ESR in the blood: what do certain values mean?
| In children (value depends on the age of the child) | Among women | In men |
|
|
|
If this value is increased during pregnancy, this is considered a normal condition.
The normal ESR rate during pregnancy is up to 45 mm/h. With such values, the expectant mother does not need to be further examined and the development of pathology is not suspected. As mentioned above, normal ESR values for a healthy man are considered to be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 mm per hour; for women, the normal value is from 2 to 15 mm/hour. Therefore, for women, a value of 12, 13, 14, 15 is considered normal. However, indicators for women in adulthood can normally be 16, 17, 18, 19, 20.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
If the value exceeds the norm by several units, then the blood condition can be considered relatively normal. That is, an indicator of 21, 22 in a woman can be considered acceptable, as well as values of 23, 24 mm/h. When a woman is pregnant, this meaning is even greater. Therefore, expectant mothers have no reason to believe that a reading of 25 means something unpleasant.
This indicator increases with age. Therefore, if an ESR value of 40 is noted in elderly patients, the doctor determines what disease this is a symptom of and what it means by the accompanying signs. Normal values for older people are 43, 50, 52, 55 mm/h, etc. However, for young people, values of 40-60 mm/h are possibly evidence of serious disorders.
Low value
As a rule, the reasons for a low value of this indicator are associated with exhaustion of the body, weight loss, taking corticosteroids, hyperhydration, and muscle atrophy. Sometimes ESR is lowered in diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
In both women and men, the level of ESR is influenced by a number of different factors, both physiological and pathological. The key factors that most influence this analysis are identified:
- When determined by different methods - according to Westergren et al. - the norm of ESR in the blood of women is higher than that of men. So, an ESR of 25 in a woman may be normal. This is due to the physiological characteristics of blood in women.
- What is the normal ESR level in a woman’s blood depends on whether she is pregnant. For expectant mothers, the norm is from 20 to 45 mm/h.
- A higher ESR is observed in women who take contraceptives. Under this condition, a woman may have a normal ESR of 30. What this means, whether there is a pathology, or whether we are talking about a normal physiological indicator, must be determined by the doctor.
- In the morning, the rate at which red cells settle is higher than in the afternoon and evening, and differences in age do not matter here.
- Signs of accelerated sedimentation are observed when exposed to acute phase proteins.
- If inflammation and an infectious process develops, the values change a day later. How does leukocytosis and hyperthermia begin? That is, on the first day of the disease the indicator can be 10, 14, 15 mm/h, and a day later it can increase to 17, 18, 20, 27, etc.
- ESR is elevated if there is a chronic source of inflammation in the body.
- A reduced value is observed with increased blood viscosity.
- A decrease in sedimentation rate occurs under the influence of anisocytes and spherocytes; the rate becomes greater under the influence of macrocytes.
What does a blood test show when ESR is elevated and leukocytes are normal?
Quite often, when examining blood in patients, it happens that the ESR is elevated, but the leukocytes are normal. The reasons for increased ESR with normal leukocytes may be different. Analysis of ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is one of the most common methods of blood testing. This procedure is quick and simple. In all public clinics, ESR testing is free; in private clinics, the cost is low. This test may show that there is inflammation or infection in the body. But it is very difficult to make an accurate diagnosis without further research.
Using this type of blood test, the doctor can determine what actions need to be taken after the results of a general examination of the body. In addition, they look at the content of leukocytes. If, with a normal number of leukocytes, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased, this slightly narrows the range of possible diseases.
Elevated ESR when other indicators are normal does not always mean the presence of pathology in the body. There are cases when a high number is not at all associated with the disease. It is also possible that the patient is sick, but the erythrocyte sedimentation rate has adequate indicators that do not go beyond the normal range. This significantly complicates diagnosis, especially if no external manifestations of the disease are detected. With all this, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be different at different ages.
Therefore, each age group has its own ESR standards.
What should the ESR norm be?
A normal indicator is not one constant value, it can be different and depends on:
- age;
- gender;
- individual characteristics of the body.
For example, the normal value for an adult male is 2-11 mm/h. An adult woman normally has slightly different indicators - 2-20 mm/h. Moreover, the older the person, the higher the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The norm for older men and women is 30-50 mm/h.
Infants have a very low ESR - 0-2 mm/h. This is their norm, there is no pathology in this. The older the child gets, the higher the rate. At 12 months of life the rate reaches 12 mm/h. By the age of 5, the indicator has such limits - 5-11 mm/h. From 7 years and more – 4 mm/h.
Pathology is a deviation from age and gender norms, usually an increase in ESR. In some cases, the analysis may give incorrect results. This happens in case of violation of blood sampling norms; donation occurs strictly in the morning on an empty stomach. Another factor that can distort the result is an excessively heavy dinner or, conversely, fasting the entire previous day. In this case, it is worth repeating the analysis to clarify the indicator.
Causes of increased ESR with normal leukocytes, not related to disease
If the study shows the result that the ESR is increased, this does not always mean that the patient is sick. In some cases, deviations are possible that are not dangerous to the body. These include:
- Individual characteristics of the body. According to statistics, 4.5% of people on the planet have an increased red blood cell sedimentation rate.
- Some medications or vitamins may cause upward changes in analysis.
- Pregnancy. Women who are carrying a child almost always have a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate, sometimes the numbers reach 80 mm/h.
- Iron deficiency, low hemoglobin. Anemia and poor absorption of iron are common causes of inadequate test results.
- Boys aged 5-12 years. From time to time, little boys experience erroneous results when there are no diseases, inflammations or infections in their bodies.
- ESR depends on other indicators of blood components: albumin, fibrinogen proteins, immunoglobulin, various pigments and bile and uric acids.
Increased ESR and leukocytes are normal in pathologies
But often such a ratio of analysis results can also indicate diseases, serious and not so serious.
Infection. The presence of infection is the most common reason for an increase in ESR with a normal white blood cell count. The overall percentage of infectious cases with this result is 40%. The rate during infection can exceed 100 mm/h.
Tumors. The presence of benign or malignant tumors is often detected after a blood test for ESR, when its indicators are greatly elevated, but leukocytes are normal. The clinical picture is the same in children, but this cannot be considered as an indication of the presence of tumors; they form extremely rarely at a young age.
Intoxication. Poisoning of various natures, painful conditions due to colds and flu, ailments from the field of rheumatology - all this can show an increased rate of sedimentation of red blood cells. At the same time, the blood becomes a little thicker, which contributes to the rapid settling of particles.
Diseases of the genitourinary system. When a patient has kidney problems or urinary tract diseases, a blood test shows this and erythrocyte sedimentation occurs very quickly, ranging from 100 to 120 mm/h.
Anisocytosis. This is a blood disease in which the erythrocyte sedimentation rate always shows high results, greatly exceeding the norm. Metabolic disease. With this pathology, many parameters of the blood test are confused, red blood cells change speed. Sometimes very low values come out here.
Endocrine diseases. Thyretoxicosis, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism - all these diseases inevitably lead to an increase in the sedimentation rate of red blood cells. These are very common diseases, so if the red blood cell rate is high, it would be a good idea to check the thyroid gland.
Cardiovascular diseases. Patients who have had a heart attack or stroke have a high ESR, which does not change for a long time. These diseases are more common in older people. Although high values are considered the norm, it is important to know where the acceptable limit is so that you can monitor your condition.
Increased blood viscosity. Blood becomes more viscous due to poisoning, constipation, and intestinal infections. In such blood, red blood cells settle much faster than usual.
Some dental diseases. For example, in the presence of dental granulomas, blood tests almost always show a significant increase in the red blood cell sedimentation rate.
An analysis to detect the erythrocyte sedimentation rate can only hint at the presence of any disease in a person who applied for it due to ailments or for a regular commission. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct many additional studies, tests not only of the blood, but also of various secretions and the entire body as a whole.
In order for the attending physician to monitor the dynamics of the identified disease, several ESR tests are performed. This way you can track how effective the treatment is, whether it needs to be extended or, conversely, needs to be reduced, medications replaced, etc.
Rate this article:
1 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5
osostavekrovi.ru
What to do if the reasons for the increase are not determined?
An increased ESR may not always indicate the presence of pathology. There are the following situations against the background of which inflated limits of this indicator are the norm:
- The presence of individual characteristics of the functioning of organs. Only a small proportion of the total number of patients has a high ESR. The reasons must be determined by a doctor.
- Some medications and vitamins can affect sedimentation rate.
- Pregnant women are also susceptible to changes in this indicator (their ESR reaches 80 millimeters per hour).
- Iron deficiency in the blood along with its poor absorption in the body. What are other reasons for high ESR with normal leukocytes?
- ESR can increase in boys aged five to twelve years, even if they do not have any pathogenic factors.
- This indicator often increases as part of changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the blood.
But often a high ESR with normal leukocytes in a child and an adult indicates that certain pathological processes are occurring in the body.
If the analysis is normal, but the causes of the increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate cannot be determined, it is important to conduct a detailed diagnosis. It is necessary to exclude oncological diseases, so lymphocytes, GRA, and the norm of leukocytes in women and men are determined. During the analysis process, other indicators are also taken into account - whether the average volume of erythrocytes is increased (what this means - the doctor will explain) or whether the average volume of erythrocytes is decreased (what this means is also determined by the specialist). Urine tests and many other studies are also carried out.
But there are cases when high ESR levels are a feature of the body, and they cannot be reduced. In this case, experts advise regular medical examinations, and if a certain symptom or syndrome appears, consult a doctor.
What to do if ESR is elevated?
Treatment for elevated ESR is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination and diagnosis. It corresponds to the nature of the disease. During the treatment period, ESR analysis is carried out several times to monitor the dynamics of the disease. With the right method, the indicators gradually decrease and return to normal.
But it should be noted that you should not expect instant results. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate returns to normal within 4-6 weeks.
There is no need to use any means to lower the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the blood for no apparent reason, since an increase in the rate itself is not a disease. It is also worth noting that if an increase in ESR in the body is accompanied by any other symptoms, then a comprehensive examination should be carried out and all tests should be repeated.
To protect yourself from possible diseases, doctors recommend taking a blood test once every six months. The study of ESR is mandatory and effective in all cases: whether for diagnosis or simply for preventive measures.
High ESR in a child
| Abbreviation | Indicator and unit of measurement | 0-1 month | 1-12 months | 1-6 years | 6-12 years | 12-16 years old |
| R.B.C. | Red blood cells, 1012/l | 4,4-6,6 | 3,6-4,9 | 3,5-4,5 | 3,5-4,7 | 3,6-5,1 |
| HBG | Hemoglobin, g/l | 140-220 | 100-140 | 110-145 | 115-150 | 115-150 |
| HCT | Hematocrit, % | 33-65 | 31-41 | 32-42 | 33-43 | 34-48 |
| RET | Reticulocytes, % | 3-15 | 3-15 | 3-12 | 2-12 | 2-11 |
| CPU | Color index | 0,75-0,95 | 0,8-0,1 | 0,85-1,05 | 0,85-1,05 | 0,85-1,05 |
| MCV | Red blood cell volume, fl | 100-140 | 75-110 | 75-95 | 70-85 | 80-95 |
| MCH | Average Hb content in Er, pg | 29-37 | 27-30 | 22-31 | 25-32 | 26-32 |
| MCHC | Average concentration of Hb in Er, g/l | 280-360 | 280-370 | 320-370 | 320-380 | 320-380 |
| RDW | Anisocytosis Er, % | 14,9-18,7 | 11,6-14,8 | 11,5-14,5 | 11,5-14,0 | 11,5-14,0 |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, mm/h | 0-2 | 4-10 | 5-11 | 4-12 | 2-15 |
| WBC | Leukocytes, 109/l | 9,5-15,0 | 7,7-15,8 | 5,0-16,5 | 4,5-13,5 | 4,4-12,5 |
| NEUT | Neutrophils,%:
|
|
|
|
|
|
| BASO | Basophils, % | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 |
| EO | Eosinophils, % | 2-7 | 2-7 | 1-6 | 1-6 | 1-5 |
| MON | Monocytes, % | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-10 | 2-10 | 2-10 |
| LYM | Lymphocytes, % | 38-72 | 38-72 | 26-60 | 24-54 | 25-50 |
| PLT | Platelets, 109/l | 180-400 | 180-400 | 180-400 | 160-380 | 160-390 |
| MPV | Average volume Tr, fl | 7,4-10,4 | 7,4-10,4 | 7,4-10,4 | 7,4-10,4 | 7,4-10,4 |
| PDW | Anisocytosis Tr, % | 10-17 | 10-17 | 10-17 | 10-17 | 10-17 |
| PCT | Thrombocrit, % | 0,15-0,4 | 0,15-0,4 | 0,15-0,4 | 0,15-0,4 | 0,15-0,4 |
If a patient has an elevated ESR in the blood, what this means is determined by the doctor during the diagnostic process. After all, this indicator is very important for diagnosis if the development of a certain disease is suspected. In the diagnostic process, a qualified doctor takes into account not only the fact that the patient has an increased value, but also determines what the presence of other symptoms indicates. But still this indicator is very important in many cases.
ESR: increased in diseases
An increased ESR in the blood of a child and an adult is observed if a bacterial infection has occurred - during the acute phase of a bacterial infection.
In this case, it does not matter where exactly the infections are localized: the picture of the peripheral blood will still reflect the inflammatory reaction.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
This value is always increased in an adult if there are viral infectious diseases. What specifically causes this indicator to increase is determined by the doctor during a comprehensive examination.
During the development of an infectious disease, this value does not increase quickly; an increase is observed after 1-2 days. If the patient has recovered, the ESR will be slightly elevated for several more weeks or months. The reasons for a high ESR with normal leukocytes may indicate that the person has recently suffered a viral disease: that is, the leukocyte count has already returned to normal, but the red cell sedimentation rate has not yet.
The reasons for increased ESR in the blood in women may be associated with pregnancy, therefore, in the diagnostic process, the doctor must take into account these reasons for the increase in ESR in the blood in women.
An increase in ESR is a typical symptom in the following diseases:
- diseases of the biliary tract and liver;
- inflammatory diseases of a purulent and septic nature (reactive arthritis, etc.);
- blood diseases (sickle anemia, hemoglobinopathies, anisocytosis);
- ailments in which tissue destruction and necrosis occur (stroke, heart attack, tuberculosis, malignant neoplasms);
- pathologies of the endocrine glands and metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes, cystic fibrosis, etc.);
- malignant degeneration of the bone marrow, in which red blood cells enter the blood that are not ready to perform direct functions (myeloma, leukemia, lymphoma);
- autoimmune diseases (scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, etc.);
- acute conditions in which the blood becomes more viscous (diarrhea, bleeding, vomiting, postoperative conditions, etc.).
When the ESR norm in children is exceeded, most likely an infectious inflammatory process develops in the body. But it should be taken into account, when determining ESR according to Panchenkov, that other indicators of the CBC (hemoglobin, etc.) are also increased (or changed) in children. Also, in children with infectious diseases, their general condition worsens significantly. In case of infectious diseases, the ESR is high in the child already on the second or third day. The indicator can be 15, 25, 30 mm/h.
If red blood cells are elevated in a child’s blood, the reasons for this condition may be the following:
- metabolic disorders (diabetes, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism);
- systemic or autoimmune diseases (bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus);
- blood diseases, hemoblastosis, anemia;
- diseases in which tissue decay occurs (tuberculosis, myocardial infarction, cancer).
It is necessary to take into account: if even after recovery the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased, this means that the process is proceeding normally. It’s just that normalization is slow, but after about one month after the disease, normal levels should be restored. But if there are doubts about recovery, then you need to do a re-examination.
Parents must understand that if a child’s red blood cells are higher than normal, this means that a pathological process is taking place in the body.
But sometimes, if a baby’s red blood cells are slightly elevated, this means that some relatively “harmless” factors are influencing:
- in infants, a slight increase in ESR may be associated with a violation of the mother’s diet during natural feeding;
- period of teething;
- after taking medications (Paracetamol);
- with a lack of vitamins;
- with helminthiasis.
Thus, if red blood cells are elevated in the blood, this means that the child is developing a certain disease. There are also statistics on the frequency of increase in this value in various diseases:
- in 40% of cases, a high value indicates infectious diseases (respiratory tract diseases, tuberculosis, urinary tract diseases, viral hepatitis, fungal diseases);
- in 23% - oncological processes of various organs;
- in 17% - rheumatism, systemic lupus;
- in 8% - cholelithiasis, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, pelvic organs, anemia, ENT diseases, injuries, diabetes, pregnancy;
- 3% - kidney disease.
In young children, the rate of subsidence may increase for the following reasons:
- The influence of improper breastfeeding (in this case, red blood cells will settle much faster due to maternal neglect of the diet).
- Impact of parasitic lesions.
- Teething (this process causes a restructuring of the child’s entire body, and therefore the rate of sedimentation increases).
- The baby is afraid to donate blood.
General blood test: deciphering “from” and “to”
ACUTE BACTERIAL INFECTION
Signs of the disease.
Leukocytes and ESR are higher than normal. The number of neutrophils and moncites in the blood is increased. The level of lymphocytes is reduced. The child may have a fever, a wet cough, a runny nose, purulent discharge from the nasopharynx, and wheezing in the lungs.
Treatment scheme.
Treatment with antibiotics. They are prescribed by doctors after examining the child and reviewing the blood test. Children are often prescribed penicillin antibiotics: Augmentin, Flemoxin Solutab, Suprax. Antibiotics from the azalide group (vilprofen, sumamed) may be prescribed.
CHRONIC OR FOCAL BACTERIAL INFECTION
Signs of the disease.
Neutrophils are slightly elevated in the upper limits of normal, while lymphocytes are decreased in the lower limits of normal. The child has a chronic or latent bacterial infection. To identify the source of the disease, it will be necessary to conduct various examinations. Important: these blood values remain in a child who has recently had a bacterial infection.
ACUTE VIRAL INFECTION
Signs of the disease.
Leukocytes and ESR are higher than normal. The number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula is higher than normal. The number of neutrophils is reduced. Monocytes and eosenophils may increase slightly.
Treatment scheme.
For a viral infection, doctors usually prescribe antiviral drugs interferon - Viferon, Genferon, Kipferon. Important: the same symptoms can be observed with a parasitic infection caused by chlamydia or mycoplasma. These infections have a distinctive feature - a long-lasting dry cough in a child, which can last several weeks. With such a cough, there is no wheezing in the lungs, and the child appears healthy in appearance.
CHRONIC VIRAL INFECTION
Signs of the disease.
ESR is normal. Leukocytes are normal or even low. Lymphocytes and monocytes are at the upper limits of normal. Neutrophils are slightly or markedly decreased. The child is often sick.
Treatment scheme.
Examine the child for possible viral diseases, namely, Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus. The cause of the malaise with such a blood test picture may be hidden in these viral infections. Important: such blood levels can be observed in a child who has recently had a viral infection, such as a viral runny nose.
Next are the norms.
RED BLOOD
The blood test can be divided into two parts: red blood indicators and white blood indicators. Red blood includes red blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin and color index. These indicators are responsible for the delivery of oxygen to cells. The presence of infection in the body usually does not affect these components. It is enough just to make sure that they comply with the norm, and you can move on to the second part.
STANDARDS
HEMOGLOBIN (Hb).
Responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood. Hb is measured in grams per liter of blood.
A one-month-old child has a hemoglobin norm of 115-175 grams/liter (the hemoglobin level can be quite high), at 6 months and up to 12 years of age, a child has a hemoglobin norm of 110-140 grams/liter (according to other sources, up to 145 is acceptable).
erythrocytes (RBC cells).
Red blood cells carry oxygen into cells using hemoglobin. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin molecules. In a one-month-old baby, the normal red blood cell count is 3.8-5.6 trillion red blood cells per liter of blood. The norm of red blood cells in a one-year-old child, as in adults, is 3.5-4.9 trillion per liter. Trillions per liter are big numbers, but further indicators will be simpler.
RETICULOCYTES (RTC).
These are the so-called young red blood cells. Their number is measured as a percentage. In children under one year of age, the norm of reticulocytes should not exceed 15%, in children over one year of age, as well as in adults, the norm of reticulocytes is 3 - 12%. If a child has a reticulocyte count of less than three percent, this indicates the presence of anemia. In this case, you need to start taking action as quickly as possible.
Platelets (PLT).
These are postcellular structures (fragments of the predecessor cell) that do not have a nucleus. These residual structures then form blood clots, which help stop bleeding if any injury occurs. The number of platelets in the blood is smaller than red blood cells and is measured in billions per liter of blood. The norm of platelets in the blood before one year of life is from 180 to 400, after one year and in adults - from 160 to 360.
ESR (ESR).
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is measured in millimeters per hour. A high erythrocyte sedimentation rate indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Therefore, when we go to the doctor with a suspected infection, it is necessary to find out the ESR indicator. Normal ESR values in a child in the first month of life are 4-10, in a six-month-old child - 4-8, from one year to 12 years - 4-12 mm per hour. With age, ESR levels differ between men and women.
There are also blood indicators such as hematocrit (HCT)
, mean erythrocyte volume (MCV), erythrocyte distribution width (RDWc), mean erythrocyte hemoglobin content (MCH), mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). Red blood counts are useful in diagnosing anemia, but we are now talking about infections. To recognize an infection, we use white blood indicators, which are also responsible for the body’s immunity.
WHITE BLOOD
Leukocytes
- These are immune protective blood cells that fight various types of infections. Some of the leukocytes act on viruses, others on bacteria, others fight allergens, and others act on multicellular parasites.
In order to determine the presence of infection in the body, just look at the number of leukocytes in the blood. If there is an infection, the number of white blood cells in the blood will increase. But this is not enough to determine what kind of infection we are dealing with. To find out this in more detail, you need to study the leukocyte formula. We will dwell on the leukocyte formula indicators in detail.
STANDARDS
A person’s red blood levels differ from birth to the first months of life. Then they level out and do not have sharp fluctuations. Indicators of white blood change unevenly, intermittently, since the immune system of a child under six years of age is constantly changing. You need to thoroughly study the characteristics of white blood so that many questions do not arise later.
LEUCOCYTES (WBC).
Measured in billions per liter of blood. The number of leukocytes in a child, even in normal condition, is higher than in an adult. The white blood cell count in a newborn is especially high. This is explained by the fact that at birth the child finds himself in a new environment, unsterile for him compared to the womb. Due to this, the number of leukocytes increases. Sterile cleanliness in the house or a quartz lamp against bacteria will not help as much as the child’s immune system itself. With age, the child's body will get used to the new environment, and the number of leukocytes will decrease. The number of leukocytes in a child in the first month of life ranges from 6.5 to 13.8 billion/liter, at six months - 5.5-12.5, from one year to six years (the period when babies are most often susceptible to various diseases) - 6-12 billion/liter. After the child’s immune system becomes more stable to many infections, the number of leukocytes is within the same normal range as in an adult - 4.5-9. You can notice that with age the number of leukocytes gradually decreases, and normally it should not exceed 9-11.
LEUKOCYTE FORMULA.
This is the percentage of different types of leukocytes. Let's consider its components.
Neutrophils (NEU).
Measured as a percentage of the total number of leukocytes. Neutrophils fight bacteria in the body. The task of these cells is to destroy invading bacteria. Neutrophils also eat cellular debris and fight foreign particles. This phenomenon is called phagocytosis. We can call these leukocytes “the body’s cleaners.”
Neutrophils are divided into two types: band and segmented.
Segmented neutrophils
are mature cells, their nucleus consists of segments. These are the main white blood cells. Their number as a percentage of all leukocytes is normally 15-45% in children under one year old, 25-60% from one to six years old, from seven years old and in adults 30-60%. Segmented neutrophils are the basis for the successful functioning of the entire immune system of the body. They perform an important function in destroying bacteria.
There are very few band neutrophils in the blood. These are immature young neutrophils with a rod-shaped cell nucleus. Just like segmented neutrophils, they affect bacteria. However, their normal amount in children from one month to six years is from 0.5 to 4.5%. Starting from the age of seven and in adults, their number increases to 6%. In infectious diseases, an increase in the number of band neutrophils in the blood is observed.
Monocytes (MON).
This is a type of white blood cell that can absorb larger cell debris during phagocytosis than neutrophils. Monocytes are mainly found in body tissues, and their number in the blood is small. When the number of neutrophils in the blood decreases, monocytes increase slightly to perform the functions of neutrophils. The number of monocytes in the blood should be from 2 to 12% in children under one year old and 2-10% in children over one year old (as in adults).
Eosinophils (EOS).
It is believed that eosenophils control allergic manifestations. This is not entirely true, since eosenophils do not produce immunoglobulin E, which is produced in the body of allergy sufferers. Their main meaning lies elsewhere. Namely, that these leukocytes are a real threat of parasites that invade the body. Eosinophils act on worms and multicellular bacteria. They do not devour these organisms, like neutrophils and monocytes, but stick to them, injecting their digestive enzymes into them and sucking out the contents of these parasites. This phenomenon can be compared to a child sucking a juice packet through a straw. As a result, all that remains of the parasites is an empty shell. Eosenophils perform their important function in clearing the body of infection. The norm of eosenophils in the blood ranges from 0.5 to 6%.
Lymphocytes (LYM).
This is the basis of the leukocyte formula. White blood cells are one of the most important cells in the immune system. They actively fight viruses, and also enthusiastically destroy their own cells overtaken by the virus. From birth to one year, the level of lymphocytes in the blood of children is high - from 40 to 72%. During this period, the child’s immune system has not yet begun its work, and lymphocytes, despite their large number, still work poorly. From one year to six years, the norm of lymphocytes in the blood is 26-60%. After six years, the immune system becomes stable and the level of lymphocytes is established within the normal range of 22-50%.
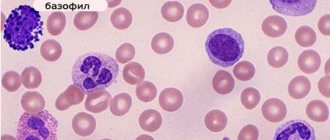
Basophils (BAS).
These are young lymphocytes. The level of basophils in the leukocyte formula is no more than 1%.
Finally, we figured out the leukocyte formula. Let's now draw conclusions...
For those who know all the blood indicators and their functions, it will not be difficult to figure out the type of infection in the body using a blood test. It's even elementary.
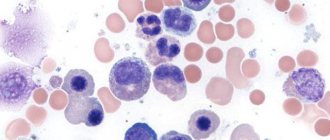
Increased ESR and leukocytes.
This means that the body is in the midst of an infection. There may be symptoms such as fever, increased body temperature to 38-40 degrees. The child needs to be treated immediately.
Neutrophils are increased.
This means that the body suffers from bacterial infection. In such cases, antibiotics are prescribed.
Lymphocytes are increased.
There is a viral infection in the body.
Source https://www.mamuski.ru/zdorove/zabolevaniya?id=2933
How to reduce ESR in the blood?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
The doctor will tell you in detail about ways to reduce this indicator with the help of medications after the study. He will prescribe a treatment regimen once the diagnosis has been made. It is strictly not recommended to take medications on your own. You can try to reduce it with folk remedies, which are mainly aimed at restoring the normal function of the immune system, as well as cleansing the blood.
When can increasing ESR be considered safe?
As you know, an increase in red blood cells in the blood, as a rule, indicates that a certain inflammatory reaction is developing in the body. But sometimes the reasons for the increase in red blood cells in the blood of women and men are not so categorical.
We are talking, first of all, about allergies, when analysis in men and women helps to judge whether anti-allergy treatment is being carried out correctly (fluctuations in the initially elevated ESR should be taken into account). That is, if the clinical effect of the drug occurs, then gradually the normal ESR level in the blood of men, as well as in women, will be restored.
A hearty breakfast before the test can also increase this indicator; a strict diet and fasting can also change it.
ROE can change during menstruation, during pregnancy and after the birth of a child.
What do leukocytes and ESR mean?
Leukocytes, also known as white blood cells, are the general name for blood cells that are quite different in appearance and function, but nevertheless work together on the most important problem - protecting the body from foreign agents (mainly microbes, but not only). In general terms, white blood cells capture foreign particles and then die along with them, releasing biologically active substances, which, in turn, cause the symptoms of inflammation familiar to us all: swelling, redness, pain and fever. If the local inflammatory reaction is very active and leukocytes die in large numbers, pus appears - this is nothing more than the “corpses” of leukocytes that died on the battlefield with infection.
Within the team of leukocytes, there is its own division of labor: neutrophils and monocytes are mainly “responsible” for bacterial and fungal infections, lymphocytes and monocytes for viral infections and the production of antibodies, eosinophils for allergies.
On the analysis form you will see that neutrophils are also divided into band and segmented . This division reflects the “age” of the neutrophils. Rod cells are young cells, and segmented cells are mature, adult cells. The more young (band) neutrophils on the battlefield, the more active the inflammatory process. It is the bone marrow that sends young soldiers who are not yet fully trained and have not been fired to war.
False-positive ESR tests
In medicine there is also the concept of a false positive analysis. An analysis of ESR is considered such if there are factors on which this value depends:
- anemia (no morphological changes in red blood cells occur);
- an increase in the concentration of plasma proteins, with the exception of fibrinogen;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- renal failure;
- high degree of obesity;
- pregnancy;
- old age of a person;
- administration of dextran;
- a technically incorrect study;
- taking vitamin A;
- recent vaccination against hepatitis B.
Physiological (false) increase in ESR

Helminth infections are among the physiological causes of accelerated ESR
The physiological reasons for the acceleration of ESR include the following factors or effects on the body:
- trauma to tissues, organs - wounds, fractures, operations;
- blood loss;
- intoxication or poisoning with harmful substances;
- helminthiases;
- high cholesterol;
- group B hypervitaminosis, childhood vitamin deficiency;
- taking medications - morphine, dextran, vitamins A and D, paracetamol (in children);
- vaccination against hepatitis B;
- use of contraceptive medications;
- in the postpartum period or during menstruation.
In a number of other cases, an elevated ESR may also be considered safe. This happens in cases where: anti-allergy therapy was carried out, the diet was violated (fasting, strict diets), the rule was not followed when taking a general analysis - there was a hearty breakfast before the examination.
Methods used to test ESR blood
Before deciphering what ESR means in a blood test, the doctor uses a certain method to determine this indicator. It should be noted that the results of different methods differ and are not comparable.
Before performing an ESR blood test, it must be taken into account that the obtained value depends on several factors. The general analysis must be carried out by a specialist - a laboratory employee, and only high-quality reagents are used. The analysis in children, women and men is carried out provided that the patient has not eaten food for at least 4 hours before the procedure.
What does the ESR value show in the analysis? First of all, the presence and intensity of inflammation in the body. Therefore, if there are abnormalities, patients are often prescribed a biochemical analysis. Indeed, for high-quality diagnostics it is often necessary to find out in what quantity a certain protein is present in the body.
The described method for determining ESR - the Westergren method - currently meets the requirements of the International Committee for Standardization of Blood Studies. This technique is widely used in modern diagnostics. For this analysis, venous blood is needed, which is mixed with sodium citrate. To measure ESR, the distance of the stand is measured, the measurement is taken from the upper limit of the plasma to the upper limit of the red blood cells that have settled. The measurement is carried out 1 hour after the components have been mixed.
It should be noted that if Westergren's ESR is elevated, this means that this result is more indicative for diagnosis, especially if the reaction is accelerated.
ESR according to Wintrob
The essence of the Wintrobe method is the study of undiluted blood that was mixed with an anticoagulant. The desired indicator can be interpreted using the scale of the tube in which the blood is located. However, this method has a significant drawback: if the reading is above 60 mm/h, the results may be unreliable due to the fact that the tube is clogged with settled red blood cells.
ESR according to Panchenkov
This method involves the study of capillary blood, which is diluted with sodium citrate - 4:1. Next, the blood is placed in a special capillary with 100 divisions for 1 hour. It should be noted that when using the Westergren and Panchenkov methods, the same results are obtained, but if the speed is increased, then the Westergren method shows higher values. Comparison of indicators is in the table below.
| According to Panchenkov (mm/h) | Westergren (mm/h) |
| 15 | 14 |
| 16 | 15 |
| 20 | 18 |
| 22 | 20 |
| 30 | 26 |
| 36 | 30 |
| 40 | 33 |
| 49 | 40 |
Currently, special automatic counters are also actively used to determine this indicator. To do this, the laboratory assistant no longer needs to dilute the blood manually and track the numbers.
What diseases cause increased ESR?
Why does ESR increase? What diseases or other causes lead to such indicators? What do the numbers in them mean? Patients ask these questions to their attending physician.
No specialist can immediately and unambiguously voice the reason for the high values recorded on the form. Only additional diagnostic methods help determine what causes an increase in ESR may be in a particular patient.
The main reasons leading to an increased number in a blood test are the presence of diseases.
If the ESR is higher than normal, this means the development of one or more diseases:
- infections of a bacterial, viral or fungal nature - their progression triggers processes in which the ESR is increased, the reaction rate increases, because leukocytes in the blood are increased. The reasons for a high test result may be influenza, bronchitis and pneumonia, viral hepatitis, tuberculosis.
- neoplasms of various natures (malignant and benign) – the development of tumors is associated with a significant increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the level of leukocytes does not increase, the number of leukocytes will increase only with the development of certain types of neoplasms,
- analysis, when the ESR indicator is increased, helps to identify diseases of the rheumatological type: arthritis, arthrosis, rheumatism, changes in connective tissues of a diffuse nature, lupus erythematosus and others,
- high rates are accompanied by diseases of the urinary tract, kidneys - urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis,
- blood diseases.
One of the main reasons that increases ESR, a process that accelerates the reaction, is considered to be poisoning of the body with harmful substances, toxins of various origins. With it, processes occur associated with changes in the qualitative composition of the blood, in which the number of leukocytes changes, its density increases, which causes increased ESR values due to the fact that the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased.
The need for additional examination
It is worth noting that a high level of ESR only suggests the presence of some disease, but never determines it. To do this, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe additional research, and in addition, make a diagnosis, after which he will determine a further therapeutic course.
As treatment progresses, it is necessary to conduct several tests after certain time intervals, which will allow you to track how much the value has changed since its increase. Based on this information, the specialist can reduce or increase the dose, replace medications if necessary, and carry out all necessary therapeutic procedures.
At the same time, an increase in ESR may signal the start of some kind of inflammation, which leads to the need for additional tests. In this regard, it is important to know what exactly triggered the increase in one blood element and the preservation of the norm of another. And in this situation there is no way to do without the help of a qualified doctor.
We looked at what a high ESR means with normal leukocytes.
Increased white blood cells and antibiotics
By the way, from what I just wrote, paradoxically, one very important thesis follows.
You will definitely see lymphocytosis there and will worry where it came from! You will rush to search the Internet for the causes of leukocytosis, you will definitely find horror stories about leukemia there, you will not sleep for two nights, you will make an appointment with a hematologist. And leukocytosis in this case was merely a “witness” of a viral infection. Moreover, it can remain in the blood for up to a month after a cold.
And the second very important idea: leukocytosis is not a disease, but only a symptom of a wide variety of conditions. Hence the conclusion, which is useful to remind not only patients, but also many doctors.
The fact is that there is no universal “broad-spectrum” antibiotic; For different infectious diseases, completely different drugs and their dosages are used. As a rule, an attempt to prescribe treatment is in a situation where the disease has not been found, but the doctor says: “You have an infection somewhere in your body. ”, only leads to further diagnostic confusion.
The fact is that pathogens of infectious diseases do not just float in circles in the blood; they always strive to “settle” somewhere, causing a picture of a specific disease. Not to mention the fact that not every fever and not every leukocytosis are signs of a bacterial infection, which, in fact, should be affected by antibiotics.
So, I repeat, with rare exceptions, there is no need to take antibiotics until there is an answer to the question of the name of the disease that we are treating.

General information
New methods for diagnosing and determining the causes of diseases appear in modern medicine regularly. However, determining ESR in human blood is still an effective diagnostic method. It is used for diagnostic purposes in both children and adults. Such a study is prescribed both when a patient who is concerned about a certain disease contacts a doctor, and during preventive examinations.
Any doctor can interpret this test. ESR is included in the group of general blood tests (CBC). If this indicator is elevated, you need to determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Determination of ESR and subtleties of the study
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
The level of erythrocyte sedimentation is currently determined in three different ways:
- The Westergren method involves venous sampling of biomaterial, which is subsequently mixed with sodium citrate. After one hour, all deposited red blood cells must be measured.
- As part of the Winthrop method, blood is mixed with an anticoagulant, after which the biomaterial is placed in a test tube with divisions. But the test tube may become clogged if the sedimentation rate is more than 60 millimeters per hour (this, of course, makes it very difficult to establish the exact sedimentation level).
- The Panchenkov method of determination involves taking blood for testing from a finger. Next, the biomaterial is combined with sodium citrate.

All of the above calculation methods are manual. Different methods are good in certain cases. The Westergren method of calculating subsidence is often the most accurate. With the development of medicine, ESR began to be calculated automatically, since this method completely eliminates the occurrence of errors in calculations.
You also need to know that leukocytes play a very important role in the process of determining sedimentation rate. Normal leukocytes in the presence of elevated ESR may indicate residual effects after the disease. As for a reduced level of leukocytes, this indicates viral sources of the disease, and an increased level indicates the presence of bacterial pathogens.
ESR standards
In a laboratory test, blood is mixed with anticoagulants, after which a separation reaction occurs into two layers: the lower layer consists of red blood cells, and the upper layer consists of plasma and leukocytes. Therefore, when determining ESR, the level of leukocytes is immediately calculated.
Research methods
The distance traveled by red blood cells in one hour is called the sedimentation rate
To determine ESR, the two most common, non-interchangeable methods are used:
- Panchenkov method - a traditional method from the heritage of the USSR;
- The Westergren method is the standard of the ICSH (International Committee for Standardization of Hematological Studies).
Why should the attending physician know exactly the method used for the analysis? Because in the case of acceleration of the OE speed, the Westergren method produces higher values.
Important! For more reliable results and to create an objective picture, you need to do a repeat analysis after 4-6 days.
This is necessary because the results of the study depend on compliance with the storage conditions of the blood sample, so it is better to repeat the analysis in another laboratory, but be sure to follow the previous examination method.
In the case of elevated ESR in subjectively healthy patients, which occurred without apparent causes or symptoms, it is advisable not to panic and avoid a detailed examination until any complaints appear. A repeat test should be taken no earlier than 6 months later, after which an annual check is advisable.
Norms for different genders and ages
A low rate is possible in the first trimester of pregnancy
Normal values for erythrocyte sedimentation rate depend on age and gender. After the examination, the resulting ESR value is recorded in mm/h in the ESR column (international designation).
The table below shows normal indicators for children under 12 years of age, and the gender of the child does not matter.
| Novo born | 1-7 days | 7-30 days | 1-6 month | 6-12 month | 1-2 years | 2-3 years | 3-6 years | 6-9 years | 9-12 years | |
| ESR | 1-4 | 4-8 | 4-12 | 12-17 | 4-12 | 4-12 | 4-12 | 2-8 | 2-8 | 2-8 |
A low ESR in a child may be a consequence of prolonged diarrhea and dehydration or indicate chronic circulatory failure or the presence of degenerative heart diseases.
For children over 12 years of age, adults and people over 60, indicators are graded according to gender. For pregnant women, the ESR norm differs significantly from the average for their age category.
| Men 12 -60 years | Women 12-60 years old | Men over 60 | Women over 60 | Pregnant women 2-3 trimester | |
| ESR | 2-15 | 2-12 | 2-20 | 2-30 | 40-50 |
A low rate is possible in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. In pregnant women, ESR returns to normal 3 weeks after birth. Why does the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increase during pregnancy? This occurs due to an increase in plasma volume, a shift in the distribution and amount of hemoglobin, an increase in cholesterol and globulin proteins, and a decrease in calcium levels.
If a low indicator is recorded in an adult, this means that this indicates a violation of water-salt metabolism or progressive muscle dystrophy. The decrease is typical for fasting, following a vegetarian diet, and occurs as a result of taking steroid hormones.
Reanalysis
If you have doubts about the correctness of the test performed and the calculation of the final results, you should apply for a repeat blood test at any paid clinic. Currently, there is an alternative method for determining the subsidence rate. This technique is used exclusively in paid clinics due to expensive equipment.
Today in medicine, determining the level of ESR plays a very important role in the treatment of various diseases, since it acts as an indirect or direct sign that indicates the presence of a certain pathology in a patient. An experienced doctor can easily recognize the disease using additional diagnostic techniques and prescribe the necessary course of therapy.
Thus, a high ESR in the presence of a normal leukocyte value usually provokes a number of questions. Many people are concerned about this condition, because when leukocytes increase, we are talking about some specific disease developing in the body.
Analysis transcript
Why there is a high ESR with normal leukocytes, we will find out below. In the meantime, let's find out what the norm is.
The normal ESR value depends most on gender, and also on the age of the person, but in any case, the readings are in fairly narrow ranges. You need to be aware of the following features:
- Newborn healthy children have an ESR of 1 to 2 millimeters per hour. Other values are possible in individual cases. This is directly related to protein changes, as well as increased cholesterol and acidity in the blood. Upon reaching six months of age, this value in children increases to 17 millimeters per hour.
- Older children have rates from 1 to 8 millimeters per hour.
- In men, ESR ranges up to 10 millimeters per hour.
- In women, the normal rate is slightly higher than in men, and reaches 15 millimeters per hour. This is explained by the presence of a certain number of androgens in the female body. It is important to know that this indicator increases during pregnancy and grows, as a rule, until the end of the term, reaching a peak at the time of birth of 55 millimeters per hour. The indicator returns to normal approximately a month after birth. The increase in ESR in this case is explained by a change in the qualitative composition of the blood.
Knowing the ESR indicator allows you to determine the presence of various diseases and prevent their development in time, along with the appearance of complications.
So, why does high ESR occur with normal white blood cells?