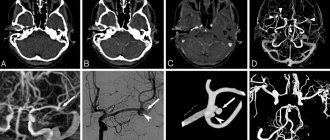
Types and functions
There are three main types of lymphocytes, which differ depending on their role in fighting infection:
- Thymus-dependent or T cells (helpers, suppressors, killers, effectors) are the main sources of “immune memory”, are responsible for recognizing and destroying foreign cells, and activate and enhance the action of monocytes (types of leukocytes capable of absorbing other cells). Thymus-dependent cells account for about 70% of the total number of cells.
- Bursa-dependent (B1, B2 and B3 cells) make up 20% of all leukocytes. The main function of B cells is to produce antibodies to each individual infection that enters the body.
- “Zero” cells - if necessary, are converted into B- or T-form.
The functions of lymphocytes are to maintain immunity at a high level due to:
- cellular and humoral immunity;
- general immune response of the body (both activation of the immune system and suppression of the reaction if necessary, for example, during pregnancy);
- “immune memory” (thanks to cloning T-effectors);
- humoral response to foreign cells and microorganisms (production of antibodies to foreign proteins);
- cleansing cells of bacterial toxins.
Types and functions
Pure they are present in the body only for a few days, and then they break down in different glands into types of different functionality. Let's take a closer look at the types and functions of lymphocytes below.
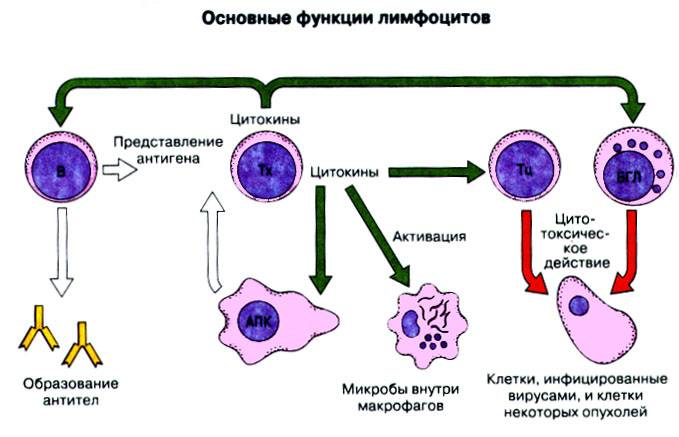
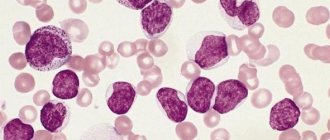
Photo of lymphocyte functions
B lymphocytes
Lymph nodes convert ten to fifteen percent of lymphocytes into B-lymphocytes. Such cells are the most important part of the immune system because they only need one contact with a disease-causing agent, such as a virus, bacteria or chemical compound, to remember and then adapt to destroy it. Exclusively thanks to these lymphocytes, the ability of immunity to the disease appears, while maintaining the ability to resist repeated infections, these cells will not die. Based on them, the vaccination procedure is successfully carried out.
T lymphocytes
The thymus contains approximately 80% of the converted T-lymphocytes from the total number; they are divided into 3 T-types: helpers, suppressors and killers, each type has its own purpose in the process of destroying disease agents. The first destroy and break down foreign cells, the second produce supporting substances for the reaction of the first, and the third reduce the strength of the immune response, thereby preventing the wholesale death of healthy cells in their body.
NK lymphocytes
NK (Natural Killer) - lymphocytes in the blood, when deciphered and translated, are literally called natural killers, this is precisely their task. This subgroup of lymphocytes is small relative to the total number, no more than fifty percent; these lymphocytes find their cells marked with lesions on the surface and destroy them. The option is to combat infected cells as well as suppress tumor cells.
Differentiation in the thymus
All particles originate from bone marrow cells that are transported to the thymus, where they are distributed into immature cells. The thymus forms a special environment suitable for the formation of functional T-particles tolerant to MHC and its own cells. Particle distribution involves different steps according to the characteristics of surface antigens.
Stages:
- At the initial stage, thymocytes do not create CD4 and CD8. They are considered double negative particles.
- At stage 2, thymocytes create these coreceptors and turn into double positive (CD4+CD8+).
- In phase 3, particles are selected that create only one coreceptor, CD4 or CD8.
The first stage is divided into several parts. In part 1 of DN1, thymocytes are a combination: CD44+CD25-CD117+. Microparticles with this combination of agents are called precursors. Then they progress, divide and lose the ability to transform into other particles.
Then the next sub-stage DN2 begins.
Thymocytes are the following combination: CD44+CD25+CD117+.
They are the early precursors of T lymphocytes. The next substage DN3 represents a combination of cells: CD44-CD25+. Then the process of β-selection begins.
Important information: What is toxogenic granularity of neutrophils in a child’s blood test?
Β selection
T-leukocyte genes consist of 3 types: V, D and J. Somatic recombination of genes that connect to each other occurs. The formation of these segments leads to the appearance of variations in each of the receptor groups. The random nature of the occurrence of combinations makes it possible to generate T-lymphocytes that detect a large number of antigens and provide immune protection against pathogens.
This mechanism often leads to the appearance of nonfunctional subunits.
The genes that present β-receptors first recombine in DN3 particles. To prevent the development of non-functional cells, the β-subunit forms a complex with the α-subunit, forming a pre-TCR. Particles that cannot create a receptor are destroyed. Bodies that have undergone β-selection enter the DN4 substage and enter the selection process.
Positive selection
Particles that have a type of pre-TKP on their surface cannot participate in the creation of immunity because they cannot interact with the bodies of the main complex. In order for receptors to recognize MHC molecules, they must have CD4 and CD8 coreceptors on their surface. The connection of the CD3 coreceptor and pre-TCR leads to rearrangement of the β-subunit genes and activates the CD4 and CD8 genes. After this, all thymocytes are converted to double positive.
DP thymocytes are transformed into the thymic cortex, where they fuse with epithelial particles that create MHC proteins. Particles that do not combine with the MHC proteins die off. Those particles that have gone through this process begin to multiply.
High lymphocytes
Since lymphocytes are measured and their number may be higher than normal from relative and absolute values, it means that these forms need to be considered separately, as absolute lymphocytosis and relative lymphocytosis. Absolute is an excess of the norm of the total number of lymphocytes in the body, relative is an increase in their share of the total number of leukocytes.
An increase in lymphocytes indicates diseases:
- diseases caused by a virus or infection;
- in a “mild” infection, lymphocytes are moderately elevated - this indicates that the turning point has passed and the healing process has begun;
- a study will show pronounced lymphocytosis in one-time diseases such as rubella, measles, mononucleosis, chickenpox, and so on;
- high lymphocytes in the blood appear in cases of bacterial diseases, exclusively in cases of tuberculosis or syphilis;
- lymphocytes also increase in case of severe poisoning of chemical origin, for example, chemicals such as lead, tetrachloroethane or arsenic; if there is suspicion of poisoning, then the fact of a large indicator indicates that there is a danger of a large dose entering the body; the medicine used can also act as a chemical agent that leads to the growth of lymphocytes - this process is a side effect of the medicine, and if its instructions contain such a clause, this fact should be shared with the doctor;
- the number of lymphocytes increases in various oncologies.
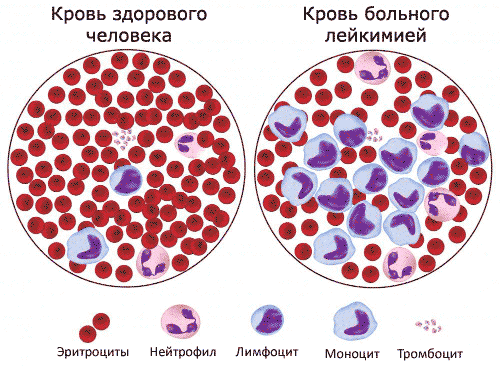
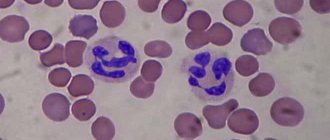
Comparison of blood structure with severe lymphocytosis
Oncological diseases should be discussed separately; in such situations, experts differentiate between malignant and reactive lymphocytosis. A normal response is considered to be when, with a given disease, the body gives a reaction in the form of reactive lymphocytosis, and malignant is a signal that it is trying to suppress a new formation. In such diseases, it is almost impossible to get by with a general blood test; additional studies will be needed to determine the exact number of atypical mononuclears.
It is known that it is incredibly difficult to defeat oncology, because according to statistics, almost all cases of recovery are people who applied in the first stages, and it is almost impossible if this is the last stage, therefore, when high lymphocytes are detected in the blood for no obvious reason: temperature, febrile states, poisoning, sweating, chills, cough, and so on; It’s better to play it safe and do additional research and diagnostics in order to identify the above-mentioned disease.
Increased performance
Now it's time to discuss what causes increased levels of lymphocytes in the blood. Most often, this condition indicates that a struggle is currently taking place in the body. An increase in lymphocytes is possible for various reasons.
It is impossible not to mention the reasons why lymphocytes in the blood are elevated, such as:
- the course of an acute respiratory viral infection provoked by influenza, herpes or hepatitis viruses;
- bronchial asthma;
- pregnancy period;
- Toxoplasma infection;
- tuberculosis bacillus;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- constant stress;
- heavy physical activity;
- lack of sleep and overwork;
- syphilis;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- hyperthyroidism;
- leukemia;
- problems with metabolism in the body;
- lymphoma;
- history of acute respiratory viral infection;
- recent surgery;
- use of certain medications;
- period;
- diseases of the immune system.
A very high level of lymphocyte cells is observed in the body of women and men during periods of illness with infections, after which immunity remains for life. It could be:
- chickenpox;
- rubella;
- whooping cough;
- measles.
Thanks to stable immunity, in most cases, re-infection does not occur. It is undesirable to suffer from such infections in adulthood, because pathologies are much more difficult to tolerate and can have consequences.
Attention! When lymphocytes exceed the norm, enlargement of the liver, spleen and lymph nodes is possible.
Why do lymphocytes increase during pregnancy?
This is due to the peculiarities of the immune system. Since the fetus contains biomaterial from the father, lymphocyte cells can regard it as a foreign element.

During pregnancy, it is important to monitor lymphocyte levels
Low lymphocyte counts are rare in pregnant women. But even after a long, steady increase, by the time of birth it returns to normal on its own.
Lymphocytes and their functions
Lymphocytes unite cells of different morphology. Despite the great diversity, all cells are combined into one group based on the function they perform - protecting a person from foreign antigens and their own mutant cells. It is customary to distinguish 3 subpopulations of lymphocytes: T-, B- and NK-cells.
B lymphocytes are capable of producing antibodies - protein molecules that have specificity for foreign antigens. The interaction of antibodies with antigens leads to inhibition of the growth and development of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as to the neutralization of their toxic substances.
In addition, B lymphocytes are able to transform into “memory” cells, which are instantly activated when pathogenic bacteria re-enter and destroy them.
T lymphocytes regulate the functioning of other types of cells by activating or suppressing their activity and producing antibodies. They destroy infected (viruses or bacteria) and cancer cells.
Natural killer cells (NK cells) synthesize information substances (protein cytokines). Due to this, the signal about infection spreads to other immune cells and a cascade of protective reactions is launched. They lyse (destroy) cells that are invisible to T lymphocytes, for example, when infected with HIV or human papillomavirus.
In addition, they exhibit cytotoxic activity against mutant tumor cells and tissues. All of the above determines the point of view of modern scientists, which determines the need to classify natural killer cells as a separate independent type of leukocytes.
Causes of lymphocytosis in adults
Conventionally, a distinction is made between reactive and malignant lymphocytosis. The first is due to the protection of the immune system from the disease and goes away a month or two after recovery, the second is associated with cancer that is not associated with external factors.
In order to determine the root cause of the deviation, one blood donation is not enough. Perhaps the doctor will prescribe additional examination, including a bone marrow examination, a more detailed analysis of the status of lymphocytes, etc.
The causes of lymphocytosis in the blood may be as follows:
- Viral (measles, whooping cough, chickenpox, HIV, hepatitis, ARVI, rubella, etc.);
- Bacterial diseases (tuberculosis, brucellosis, syphilis, etc.);
- Injuries;
- Burns (including sunburn);
- Hypersensitivity to drugs;
- Blood transfusions;
- Postoperative condition after removal of the spleen;
- Autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis);
- Emotional stress, nervous breakdowns;
- Constant and frequent smoking;
- Vitamin B12 deficiency in the body;
- Condition with risk of tumor development (malignant thymoma);
- Oncological diseases (chronic lymphocytosis, lymphoblastic leukemia, malignant lymphoma).
The causes of lymphocytosis in children are usually due to imperfections of the immune system in childhood. However, the reasons listed above should not be excluded, especially if lymphocytosis in a child is observed over a long (more than six months) period of time.
Lymphocytosis is often observed in preschool children, but generally this does not indicate a serious illness.
Lymphocytosis in children under one year of age may also appear due to incompletely formed immunity.
It is important to pay attention to the child's behavior and not engage in self-analysis if you do not have a medical education. Do not hesitate to clarify the primary diagnosis with your doctor, perhaps he will prescribe medications to support immunity or intestinal microflora
What to do
If elevated lymphocytes are detected in the blood of an adult or child, the doctor must decide on further examination tactics. First you need to identify the disease that causes the appearance of elevated lymphocytes.
If the number of leukocytes begins to increase, this means that the body’s functioning is impaired. Treatment should not be aimed at reducing the concentration of white blood elements, but at normalizing health and getting rid of diseases.

Depending on the condition, the doctor may recommend taking anti-inflammatory drugs if lymphocytes in the blood of an adult are elevated and signs of activation of the inflammatory process appear. For viral diseases, antiviral therapy is prescribed. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are selected. Specific therapy is necessary if the cause of a large volume of lymphocytes is autoimmune processes.
For patients with oncological pathologies, treatment tactics are selected individually. Most patients are prescribed chemotherapy, radiation, and some require a bone marrow transplant for recovery. After radiation therapy, cancer patients experience lymphopenia, the number of lymphoid cells decreases, and the immune system stops working. You can increase lymphocytes in the blood of men and women with cancer by reviewing your diet, lifestyle, and adding vitamins to your diet. Actions should be aimed at strengthening protective forces.
Children: normal white body count
Activated lymphocytes in a child’s blood test can increase significantly when harmful bacteria or foreign bodies enter the body. An increased content of cells in the analysis may indicate the beginning of a pathological process (the spread of bacteria, fungus, parasites or viruses.
Depending on the age, the norms of activated lymphocytes in the analysis of a child differ greatly:
- In infants – from 14 to 32%.
- From one week to several months – from 21 to 48%.
- From one to six months – 42-67%.
- Up to one year – 40-62%.
- From 1 to 3 years – 32-34%.
- Up to the age of 5 years – 30-52%.
- Up to 13 years – from 27 to 48%.
Activated lymphocytes are elevated in a child due to diseases in the body. You should not try to independently identify the cause of this condition and self-medicate your child. The interpretation of test results is carried out exclusively by the attending physician.
Functions of lymphocytes in the body
The main function of lymphocytes is to maintain the health of the body by working in the immune system. However, in order to achieve it, cells are needed, each responsible for its own task.
- B lymphocytes
They remember pathogenic cells and microbes as harmful and foreign and store information about this throughout their existence. It is thanks to them that vaccination and immunity against once-in-a-lifetime diseases becomes possible. In total, such cells make up 10-15% of the total number of lymphocytes.
- T lymphocytes
Responsible for destroying harmful microorganisms or viruses. T-cells are in turn divided into T-killers (break down foreign cells), T-helpers (help maintain the main reaction), T-suppressors (make sure that the destruction of cells does not spread to native healthy blood cells). T cells occupy approximately 80%.
- NK lymphocytes
Sometimes it’s not just foreign cells that can cause harm to the body. The action of NK lymphocytes is aimed at destroying tumor cells, as well as body cells exposed to the virus and located in the infection zone.
Reduced lymphocytes in the blood of a child
A reduced level of lymphocytes is called lymphocytopenia (or lymphopenia). There are two types of lymphocytopenia: absolute and relative.
- Absolute lymphopenia occurs when there is an immune deficiency (acquired or congenital). It can appear in patients with leukemia, leukocytosis, exposure to ionizing radiation, and neutrophilia.
- With relative lymphopenia, the development of the lymphoid system is disrupted, then lymphocytes die very quickly. It also occurs as a consequence of chronic infections and acute infectious diseases.
Lymphopenia in a child does not show any visible symptoms. But due to cellular immunodeficiency, symptoms such as:
- significant reduction in lymph nodes and tonsils;
- eczema, pyoderma (purulent skin lesions);
- alopecia (hair loss);
- splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- jaundice, pale skin;
- petechiae (hemorrhagic spots on the skin).
If lymphocytes are low in the blood, the child often experiences relapses of infectious diseases, and rare types of microorganisms often act as pathogens.
Symptoms of low lymphocytes in women
In most cases, lymphopenia is characterized by an asymptomatic course.
Sometimes this condition can manifest itself as follows:
- general weakness;
- hair loss;
- skin rashes and eczema;
- pale skin, acquiring a jaundiced tint;
- the presence of purulent lesions of the skin;
- reduction in size of tonsils and lymph nodes;
- elevated body temperature.
Treatment for low lymphocyte levels
There is no specific therapy for this condition, since we are not talking about a separate disease, but about a symptom. Therefore, to normalize the level of lymphocytes, it is necessary to combat the root cause of their decrease.
Most often, treatment for women comes down to the following procedures:
- If the cause of lymphopenia is the use of certain medications, then they are replaced with analogues that do not cause a decrease in the level of lymphocytes.
- In case of poisoning, therapy is carried out to eliminate intoxication.
- In the case of infectious and inflammatory lesions, drug therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating the pathological focus.
- Taking medications to increase local immunity.
- Following a protein diet.
Norms and functions of immune cells
Despite the general heterogeneity of leukocytes, their functionality is limited to the implementation of cellular and humoral immunity in response to infectious infection of cells.
Neutrophils are the predominant type of leukocytes in the human systemic circulation. In adults, their number ranges from 45 to 75%, while the content of lymphocytes should not exceed 35%.
The exception is infants under 1 year of age, for them the norm of lymphocytes is from 55 to 75%, and neutrophils - from 15 to 35% of the total number of leukocytes. This ratio is necessary to ensure enhanced protection of the child’s body from infection while the immune system is not sufficiently formed and there is no acquired immunity.
Functions of leukocytes
Lymphocytes are represented by three subpopulations:
- T cells are divided into 2 types: cytotoxic (destroy cells infected with intracellular parasites and cancer cells) and regulatory (determine the severity and duration of the immune response);
- B cells are responsible for the implementation of humoral immunity. After interaction with foreign antigens (on the surface of viruses or bacteria), plasma cells transform. After which they begin to actively secrete antibodies that can stop the growth of microorganisms and neutralize their toxic substances;
- natural killer cells - destroy infected (HIV, papillomavirus) and cancer cells, on the surface of which there is no MHC 1 (major histocompatibility complex). Since this condition makes them inaccessible to recognition and destruction by other types of lymphocytes.
Functions of neutrophils
Neutrophil leukocytes realize their protective function in several ways. Phagocytosis is the process of absorption and further destruction of relatively small foreign particles. The death of neutrophils is accompanied by the release of active molecules with antifungal and antibacterial activity into the intercellular space.
The mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptides is based on disruption of the integrity of the cell membrane, which explains the predominant effect on bacteria and microscopic fungi. It should be noted that neutrophil lymphocytes do not exhibit significant activity in the fight against cancer cells and helminths.
At the beginning of the 21st century, the role of neutrophils in the process of NETosis was established - the programmed destruction of cells by creating a network of neutrophil DNA, proteins and antimicrobial substances. The network traps pathogenic bacteria and they die.
Elevated lymphocytes
A condition in which there is an increase in the level of lymphocytes is called lymphocytosis. In the vast majority of cases, it indicates the body’s struggle with a harmful agent. Therefore, an increase in lymphocytes signals the presence of an inflammatory or oncological process in the body.
In addition to infection, an increase in lymphocytes can be caused by constant exposure to stress
Causes
Lymphocytosis can be caused by a number of diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- infection with tuberculosis bacillus;
- syphilis;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- acute respiratory viral infection;
- hyperthyroidism;
- diseases of the immune system;
- leukemia
In addition, the following can cause an increase in lymphocyte levels:
- heavy physical activity;
- recent operations;
- constant exposure to stress;
- overwork;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- lack of sleep.
An increase in lymphocyte levels often occurs during menstruation and pregnancy.
Treatment
Since, as in the case of a low level of lymphocytes, lymphocytosis is not a separate disease, the features of its treatment are determined by the root cause of the development of this condition. An increase in the number of lymphocytes does not occur just like that - it indicates increased protection of the body from the intervention of any foreign agent.
It should be understood that normalization of the number of white blood cells is possible only with careful diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Most often, lymphocytosis is a consequence of the development of infectious diseases. And to lower the level of these cells, it is necessary to carry out a course of drug therapy. For this, the patient is prescribed the following drugs:
- antiviral;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the disease is caused by serious diseases: leukemia, cancer, then therapy is quite difficult and lengthy. The patient requires chemotherapy and a bone marrow transplant is possible.
Ratio of indicators
The body has functional blood cells. The percentage of their ratio indicates various diseases. The main markers are lymphocytes, monocytes and neutrophils. They are responsible for absorbing foreign bacteria. Monocytes cleanse the body of foreign bodies and viruses. A leukocyte is a white cell that is capable of being responsible for the body’s immune response.
Increased lymphocytes and decreased neutrophils
This state of the body indicates an active fight and activation of the immune system to eliminate infection or bacterial influence. It is possible to develop an acute viral infection: ARVI, acute respiratory infections, AIDS, HIV, tuberculosis, excessive production of thyroid hormones, malignant skin diseases.
Reduced neutrophils in the body
Neutropenia (when neutrophils are low) manifests itself in a number of infectious diseases, vitamin deficiency, leukemia, various types of anemia, chemotherapy or irradiation of the body.
Increased lymphocytes and monocytes
The formed elements function to fight germs and infections. An increase means a strong infectious outbreak. These are measles, rubella, herpes, chickenpox, ARVI and acute respiratory infections.
The cases presented are individual; for an accurate diagnosis and selection of the correct treatment, consultation with a hematologist and therapist is necessary. Ordering additional studies to clarify the diagnosis.
Treatment
Lymphocytopenia is not an independent disease, so there is no special treatment. To correct its manifestations as much as possible, you need to identify the true cause of this condition and fight it.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, if lymphocytes are low, drugs that stimulate the immune system can be prescribed. Treatment with antiviral or anti-inflammatory drugs may be recommended, since a decrease in lymphocytes may be caused by the development of an inflammatory process.
The list of necessary medications and other treatment methods depends on what disorders have been recorded in the body. Self-treatment can cause complications.

In most cases, a full examination is prescribed to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment for the underlying disease.
In some cases, a low blood cell count is a congenital condition indicating an immunodeficiency that appears in the first days of a child's life. Medicine knows methods to combat this problem. The patient surgically receives stem cells from a healthy donor. In most cases, operations end favorably.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a blood test reveals low lymphocytes, adult patients should consult a physician. For children, visit a pediatrician.
ethnoscience
If lymphocytes in the blood are slightly reduced, most often this situation occurs during the period of colds. In this case, you need to improve your immunity.
Traditional medicine recipes will help strengthen your immune system:
- Flower pollen and honey should be mixed in a 2:1 ratio. Eat 1 tsp daily on an empty stomach. mixture with 150 ml of milk.
- At least 3 times a day, drink ½ glass of any fresh juice: pomegranate, beets, blackberries, cranberries, apples, carrots.
- Finely chop fresh pine needles. 5 tbsp. pour 1 liter of hot water. Cook over low heat for 15 minutes. Leave for 2 hours, strain. Add 2 tbsp. honey Take a glass of the product 2 times a day.
Regular consumption of vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins, incl. citrus fruits. It is useful to drink herbal teas and consume natural honey. Rosehip decoction helps not only improve immunity, but also reduce the risk of developing anemia.
The patient's diet should be supplemented with:
- greens, berries;
- beef, poultry, fatty fish;
- cheese, milk;
- legumes;
- nuts.
It is necessary to increase the consumption of clean water to 2 liters per day.
Taking tinctures and decoctions of medicinal plants will help adjust the composition of the blood, but this is not enough. Traditional medicine recipes can only be considered as an addition to the main therapy. In addition, before taking folk remedies, you should consult your doctor.
Norms for the content of lymphocytes in the blood
To determine the number of immune cells, a clinical blood test is prescribed; in some laboratories it is positioned as a detailed one, with a leukocyte formula or leukogram. In the results, cells are designated LYMPH, LY, or LYM. Not only quantitative indicators per unit volume of biomaterial are important, but also the proportion of lymphocytes among other bodies, reflected in %.
Table - Normal leukogram values
| Leukocyte type | Share, in % | Absolute indicator, 10⁹/l |
| Band neutrophils | 1‒6 | 0,04‒0,3 |
| Segmented neutrophils | 46‒72 | 2,0‒5,5 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5‒5 | 0,02‒0,3 |
| Basophils | 0‒1 | 0,0‒0,065 |
| Monocytes | 19‒37 | 0,09‒0,6 |
| Lymphocytes | 3‒11 | 1,2‒3,0 |
White blood cell levels are the same for men and women. The level of lymphocytes changes as a person grows older and the immune system improves. In adults, slightly reduced corpuscle counts are observed, which is associated with the natural decline of the bone marrow and thymus gland.
Table - Lymphocyte norms by age
| Population category | Proportion among leukocytes, % | Absolute quantity, *10⁹/l |
| Up to a year | 45‒70 | 2‒11 |
| Up to 2 years | 39‒60 | 3‒9 |
| 2‒4 | 33‒50 | 2‒8 |
| 4‒10 | 30‒50 | 1,5‒6,8 |
| 10‒18 | 30‒44 | 1,2‒5,2 |
| Adults | 19‒40 | 1‒4,8 |
Deviations from the norm of up to 10% are not considered a cause for concern. The minimum acceptable values are 19% or 1*10⁹/l. If the level is lower, lymphocytopenia is stated. The condition is considered relative if there is an increase in other types of leukocytes, or absolute if the concentrations of all cells are reduced at the same time.
An increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood of an adult of more than 5*10⁹/l when their share among other protective cells is more than 41% is called lymphocytosis - read more about this condition in the article “Increased lymphocytes in the blood.”
Activation of lymphocytes
The human body begins to actively develop immunity to the following diseases:
- chickenpox;
- rubella;
- measles.
Activated lymphocytes in the blood can be a sign of a developing cold. When the body is restored and the disease is eliminated, the level of lymphocytes should return to normal in the near future. If this does not happen, it is important to make an appointment with a doctor immediately. He will prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis and help identify the cause of this condition. In some cases, the doctor writes a referral to an oncologist.
The value of normal indicators
In the analysis form, the normal neutrophil count is most often written as a percentage. Normally, the indicator of segmented neutrophils will be from 47 to 72. If we talk about absolute indicators, then there will be other numbers - from 2.0 to 5.5 per 109 per liter.
There may be no band neutrophils at all, that is, in the form opposite this indicator there may be the number 0. But this rarely happens. Typically, the normal amount of these cells is from 1 to 6%.
The number of lymphocytes in a normal blood test will range from 19 to 37%. But most often the absolute value is written on the form from the laboratory, which ranges from 1.2 to 3.0 per 109 per liter.
The norm of lymphocytes and neutrophils in men and women does not have any difference in indicators. But a child's blood test will normally be different.
In children, the percentage of neutrophils is lower than in adults.
- Up to 12 months, this figure will be from 30 to 50.
- For children from one to six years old, the numbers will be different - from 35 to 55.
- At the age of 6 to 13 years, the number of neutrophils approaches the adult value - from 40 to 60.
The number of lymphocytes in the blood of a child is greater than that of an adult. Up to a year, this figure should not exceed 40 - 60%; from one to five years the numbers will be different - from 45 to 65%. And for older children this figure is 30–45%.
We can talk about them for a long time and a lot
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood is 18 – 40% of all leukocyte cells, which corresponds to absolute values in the range of 1.2 – 3.5 x 109/l.
As for the norm in women, they have more of these cells physiologically, therefore the increased content of lymphocytes in the blood (up to 50 - 55%) associated with menstruation or pregnancy is not considered a pathology. In addition to gender and age, the number of lymphocytes depends on the psycho-emotional state of a person, nutrition, environmental temperature, in a word, these cells react to many external and internal factors, but a change in level of more than 15% is clinically significant.
This is interesting: Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): the norm in children and adults, why it is increased and decreased
The norm in children has a wider range of values - 30-70% , this is explained by the fact that the child’s body is just getting acquainted with the outside world and forming its own immunity. The thymus gland, spleen, lymphatic system and other organs involved in the immune response function much more actively in children than in an adult (the thymus disappears altogether in old age, and its function is taken over by other organs consisting of lymphoid tissue).
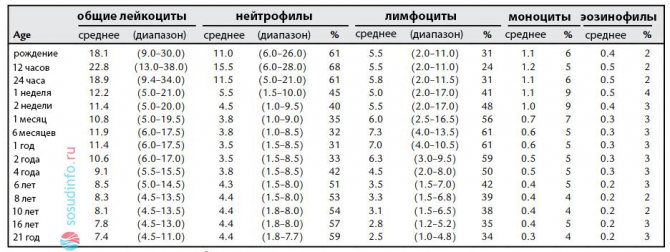
Table: norms of lymphocytes and other leukocytes in children by age
It should be noted that the number of cells contained in the peripheral blood is a small fraction of the circulating fund, and the bulk of them are represented by T-lymphocytes, which, like all “relatives”, originated from a stem cell, separated from the community in the bone brain and went to the thymus for learning, in order to then carry out cellular immunity.
B cells also go through a considerable development path from a stem cell, through immature forms. Some of them die (apoptosis), and some of the immature forms, called “naive”, migrate to the lymphatic organs for differentiation, turning into plasma cells and mature full-fledged B-lymphocytes, which will permanently move through the bone marrow, lymphatic system, spleen and only a tiny fraction of them will go into the peripheral blood. Lymphocytes enter the lymphoid tissue through capillary venules, and enter the blood through the lymphatic tract.
There are few B-lymphocytes in the peripheral blood; they are antibody-formers, so in most cases they wait for the command to begin humoral immunity from those populations that are everywhere and know everything - lymphocytes called helpers or helpers.

Lymphocytes live differently: some live for about a month, others for about a year, and others persist for a very long time or even for life, along with the information received from an encounter with a foreign agent (memory cell). Memory cells are located in different places, they are widespread, very mobile and long-lived, which provides long-term immunization or lifelong immunity.
All the complex relationships within a species, interaction with antigens that have entered the body, the participation of other components of the immune system, without which the destruction of foreign substances would become impossible, is a complex multi-stage process that is practically incomprehensible to the average person, so we will simply omit it.
What does deviation from the norm indicate?
Elevated lymphocytes may indicate the presence of the following diseases, viral, bacterial or parasitic: influenza, measles, chicken pox, whooping cough, rubella, tuberculosis, diphtheria, mononucleosis, syphilis, malaria, brucellosis, toxoplasmosis, etc.
It happens that lymphocytes in the blood are elevated, and neutrophils are lower than normal. This happens when:
- There are side effects from medications;
- The central nervous system is not in order;
- There are endocrine disorders - thyrotoxicosis, Addison's disease, myxedema, etc.;
- Connective tissues suffer - rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus;
- The body is affected by ARVI, HIV and hepatitis viruses, as well as some bacterial and fungal infections.
Some diseases are, as they say, “childhood”; memory cells must remember these infections so that they do not infect the body again. People are protected during vaccination in the same way, so that foreign microorganisms no longer cause harm.
A reduced level of lym in a blood test may indicate the presence of purulent or acute infectious diseases. This also indicates anemia. In addition, lymphopenia is a sign of toxic poisoning of the body with chemicals, alcohol and/or drugs. People with low lymphocyte levels may be referred for cancer tests.
If the number of lymphocytes in a blood test has reached a critical low level of 12% or lower, this is a cause for serious concern. It is necessary to donate blood for immunodeficiency and examine lymphocyte subpopulations. An extremely low level is called lymphocytopenia, in which the following diseases are observed:
- AIDS;
- Tuberculosis;
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Severe combined immunodeficiency;
- Kidney failure;
- Protein deficiency
Sometimes lymphocytopenia can be temporary and is associated with the use of certain strong medications (prednisolone, corticosteroid drugs, chemotherapy treatment, radiation therapy), as well as recent severe stress.
No matter what test results you receive, you should not diagnose yourself. The immune system is a complex thing. Human blood contains many cells, the number of which may indicate the presence of a particular disease. A qualified specialist will compare all the values of the test results,, if necessary, prescribe repeated or additional tests, and only then make a final, and most importantly, correct diagnosis, and also prescribe appropriate treatment or supportive therapy.
Soldiers of the invisible front
Lymphopenia itself occurs in various pathological conditions: due to prolonged viral infection, immunodeficiency, bone marrow pathologies, etc. The most common infectious disease that causes a decrease in lymphocytes is AIDS, in which HIV-affected CD4 T cells are destroyed (CD4 stands for cluster of differentiation; this is a special group of T cells, namely T helper cells, which help other cells destroy infecting organisms ). However, in this case, the damage to the immune system is chronic.
virus

Photo: IZVESTIA/Pavel Bednyakov
Wake-up call: Platelet levels predict death from COVID-19
Scientists have proposed a new technique that can be used to determine the severity of the condition of patients with coronavirus
In the case of coronavirus, we are talking about long-term, but reversible dysfunction of the immune system. When a person becomes infected with a new pathogen, an expansion of lymphocytes occurs in his body. These are a kind of soldiers who must fight a harmful virus, Pavel Volchkov, head of the MIPT laboratory of genomic engineering (a university participant in the 5-100 project), explained to Izvestia.
“And after an infection, “demobilization” occurs in the body, since such a number of activated T-cells and B-cells are no longer needed, the expert emphasized. “After activation, immune cells do not live long and then disappear or become “memory cells.” This is what we call immunity. The system is designed in such a way that when lymphocyte soldiers are sent “to reserve,” slight fluctuations in their number can be detected. But then the failure will be restored by new cells.
Increased lymphocytes in the blood in men
An increase in lymphocytes in the blood of men is a serious reason to conduct a diagnosis and visual examination. Lymphocytes are biochemical blood particles that serve as protectors of the body from foreign bodies. Their number is affected by age and gender, so the norm for males is slightly different from that of females.
Everyone donates blood for lymphocytes, even with a common cold. A biochemical blood test helps determine the state of the body.
Norm of lymphocytes in the blood
Based on their structure and functions, lymphocytes are divided into the following groups:
- T-cell (detects, checks the microbe for foreignness, activates the protective function);
- B-lymphocyte (destroys foreign bodies);
- NK cell (prevent the formation of malignant tumors).
When you receive a sheet with the results of a blood test, it contains only the leukocyte formula - this is a relative indicator.
In order to determine the actual level of lymphocytes, you must use the following formula: (Total level of leukocytes * Lymph content in % ratio) / 100 = number of lymphocytes per μl.
Norm of lymphocytes according to age category:
- From 10 years – 1.5–6 µl/l, 38%.
- From 21 years old – 1-4.8 µl/l, 34%.
- From 22 years to 50 – 4.2-9 µl/l, 34%.
- From 50 years old – 3.9–8 µl/l, 25%.
According to the immunological theory of aging of the body, the main culprit in this process is the transformation of the thymus gland, a sharp decline in the production of antibodies.
The thymus gland turns into layers of fatty tissue, completely losing its function. This transformation occurs in men between 35 and 40 years of age, during which time lymphocyte levels may be low or high. The body reacts ambiguously to harmful bacteria. It is believed that during this period the body is weakest and more toxins accumulate in it.
An increase in lymphocytes in the blood of men does not occur just like that. At an appointment with a doctor who has received your blood test, you should tell in detail about your condition and medical history. Based on the results of the consultation and examination, the doctor will be able to determine the etymology of their growth.
Reactive growth of lymphocytes is a natural, antibody response to a foreign body that poses a danger to the body. Typically, the level of lymphocytes during reactive growth returns to normal within 1-3 months.
Reasons for reactive growth:
- rubella;
- chicken pox;
- measles;
- whooping cough;
- flu;
- colds;
- diphtheria;
- sexually transmitted infections (syphilis, chlamydia);
- tuberculosis, pneumonia;
- autoimmune diseases;
- allergic reaction;
- candidiasis;
- severe stress;
- diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, renal failure, cystitis, prostatitis);
- poor nutrition;
- changes in levels may be observed immediately after intense physical activity.
Malignant growth occurs due to lymphoproliferative disease, when there is a failure in cell production, neoplasms appear - leukemia develops.
So that the doctor can determine in which direction the change in the number of lymphocytes is occurring - reactive or malignant, an additional examination is prescribed - a biopsy of the spinal cord fluid, a study at the molecular genetic level, specialists often resort to ultrasound.
Is it possible to bring the level of lymphocytes back to normal?
The methods, duration, and need for the unnatural return of lymphocytes to the normal range depend on the reason that provoked the sharp increase.
If the cause is an infection, then therapy with the following drugs is prescribed:
- Antiviral agents that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria destroy them.
- Corticosteroids. They suppress the inflammatory process and the negative changes it provokes in the body.
- Antacids.
- Probiotics, special agents that restore intestinal microflora and the functioning of the digestive tract. Viruses often disrupt their work, worsening the patient’s well-being and the course of the disease.
- A special diet that saturates and cleanses the blood. Eating red vegetables and fruits is especially beneficial.
If cell growth is provoked by an oncological process, then the main method of correction is blood purification and systematic blood transfusion.
Even if you have been diagnosed with a sharp increase in the level of lymphocytes, there is no need to worry, perhaps it is just a viral disease that can be treated. There is no need to worry about determining the diagnosis - the doctor himself will offer the necessary set of diagnostics if he notices deviations.
Reasons for deviations from the table of lymphocyte norms in women by age
The female body is an amazing structure. To keep everything in harmony, it is important to regularly monitor your health. One of the ways to do this is to take a clinical blood test and check whether all blood cells are normal. Not only your well-being depends on the correct formula. Changes in the composition of the blood will warn a woman about the presence of severe pathologies that require treatment. What is the norm of lymphocytes in the blood of women? Why is the rate increasing? What research is needed to determine the reason for the change in value?
Getting to know lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are cells responsible for protecting a woman’s body from the effects of pathogenic factors. Every day, a closed system is attacked by viruses, fungi and bacteria. How well the immune system fends off attacks depends on the activity of lymphocytes.
Lymphocyte cells belong to the group of leukocytes. Their amount in the blood is determined as a percentage. A blood test gives an idea of the general content of these cells, without dividing them into subtypes.
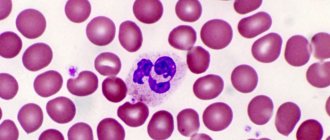
Appearance of a human blood lymphocyte cell
During periods when the human body does not encounter any pathogens, lymphocyte cells are “free floating”, not performing any functions. Each lymphocyte has the ability to distinguish between human organ cells and external harmful agents. The faster it determines the harmfulness of a microorganism, the more likely it is that a person will not get sick and will not even feel the risk of infection.
Important! Some types of lymphocyte cells signal the presence of harmful microorganisms, starting to fight them, while others begin to actively produce antibodies to effectively cope with the causative agent of the disease.
Where do lymphocytes develop?
Large numbers of lymphocytes develop in the thymus (or thymus gland), bone marrow, lymph nodes and spleen. As the thymus gland ages, it self-destructs, so the burden of producing lymphocyte cells is distributed among other organs.
The thymus, or thymus gland, at a young age performs the main function of producing lymphocytes
The death and utilization of lymphocytes occurs in the spleen. If lymphocytes in the blood are elevated, in some this organ becomes enlarged, as it is difficult for it to process more cells. With pathology, the same process occurs inside the spleen - an increase in lymphocytes in the blood.
Types of lymphocytes
Every minute, amazing processes occur in the body of a man and a woman. Although the precursor of all lymphocytic compounds is a stem cell, lymphocytes with different functions and purposes arise from the same material. There are three types of cells:
- NK lymphocytes;
- T cells;
- B cells.
It is worth taking a closer look at each group.
The role of NK lymphocytes
NK lymphocytes are the largest representatives of the group. They exercise control over other lymphocyte cells, disposing of damaged or aged tissue. It is these compounds that can stop the growth of a cancer tumor by recognizing the body’s own tissues that have undergone pathological changes.
NK lymphocytes are the only ones that identify those groups of viruses to which neither B nor T cells have activity. For example: some types of herpes virus. When an extended blood test is performed, you can see that these cells occupy 5-20% of all lymphocytes.
Important! The indicator is influenced by the condition of the body and the presence of pathologies.
Role of T cells
The purpose of T cells is to identify and destroy harmful microorganisms. This group is divided into 3 subgroups:
- killers;
- helpers;
- suppressors.
Killer cells are the cells that are the first to “meet” the infection and begin neutralizing it. They give a signal to helper cells, and they stimulate the active production of antibodies. This completes the destruction of pathological pathogens that attack the human body.
The human body is uniquely structured. The purpose of suppressor cells is to control the activity of other T lymphocytes. If these compounds were not present or for some reason the mechanism stopped working, immunity would affect the person. If killers and helpers are overactive, suppressors suppress them.
Of the total number of lymphocytes, T cells occupy 65-80%.
Role of B cells
In the general blood formula, these cells make up 8-20%. Their purpose is to recognize foreign bodies and produce compounds that act on them.
The lifespan of lymphocyte cells varies. Some remain in the blood only for a while, others live throughout a person’s life. When lymphocyte cells are destroyed, they are able to “pass on inheritance,” that is, accumulated information about the invasion of foreign agents. This helps new generations of lymphocyte cells respond faster to attacks and resist. This is how immunity to infections is formed.
Functions of lymphocyte cells
To understand how negatively low or high lymphocytes affect the body, it is important to understand what functions they perform. Much depends on the level of these cells in the blood.
If we combine all the functional features of lymphocyte cells, we can derive the following list:
- lymphocytes develop and maintain immunity to past diseases;
- retain information after vaccination;
- help fight cancer and benign tumors;
- infect cells damaged by viruses;
- eliminate their own altered cells;
- fight against foreign organisms.
Decreased and elevated lymphocytes in the blood of women indicate pathological processes. It is very important to control the blood count, because this way you can diagnose pathologies at the initial stage.
In order to pay due attention to the increase in indicators, it is important to know what the norm of lymphocytes in the blood is in women and men.
How calculations are carried out
The number of lymphocytes in the blood can be described in several terms. There are 2 indicators:
- relative;
- absolute.
The relative rate is measured as a percentage and indicates the number of cells in relation to other leukocyte cells. The absolute number indicates the content of lymphocyte cells in the specified volume of blood.
How is the analysis performed?
In order to correctly calculate the increases that have occurred in the blood formula, it is important to take the test correctly. The normal rate for men and women is the same; the rate fluctuates only due to age-related changes.
Blood for laboratory testing is taken from a finger
To determine whether the level of lymphocytes is low or high, blood is taken from a finger prick. The biomaterial must be taken on an empty stomach in the morning. Depending on the method used to test the blood, it depends on how much is required for analysis.
Normal indicators
The main cells responsible for the functioning of the immune system are lymphocytes. It is important to understand what this or that number means in the transcript of the analysis, because sometimes doctors say little about the data obtained during the study.
In the blood, the normal content of lymphocyte cells is as follows:
- for newborn girls up to the first year of life – 37-60% (relative indicator) and from 3.0-9.5 (absolute content);
- from 2-4 years – 33-49% and from 2.0-8.0 units;
- from 5-9 years the norms are 30-50% or 1.5-7.0;
- from 10-16 years old – 30-45% or 1.2-5.3;
- after 16 years throughout life – 20-37% or 1.0-4.8.
In most cases, relative values are taken as the basis for deciphering clinical analysis. When additional diagnostics are required, the attending physician takes both indicators into account.
Let's look at a few examples. In a 50-year-old woman, the relative level of lymphocytes showed 40-47%. What do these numbers say? That lymphocytes are elevated.
If 42-46% was shown by the study result in the first months after birth, then the indicators are normal. For a teenage girl at 14 years old, the indicators are high - 48-52% of lymphocytes.
Lymphocyte levels such as 38%, 41%, 43% and 44% or less are normal for girls and girls under 16 years of age. If the figure increases after this age, it is necessary to determine the reasons for the excess of the indicators.
Increased performance
Now it's time to discuss what causes increased levels of lymphocytes in the blood. Most often, this condition indicates that a struggle is currently taking place in the body. An increase in lymphocytes is possible for various reasons.
It is impossible not to mention the reasons why lymphocytes in the blood are elevated, such as:
- the course of an acute respiratory viral infection provoked by influenza, herpes or hepatitis viruses;
- bronchial asthma;
- pregnancy period;
- Toxoplasma infection;
- tuberculosis bacillus;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- constant stress;
- heavy physical activity;
- lack of sleep and overwork;
- syphilis;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- hyperthyroidism;
- leukemia;
- problems with metabolism in the body;
- lymphoma;
- history of acute respiratory viral infection;
- recent surgery;
- use of certain medications;
- period;
- diseases of the immune system.
A very high level of lymphocyte cells is observed in the body of women and men during periods of illness with infections, after which immunity remains for life. It could be:
- chickenpox;
- rubella;
- whooping cough;
- measles.
Thanks to stable immunity, in most cases, re-infection does not occur. It is undesirable to suffer from such infections in adulthood, because pathologies are much more difficult to tolerate and can have consequences.
Attention! When lymphocytes exceed the norm, enlargement of the liver, spleen and lymph nodes is possible.
Why do lymphocytes increase during pregnancy?
This is due to the peculiarities of the immune system. Since the fetus contains biomaterial from the father, lymphocyte cells can regard it as a foreign element.
During pregnancy, it is important to monitor lymphocyte levels
Low lymphocyte counts are rare in pregnant women. But even after a long, steady increase, by the time of birth it returns to normal on its own.
Decreased lymphocyte counts
When lymphocytes in the blood are low, this is also bad. The condition indicates pathology. The risk of additional infection is high, since the body, due to a decrease in the content of lymphocyte cells, is practically defenseless against infections.
A decrease in lymphocyte cells in the blood count indicates the presence of the following pathologies:
- oncological tumors;
- diseases of the lymph nodes;
- presence of HIV infection;
- anemia;
- chemotherapy or radiation exposure;
- primary stage of infectious diseases.
If a clinical blood test shows a shift in the lymphocyte formula, the attending physician recommends additional laboratory testing. Such a complete diagnosis will help to identify pathologies at the initial stages and begin treatment.
Recommendations
To maintain the circulatory formula in balance, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not stay in places where large numbers of people gather during epidemics;
- regularly eat protein foods;
- try to drink up to 2 liters of clean water daily;
- take vitamin complexes as recommended by your doctor.
Do not self-medicate. Some sulfonamides and antibiotics have a powerful effect on the human body. In order not to cause harm, such drugs are taken only after undergoing a full examination by a specialist and selecting a medicine.
You can learn more about deciphering the number of lymphocytes and other blood cells from the video:
Paying close attention to your own well-being will help you detect problems in the early stages and treat them. This way you can keep your health in order for many years.
lechiserdce.ru
What to do?
If the results of the CBC show that lymphocytes are high, this is not a reason to panic. However, it is necessary to consult a general practitioner to determine the cause of this change. Based on the test results, the therapist will determine why lymphocytes in the blood of an adult are increased, what this means and what it can lead to. He can either prescribe treatment himself or, if necessary, write out a referral to a specialized specialist.
After identifying the cause of lymphocytosis, the attending physician must develop treatment tactics aimed at solving this problem. For example, if elevated lymphocytes in the blood appeared during treatment for a viral or bacterial infection, this means that it is enough to simply complete the course of treatment and take a control blood test after a while.
There are no drugs aimed directly at reducing the number of lymphoid cells. Therefore, you should not look for them at the pharmacy or ask your doctor. Folk remedies and recommendations will also not help.
A proper diet limiting fatty, smoked, and spicy foods will not directly reduce the elevated level of lymphocytes, but will have a beneficial effect on the body as a whole and will help it cope with the consequences of the disease. What does a low level of leukocytes in the blood indicate and is it possible to increase them?
An approximate plan of action to reduce lymphocytes looks like this:
- Clinical and instrumental studies to detect the causes of lymphocytosis.
- Establishing a diagnosis.
- Treatment of the underlying disease that provoked increased growth of lymphocytes.
- Correct lifestyle (diet, moderate physical activity, sleep and rest schedule, etc.).
- Follow-up tests and visit to the attending physician.
As a result of this plan, the elevated lymphocyte level will return to normal within a few weeks after the course of therapy.
Lymphocytes are elevated in an adult - what does this mean?
Important: a one-time slight (several units) excess of the norm has no diagnostic value and can be caused by improper preparation of the patient for the donation of biomaterial or other physiological reasons.
However, deviations of several times are a sufficient reason to prescribe a comprehensive (laboratory and instrumental) examination of a person in order to establish the causes.
An increased level of lymphocytes in the blood indicates a number of pathological conditions:
- infection with a viral infection. For example, rubella, chickenpox or enterovirus infection;
- parasitic infestation. For example, toxoplasmosis, which is characterized by a long course without the manifestation of clinical signs of the disease. Early diagnosis is of particular importance for pregnant women. Since infection with this parasite in the first trimester of pregnancy leads to mutations in the fetus that are incompatible with life;
- diseases, bacterial etiology. For example, tuberculosis, whooping cough, dysentery, gonorrhea, tetanus, anthrax and others. It is important not only to determine the nature of the pathogen, but also to identify it to its species. Such tactics are necessary to perform a sensitivity test to certain groups of antibiotics and select the most appropriate therapy;
- oncopathologies affecting the bone marrow or lymph nodes. For example, chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a malignant pathology accompanied by excessive deposition of B cells in certain organs. The prognosis of the outcome largely depends on the stage of the disease at which it was diagnosed. And also on the timeliness and adequacy of the chosen treatment tactics.
A very kind and informative film about the work of lymphocytes:
Patients ask themselves: what do low lymphocytes in the blood mean? A decrease in this criterion below normal levels may indicate autoimmune diseases. Also AIDS, the acute stage of a viral or bacterial infection, for genetic pathologies. For example, congenital aplasia of the thymus and parathyroid glands. In addition, taking certain medications affects the concentration of immune cells in human blood (prednisolone).
Read further: The norm of leukocytes in the blood by gender and age and the causes of deviations
Absolute and relative lymphocytosis
Looking at the results of a general blood test, you can pay attention to the fact that the lymphocyte indicator appears in two forms: relative and absolute lymphocytosis. The absolute value characterizes the number of lymphatic cells per liter of blood
With absolute lymphocytosis, the values exceed 3.6*109/l. The relative indicator is the percentage of lymphocytes in the blood, if the total number of leukocytes is taken as 100 percent. In addition to lymphocytes, these include neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils. The norm of the relative indicator is 19-37%
The absolute value characterizes the number of lymphatic cells per liter of blood. With absolute lymphocytosis, the values exceed 3.6*109/l. The relative indicator is the percentage of lymphocytes in the blood, if the total number of leukocytes is taken as 100 percent. In addition to lymphocytes, these include neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils. The norm of the relative indicator is 19-37%.
It also happens that the absolute content of lymphocytes is within the normal range, but the relative content is not, and vice versa. Relative lymphocytosis in adults is more common than absolute lymphocytosis. In this case, the absolute indicator may even be reduced.
Relative lymphocytosis is observed in diseases during which the number of other types of leukocytes listed above decreases: for example, neutropenia and relative lymphocytosis are quite combined as a result of a general blood test. This means that for some reason there are much more lymphocytes than other leukocyte cells, that is, relative lymphocytosis is observed. What is granulopenia? This is another option for reducing the number of white blood cells and can also be seen with lymphocytosis. Such deviations from the norm are typical for children under 6 years of age.
Diseases that occur with relative lymphocytosis are usually caused by viruses, infections and a decrease in the body's protective function: typhoid fever, leishmaniasis, brucellosis, etc. Other causes of relative lymphocytosis in adults:
- Presence of autoimmune disorders;
- Addison's disease;
- Splenomegaly;
- Hyperthyroidism.
Children under two years of age are especially susceptible to relative lymphocytosis.
Absolute lymphocytosis is a symptom characteristic of acute infections: measles, rubella, whooping cough, chickenpox, scarlet fever, as well as tuberculosis, hepatitis C, hyperthyroidism, AIDS, lymphosarcoma, etc.
In any case, when making a diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account other factors: individual characteristics, genetic predisposition to diseases, general leukocyte formula, results of more specific tests and a comprehensive examination of the body.