviations in sensitivity and loss of vision.
If the first to appear are disturbances of the motor apparatus and loss of coordination, then the prognosis worsens, indicating damage to the subcortical pathways and the cerebellum.
Foci of demyelination on MRI scans: multiple sclerosis or not? – Medical
Our clinic diagnoses and treats demyelinating diseases: both purely autoimmune and those provoked by infection. In particular, we are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis, neuroborreliosis, chronic disseminated encephalomyelitis, etc.
Foci of demyelination in the brain or spinal cord found on MRI may be:
- A safe accidental discovery - a trace of a long-term disease that no longer requires treatment;
- A sign of ongoing demyelinating disease that needs to be treated.
Our task is to figure this out.
The focus of demyelination in the substance of the brain or spinal cord is an area where there once was or is currently an inflammatory process with the destruction of myelin - the sheath of the nerve pathways. More about demyelination
If foci of demyelination are found in the brain or spinal cord, the first thing to do is to find out the nature of the foci, the degree of their danger and the presence/absence of the need for treatment.
To clarify the diagnosis, we will offer you an examination by a neurologist and research for neuroinfections, autoimmune process (multiple sclerosis, autoimmune encephalomyelitis), rheumatic diseases involving the brain and/or spinal cord.
The results of these studies will clarify the situation and help to properly construct treatment, if necessary.
What finds are possible:
- Demyelination that was suffered and completed long ago (even in childhood) is a neuroinfection or an abnormal reaction to a vaccine, or some other completed inflammatory process. In this case, foci of demyelination can persist throughout life without presenting any danger. This situation usually does not require treatment.
- The current demyelinating inflammatory process is in the active phase or in the stage of temporary stop - remission. This inflammatory process can be caused either by excessive aggression of the immune system, when myelin proteins are mistakenly recognized by the immune system as foreign and dangerous, or by neuroinfection, or a combination of both processes. In this case, we will offer you treatment, and, if possible, immediate treatment - we are talking about the loss of working tissue of the brain and/or spinal cord. Read more about emergency treatment for multiple sclerosis attacks
| Foci of demyelination on MRI before and after treatment. After 4 months from the start of treatment, a decrease in lesions is visible - remyelination (diagnosis - multiple sclerosis, which occurred against the background of infection with the Epstein-Barr virus, mycoplasma and chlamyia). The earlier treatment is started, the better the prognosis for recovery. |
| Focus of demyelination in the substance of the spinal cord |
Are demyelination foci active or not? MRI of the brain with contrast, oligoclonal IgG in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood
The presence/absence of activity of demyelination foci at the current time can clarify a lot in the diagnosis and indicates the urgency of treatment. What is an active focus of demyelination: this is an area in the brain or spinal cord where the active process of myelin destruction is currently underway (exacerbation or debut of a demyelinating disease).
The answer to the origin and activity of demyelination foci in the brain can be obtained from MRI with gadolinium contrast. Foci in which demyelination is occurring right now accumulate a contrast agent, and this can be seen with MRI.
However, foci of demyelination accumulate contrast only during the period of active inflammation, and in the stage of remission (temporary stop of the disease) a false negative result is possible.
In this case, the diagnosis can be clarified by examining oligoclonal IgG in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood.
Oligoclonal IgG provides information about the presence/absence of increased immune system activity in the brain and spinal cord.
With a sufficient degree of reliability, the results of studies of oligoclonal IgG and MRI with contrast are interpreted as follows:
- There is no current demyelinating disease - foci of demyelination do not accumulate contrast on MRI, oligoclonal IgG is normal. Treatment most likely will not be needed.
- There is a current demyelinating disease, but at the moment it is inactive (remission) - on MRI, contrast does not accumulate in the foci of demyelination, oligoclonal IgG in the cerebrospinal fluid is increased. Planned treatment will be required.
- There is a current demyelinating disease, and at the moment it is active (exacerbation or debut) - foci of demyelination accumulate contrast on MRI, oligoclonal IgG in the cerebrospinal fluid is increased. In this case, we will offer you urgent treatment to stop the process of destruction of brain tissue. Read more about emergency treatment for multiple sclerosis attacks
How will the examination be structured if foci of demyelination are detected in the brain or spinal cord?
To help clarify the situation:
- Detailed neurological examination.
Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases are characterized by very specific symptoms. These disturbances of reflexes, sensitivity, coordination, gnosis, praxis, etc. according to a certain scheme. A neurological examination helps narrow down the search, reduce examination time and reduce diagnostic costs. - Laboratory examination. These are tests for neuroinfections, autoimmune diseases, immunological studies. Typically these are several of the studies listed on this page.
- The study of evoked potentials is included in the standard examination for demyelinating diseases, incl. when confirming the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis.
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG) is a set of methods for studying the conduction of nervous excitation along the pathways of the nervous system (brain - spinal cord - peripheral nerves - muscles).
Often it is ENMG that brings final clarity to the diagnosis when foci of demyelination are detected in the brain or spinal cord.
| Clinical examination by a neurologist for suspected multiple sclerosis. Testing reflexes, sensitivity, coordination, etc. |
If foci of demyelination are active (accumulate contrast), if neurological symptoms increase, we will offer treatment immediately. In this situation, it is urgent to stop the destruction of the brain and/or spinal cord.
During the treatment process, we will clarify the diagnosis, and as soon as the diagnosis is clear, we will offer you planned treatment based on the diagnostic results. If there is no active demyelination at the moment, there is time to calmly figure out what is happening. The research data obtained helps to understand the cause of demyelination and forms the basis for treatment regimens.
Does it make practical sense to measure myelin basic protein and myelin antibodies? Usually it doesn't. Why:
- With infectious, rheumatic and even traumatic damage to the nervous system, myelin may be destroyed, its disposal will be required, and antibodies to its proteins may increase naturally. It is reliably impossible to differentiate the diagnosis in these cases.
- Immune aggression can be directed not against myelin basic protein, but against its other proteins (possibly several at once), the molecular structure of which is quite different. In this case, there will not be high levels of antibodies to myelin basic protein, despite ongoing demyelination.
Devic's disease
As this disease progresses, demyelination occurs, which affects the visual apparatus and spinal cord. This disease begins abruptly and develops quickly, leading to serious visual impairment and complete blindness.
Damage to the spinal cord manifests itself in loss of sensitivity, disruption of the functioning of the pelvic organs, as well as partial or complete paralysis.
Full symptoms may take two months to develop.
The prognosis for Devic's disease is unfavorable, especially for the adult age category.
The prognosis is more favorable in children with timely administration of immunosuppressants and glucocorticosteroids.
The exact treatment methods have not yet been finalized. The main goal of therapy is to relieve symptoms, use hormones and supportive care.
Forecast
The survival prognosis depends on the type of pathology, the nature of the course and the extent of brain damage. Partial or complete restoration of brain function is possible.
Demyelinating diseases, affecting the structures of the central nervous system and PNS, are associated with the destruction of the sheath surrounding the nerve fibers. In the initial stages of the disease, they may be asymptomatic. The prognosis with early diagnosis is more favorable. The disease cannot be completely cured and often leads to disability and death of the patient.
Our task is to figure this out.
What is special about Guillain-Barré syndrome?
This syndrome is characterized by characteristic damage to the peripheral nervous system, similar to progressive multiple nerve damage. This disease affects predominantly males, without an age limit.
The manifestation of symptoms is reduced to pain in the limbs, joints, back pain, complete or partial paralysis.
There is a frequent disturbance in the rhythm of heart contractions, increased sweating, and deviations in blood pressure, which indicates a violation of the vegetative-vascular system.
The prognosis for this syndrome is favorable, but a fifth of patients still have signs of damage to the nervous system.
Types and symptoms of damage to the peripheral nervous system
- Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. It begins acutely with severe pain in the muscles of the legs or arms, in the spine. A person experiences numbness, paresthesia, weakness, etc.
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Manifested by weakness in the limbs, areflexia, disturbances of autonomic and other functions in the limbs.
- Miller-Fisher syndrome. A rather rare disease that manifests itself as a combination of ataxia, ophthalmoplegia and areflexia.
and etc.
Marburg disease
This disease is one of the most dangerous forms of demyelination. This is explained by the fact that it begins to progress unexpectedly, the symptoms rapidly intensify, leading to death within a few months.
The onset of the disease resembles a simple defeat of the body by an infectious disease; fever and body convulsions may occur.
Lesions develop quickly, leading to serious damage to the musculoskeletal system, loss of sensitivity and loss of consciousness. Meningeal syndrome with vomiting and severe headaches is characteristic. There is often an increase in pressure inside the skull.
The unfavorable prognosis is explained by damage to a large part of the brain stem, in which the main pathways and nuclei of the cranial nerves are concentrated.
Death occurs within a few months.
What is special about progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy?
The abbreviation for this disease is PMLE, and is characterized by demyelination of the brain, more often recorded in older people, and accompanied by a large amount of the central nervous system.
Symptoms manifest themselves in paresis, convulsions, loss of space, loss of vision and intellectual activity, leading to severe dementia.
The peculiarity of this disease is that demyelination is observed along with damage to the immune system.
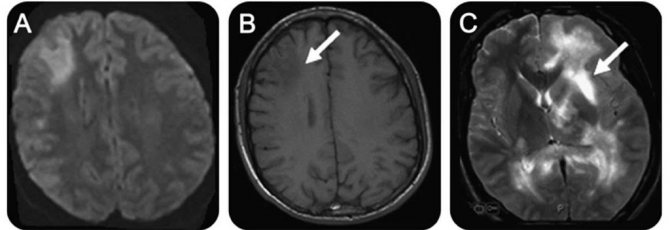
Demyelinating lesions of the white matter of the brain in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
All about the demyelinating process in the brain
Demyelinating process of the brain is a disease in which the sheath of the nerve fiber atrophies. In this case, neural connections are destroyed and the conductive functions of the brain are disrupted.
It is customary to refer to pathological processes of this type as multiple sclerosis, Alexander disease, encephalitis, polyradiculoneuritis, panencephalitis and other diseases.
What can cause demyelination
The causes of demyelination are still not fully understood. Modern medicine makes it possible to identify three main catalysts that increase the risk of developing disorders.
It is believed that demyelination occurs as a consequence of:
- Genetic factor - the disease develops against the background of inherited diseases. Pathological disorders occur against the background of aminoaciduria, leukodystrophy, etc.
- Acquired factor - the myelin sheaths are damaged due to inflammatory diseases caused by an infection that has entered the blood. It may be a consequence of vaccination. Less commonly, pathological changes are caused by injury; demyelination is also observed after tumor removal.
- Against the background of diseases, disruption of the structure of nerve fibers, especially the myelin sheath, occurs as a consequence of acute transverse myelitis, diffuse and multiple sclerosis. Metabolic problems, deficiency of vitamins of a certain group, myelinosis and other conditions are catalysts for damage.
Symptoms of demyelination of the head brain
Signs of the demyelinating process appear almost immediately at the initial stage of the disorders. Symptoms help determine the presence of problems in the functioning of the central nervous system. Additional examination using MRI helps to make an accurate diagnosis.
The following symptoms are typical for violations:
- Increased and chronic fatigue.
- Fine motor skills disorders – tremor, loss of sensation in the limbs of the hands.
- Problems in the functioning of internal organs – the pelvic organs often suffer. The patient experiences fecal incontinence and voluntary urination.
- Psycho-emotional disorders - multifocal brain damage of a demyelinating nature, are often accompanied by problems in the patient’s mental state: forgetfulness, hallucinations, decreased intellectual abilities. Until precise instrumental methods began to be used for diagnosis, there were cases when patients were treated for dementia and other psychological pathologies.
- Neurological disorders - focal changes in the substance of the brain of a demyelinating nature are manifested in disturbances in the motor functions of the body and motility, paresis, and epileptic seizures. Symptoms depend on which part of the brain is damaged.
What happens during the demyelinating process?
Foci of demyelination in the cerebral cortex, white and gray matter lead to the loss of important body functions. Depending on the location of the lesions, specific manifestations and disorders are observed.
The prognosis of the disease is unfavorable. Often, demyelination, which appears as a result of secondary factors: surgery and or inflammation, develops into a chronic form. As the disease develops, gradually progressive atrophy of muscle tissue, paralysis of the limbs and loss of essential body functions are observed.
Single foci of demyelination in the white matter of the brain are prone to proliferation. As a result of a gradually progressing disease, a condition may occur in which the patient will not be able to swallow, speak, or breathe independently. The most severe manifestation of damage to the nerve fiber sheath is death.
Diagnostics
The first sign that may be detected during the initial examination is a violation of the speech apparatus, impaired coordination of movements and sensitivity.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used for definitive diagnosis. Only on the basis of this study can the doctor make a final diagnosis. MRI is the most accurate method for diagnosing many diseases.
Also, the affected person is prescribed a laboratory blood test. Deviations in the number of lymphocytes, or platelets, may indicate an exacerbation of diseases.
The most accurate diagnostic method is MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent.
It is with the help of such a study that it is possible to identify both a single focus of demyelination and multiple lesions of the brain and nerve tissue.
Can lesions disappear on MRI?
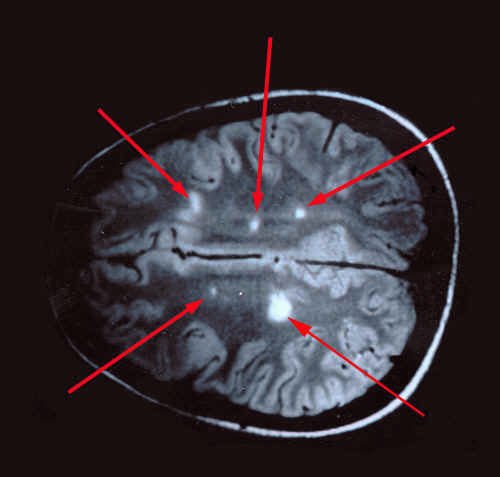
If foci are detected during the first pass of magnetic resonance imaging, and on a subsequent pass it is noted that one of the foci has disappeared, then this is characteristic of multiple sclerosis.
On the MRI screen, lesions are displayed as white spots, from which it is impossible to determine the inflammatory process, demyelination, remyelination, or what other process is occurring in the tissues.
If the lesion disappears upon repeated examination, this indicates that deep tissue damage has not occurred, which is a good sign.
On the way to diagnosis
The symptoms of demyelination are extremely varied and depend on the location of the lesion, the characteristics of the course of a particular disease, and the rate of progression of symptoms. Typically, the patient experiences neurological impairment, which is often transient. The first symptoms may be visual disturbances.
When the patient feels that something wrong is happening, but it is no longer possible to justify the changes with fatigue or stress, he goes to the doctor. It is extremely problematic to suspect a specific type of demyelinating process only based on the clinic, and the presence of demyelination itself is not always clear to a specialist, so additional research is indispensable.
This is interesting: Facial care for men: important rules
example of demyelination foci in multiple sclerosis
MRI is traditionally considered the main and very informative way to diagnose the demyelinating process. This method is harmless, can be used for patients of different ages, pregnant women, and contraindications include excessive weight, fear of closed spaces, the presence of metal structures that react to a strong magnetic field, and mental illness.
Round or oval hyperintense foci of demyelination on MRI are found predominantly in the white matter under the cortex, around the ventricles of the brain (periventricular), diffusely scattered, and have different sizes - from a few millimeters to 2-3 cm. To clarify the time of formation of foci, contrast enhancement is used, with In this case, “younger” fields of demyelination accumulate contrast agent better than those that have existed for a long time.
The main task of a neurologist when detecting demyelination is to determine the specific form of pathology and choose the appropriate treatment. The prognosis is ambiguous. For example, with multiple sclerosis, you can live a dozen or more years, while with other types, life expectancy can be a year or less.
Treatment of demyelinating brain disease
Two methods are used to treat diseases of this group: pathogenetic treatment and symptomatic therapy.
Symptomatic treatment is used to eliminate symptoms that bother the patient.
It consists of nootropics (Piracetam), painkillers, anti-seizure medications, neuroprotectors (Semax, Glycine), as well as muscle relaxants (Mydocalm).
B vitamins are used to improve the transmission of nerve impulses. It is possible to prescribe antidepressants for depression.
Treatment aimed at preventing further destruction of the myelin sheath is called pathogenetic. It also eliminates antibodies and immune complexes that attack the membrane.
The most common medications are:
- Betaferon . It is an interferon actively used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Studies have proven that with long-term therapy, the risk of progression of multiple sclerosis is reduced by three times, the risk of disability, and the number of relapses are reduced. The drug is used subcutaneously a day, every other day. Similar medications are Avonex and Copaxone;
- Cytostatics . (Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate) - used during severe forms of the pathological process with obvious damage by autoimmune complexes;
- Filtration CSF ). This procedure removes antibodies. The course of therapy consists of eight procedures, in which up to one hundred and fifty milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid are passed through specialized filters;
- Immunoglobulins (ImBio, Sandoglobulin) are used to reduce the production of autoimmune antibodies and reduce the formation of immune complexes. The drugs are used for exacerbations of demyelination for five days. Medicines are administered intravenously at a dosage of 0.4 grams per kilogram of the patient’s weight. If there is no result, then therapy is continued with a dose of 0.2 grams per kilogram of weight;
- Plasmophoresis . Helps remove antibodies and immune complexes from the blood circulation;
- Glucocorticoids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) - help reduce the activity of the immune system, suppressing the formation of antibodies against myelin proteins, and also help relieve the inflammatory process. Used for no more than seven days in large dosages.
Any treatment for demyelination is prescribed by the attending physician based on the patient’s individual characteristics.
Course of therapy
Demyelinating diseases of the nervous system are extremely difficult to cure. Sometimes you have to fight the disease for life, as is the case with multiple sclerosis, and for successful treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome you will need to undergo a course of plasmapheresis and immunoglobulin injections.
Basically, the course of treatment for diseases characterized by destruction of the myelin sheath includes the following groups of drugs:
- Monoclonal antibodies. Drugs like Tysabri serve to stop pathology at the stage of active lymphocytes entering through the destroyed blood-brain barrier. In Europe, such a remedy is considered extremely promising and sick people rely heavily on it, but in the Russian Federation many people cannot afford the medicine. After all, 1 injection costs more than 2 thousand euros, and it needs to be administered once a month;
- Cytostatics. Such drugs, for example, Cyclophosphamide, suppress the immune system by destroying its cells;
- Immunomodulators. Medications like Copaxone serve to reduce lymphocyte activity, reduce cytokine production, and reduce immune inflammation;
- Corticosteroid hormones. They are used in the form of pulse therapy, that is, in extremely large doses, but for a short period of time.
In addition to the main groups of medications designed to combat the pathological process, sick people will need symptomatic treatment. After all, it is necessary to stop the following signs of the disease:
- Paralysis and muscle paresis;
- Movement disorders;
- Problems with urination and defecation.
The main role in the course of therapy should be given not only to the increased use of medications, but also to psychological assistance to the patient. A person must understand that he must lead an active lifestyle and be cheerful. In this case, the patient will be able to live until old age with minimal consequences, for example, with movement disorders (trembling in the limbs, inability to move quickly).
Demyelinating brain disease is not always treatable, but without it it will soon lead to death. That is why it is important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and begin a course of therapy in order to have a chance to maintain a full life. https://www.youtube.com/embed/SpqdT7KG5hw
What lifestyle should I lead after diagnosis?
When diagnosing demyelination, to avoid complications, you must adhere to the following list of actions:
- Avoid infectious diseases and carefully monitor your health. In case of illness, treat persistently and effectively;
- Lead a more active lifestyle . Play sports, exercise, spend more time walking, and toughen up. Do everything to strengthen the body;
- Eat properly and balanced . Increase the amount of consumed fresh vegetables and fruits, seafood, herbal ingredients, and everything that is rich in vitamins and minerals;
- Avoid alcoholic beverages, cigarettes and drugs;
- Avoid stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress.
What's the forecast?
The prognosis for demyelination is not favorable. If a timely course of therapy is not carried out, the disease can progress to a chronic form, leading to paralysis, muscle atrophy and dementia. The latter can lead to death.
When lesions grow in the brain, a disruption in the functioning of the body will occur, namely a disruption of the respiratory processes, swallowing and speech apparatus.
Multiple sclerosis leads to disability. It is important to understand that multiple sclerosis cannot be cured, you can only prevent its development.
If you notice the slightest signs of demyelination, consult a doctor.
Do not self-medicate and be healthy!
Is there an effective treatment?
The effectiveness of treatment of demyelinated diseases depends on the type of pathology, the location and extent of the lesion, and the advanced stage of the disease. With timely consultation with a doctor, positive results can be achieved. In some cases, treatment is aimed at slowing down the process and prolonging life.
Drug therapy is based on the following methods:
- Preventing myelin destruction by blocking the formation of antibodies and cytokines using interferons. The main drugs are Betaferon, Relief.
- Impact on receptors to slow down the production of antibodies using immunoglobulins (Bioven, Venoglobulin). This technique is used in the treatment of acute stage diseases.
- Instrumental methods – purification of blood plasma and liquid using immune filtration.
- Symptomatic therapy – drugs from the group of nootropics, neuroprotectors, antioxidants, and muscle relaxants are prescribed.
Traditional medicine offers the following remedies for the treatment of pathology: a mixture of onions and honey in a wound proportion; blackcurrant juice; alcohol tincture of propolis; garlic oil; Echinops seeds; medicinal collection of flowers and leaves of hawthorn, valerian root, rue. Of course, folk remedies themselves are not capable of seriously affecting the pathological process, but together with medications, they help increase the effectiveness of complex therapy.
Therapy focuses on influencing the immunoreactive process. Unfortunately, the cause of multiple sclerosis cannot be eliminated. Therefore, treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s health and mitigating his condition. The methods used can be divided into 3 groups:
- Corticoids are the dominant drugs during an exacerbation. They are administered mainly during an attack, mainly intravenously in infusions. Methylprednisolone is used. If the therapeutic effect is insufficient, Cyclophosphamide can be used once.
- During the period of relapse prevention, maintenance doses of Prednisone or other immunosuppressants (Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide) are used to slow down further attacks and stabilize the process. This type of treatment is mainly used in the early stages of the paroxysmal form. Long-term use of corticosteroids is fraught with a number of possible side effects, so they are always administered in a single daily dose every other day (alternating method).
- Symptomatic treatment is guided by clinical manifestations. For spasticity, muscle relaxants (Baclofen, Tizanidine, Tetrazepam) are used. Cerebral symptoms are improved by Physostigmine, tremor by Clonazepam, sometimes in combination with Trimepranol. Paresthesia may be relieved by carbamazepine, amitriptyline, or hydantoins. Melipramine or Ditropan can be used against urinary problems. Part of the treatment is well-chosen rehabilitation. Regular targeted treatment is important in the presence of certain provoking factors and improvement of prognosis.
Demyelinating disease of the central nervous system is classified as incurable. Therapeutic measures are aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and eliminating symptoms. For symptomatic therapy, the following is prescribed:
- analgesics;
- sedatives;
- nootropics;
- muscle relaxants;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- neuroprotective drugs.