Immature granulocytes are reduced - what does this mean?
The materials are published for informational purposes only and are not a prescription for treatment!
We recommend that you consult a hematologist at your medical institution! Co-authors: Natalya Viktorovna Markovets, hematologist
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell. These cells can be present in human blood in three stages: immature (or young), not fully mature and mature.
Since these blood cells reach full maturity within three days, they remain in an immature state for a minimum period of time. Therefore, their amount in the blood is normally minimal.
Pathology is most often spoken of when the number of granulocytes is increased, however, their too small presence in the blood also indicates the development of diseases.
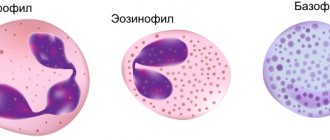
What types of granulocytes are there: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils
Granulocytes are one of the subtypes of leukocytes. These cells got their name due to their granular structure, which resembles granules. They are produced by the bone marrow.
These cells provide protection to our body from germs and infections. They are able to be the first to recognize that something is wrong and move to the source of the lesion. Thus, if their number is increased, this indicates the development of inflammation. They also correct the immune system.
Types of granulocytes
Granulocytes are of the following types:
- Neutrophils. They belong to one of the most numerous groups, accounting for up to 80% of the total number of leukocytes. The main task of neutrophils is phagocytosis, or the search and destruction of harmful bacteria and viruses.
- Basophils. Small cells with large nuclei and a small amount of cytoplasm. They fight inflammation and participate in anaphylactic processes.
- Eosinophils. Make up less than 5 percent of the number of leukocytes. These cells are responsible for phagocytosis.
Read also on the topic Eosinophil Norm in Children in addition to the current article.
What does a low granulocyte count indicate?
Low granulocyte content in the blood
As mentioned above, the relative content of granulocytes in the blood is very small. However, there are situations in which immature granulocytes are reduced. What does it mean? This may indicate the development of serious diseases in the body.
For example, with a decrease in neutrophil granulocytes, the following diseases may be diagnosed in a patient:
- malaria;
- lupus erythematosus;
- tularemia;
- rubella, influenza;
- hepatitis;
- AIDS;
- radiation sickness;
- enlarged spleen.
Important! In a breastfed child, a decrease in neutrophil levels may occur due to congenital neutropenia. This disease can lead to disastrous consequences, including death. It manifests itself in the form of chronic infectious diseases or on the skin.
Also, a decrease in neutrophil granulocytes can occur due to alcoholism.
Large physical overloads can lead to a decrease in the number of granulocytes
The reasons for the decrease in the number of eosinophils may be as follows:
- physical stress;
- previous surgical interventions;
- anemia;
- polytrauma;
- extensive burns;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- acute bacterial infections, etc.
We also recommend that you pay attention to the article: “Reduced eosinophils in the blood of an adult.”
If granulocytes are low in a very young child, this indicates that the immune and hematopoietic systems are not fully formed. Everything will return to normal in time. With a decrease in the number of basophils, basopenia develops, which occurs against the background of such diseases:
- pneumonia;
- acute infections;
- Cushing's syndrome;
- stress;
- diseases of the thyroid gland.
Important! A decrease in the level of basophils can also occur when taking hormonal drugs or due to any hormonal imbalances in the body.
A decrease in granulocytes can occur against the background of constant stress
A decrease in the level of granulocytes in an adult and a child can be caused by serious pathologies of the body, and therefore in this case a comprehensive examination is required to identify the cause and treat the disease that has led to a deviation in the level of blood cells.
We recommend studying similar materials:
- 1. Reasons for an increase or decrease in neutrophils in a blood test in children?
- 2. What does a high level of neutrophils mean and is it dangerous?
- 3. What do elevated eosinophils mean in a blood test in adults?
- 4. What to do if there is an increased level of bilirubin during pregnancy?
- 5. What to do if the level of basophils increases and what does this mean?
- 6. Low level of total bilirubin in the blood: reasons for the decrease
- 7. Lymphocytes during pregnancy: increase and decrease in indicators
Source: https://MoyaKrov.ru/normy-i-patologii/prichiny-ponizheniya-granulotsitov/
Reasons for the increase in granulocytic elements
An increase in the concentration of immature granulocytes is observed with the development of pathologies such as:
- malignant processes, leukemia;
- infectious diseases of various localizations (typhoid fever, malaria, tuberculosis, rubella, meningitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis and others);
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome during major surgical interventions;
- liver diseases - cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- autoimmune disorders;
- extensive burns or heavy bleeding;
- severe intoxication;
- allergy;
- acute inflammatory processes (abscesses, peritonitis, appendicitis, phlegmon and others).
The phrase “granulocytes are increased” often indicates the presence of problems of pathological etiology, however, in some situations, increased coefficients are not a reason for panic. A slight increase in granulocytes is considered normal in the following situations:
- For women, increased granulocytes are considered to be a physiological characteristic of the body during the premenstrual period and during pregnancy. This phenomenon is especially often observed in the test results of pregnant women in the last months of pregnancy, as well as within a few days after childbirth.
- With significant physical and psycho-emotional stress for different categories of subjects.
- In case of overeating prior to donating blood for analysis.
After excluding the influence of physiological factors on the results of the study, the reasons for the increase in granulocytic forms of leukocytes should be sought in the following directions:
- Progression of infectious diseases in acute form.
- Allergies of a complex course.
- Malignant formations of different localization.
- Intoxication of the body, and the cause may lie in acute poisoning with food, poisons and toxins, or be hidden under the uncontrolled use of medications.
- Development of diseases accompanied by tissue necrosis.
In children, immature granulocytes can be elevated for the same reasons as in an adult, as well as against the background of preliminary vaccination, when the child’s body intensively resists the administered drug, in the process of developing immune memory for further resistance to similar pathogens.
When interpreting the results, the doctor takes into account not only the fact that granulocytes are elevated, but also considers which specific groups of granulocytic leukocytes are produced in excess. If an increase in neutrophils is observed, the probable cause of the precedent may be intoxication poisoning, hemorrhage in the acute phase, or bacterial infection of the body.
Let's consider what it means when granulocytes are low, and whether such a doctor's verdict is dangerous to health. The reasons for the decrease in granulocytes are determined by assessing the quantitative indicators of each cell subtype. If a decrease in the total number of granulocyte cells is determined against the background of eosinophil deficiency, then the root causes of the phenomenon should be sought in the following directions:
- Presence of infection or sepsis.
- Deficiency of B vitamins and anemic conditions.
- In the postoperative period.
- Against the background of internal or external bleeding.
If eosinophils in the baby’s blood are low, the root cause of the problem is often problems with the functioning of the hematopoietic system. Precedents when granulocytes in the blood are reduced against the background of a parallel deficiency of basophils are very rare in medical practice and are a consequence of disturbances in the hematopoietic processes of genetic or acquired etiology.
Situations where neutrophil granulocytes are low are considered health and life-threatening conditions. With neutropenia, there is a decrease in cellular immunity, against which there is a likelihood of progression of complex inflammatory processes. A similar picture in the analysis form may indicate progression in the subject:
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Autoimmune diseases of complex etiology.
- Malignant neoplasms in the bone marrow.
- Anemia with critical indicators.
- Intoxication with alcohol, medications or toxic substances.
If neutrophil granulocytes are low in a child, parents should be prepared to hear from doctors a diagnosis that may support pathology of congenital etiology.
The main reasons for the decrease in granulocytes in the blood
Granulocytes are white blood cells that contain granularity - small granules filled with active biological substances. They are formed in the bone marrow from the granulocytic germ of hematopoiesis and are represented by three types of cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
Leukocytes are determined by studying a general blood test, which is the most common laboratory test in medical practice.
The study results often show decreased granulocytes, which indicates a pathological process in the body and requires specific treatment.
Neutrophils
Neutrophil granulocytes represent the most numerous group and make up 45-75% of the total number of white blood cells. Segmented and band forms are found in the peripheral blood of a healthy person. Segmented granulocytes have a large amount of cytoplasm and a small nucleus, which is divided into 5-6 segments.
Band granulocytes belong to younger forms of leukocytes, having a horseshoe-shaped or S-shaped nucleus, their number is no more than 6%. In the blood of a child in the first year of life, the content of leukocytes with a band nucleus can reach 20%, which is a physiological variant of the norm.
With age, the number of rods gradually decreases.
The main function of cells is considered to be the process of phagocytosis - searching, capturing and digesting foreign agents (bacteria, tumors, viruses, protozoa). Numerous granules in neutrophils contain hydrolase, myelopyroxidase, and lysozyme, which destroy pathogenic particles and are an important part of cellular immunity. As a result, pus is formed at the site of inflammation, consisting of destroyed tissue cells, granulocytes, infectious agents, and inflammatory fluid.
The maturation of neutrophil leukocytes in the bone marrow occurs in 9-12 days, after which they enter the blood, where they circulate for no more than 10 hours.
The main function of cells is carried out in tissues affected by infectious agents, parasites, and tumors.
The appearance of immature granulocytes, such as myeloblasts, promyelocytes, metamyelocytes, and myelocytes in the peripheral blood indicates the development of a pathological process in the body.
View of neutrophils under a microscope
A decrease in the concentration of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia (less than 1.7 * 109/l) and occurs in the following cases:
We also recommend reading: Causes of low neutrophils in the blood
- radiation sickness;
- bone marrow tumors (acute and chronic leukemia, primary myelofibrosis);
- aplastic, iron deficiency anemia;
- rickettsiosis (typhoid fever);
- viral infections (flu, hepatitis, rubella, AIDS);
- parasitic infestations (malaria);
- bacterial infections (tularemia, typhoid, brucellosis);
- autoimmune pathology (collagenosis, lupus erythematosus);
- exhaustion of the body (chronic alcoholism, cachexia);
- enlarged spleen (hypersplenism);
- taking toxic medications (tranquilizers, immunosuppressants, non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics).
An infant may experience congenital neutropenia - Kostman's syndrome, which is a disease with an autosomal recessive inheritance mechanism.
As a result of insufficient formation of neutrophils in the bone marrow, chronic foci of infection develop on the skin and internal organs, which can lead to death due to insufficient functioning of cellular immunity.
Eosinophils
Eosinophilic granulocytes make up 1-5% of the total number of white blood cells and contain a large nucleus with fewer segments than neutrophils. They take part in phagocytosis and maintenance of an allergic reaction of the anaphylactic (immediate) type, interact with mast cells and basophils.
The formation of eosinophils stimulates the appearance of antigen-antibody complexes, mainly represented by Ig E. The cells circulate in the blood for 2-4 hours, after which they migrate to sensitized tissues, where they absorb immune complexes, release histamine and substances to destroy parasites. The life cycle of granulocytes is 8-11 days.
View of eosinophils under a microscope
A reduced level of eosinophils is called eosinopenia (less than 0.05*109/l) and manifests itself in the following cases:
- taking glucocorticoids;
- acute course of infections, predominantly of a bacterial nature (paratyphoid, typhoid, tularemia);
- physical stress;
- prolonged stressful situations;
- septic condition;
- surgical interventions;
- extensive burns;
- polytrauma;
- aplastic processes in the bone marrow;
- anemia associated with folic acid deficiency.
Low levels of eosinophils occur in cases of severe pathology, especially in children, which is associated with imperfections in the process of hematopoiesis in early childhood.
Basophils
Basophilic granulocytes are small cells with a small amount of cytoplasm and a large nucleus, divided into 2-3 segments. Entering the peripheral blood from the hematopoietic organ, they circulate for 3-4 hours, after which they move to tissues with predominantly allergic inflammation.
Basophils take part in anaphylactic-type reactions and indirectly in delayed-type reactions when interacting with lymphocytes. In the pathological focus, they secrete biologically active components - inflammatory mediators: histamine, serotonin, heparin.
The life cycle of the cells is 9-12 days, their content in the blood is insignificant and amounts to up to 0.5% of the total number of white blood cells.
View of basophil under a microscope
The reasons for a decrease in the number of basophils - basopenia (less than 0.01 * 109 / l) - include:
- stressful situations;
- pneumonia;
- acute infectious diseases;
- pathology of the thyroid gland with increased functional activity (hyperthyroidism, Graves' disease);
- Cushing's syndrome;
- taking hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (hydrocortisone);
- period of gestation and ovulation.
Reduced basophils are quite rare and indicate severe inhibition of hematopoietic function.
A decrease in granulocytes in a general blood test appears with the development of a pathological process in the body, which means it requires additional diagnostic examination and the prescription of complex therapy for a disease that has led to a change in cell content.
Source: https://icvtormet.ru/krov/osnovnye-prichiny-snizheniya-granulocitov-krovi
Taking a blood test
There are a number of rules that will help make the analysis results “truthful”:
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach.
- A couple of days before the test, it is forbidden to drink alcohol, fatty and salty foods.
- You should also avoid heavy physical activity.
- It is strongly recommended not to take various medications before the study.
The following abbreviations are found in the analysis results:
- Abs – means the “absolute” indicator of the number of cells in 1 liter of blood;
- Lic – indicates the presence of large immature cells.
A general blood test of a detailed type can be performed in any laboratory, either at a clinic or hospital, or in private institutions on a paid basis. For research, the patient donates capillary blood from a finger. The procedure for preparing for the analysis requires the patient to comply with certain rules, such as giving up bad habits and junk food a few days before the test, minimizing physical and stressful overexertion.
Blood is donated in the morning, on an empty stomach: often laboratories limit the possibility of donating biomaterial for research to ten o’clock in the morning. Doctors strongly recommend in the morning not to take any medications that can distort the results of the study, to refuse any food and drink allowed for consumption, only plain water is considered.
Immature granulocytes are increased or decreased - what does it mean, reasons and other aspects
A clinical blood test is a reliable and informative indicator of a person’s health status.
Based on blood components, pathology can be identified in time and measures can be taken to restore normal body function.
The first cells that notice abnormalities in the body and encounter infection are granulocytes. What are they and what does the presence of immature granulocytes in a blood test indicate?
Immature granulocytes in a blood test - what are they?
Granular leukocytes (granulocytes) are a subgroup of white blood cells that are characterized by the presence of irregularly shaped nuclei and the presence of granules (grains). This is where their name comes from. Cells become visible under a light microscope when stained with a special dye.
Granulocytes are produced in the bone marrow and have a fairly short lifespan. After entering the bloodstream and exiting into the tissues, they live for 2–3 days. This is the most numerous representative of white blood cells - their number is up to 80% of all leukocytes.
Granulocytes are a subgroup of white blood cells that have nuclei and specific granules
Granular cells are divided into:
- neutrophils - the total amount is up to 70%. There are mature (segmented) and immature (young);
- eosinophils - up to 5%;
- basophils - up to 1%.
Each subspecies takes an active part in recognizing and protecting the body from pathogenic microflora.
Normally, granulocytes are absent in a general blood test, with the exception of the presence of immature neutrophils in newborns and pregnant women.
If there is an infection in the body, cells capture pathogenic microorganisms and digest them within themselves. After 2-3 days, having completed their task, they die, and a deficiency of granulocytes capable of fighting bacteria is immediately created in the blood.
Immature neutrophils come to the aid of the remaining cells, which are detected in the blood when tested.
An increased level of young granulocytes indicates an inflammatory process in the body or the first response of the immune system to an infection. An increase in the indicators of other components indicates various diseases: the number of basophils increases with allergies or poisoning, eosinophils - with autoimmune diseases, viral and bacterial infections.
Since the process of cell maturation in the blood occurs quickly, the following indicators of the level of neutrophils from the total number of leukocytes are considered normal:
- segmented - up to 65%;
- unripe - up to 5%.
The number of granular granulocytes in an adult varies from 45 to 70%. The norms for children are somewhat different and depend on the age of the child.
Find out about the norm of segmented neutrophils: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/normy-segmentoyadernyx-nejtrofilov-v-krovi-cheloveka.html
Features during pregnancy
Granulocyte indices do not depend on gender. The exception is pregnant women.
During pregnancy, significant fluctuations in the level of leukocytes occur under the influence of estrogens (the production of female sex hormones increases during this period).
They reach their maximum value at 30 weeks of pregnancy. With the onset of labor, the level of leukocytes increases to 25–30 x10 9 /l (10 to the 9th power).
An increase in the number of leukocytes leads to increased formation of granulocytes. In pregnant women, the rate of immature neutrophils can reach up to 3%.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The appearance of immature granulocytes in the blood indicates an inflammatory process in the body.
The immune system begins to intensively produce neutrophils to remove pathogenic microflora.
An increase in indicators is observed when:
- intoxication;
- purulent processes;
- heavy bleeding;
- allergic reactions;
- burns;
- myocardial infarction;
- peritonitis - inflammation in the abdominal cavity;
- blood diseases;
- infectious and viral diseases (scarlet fever, cholera, typhoid fever, influenza);
- taking certain medications after vaccination;
- liver damage;
- tumors.
However, the level of neutrophils also increases during certain physiological processes:
- second half of pregnancy and childbirth;
- heavy physical activity;
- menstrual cycle;
- stress;
- after meal.
Interesting information about how much blood a woman loses during menstruation: https://krasnayakrov.ru/organizm-cheloveka/zhenshina/mesyachnaya-krov.html
In newborns, the level of immature neutrophils is also increased. The fact is that the baby in the womb was in ideal conditions for him; at birth, the body experiences a certain stress. Organs and systems have not yet had time to adapt to new conditions, so the immune system’s response to a stressful situation is the increased production of granulocytes.
In other cases, an increase in indicators in children should alert doctors and parents.
The number of immature neutrophils in a child’s blood increases when:
- inflammatory process: otitis media, pneumonia, appendicitis;
- purulent processes;
- burns;
- blood diseases.
A slight increase in granular cells indicates the onset of the disease, so it is necessary to take all possible measures to cure the disease. A sharp jump may indicate blood poisoning.
A reduced level of neutrophils is observed in the following diseases:
- anemia of various types - decreased hemoglobin in the blood;
- diabetes;
- acute bacterial and viral infections - abscesses, sore throat, meningitis, influenza;
- acute leukemia is a malignant disease of the hematopoietic system.
More details on how to increase a child’s hemoglobin at home: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/povyshaem-gemoglobin-rebenku-v-domashnix-usloviyax.html
A low rate of immature granulocytes also indicates lead poisoning, radiation exposure, and autoimmune diseases.
It is not recommended for a child to receive vaccinations if the number of neutrophils in the blood test is reduced.
A reduced or increased level of immature granulocytes indicates serious diseases, so you need to consult a hematologist, undergo examination and begin treatment.
How can I get my blood test back to normal?
An increase in the number of neutrophils (neutrophilia) or a decrease in them (neutropenia) indicates the presence of pathology in the human body.
Sometimes the patient may not be aware that there is an inflammatory process in the body, for example, with sepsis (a purulent infectious disease) of the brain, kidneys, and liver.
To bring neutrophil levels in a blood test back to normal, it is necessary to find out the cause of the deviation and cure the underlying disease.
Blood tests for granulocytes are carried out for various diseases
Based on the number of granulocytes, it is impossible to accurately determine what a person is sick with, so it is strictly forbidden to carry out treatment on your own.
The patient should contact a hematologist, who will prescribe additional examination and make an accurate diagnosis.
Granulocytes play an important role in the body of adults and children; the cells are the first to respond in inflammatory processes of various natures. If the values increase or decrease, you should consult a doctor to identify the exact cause of the deviation from the norm. In some cases, this is not caused by a physiological phenomenon, but by a serious illness.
- Irene Saratova
Source: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/nezrelyie-granulotsityi-v-analize-krovi-vazhnyiy.html
Types of granulocytes
The term “granulocytes” is a collective one; the category of cells of the granulocytic type consists of several varieties. The composition of granulocytes includes:
- Eosinophils, whose functionality is to perform cytotoxic tasks by neutralizing and removing parasitic components from the body. Their ratio to the total number of granulocytes is normally from one to five percent.
- Basophils, making up no more than one percent of all granulocytes, are responsible for the allergic message to the body about the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms, simultaneously attracting other granulocytic forms to the problem area in order to eliminate pathogenic components. In addition to the informative function, the tasks of basophils include increasing vascular capacity, improving the circulation of body fluids, and normalizing blood clotting.
- Neutrophils are the largest group of granulocytic cells: their total number is up to seventy percent of all granulocytes. The function of cells is to directly destroy all types of pathogenic components, at the cost of their lives. When neutrophils die, superactive substances are released that can prevent further progression of inflammatory processes.
In terms of quantitative composition, the group of elements of the granulocytic configuration is large-scale, accounting for slightly more than seventy percent of the total volume of cells belonging to the leukocyte type.
Granulocytes are reduced: what does this mean, reasons
If, as a result of examining a blood sample, it turns out that granulocytes are low, then this should be regarded as a deviation from the norm, which indicates the presence of pathologies.
Let's try to figure out what are the reasons for their appearance.
Types and functions of blood cells
Granulocytes are white blood cells, a type of leukocyte. Under a microscope, it can be seen that the structure of these cells is similar to grains or granules - hence the name.
The main center for the production of all types of leukocytes is the bone marrow, and their main purpose is to protect the body from external and internal pathogens.
Although white blood cells are considered blood cells, they are able to leave the bloodstream by penetrating through capillary walls into the spaces between other cellular particles in the body.
Being in the intercellular space, leukocytes actively suppress the activity of foreign elements.
Some types of white cells have the ability to absorb foreign bodies - this process is called phagocytosis in medicine.
In confrontation with foreign elements, white blood cells die, but new ones immediately rush to their place, produced by the bone marrow and stored there until a certain moment, as in a warehouse.
There are two types of white blood cells - the granular type, known as granulocytes, and the non-granular type, known as agranulocytes.
The bloodstream of a healthy person contains a certain amount of each type of cell; any deviations from the norm are considered as a sign of unhealthy processes and require medical intervention.
In relation to other types of leukocytes, granulocytes are the most numerous and make up up to 80 percent. In the results of a blood test, the quantitative composition of white cells is indicated in the leukocyte formula.
There are three types of granulocytic type cells:
- neutrophilic;
- eosinophilic;
- basophilic.
Neutrophil granulocytes are segmented or band cells, the main type of leukocytes in human blood.
Neutrophils are called segmented because their nucleus is divided into several segments.
The task of these cells is to perform an antimicrobial function in the body, neutralizing bacteria and fungi through phagocytosis (absorption).
Immature forms of cells are called rod cells; they are practically absent in the blood of a healthy person.
READ For what reasons are leukocytes in the blood low in women?
Exceptions include expectant mothers and newborn children, for whom the presence of immature neutrophils in the blood is considered normal.
In newborns, high levels of band granulocytes can persist for up to a year.
:
An increase in the number of immature cells indicates depletion of cell mass reserves, which occurs during intense inflammatory processes. A low level of neutrophil granulocytes is called neutropenia.
Eosinophils are granulocytes with a bilobed nucleus. Moving towards the affected inflamed tissues, eosinophil cells actively participate in antiparasitic immunity, ensuring the maintenance of immediate allergic reactions and absorbing foreign particles. Low levels of eosinophils are called eosinophilia.
Basophils are a subtype of granulocytes with large nuclei. The mission of these cells is to maintain immediate allergic reactions and participate in blood clotting processes. A decrease in the level of basophils in the blood is called basopenia.
Reasons for the decrease in eosinophilic and basophilic granulocytes
When the results of a blood test show a decrease in granulocytes, it is difficult to understand what this means without medical education. You need to know what analysis indicators are considered normal.
Quantitative norms of granulocyte cells in the blood are designated using the abbreviation GRA and are indicated either as a percentage of the total number of leukocytes (GRA%) or as an absolute indicator (GRA #).
Accordingly, when deciphering the results of the analysis, doctors are guided by this normal indicator - 1.2 - 6.8 * 10⁹ per liter of blood or 47 - 72 GRA% of the total level of leukocytes.
The results of the analysis indicate the number of immature granulocytes. The normal level of indicators of such cells can range from 1 to 5 percent.
If the analysis shows that immature granulocytes are low, then this is regarded as a sign of problems with the functionality of the immune system.
:
For each type of granulocytes, there are normal indicators established by medicine.
Reduced granulocytes cannot be regarded as evidence of any one disease. The diagnosis may differ depending on which subtype the indicators are not normal.
READ Why might blood urea be low?
A decrease in the level of eosinophilic granulocytes (eosinopenia) is diagnosed when the number of cells is less than 5*10⁴/ml, which may indicate:
- septic condition;
- acute form of bacterial infection;
- physical overload;
- burn disease;
- anemia due to folate deficiency;
- side effects of glucocorticoids;
- as a result of a stressful situation;
- numerous injuries;
- hypoplastic anemia;
- post-surgical intervention.
In children, a decrease in eosinophil cells is considered a sign of pathological processes in the hematopoietic system.
Basophils are considered the largest granulocytes, the functionality of which is determined by the presence of prostaglandins, histamine and serotonin in their composition, and the ability to produce heparin, which regulates blood clotting.
Basophil activity increases as soon as any toxins enter the body.
Even when bitten by bees or poisonous snakes, basophilic granulocytes not only block the action of the poison, but also remove toxic substances from the body.
A decrease in the level of basophils in the blood (basopenia) is not only a rare phenomenon, but also difficult to diagnose. A deviation from the norm is considered to be a decrease in values from 0.01*10⁹/l.
In most cases, a decrease in the level of basophils is a consequence of insufficient functionality of the hematopoietic system.
Most often, basopenia develops against the background of such pathologies as:
- pneumonia;
- infections;
- pathologies of the endocrine system - Graves' disease, hyperthyroidism;
- Cushing's syndrome.
In addition, basophils decrease as a result of stressful situations, after taking hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, as a result of chemotherapy, in women - during ovulation and during pregnancy.
Reasons for the decrease in neutrophil granulocytes
Typically, granulocyte levels change throughout a person's life. Indicators in an adult differ from the level of white cells in children under one year old.
If the granulocyte counts are lower than normal, then the doctor’s task is to determine the cause of the pathology and eliminate it by prescribing a course of treatment.
Neutrophil granulocytes mature in the bone marrow. This period takes an average of 10 days, and then the cells enter the bloodstream and perform their protective functions for 10 hours. The highest concentration of neutrophils is observed in the affected tissues.
READ Why are leukocytes in a child’s blood elevated?
A decrease in the level of neutrophil cells (neutropenia) can be a symptom of the following human pathological conditions:
- radiation injury;
- neoplasms in the bone marrow - leukemia, myelofibrosis;
- various types of anemia;
- typhoid fever;
- diabetes mellitus;
- toxic goiter;
- malaria;
- bacterial infections - brucellosis, tularemia;
- viral infections - influenza, rubella, various subtypes of hepatitis, AIDS;
- autoimmune pathological conditions - collagenosis, lupus erythematosus;
- depletion of the biological potential of the body against the background of chronic alcoholism, cachexia;
- hypersplenism;
- taking medications with toxic effects - tranquilizers, antibiotics, immunosuppressants;
Neutrophils may be low in a child with congenital Kostman syndrome. As a result of the development of this pathology, the bone marrow loses the ability to produce the required number of neutrophils.
The consequences of the disease are more than serious - a general weakening of cellular immunity is accompanied by multiple inflammatory lesions of the skin and internal organs, which often leads to death.
The degree of development of neutropenia is reflected in the results of a blood test as follows:
- mild form - the number of neutrophils is from 1*10⁶/ml;
- severe form - the number of neutrophils is less than 5*10⁵/ml.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is very important to know the degree of relationship between mature and immature forms of granulocytes. Autoimmune diseases and congenital forms of leukopenia can reduce the levels of immature white cells.
A decrease in granulocytes against the background of an increase in the number of leukocytes is always a symptom of intense inflammatory processes.
:
In addition, granulocyte counts often change during the summer. Summer is the time of activity of allergens, bacteria and fungi, the damage to which is reflected in a blood test.
In children under one year old, the rate of immature granulocytes cannot exceed 4%, from one year to 6 years - 5%, upon reaching 15 years - no more than 1 - 5%.
Any pathologies that occur in the body require medical supervision and accurate diagnostic conclusions, therefore, even understanding the meaning of granulocyte indicators, you should not self-medicate.
Are you here:
17663 0
Source: https://moydiagnos.ru/analizi/krovi/granulotsity-ponizheny.html
The role of cells in the body
Granulocytes are the largest type of white blood cells (up to 80%). The main role of these cells is the stable functioning of the immune system. The abbreviation for granulocytes is GRA or Gran. The cells are heterogeneous; there are three types of granulocytes: baso-, neutro- and eosinophils. Each cell has its own role, which is correlated with the structure and number of cellular elements, however, in a general context, granulocytes perform the following functions:
- are the first to respond to the introduction of foreign agents into the body, inactivating them, which is due to the large number of cells;
- create a barrier for the penetration of pathogenic microbes into tissues;
- all cells of the immune system notify about the appearance of a “stranger”;
- limit the rate of virus reproduction or destroy bacteria.
Neutrophils, as the most numerous representatives of the group, undertake the main work of directly protecting the body. Basophils and eosinophils help them, providing comprehensive protection for the body in a constant, dynamic manner.
immature granulocytes are below normal what does this mean
There are two types of leukocytes: granulocytic and agranulocytic. The first row includes granulocytes in the form of eosinophils, neutrophils and basophils.
Neutrophils, in turn, are divided into mature or segmented, not fully mature or band, and immature granulocytes (young).
Due to the short lifespan of this type of leukocyte, about 3 days, they mature almost immediately.
What are “immature granulocytes” in a blood test?
The form with the results of a laboratory study of biological fluid does not indicate the number of incompletely mature and young granulocytes, since it is not counted during the analysis. Only the total concentration of segmented and band neutrophils is indicated.
To calculate the IG value (number of granulocytes), you need to subtract the sum of monocytes and lymphocytes from the total leukocyte concentration.
The number of immature granulocytes is normal
In an adult, the process of neutrophil maturation occurs quickly, within 72 hours, so their volume in the blood is small. The norm for band and young granulocytes is up to 5% of the total number of all white blood cells (leukocytes).
Why are immature granulocytes low or high?
In fact, the group of neutrophils in question should not be found in a healthy adult. Therefore, in medicine there is no such thing as “a decrease in immature granulocytes.”
A pathology is considered if the number of these cells is higher than the established norms. The reasons for this may be pregnancy, intense physical activity, heavy meals, stress. Also, the concentration of young neutrophils increases in the following diseases and conditions:
- osteomyelitis;
- purulent abscess;
- pneumonia;
- meningitis;
- phlegmon;
- peritonitis;
- severe burn;
- sepsis;
- inflammation of the appendix;
- purulent sore throat;
- infectious hepatitis;
- cholera;
- otitis;
- psoriasis;
- typhoid fever;
- pyelonephritis;
- scarlet fever;
- gout;
- thrombophlebitis;
- malaria;
- cholecystitis;
- measles;
- some types of dermatitis;
- tuberculosis;
- acute bleeding;
- flu;
- diabetic acidosis;
- rubella;
- lead poisoning;
- Cushing's syndrome;
- malignant tumors;
- uremia;
- gangrene;
- serum sickness;
- myocardial infarction;
- poisonous insect bites;
- chronic myeloplastic pathologies;
- pulmonary infarction;
- taking lithium, androgens, glucocorticosteroid hormones.
Source: womanadvice.ru
Immature granulocytes are elevated - what does this mean?
Probably, even the most experienced researchers and doctors will not be able to immediately name all the existing blood components and their norms. There are many different types of blood cells.
And a change in the amount of each of them indicates disturbances in the functioning of the body.
If you know what it means when immature granulocytes are elevated, it will be much easier to decipher your test results and, if necessary, speed up an appointment with a specialist.
What is increased immature granulocytes in the blood?
Granulocytes are a subgroup of granular leukocytes. These include basophils, neutrophils and eosinophils. The name of blood cells is explained by their structure - small granules or grains are clearly visible under a microscope. The bone marrow is responsible for the production of granulocytes. After entering the body, these particles do not live very long - no more than three days.
It is normal if the blood contains from one to five percent of young neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. If immature granulocytes are elevated, most likely an infection, inflammatory or pathological process is developing in the body. At the same time, neutrophils actively begin to be produced. And accordingly, an increase in the number of blood cells is the result of the reaction of the immune system.
Reasons for the increase in immature granulocytes
A slight increase in this indicator is considered normal for pregnant women and newborns. The test result may also be distorted if blood is taken immediately after a meal, physical activity, or from a patient experiencing severe stress. In all other cases, increased immature granulocytes in the blood are an unhealthy phenomenon. And it can indicate the following pathologies:
- gout;
- gangrene;
- psoriasis;
- hepatitis;
- tuberculosis;
- malaria;
- different types of dermatitis;
- cholera;
- sepsis;
- angina;
- burns;
- acute bleeding;
- meningitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- serum sickness;
- myocardial infarction;
- intoxication caused by insect bites, chemical poisoning;
- chronic myeloplastic diseases;
- flu;
- rubella;
- otitis;
- cholecystitis;
- scarlet fever;
- peritonitis;
- pneumonia;
- appendicitis.
In some people, increased levels of immature granulocytes in the blood are observed while taking drugs containing lithium or glucocoricosteroids.
With purulent processes, the jump in the indicator is significantly greater than in all other cases.
Source: womanadvice.ru
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose the presence of a certain range of diseases, you need to know the range of values of the number of all types of granulocyte particles. These indicators in the blood are independent of the patient’s gender; age matters.
When diagnosing the content of granulocytes in the blood, the specialist prescribes a detailed general examination.
Blood for diagnostic activities is donated in the early hours (with the exception of emergency diagnostics in a hospital setting) and on an empty stomach (eating is allowed no later than 22:00 on the day preceding the day of blood donation).
24 hours before the procedure, stop eating fatty foods and fried foods. Alcoholic libations are not allowed.
Experts strongly recommend that you stop playing sports for the reason that high physical activity can lead to unreliable test results.
It is necessary to stop taking medications and refuse medical procedures. If following the listed recommendations is impossible, then you need to tell your doctor about it.
Blood sampling to study the level of leukocytes is carried out from a finger, but in some cases (emergency operations, comprehensive examination) biomaterial can be taken from a vein.
Laboratories equipped with new technology make it possible to calculate the number of blood elements very quickly, without requiring much participation of laboratory assistants, so the results can be seen the next day; in emergency cases, the examination can be completed in half an hour.
The results of a detailed blood test record the percentage of all types of leukocyte cells (for this, the so-called leukocyte formula is written).
READ Why are band neutrophils elevated?
Granulocyte cells are listed in order of maturity from left to right, with 45 to 65% of mature granulocytes considered normal, and 1 to 5% of the total number of leukocytes considered immature.
The normal level of granulocytes in a child’s blood is determined based on his age. For convenience, the ranges of values are shown in the table:
| Child's age | Norms of granulocyte content | Norms for the content of immature forms of granulocytes |
| First year of life | From 15 to 30% | Up to 4% |
| 1 year – 6 years | From 25 to 60% | Up to 5% |
| 7 – 12 years | From 35 to 64% | Up to 5% |
| 13 – 15 years | From 40 to 70% | Up to 5% |
| 15 and older | About 45 to 70% | From 1 to 5% |
What could affect the validity of the study?
The following factors may affect the results of the analysis:
- patient failure to comply with preparation rules;
- use of medications (you must notify your doctor about taking them in advance; you may need to stop taking them a few days before donating blood);
- laboratory technician errors - uneven distribution of blood cells on the smear (this depends on the qualifications of the personnel), incorrect counting of immature granulocytes, statistical error.
Blood testing in automatic analyzers is the most preferable, since up to 30,000 cells are studied, while with the microscopic method - only 100.
Deviation from the norm
Quite often in a blood test there is a deviation of granulocytes from the norm in one direction or the other. Depending on the developing pathology, the number of polymorphonuclear cells changes.
The reasons for the increase in granulocytes in the blood may be the following:
Neutrophilia develops: in acute infections of bacterial etiology with copious discharge of pus; with damage to organs that occurs with the process of necrosis and tissue rejection; intoxication of various origins; malignant blood diseases and anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12; bleeding (including hidden); long-term hormone therapy.
Basophilosis occurs: with allergic reactions; lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, especially in ulcerative forms of diseases; for hemolytic pathologies and oncological lesions of the blood; when treated with certain medications.
An increase in granulocytes is possible with allergies
Eosinophilia in the blood is detected: in acute viral inflammation; allergies; parasitic infestation; for diseases of the endocrine system; diffuse connective tissue diseases; for some heart pathologies; dermatological diseases.
A physiological increase in granulocytes in a blood test is possible during: intense physical labor, rich food, during pregnancy and childbirth, during the period of ovulation.
What are the reasons for the decrease in granulocytes in the blood? The decrease in the level of granulocytes in the blood also does not occur in the same way; different pathologies have different effects on the number of cells of each type.
Reasons for a decrease in neutrophils in the blood:
- for bacteriological infections;
- with myeloblastosis;
- different types of bleeding;
- with specific drug therapy.
Causes of low basophils in the blood:
- thyroid diseases;
- stressful situations that cause significant biochemical changes in the body;
- pregnancy;
- long-term hormone therapy.
Causes of eosinopenia:
- persistent infectious diseases
- intoxication of various origins
- severe injuries and surgical interventions
- treatment with corticosteroids.
A persistent change in the level of granular leukocytes in human blood indicates the occurrence of disorders in the human body. These cells take the first hit and form the primary immune response. If there is a violation of the number and decrease in the level of granulocytes in the body, it is necessary to promptly identify the cause and eliminate it. We hope you understand what causes an increase or decrease in granulocytes in human blood.