Medicines to prevent stroke
Drugs with a preventive effect to reduce the risk of stroke (hemorrhagic, ischemic) are divided into 2 large groups:
- Anticoagulants , which thin the blood (for example, Warfarin and Heparin).
- Antiplatelet agents that have a preventive effect on thrombus formation (for example, Dipyridamole and Acetylsalicylic acid).
The drugs included in each group have their own indications, contraindications, and features of use.
Anticoagulants are useful drugs for cerebral vessels
Drugs from this group help reduce the ability of blood to thicken, change the functioning and formation of its components, causing the formation of blood clots. Such drugs are used in the treatment of limb thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. These drugs are no less effective for preventing stroke.
One of the representatives of this group is Heparin, which is administered subcutaneously or intravenously. The medicine is not intended for oral use. For this reason, it is more often used in hospital settings to thin the blood if there is a predisposition to thrombosis.
Another drug related to anticoagulants is Warfarin, which is prescribed as a prophylactic drug to reduce the risk of blood clots forming in the heart. Released in oral form for internal use.
Some other medications and foods may reduce the effectiveness of Warfarin when used together. For this reason, before taking the pills, it is important to consult a doctor and provide a list of medications that are currently being taken.
Foods rich in vitamin K, for example, lettuce, liver, cauliflower, have an effect on the process of blood clots. Such products are limited during the period of warfarin therapy.
Antiplatelet agents
The drugs included in this group prevent and reduce platelet cell aggregation. This process occurs against the background of platelets leaving the site of damage to the blood vessel and gluing them in this place. The result is the formation of a blood clot, which after a certain time can break off and go with the blood flow into a smaller artery and block its lumen.
In this regard, antiplatelet drugs reduce the risk of stroke in people who have suffered a transient ischemic attack or ischemic stroke.
Acetylsalicylic acid or Aspirin is a drug used to reduce pain and relieve fever, but is often prescribed as an antiplatelet agent to reduce the risk of stroke. Due to possible irritation of the gastrointestinal mucous membranes, tablets are taken with plenty of water.
Another antiplatelet agent is Dipyridamole, which has a different effect compared to Aspirin. The drug prevents the formation of blood clots. Dipyridamole often causes a headache, which is a side effect, but goes away on its own after a certain time.
Drugs for the treatment of ischemic cerebral stroke
IN AND. Skvortsova Modern approaches to the treatment of ischemic stroke
Russian State Medical University, Moscow
Over the past decades, the problem of acute stroke has become increasingly important due to the widespread prevalence of cerebrovascular pathology, high mortality rate, frequent development of disability and social maladjustment of patients who have suffered it.
Timely diagnosis of ischemic stroke is extremely important for adequate therapy. It is based on an analysis of the medical history and clinical picture of the disease, the results of the use of additional research methods: blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, Doppler ultrasound of the great vessels of the brain, and, if necessary, angiography and echocardiography.
The treatment system for acute stroke is based on the ideas about the mechanisms of its development that have developed in recent years; This system includes a set of therapeutic measures carried out regardless of the nature of the stroke (the so-called basic therapy), as well as differentiated therapy for ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
The vast majority of patients with stroke require hospitalization as early as possible. The intensive care phase is usually carried out in the neurocritical care unit or the intensive care unit of the neurological department. The principles and methods of basic therapy in the acute period of stroke allow for the correction of respiratory and cardiac disorders, acid-base and osmolar homeostasis, water-electrolyte balance, treatment and prevention of increased intracranial pressure and cerebral edema, autonomic disorders and complications of acute stroke.
Differentiated therapy for acute ischemic stroke is carried out depending on the pathogenetic features of the development of the disease, the location and extent of the lesion.
Currently, there are 4 pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke: 1) atherothrombotic; 2) embolic; 3) hemodynamic; 4) microcirculatory.
The results of studies conducted in recent years indicate the staged nature of hemodynamic and metabolic changes occurring in brain tissue at different stages of insufficient blood supply and leading to the formation of cerebral infarction through two main mechanisms: necrosis and apoptosis, or programmed cell death. It has been established that the formation of most of the infarction ends within 3–6 hours from the moment the first symptoms of a stroke appear; “additional formation” of the lesion continues for 48–72 hours or longer. A scheme of successive stages of the “ischemic cascade” is proposed based on their cause-and-effect relationships and significance for therapy: 1) decrease in cerebral blood flow; 2) glutamate “excitotoxicity”; 3) intracellular accumulation of calcium; 4) activation of intracellular enzymes; 5) increased synthesis of nitric oxide and development of oxidative stress; 6) expression of early response genes; 7) long-term consequences of ischemia (local inflammation reaction, microvascular disorders, damage to the blood-brain barrier); apoptosis.
It has been established that the formation of most of the infarction ends within 3–6 hours from the moment the first symptoms of a stroke appear; “additional formation” of the lesion continues for 48–72 hours or longer. A scheme of successive stages of the “ischemic cascade” is proposed based on their cause-and-effect relationships and significance for therapy: 1) decrease in cerebral blood flow; 2) glutamate “excitotoxicity”; 3) intracellular accumulation of calcium; 4) activation of intracellular enzymes; 5) increased synthesis of nitric oxide and development of oxidative stress; 6) expression of early response genes; 7) long-term consequences of ischemia (local inflammation reaction, microvascular disorders, damage to the blood-brain barrier); apoptosis.
Each stage of the cascade can be a unique target for therapeutic interventions. Interrupting the cascade at earlier stages may be accompanied by greater treatment effect. In accordance with existing ideas about the development of the “ischemic cascade,” two main directions of therapy for ischemic stroke are distinguished: 1) improving the perfusion of brain tissue (impacting the 1st stage of the cascade); 2) neuroprotective therapy (impacts on stages 2–8 of the cascade).
The most radical method of reperfusion therapy is the use of thrombolytic agents. However, the use of tissue plasminogen activator turned out to be possible only in the first 3-6 hours from the onset of atherothrombotic stroke when the thrombus is located in medium- and large-caliber arteries. Intra-arterial, intravenous or local administration at a dose of 0.9 mg/kg body weight allows for rapid recanalization of the affected vessel.
To improve cerebral perfusion, under the control of laboratory parameters and functions of the cardiovascular system, hemodilution is performed with low molecular weight dextrans (reopolyglucin or reomacrodex; 250-500 ml IV drip over 1 hour). The main indicator of the effectiveness of hemodilution is considered to be a decrease in hematocrit to 30-35%.
In the acute period of ischemic stroke, it is advisable to use antiplatelet therapy, which is selected individually depending on the localization of the pathological process, the characteristics of systemic hemodynamics, and hemorheological properties of blood. The use of anticoagulant therapy in the first hours and days of ischemic stroke is currently limited to two main indications: the progressive course of stroke (usually due to an increase in the atherothrombotic process) and cardiocerebral embolism. However, even in the presence of contraindications, anticoagulant therapy must be used in the event of the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. It is preferable to prescribe the direct anticoagulant heparin during the first 2-5 days of the disease in a daily dose of up to 10,000 units under the skin of the abdomen (in 4 injections) or through an infusion pump intravenously. In this case, the bleeding time should be extended by 1.5-2 times, the activated partial thromboplastin time should not increase more than 2 times. 1-2 days before the end of the heparin course, it is advisable to gradually reduce its dose under the cover of indirect anticoagulants. Since patients with ischemic stroke often have a deficiency of antithrombin-3, it is recommended to administer fresh frozen plasma (100 ml 1-2 times a day) simultaneously with heparin.
Antioxidants (unithiol, tocopherols, essentiale) are used in ischemic stroke to optimize redox processes. Experimental and clinical studies have revealed the high effectiveness of the domestic drug Mexidol, which has a pronounced antioxidant effect when administered intravenously at a dose of 100 to 1000 mg/day.
Another direction of anti-ischemic brain protection is the interruption of the primary links of the glutamate-calcium cascade in order to correct the imbalance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter systems. A natural activator of inhibitory neurotransmitter systems is glycine, developed at MNPK "Biotiki" and having a multicomponent anti-ischemic effect. The use of glycine in the first days of stroke at a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight (on average 1.0-2.0 g/day) allows for anti-ischemic protection of the brain at different locations of vascular damage and varying severity of the condition.
An important area of neuroprotective therapy is the use of drugs with neurotrophic and neuromodulatory properties.
One of the most well-known neurotrophic drugs is Cerebrolysin, which optimizes brain energy metabolism and calcium homeostasis, stimulates intracellular protein synthesis, slows down the processes of the glutamate-calcium cascade and lipid peroxidation. The optimal daily dose of the drug for the treatment of moderate ischemic stroke is 10 ml, for severe strokes - 20 ml (intravenous drip for 7-10 days).
Because polypeptide neurotrophic factors do not cross the blood-brain barrier, their clinical use is limited. In this regard, much attention is paid to studying the properties of low molecular weight neuropeptides. These compounds freely penetrate the blood-brain barrier, have a multifaceted effect on the central nervous system and are characterized by high efficiency at very low concentrations in the body.
At the Research Institute of Molecular Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, a synthetic analogue of the ACTH fragment (4-10) was created - the drug "Semax", which is a heptapeptide (Met-Glu-His-Phe-Pro-Gly-Pro) devoid of hormonal activity. Semax is an endogenous regulator of central nervous system functions; it has neuromodulatory and neurotropic activity, as well as a pronounced nootropic effect. Clinical studies have shown that the inclusion of Semax in the complex of intensive therapy for acute hemispheric ischemic stroke reduces early mortality rates and has a beneficial effect on the severity and speed of recovery processes. The optimal dose of the drug for moderate strokes is 12 mg/day, for severe strokes - 18 mg/day (intranasal).
What medications to take after an attack
Taking any pills or giving injections before the ambulance arrives is strictly prohibited. Drug treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Taking medications after ischemic stroke
In the event of an ischemic stroke attack, thrombolytic therapy is prescribed. Timely treatment with such drugs helps reduce, and in some cases eliminate, the negative consequences of a stroke, as well as speed up recovery.
The victim is injected intravenously with a drug that dissolves a blood clot that is blocking the lumen of a cerebral artery. They use drugs from the group of antiplatelet agents, for example, acetylsalicylic acid, Dipyridamole, Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel, or others. The administration of anticoagulants is also required - Heparin, Enoxaparin, or others.
It is important to carry out such treatment in the first 3 hours after an attack. In this case, possible complications can be minimized.
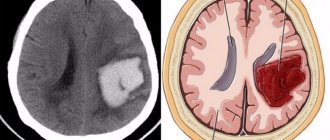
Hemorrhagic stroke attack
The first-priority treatment measure is surgery to eliminate the source of hemorrhage, which helps reduce swelling of the brain. If surgical intervention is not possible, drug therapy is carried out, which helps eliminate negative consequences (cerebral edema, etc.) and reduce the area of damage.
Drug treatment involves the administration of drugs from the following groups: diuretics, neuroprotectors, antioxidants, nootropics, metabolic agents, antihypertensive solutions.
The doctor determines which drug is suitable for the patient, based on the characteristics of the stroke and the state of general health.
What medications are taken during rehabilitation?
After first aid is provided in a hospital setting and the general condition is normalized, the patient is transferred to a regular ward, where they begin the fight to restore those areas of the brain that were damaged during the attack. For this purpose, certain medications are prescribed.
Treatment after ischemic stroke
Thrombolytic treatment and metabolic protection of the brain – neuroprotection – will help restore local cerebral circulation. Drugs from the group of platelet and erythrocyte antiplatelet agents are prescribed: Cardiomagnyl, Therapin, Pentoxifylline, Tiklid. It is also necessary to take direct-acting anticoagulants - low molecular weight heparins, sodium enoxaparin, and over time - drugs with indirect action: Warfarin, Phenilin.
To improve metabolic processes in the area of damage, vasoactive agents are used: Vasobral, Nicergoline, Instenon, Cinnarizine.
Angioprotectors (Ascorutin, Etamzilat) are prescribed, as well as neuroprotection using calcium channel blockers (Nimotop, Nimodipin), antioxidants (Mildronate, Mexidol), neurotrophics (Piracetam, Nootropil).
In case of hemorrhage
The main goal of drug treatment after an attack of hemorrhagic stroke is to normalize blood pressure using special means. For this purpose, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed:
- from the group of beta-blockers (Atenolol, Vasocardin);
- from the group of calcium channel blockers (Adalat, Corinfar);
- from the group of ACE inhibitors (Enap, Capoten);
- from the group of diuretics (Hypothiazide, Triampur).
Diuretics can also reduce swelling of the brain. They use drugs from the osmotic group: Lasix, Mannitol, etc.
Therapy during the hospital period
The sooner help is provided to the patient, the greater the likelihood that he will be able to recover from an ischemic stroke.
The treatment strategy for cerebral infarction is to maintain vital functions and restore normal blood circulation.
Basic treatment is aimed at normalizing a person’s condition after an ischemic stroke. Body temperature should not exceed 37.5 degrees, you need to monitor the normalization of breathing.
Basic drugs should balance the level of vital substances in the body. For example, glucose levels and water-salt balance. The patient is prescribed medications to help maintain normal metabolism.
Specific treatment is that a person who has suffered an ischemic stroke has to take medications that prevent the formation of new blood clots and restore blood supply to the brain.
In the hospital, the victim may be given:
Encephabol. A medication that increases metabolic activity and stabilizes nerve cell membranes. Side effects are rare, mainly due to individual reactions to the components of the drug.
- Actovegin. Promotes better saturation of the brain with oxygen, improves glucose metabolism. But allergies may occur.
Medicines for specific treatment:
Chimes. A drug that prevents the formation of new blood clots. The medication also improves blood circulation and lowers blood pressure. Basically, contraindications are associated with any abnormalities in the cardiovascular system, including the heart. If you follow the rules of administration, it does not cause side effects.
- Detralex. Increases the tone of veins, reduces their extensibility. Thanks to this, there is a better outflow of venous blood from the brain, the blood does not stagnate. The only contraindication is hypersensitivity to the drug. Nausea may occur during the course of treatment. In addition, if any side effects associated with taking the medication occur, the patient should immediately inform the doctor.
Drugs to improve cerebral circulation
To improve cerebral circulation after a stroke, drugs of synthetic or herbal origin are prescribed. You can take Glycine, Aminalon, Bilobil, and Aspirin tablets without a doctor's prescription. Mandatory consultation requires taking Piracetam, Encephabol, Phenotropil.
Products containing the alkaloid of the periwinkle plant will be effective. These include Vinpocetine, which has an antispasmodic effect, dilates blood vessels, and improves blood circulation.
Prescribed medications
Remember that all medications taken by a patient after a stroke are prescribed only by a physician. Self-prescribing and taking medications can be dangerous to the patient’s health.
The choice of medications prescribed after a stroke depends on the stage of development of the disease:
- During the initial development of a stroke, the patient is prescribed medications that help remove unpleasant symptoms. For example, if a patient has hypertension, he is prescribed medications to help lower blood pressure. Nootropics help normalize blood circulation in the brain.
The duration of their use depends on the severity of the patient’s health condition. If the development of a stroke is associated with prolonged stress or overwork, then a sedative is prescribed.
- During the critical period of the disease (the first 2-3 hours), the patient is prescribed drugs that help stabilize normal blood circulation in the brain.
Additionally, medications are prescribed to help reduce blood clotting. They prevent the patient from developing paralysis. And medications that improve blood circulation reduce the risk of recurrence of paralysis. Also during this period, analgesics are prescribed to relieve pain syndromes.
When the patient's condition returns to normal, he is sent home.
If the patient is afraid of a recurrence of a stroke, then he needs to take sedatives and medications that help improve sleep, and mild antidepressants.
Due to the high risk of blood clots, the patient needs to take medications that help thin the blood.
If a person suffers from seizures, then he needs to take appropriate medications. If he is in severe pain, then he needs to take analgesics.
Medicines to normalize blood pressure
Drug treatment for stroke would not be complete without taking medications to normalize blood pressure. For hypertension you need to take:
- beta-blockers (Coriol, Metoprolol, Acebutolol);
- alpha-blockers (Arfonad, Ebrantil, Phentolamine);
- calcium antagonists (Cordafen, Corinfar, Isoptin);
- myotropic antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa, Drotaverine);
- nitrates (Sustak, Nitrong, Sustonit);
- diuretics (Uregit, Trifas, Lasix);
- central alpha stimulants (Dopegit, Clonidine, Gemiton).
For hypotension, cardiac glycosides (Celanide, Digoxin), adrenomimetics (Gutron, Metazon), and sympathomimetics (Ephedrine) are required.
Effective medications for recurrent stroke
For recurrent stroke, thienopyridine derivatives are often prescribed. These include Clopidogrel and Ticlopidine. These contribute to a pronounced suppression of platelet cell aggregation.
The drug Ticlopidine is used twice a day, 250 mg. The medicine acts not only for therapeutic purposes, but also for prophylactic purposes, reducing the risk of recurrent stroke. Ticlopidine often causes gastrointestinal complications, skin rash, and diarrhea. Treatment in such cases is symptomatic. The drug Clopidogrel has chemical similarities with Ticlopidine, but is accompanied by less severe side symptoms.
Means for different population groups
For each group of people who have suffered a stroke, medication treatment is selected individually.
Medicines for the elderly
Restoring lost functions and reducing the possibility of negative consequences is important for older people who have suffered an attack. In such cases, gentle nootropic drugs are used that increase resistance to oxygen starvation.
Due to the fact that older people have an increased risk of complications and side symptoms, the drugs used are prescribed in lower dosages and for a longer period (up to 4 months).
Medicines for pregnant women
If a stroke was diagnosed during pregnancy, the same treatment measures are carried out as for other people. Medications are used in smaller dosages.
The advisability of prescribing prohibited drugs during this period is determined by the doctor if the potential benefit outweighs the possible harm to the mother and fetus.
Treatment of children
Treatment of stroke in children is no different from that carried out for other people who have suffered an attack. They use antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, and other drugs that help normalize blood circulation in the area of brain damage and restore lost functions.
Medicines that cause stroke
There are medications that increase the risk of stroke at any age. This is especially true for the elderly and children who have a weakened immune system. Such drugs include:
- a drug used in the treatment of diarrhea – Imodium;
- antidepressant drug – Valium;
- anesthetic agent – Codeine;
- trouble blockers.
With constant irregular use of drugs, a stroke occurs in 59% of cases, and death occurs in 86% of cases.
Medicines used during an attack and to restore lost functions after a stroke should only be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable. Otherwise, you can not only slow down recovery, but also cause irreversible consequences, including death.
Acute cerebral ischemia (ACI) occurs suddenly, causing disorders of speech, movement and other body functions. How reversible the resulting disorders will be depends on timely assistance provided and on taking prescribed medications. Let's consider which medicine for stroke will help restore impaired functions and reduce the risk of relapse.
What drugs help recovery?
After an ischemic attack, to reduce brain damage, the patient is prescribed drugs to improve cerebral circulation and drugs that stimulate the restoration of nerve conduction. Medicines are selected taking into account the severity of brain damage and the localization of the pathological focus after acute cerebrovascular accident.
Let's look at the main medications after a stroke and their effect on the human body:
- Preparations based on Citicoline (Ceraxon). When taking the medicine, metabolism in the nervous tissue improves and swelling decreases. Medicines help restore neural circuits responsible for memory, attention, thinking and other cognitive processes.
Gliatilin. Reduces degenerative phenomena, improves cerebral blood flow and stimulates metabolic processes in nerve cells.
Actovegin. In case of stroke, it protects and stimulates the restoration of brain tissue. The drug is used to treat and prevent stroke in people suffering from transient ischemic attacks.
Mexidol. The medicine is prescribed in tablets or injections. In case of stroke, Mexidol reduces tissue oxygen demand and prevents the death of brain cells.
Glycine and Cerebrolysin. The drugs restore cerebral blood flow and do not cause adverse reactions. They can be given to the victim if it is not possible to urgently (within the first three hours) transport the person to a hospital.
Nootropic drugs. This group of drugs improves brain metabolism. Nootropics after a brain stroke (Encephabol, Nootropil) stimulate partial tissue regeneration, improve amino acid metabolism and prevent hypoxia.
Piracetam or Aminalon. In patients with VSD, medications that combine the effects of nootropics and vasoactive drugs are recommended. Piracetam after a stroke promotes mild psychostimulation of the brain, improving thinking and memory.
Blood thinners (Aspirin, Warfarin). Therapy with blood thinners is necessary to facilitate cerebral blood flow and reduce the risk of intravascular thrombus formation. Blood thinners reduce the risk of relapse.
- Sedatives. Sleeping pills and antidepressants after stroke are indicated in the early recovery period. At this time, the victim’s nervous tension can provoke a second attack, which will end in death. Sedatives help relieve the patient's anxiety and provide peace.
- Antihypertensive drugs. Antihypertensive drugs are prescribed to everyone. This is necessary to prevent hypertensive crises, which negatively affect cerebral circulation.
Drugs for the treatment of cerebral stroke are selected individually, taking into account the processes occurring in the brain tissue.
How effective anti-stroke drugs will be depends not only on the drugs selected, but also on the general condition of the patient. In older people or people with severe chronic diseases, the effect of using medications will be weaker than in a relatively healthy person.
But painkillers with an antispasmodic effect are prohibited for acute stroke. Taking antispasmodics provokes a decrease in vascular tone and worsening of already impaired blood circulation in the brain. If there is a need to eliminate vascular spasms, then antispasmodic drugs for the treatment of ischemic stroke are used under medical supervision.
Rehabilitation and rehabilitation therapy
Rehabilitation therapy begins after the stroke has stabilized and in different cases lasts from 3 to 7 days. The research is aimed at redistributing functions by brain cells and supplying nutrients for increased metabolism. The recovery stage has two goals: eliminating the consequences of brain damage and preventing its reoccurrence.
To restore lost functions, processes and prevent damage to the nervous system, improve supply to the brain, neuroprotectors or nootropics are used during the recovery period. Piracetam restores the conductivity of nerve impulses, enhances the synthesis of substances necessary to restore brain function, and is at the same time an antidepressant and psychostimulant. This is one of the most studied drugs, Encephabol is used for anti-ischemic action. It is designed for use in the early recovery period. “Emoxipin” is an antioxidant, “Thiotriazolin” is effective in 3 areas: anti-stroke, membrane stabilizing and antioxidant. "Picamilon" ("Gammalon") accelerates the process of rehabilitation of brain neurons. Can serve as an antidepressant, increases microcirculation of the spinal cord and brain.
New generation neuroprotectors (Solcoseryl, Glycine, Cyto-Mac, Vinpocetine) simultaneously perform several functions, including activating the cerebral cortex, accelerating the conduction of nerve impulses and improving cerebral circulation. Therefore, their use in the recovery period is becoming increasingly widespread.
Rehabilitation requires a differentiated approach, careful medical monitoring of the patient’s condition, prescribing or discontinuing certain medications based on individual indicators and the general condition of the patient.
Not only early treatment and intensive therapy in the acute and early recovery period are of great importance in the successful resolution of the disease. Much depends on rehabilitation, in which a significant degree of responsibility is assigned to other methods of conservative therapy: exercise therapy, restorative gymnastics, physiotherapy, therapeutic massage, folk remedies and methods. Of no small importance are the correct prescription of medications, the thoroughness of their administration, and the patient’s ardent desire to fully recover and begin the normal course of the life process.
What kind of IVs are used for a stroke?
Restorative therapy in the early post-stroke period is aimed at improving cerebral circulation and restoring neural connections. Droppers after a stroke consist of a basic solution: 0.9% sodium chloride, to which is added:
Other drugs for the treatment of stroke can also be administered by drip. Simultaneous infusion of 2-3 compatible drugs is possible.
Intravenous drip infusion allows you to administer medications slowly, maintaining a certain level of active substances in the blood for a long time. This provides a higher effect compared to that given by intravenous and intramuscular injections.
Tablets for dizziness after a stroke
Dizziness is a common occurrence after a stroke, because a stroke is a disease of the central nervous system (ACVA - acute cerebrovascular accident).
Medicines to relieve acute phases of dizziness should be prescribed by the attending physician. I can only recommend the following drugs: diazepam, torecan, cerucal, atropine, sulfate - as a rule, they are administered intramuscularly or intravenously and in combination. Dizziness, like headaches, can be caused by low or, conversely, high blood pressure. Then you need drugs that lower blood pressure (atenalol, concor-cor), or increase it (coffee, strong tea, etc.). In the most rare cases, dizziness is treated surgically. I highly recommend not using them. If a problem can be solved without using these methods, then it should be solved if possible. Try meditation and osteopathy to solve this problem
Vitamins after a stroke
Vitamins are necessary to strengthen the body weakened by disease.
List of vitamins necessary for a stroke patient:
- A. Stimulates the growth and regeneration of damaged tissues.
- B1 and B6. They help stabilize blood pressure, improve cerebral blood flow, and improve neuronal conductivity.
- C. Strengthens the vascular wall and accelerates the restoration of damaged vessels.
- B. Affects blood circulation and the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. Necessary for normalizing blood composition and restoring neural connections.
- E. prevents the appearance of free radicals that disrupt metabolism and cause cellular aging.
In addition to vitamins, to strengthen the defenses, minerals are prescribed: potassium, magnesium and others. Patients are recommended vitamin and mineral complexes. The list of drugs for recovery is large and often drugs produced by different pharmacological companies, despite the same composition, have different names. Before taking the purchased medication, you need to consult your doctor - an incorrect ratio of vitamins and minerals is unsafe for a stroke patient.
Types of therapy
Drug treatment for stroke can be divided into groups:
- hypotensive;
- nootropic;
- blood thinners;
- decongestants;
- cardiotonic;
- cerebral.
Drugs for brain stroke are selected taking into account the symptoms. In addition to the symptoms that have arisen, the doctor, when selecting treatment, takes into account the mechanism of development of stroke: ischemia or hemorrhage.
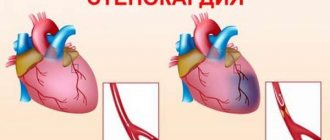
For ischemic stroke
In this form, the cessation of blood flow to an area of the brain occurs due to blockage of the artery by a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque.
Treatment of cerebral ischemia is aimed at restoring blood flow to an area of brain tissue. Let's see what drugs are prescribed:
- Nootropic drugs. Neuroprotectors will reduce hypoxia, reduce the area of the affected area and prevent further damage to neurons.
- Blood thinner. Medicines after stroke that reduce blood viscosity are necessary to improve cerebral blood flow and prevent the recurrence of blood clots.
- Sedatives. Sleeping pills and sedatives for cerebral stroke accompanied by an ischemic process are necessary in the acute stage of the disease. Providing rest reduces the area of damage to brain cells and prevents early post-stroke complications.
- Hypotensive. Blood pressure-lowering medications are needed to prevent unwanted stress on blood vessels.
- Diuretics. Necessary to prevent cerebral edema in the acute stage of the disease.
The list of medications can be supplemented with statins and vitamin-mineral complexes. Which medications to take and in what dose are selected individually.
In the acute stage, these are droppers or injections for recovery after a stroke, and in a later period, when rehabilitation of post-stroke complications is carried out, medications are prescribed in tablets. Drugs for ischemic stroke are selected individually, taking into account the abnormalities that have arisen and the stage of the disease.
You can often hear requests from relatives to prescribe the most effective pills for the brain after a stroke or to prescribe injections to speed up rehabilitation. But there is no “super remedy” and treatment after stroke is lengthy, despite the fact that the doctor decides what medications to treat, taking into account the mechanism of the pathology and the nature of the abnormalities that have arisen.
For hemorrhagic stroke
Rupture of a vessel, accompanied by the formation of an intracranial hematoma or blood soaking of the brain tissue.
Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke with blood soaking into brain tissue differs slightly from ischemic brain damage. Medicines are prescribed for recovery after stroke with decongestant, hypotensive, neuroprotective and sedative effects.
The only difference is that medications for hemorrhagic stroke should not only prevent the development of oxygen starvation in brain cells, but also prevent further hemorrhage. The list of stroke medications is expanding:
When a large hematoma forms, to prevent compression of the brain structure, patients undergo surgical removal of blood accumulations. After the blood clot is removed, standard drugs are used to treat stroke.
"Semax 0.1%" restores nervous tissue
Neuropeptide Neuropeptide or regulatory peptide are compounds of amino acids that regulate various functions in the body. "Semax 0.1%" is effective in the late period of recovery after a stroke due to the following properties:
- Helps restore speech, memory, attention, improve cognitive functions Cognitive functions
Functions of the brain through which the process of understanding the world is carried out. These include memory, attention, psychomotor coordination, speech, counting, thinking, orientation, planning and control of higher mental activity.; - Increases the survival of neurons Neuron
A nerve cell consisting of a body and processes extending from it. Structural unit of the nervous system. and normalization of nervous tissue functions; - Strengthens the adaptive capabilities of the nervous system;
- Normalizes the work of vegetative centers. Autonomic centers.
Centers of the nervous system that regulate the work of internal organs.; - Prevents the development of depression after a stroke;
- Provides restoration of the sleep/wake cycle.
Another advantage of Semax 0.1% is its ease of use. The dosage form in the form of nasal drops is excellent for regular independent use by the patient or his relatives after a stroke .
Preventive measures
A healthy lifestyle and exclusion of harmful foods (fatty foods, smoked foods, pickles) from the menu can help reduce the risk of developing acute ischemia.
Drug prophylaxis is indicated only for persons who have suffered a stroke. This is necessary because stroke patients have an increased risk of developing a second attack. Some medications are prescribed in short courses, while others need to be taken for life. Let's look at what medications you need to take regularly after a stroke:
- hypotensive;
- blood thinners (under the control of PTV);
- statins (if you have high cholesterol).
Prevention by other means is carried out with maintenance courses twice a year. The patient is given IVs, injections and prescribed some medications in tablets.
List of what is injected to prevent stroke:
Medicines are administered by drip or intramuscular injection. Piracetam is prescribed in long courses to prevent possible complications after a stroke. Some neurologists call this drug “memory restoration pills” due to the fact that drug psychostimulation increases brain activity. In addition to medications that affect brain function, therapy includes vitamins and other medications to generally strengthen the body. What to drink after stroke during the rehabilitation period is prescribed by a neurologist.
Medicines for the prevention of stroke help maintain metabolic processes in brain tissue, improve metabolism and prevent the formation of blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques in the early and late post-stroke period.
Medicines after stroke help reduce damage to brain tissue and prevent serious complications. What to take is decided by the doctor, taking into account the post-stroke period and the nature of the disorders identified in the patient, so drugs for prevention are selected individually for each patient. But it is impossible to prevent stroke, but giving up bad habits and a healthy lifestyle will help reduce the risk of an attack.
Treatment of stroke with drugs allows you to restore normal blood circulation to the affected area and minimize the risk of complications. The attending physician will help you select therapy and explain what medications are prescribed after an acute cerebral circulation disorder. Medicines in some cases help to partially restore lost functions and narrow the affected area. Medicines may be prescribed as a preventive measure against possible relapses of the disease.
Recovery after a stroke at home
Emergency care during an attack is provided in the hospital, but later treatment after a stroke is carried out at home. An important part is the restoration of motor functions, which takes place in the form of special exercises. Below we will describe how to treat a stroke with medication. The doctor will definitely prescribe a course that will include medications from the list below:
Group
Titles
Normalizing metabolic processes in brain cells.
- Ginkgo Fort;
- Solcoseryl;
- Cortexin;
- Ceraxon.
- Noofen;
- Lutsetam;
- Piracetam.
Improving cerebral blood supply.
- Cerebrolysin;
- Pentoxifylline;
- based on aspirin;
- Pentoxifylline.
- Sirdalud – relieves hypertension, muscle spasms;
- Glycine – reduces the excitability of the nervous system;
- Adaptol, Gidazepam are antidepressants that increase stress resistance.
Traditional medicine recipes can be used as an additional remedy in combination with drug treatment for stroke and therapeutic exercises. They cannot be a monotherapy method, but they contribute to a speedy recovery. Folk remedies are used in the form of:
- decoctions for baths from pine needles, rosehip bark, sage;
- drinks: wormwood juice, celandine decoction, pine needles with lemon, peony;
- ointments for paralyzed limbs in cases of ischemic stroke.
Drugs that improve memory and cerebral circulation
Any type of stroke affects and impairs the functioning of the brain, which leads to the need to take medications to improve cerebral circulation. This group is represented by nootropic medications – neuroprotectors. This drug treatment for stroke is aimed at restoring higher functions and processes in the brain, preventing damage to the nervous system, and having an antioxidant effect. Commonly used treatment options include:
- Thiocetam – relieves headaches, reduces dizziness, the threshold of fatigue.
- Encephabol has a clear anti-ischemic effect. It has a positive effect on the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which accelerates energy metabolic processes in the brain and activates plastic functions.
- Piracetam is the most scientifically studied and proven medicine. It has a multifactorial effect.
- Picamilon is an analogue of GABA.
- Thiotriazolin – has a wide spectrum of action, has an antioxidant, anti-ischemic, membrane-stabilizing effect.
Modern neuroprotectors have been used for medical treatment of stroke. Below is a list of drugs that have successfully passed tests and show good results in restoring and treating the disease:
Medicines to prevent stroke
In cases where a possible stroke is suspected, preventive drug treatment should be started. Stroke can be hemorrhagic and ischemic; the list of drugs to prevent them differs:
- Calming, sedative drugs to reduce nervous excitability: Phytosed, Persen, valerian, Gidazepam.
- Medications to reduce high blood pressure: Liprazide, Metoprolol, Enalapril, Furosemide.
- Preparations for the prevention of atherosclerosis, strengthening blood vessels: Ginkgo forte, Ascorutin, Atorvastatin.
- Cerebroprotectors.
- Persons over 45 years of age take antiplatelet agents daily: Clopidogrel, Cerebrolysin.
- Taking cerebroprotectors: Phezam, Cerebrolysin, Piracetam, Ceraxon, Lucetam.
- Relieving the development of atherosclerosis: Atoris, Cerebrolysin, Lovastatin, Atorvastatin.
- Normalization of microcirculatory processes: Vinpocetine, Trental, Actovegin.
The effectiveness of drug treatment
One of the options for treating ischemia in a limited area of the brain is drug therapy. Medicines are taken after a stroke for 3 main reasons:
- As a means of preventing a second strike. In this case, nootropic drugs, vitamins and nutritional supplements may be prescribed to improve the blood supply to neurons with oxygen and nutrients.
- Pathogenetic technique. This method of therapy involves reducing the activity of pathological processes that lead to loss of function after a stroke. In the presence of cerebral vascular diseases, such drugs are constantly needed to treat the pathology and reduce the likelihood of developing a stroke.
- As a syndromic method of treatment. Drug therapy is aimed at accelerating rehabilitation. When using medications, cognitive functions, muscle tone, speech, motor coordination and psycho-emotional state are restored.
In the presence of acute pain and frequent vascular spasms, take painkillers.
After ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke develops when there is an acute disturbance of cerebral circulation due to blockage of a cerebral artery by a thrombus or cholesterol plaque. As a result, a limited area of the brain does not receive nutrients and oxygen. In the first 2-3 hours after the development of ischemia, thrombolytics are required to break down blood clots and restore natural trophism.
Stroke - treatment (basic principles)
Basic (main) therapy for IS is aimed at:
- carrying out adequate reperfusion (restoring full blood supply to brain tissue);
- maintaining the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems;
- ensuring complete oxygenation;
- maintaining body temperature, blood pressure and central hemodynamics;
- elimination of complications (metabolic disorders, blood clotting disorders, relief of cerebral edema, seizures, manifestations of hydrocephalus, dislocation of brain areas, etc.);
- ensuring prevention of late complications and earlier rehabilitation treatment (restoration of lost functions).
Non-drug treatment of ischemic stroke
Important. After a stroke, the patient requires maximum rest and strict bed rest. Even with timely medical care and a small lesion, the patient should lie with the head of the bed elevated for the first four days. Getting out of bed is prohibited.
Subsequently, the patient is gradually verticalized. In the case of an uncomplicated course of IS, on the fourth day the patient can be slowly sat up on the bed (legs should be down). In this case, all movements of the patient should be as passive as possible. He needs to be provided with full support under his back and sides, his feet should be placed on a special stand or on the floor.
The transition to a vertical position is possible only by the seventh day (also if the course is uncomplicated and there are no contraindications). Trying to stand up on your own is prohibited. The patient should be explained that overexertion when trying to get out of bed without help, physical or emotional stress (stress from realizing one’s own helplessness), loss of balance and falling, etc. may lead to recurrent stroke or complications.
Important. The patient's transition to a standing position should be carried out with the help of two people supporting the patient by the arms. Rehabilitation treatment after an ischemic stroke is prescribed as early as possible, but gradually, with minimal stress for the patient.
Diet for ischemic stroke
All food in the first days after a stroke should be exclusively boiled and pureed (the diet is aimed at maximizing the ease of digestion of food).
The amount of fats and EFAs (unsaturated fatty acids) is sharply limited. Foods high in cholesterol are excluded from the diet. Salt intake is limited to three to five grams per day. In the diet, increase the consumption of foods containing fiber (vegetable and fruit purees). Fatty foods, strong broths, spicy, sweet, etc. are excluded. It is advisable to replace the meat with boiled lean fish (contains healthy polyunsaturated fatty acids - PUFAs).
Attention! The bread must be yesterday's bread (fresh bread is prohibited), preferably with bran or wholemeal flour.
Dairy products can only be consumed in low-fat form (hard low-fat cheeses, low-fat yoghurts).
During the rehabilitation period after an ischemic stroke, you should also follow a diet aimed at normalizing body weight and lipid balance (a special diet prescribed to patients with atherosclerosis).
Smoking and drinking alcohol, strong coffee and tea are completely excluded. Additionally, all risk factors are reduced (treatment of diabetes, blood pressure control, normalization of blood clotting and reduction of the risk of blood clots).
For reference. This is necessary to reduce the risk of another stroke.
Parenteral nutrition
On average, stroke patients require 1,400 to 1,800 kcal per day. With the development of multiorgan dysfunction syndrome, calorie intake should be increased by seventy percent.
Attention. If proper natural nutrition is not possible, power is connected through a feeding tube. For tube feeding, special high-calorie mixtures are used. In this case, all parenteral nutrition is carried out under the careful supervision of tests (the degree of protein deficiency, high urea levels, etc. are assessed).
How often to give IVs after a stroke
All treatment, including IVs, is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, individually, depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the time of his admission (time from the onset of the stroke), the presence of complications and underlying diseases (diabetes mellitus, heart or kidney failure, etc. .).
Main directions of drug therapy
An important step in the treatment of ischemic stroke is:
- elimination of water-electrolyte imbalances;
- correction of hypovolemic disorders and maintenance of bcc (circulating blood volume);
- stabilization of central venous and blood pressure;
- relief of signs of cerebral edema.
Important. The administration of hypoosmolar solutions (five percent glucose solution) is contraindicated due to the high risk of an even greater increase in intracranial pressure.
Reducing blood pressure in the acute period of ischemic infarction is also not recommended. The exception is arterial hypertension over 220/110 millimeters of mercury (in this case, the pressure is reduced by fifteen percent during the day), the patient has acute renal failure or chronic renal failure (acute or chronic renal failure), MI (myocardial infarction), HF (heart failure) .
What drugs are prescribed
Only the attending physician has the right to determine the list of medications that need to be used to treat a cerebral stroke. It is strictly forbidden to resort to independent treatment, because there is a high probability of complications or relapse.
The list of drugs for cerebral stroke is selected depending on the severity of the pathological process:
- At the initial stage of development of the disease, the first symptoms appear, on the basis of which appropriate medications are selected. Medicines are aimed at eliminating one or more signs of the clinical picture of stroke. Arterial hypertension requires antihypertensive drugs to normalize blood pressure. To improve cerebral circulation and neuronal trophism, nootropic drugs are prescribed. Against the background of stress or fatigue, sedative medications are prescribed. The duration of therapy depends on the patient’s well-being.
- If a stroke worsens in the first 2-3 hours, only those drugs are required that will help stabilize normal cerebral circulation. The most effective means in a critical situation are blood thinners. They reduce plasma coagulability and platelet aggregation, thereby reducing the risk of thrombosis and complete blockage of small vessels. Thanks to the anticoagulant effect, in 95% of cases it is possible to avoid paralysis and prevent the recurrence of a stroke. Analgesics help relieve pain.
- After discharge from the hospital, drug therapy continues at home. In this case, it is necessary to take anti-stroke medications on an ongoing basis. If the patient develops a feeling of restlessness and anxiety about the possibility of a relapse, the doctor prescribes sedatives, mild antidepressants and drugs that improve sleep. You will need to take blood thinning medications for about 2-3 years due to the high risk of blood clots.
Only complex therapy with several drugs can restore blood circulation.
Muscle relaxants
Stroke medications, which are necessary to relax skeletal muscles, are in most cases used as agents to restore motor function. By 3 months after the pathology, increased muscle tone develops, which provokes the occurrence of severe spasms and convulsions. As a result of the contraction of a muscle group, it becomes difficult for the patient to move. The patient experiences severe cutting pain. Therefore, treatment with muscle relaxants is aimed at eliminating hypertonicity.
Treatment with muscle relaxants lasts until the completion of rehabilitation measures to resume the patient’s motor activity. Muscle tone will return to normal on its own over time. Until this happens, do not stop taking the pills.
Antidepressants
During the rehabilitation period, 80% of patients are depressed. This behavior is caused by the loss of certain functions and the loss of motivation to restore them. To improve psycho-emotional control, antidepressant drugs are prescribed after a stroke. They belong to the group of psychotropic drugs, therefore they are taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants are medications designed to reduce seizure activity. When using this group of medications, you must be careful because they cause drowsiness, weaken memory, and cause severe weakness and frequent dizziness. Carbamazepine is prescribed as an anticonvulsant in 80% of cases, and Phenytoin in the remaining cases.
Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants
These medications for cerebral stroke are necessary to prevent relapses. Antiplatelet agents reduce the ability of platelets to stick together, thereby serving as a means of preventing thrombus formation. Anticoagulants are necessary to reduce blood clotting. Under conditions of increased viscosity in the blood, the likelihood of blood clots increases.
The most popular antiplatelet agents on the pharmacological market:
Injections into the abdomen with Heparin are carried out only by medical personnel.
Anticoagulants are prescribed to patients prone to increased blood clotting. The pathology is dangerous due to disruption of natural blood circulation. When platelet aggregation increases, there is a risk of blood clots and vessel blockage with subsequent rupture.
It is important to remember that when antiplatelet drugs are prescribed simultaneously with anticonvulsants, it is necessary to periodically donate blood for biochemical analysis. This need is due to the high risk of bleeding. The first signs of complications when taking 2 drugs will be:
- dizziness;
- gagging;
- causeless appearance of hematomas on various parts of the body;
- diarrhea.
If symptoms develop, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Neurometabolic cerebroprotectors
Stroke medications are complemented by neurometabolic cerebroprotectors, the main task of which is to stimulate metabolic processes in the tissues of the central nervous system. The second name for medications is nootropic drugs or neuroprotectors. The use of this group of drugs makes it possible to eliminate some pathological processes: ischemia, cerebral hypoxia, intracellular intoxication after necrosis. Cerebroprotectors allow you to increase glucose consumption by neurons and stimulate the metabolism of nucleic acids.
Vitamins
Clinical studies have proven that after a stroke, vitamins can speed up the rehabilitation process. In this case, the dosage should be adjusted by a specialist depending on the diet and laboratory parameters. In case of drug abuse, hypervitaminosis is possible. Vitamins are prescribed in the form of injections for stroke. The following groups are most effective:
- vitamin A - stimulates cell growth and division, increases tissue regeneration;
- thiamine and riboflavin stabilize blood pressure, improve neuron function and cerebral circulation;
- ascorbic acid activates the regeneration of the vascular endothelium and promotes the formation of new vessels;
- Vitamin D maintains the amount of formed elements within normal limits, preventing the blood from thickening, and also has a positive effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems;
- Vitamin E is a natural antioxidant and prevents the development of oxidative reactions caused by free radicals.
Dietary supplements made from natural products can be taken at all stages of stroke therapy. In the first 1-2 months, medical specialists prescribe dietary supplements to improve cerebral circulation and accelerate tissue regeneration processes. Over the next 6 months, biological supplements help correct deficiencies in the diet and replenish the supply of microelements in the body.
In the first few months, the main task for the patient is to normalize the functional activity of the digestive and immune systems. Therefore, nutritional supplements are essential for recovery after a stroke. Dietary supplements, along with other medications, must be taken under the supervision of a physician.
Encephabol is an effective drug for neurorehabilitation
To restore blood flow in the ischemic zone, platelet and erythrocyte antiplatelet agents are used:
- acetylsalicylic acid (thrombo ACC; cardiomagnyl; cardioaspirin; terapin);
- dipyridamole;
- ticlopidine (ticlid);
- clopidogrel (Plavix);
- pentoxifylline (trental, agapurine, flexital).
Anticoagulants are effective drugs for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe direct-acting anticoagulants (heparin, low-molecular-weight heparins, sodium enoxaparin) to patients, and then indirect-acting ones (phenylin, warfarin). Doctors use the following vasoactive drugs:
- Vinpocetine (Cavinton);
- nicergoline (sermion);
- instenon;
- aminophylline (aminophylline);
- collected the vase;
- cinnarizine (stugeron).
Angioprotectors include parmidin (Prodectin), ascorutin, troxerutin, etamsylate. In the acute period of ischemic stroke, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide patients with intravenous infusions of biorheological drugs: plasma, albumin, rheopolyglucin (rheomacrodex).
Neuroprotection in patients with ischemic stroke is carried out using drugs such as:
- calcium channel blockers (nimodipine (nemotan, nimotop);
- antioxidants (emoxipine, mexidol, mildronate, alpha-tocopherol acetate, ascorbic acid;
- neurotrophic action (piracetam, lucetam, nootropil, cerebromedin, Semax, picamilon);
- improving tissue energy metabolism (cytochrome C, actovegin, solcoseryl, diavitol, riboxin, lipoic acid.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients with ischemic stroke have the opportunity to receive modern drugs that have passed all stages of clinical research.
In order for the patient to recover as quickly as possible, medications with different effects are prescribed. The therapeutic plan is drawn up by the attending neurologist according to an individual scheme. Afterwards it can be changed under the supervision of a local doctor. Types of medications used:
- Nootropics and neuroprotectors - accelerate metabolic processes in brain tissues and cells.
- Neuroleptics, anticonvulsants, sedatives - relieve symptomatic manifestations after a stroke.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents - normalize the condition of the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Means for normalizing blood pressure.
- Multivitamins, dietary supplements.
These drugs are indicated for all types of stroke. They regenerate neural networks, restore the neurocytic structure, and protect nerve cells from the effects of oxygen starvation. The patient's cognitive and motor functions are normalized, and speech improves. The group of nootropic drugs includes: “Nootropil”, “Semax”, “Glycine”.
Together with this group of medications, vitamin complexes with B vitamins are prescribed. They speed up the recovery process. They are injected intramuscularly or intravenously for about 7 days, and then prescribed in perioral form (tablets). These are “Neurorubin”, “Milgamma”, etc. Prescription regimen: 2 ml of Milgamma once a day for a week, then the injections are replaced by pills. The duration of taking vitamins and nootropics is at least four weeks.
Drugs that normalize vascular tone are also necessary in the treatment of stroke in the acute and recovery stages. Prescribed course:
- "Instenon";
- "Vazorbala";
- "Trentala";
- "Cavinton".
Please note that vasoactive drugs can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, even in tablets. The neurologist looks at the type of disease suffered, complications, and the general condition of the body.
Treatment after a stroke includes drug therapy and other rehabilitation methods. Stroke patients take nootropic and antiplatelet drugs to normalize blood pressure and blood glucose levels. During this period, it is important to prevent a recurrence of stroke, which occurs if you do not take the prescribed medications. The consequences of relapse are more severe and difficult to treat.
The most effective medications for treatment and recovery after injury:
- "Mexidol" - Experienced neurologists recommend treating stroke with Mexidol. It does not have a nootropic effect, but gives good results when used in the acute stage of stroke. This is due to the property of protecting neurons from hypoxic effects. In hospital settings, Mexidol is prescribed in ampoules. In home therapy, tablets are prescribed in a dosage of 2 times a day for a month.
- “Gliatilin”, “Choline” - prescribed in the acute and recovery stages of stroke. Most effective in ischemic form. The drug reduces the risk of the formation of degenerative brain lesions, which can lead to irreversible consequences. It increases blood flow to brain cells and helps them regenerate. The course of treatment is 3-6 months.
- "Ceraxon", "Citicoline" - activates metabolic processes in nerve cells. The drug reduces cerebral edema, which prevents the risk of serious problems in the functioning of the organ, and promotes recovery at any stage of stroke.
- "Actovegin" is a medicine used by diabetics. And helps in treating the consequences of a stroke. If you use Actovegin and Cortexin together, the protective system of brain structures is strengthened, the patient recovers faster and the risk of relapse is reduced.
- "Mydocalm" is a drug from the group of muscle relaxants. Recommended by neurologists to get rid of muscle strain, which is a consequence of a stroke.
- "Trental" is an effective vasoconstrictor that stimulates blood circulation in the affected areas of the body.
- "Instenon" is a medicine with complex effects, acting as a vasoactive and at the same time stimulating drug for brain structures. In the hospital it is carried out intravenously, through droppers. Next, they are prescribed orally - three pastilles daily for six weeks. Another remedy is Cavinton. It is used in the active and rehabilitation period of treatment.
A number of clinical studies make it possible to conclude that the active substance encephabol has a high penetrating ability through the hematoplacental barrier and does not have an embryotoxic effect.
You need to know that there have been insufficient clinical studies to confirm the safe effects of peritinol on the fetus and the course of pregnancy in general. If the drug must be taken while breastfeeding, the child should be switched to artificial feeding.
In pediatric practice, encephabol is used to treat the following diseases:
- mental retardation with delayed speech development, poor memory, increased excitability or excessive inhibition
- encephalopathy is a brain pathology characterized by active death of neurons due to disruptions in cerebral circulation
- encephalitis – inflammation of the brain due to a viral or bacterial infection
- cerebrasthenic syndrome is a neurological disease, the symptoms of which are increased absent-mindedness and fatigue, exhaustion of the nervous system, poor reaction
- oligophrenia - deviations from the norm in the intellectual and emotional development of a child, delays in speech development, motor skills
Encephabol dosage for children
It is better to use the drug for children in the form of a suspension during or after meals. For an infant, this remedy can be used already on the third day after birth.
Age dosage:
- in the 1st month of life, the child should be given 1 ml of the drug per day
- at 2 months, 2 ml of suspension is prescribed, adding another 1 ml every week until the daily dose of the drug is 5 ml
- from 1 year to 7 years should be taken 2.5-5 ml 1-3 times a day (the exact dose is determined by the attending physician)
- after 7 years, you should take 2.5-10 ml 1-3 times a day. You can also take the medicine in tablet form (1-2 tablets at a time)
A sharp disruption of the blood supply to the brain structures can be accompanied by a rupture of an artery, in which case a hemorrhagic form of the pathology is diagnosed, or a blockage of a vessel - an ischemic form.
Regardless of the type of stroke and the extent of brain damage, the patient exhibits the following first signs:
- paralysis;
- numbness of various parts of the body;
- decreased sensitivity;
- intense pain in the head;
- partial amnesia;
- violation of speech skills;
- problems with hand motor skills;
- decrease in intellectual abilities.
Painful symptoms occur due to lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Medicines after a stroke are also needed in the psychotherapeutic field. Many victims fall into deep depression after an attack, the reason for this is helplessness. Therefore, treatment for stroke is aimed at taking various drug groups. In the post-stroke period, complex therapy is required, including taking pills after a stroke, physiotherapeutic procedures, and classes with a speech therapist. An integrated approach will help avoid irreversible consequences of the disease.
Since ischemic stroke occurs against the background of vascular blockage and impaired blood microcirculation, therapy is aimed at normalizing healthy blood flow in the brain tissue.
Anticoagulants are not prescribed for extensive lesions, since the drugs can cause bleeding and a hemorrhagic form of blockade. Medicines increase blood pressure. Other contraindications include liver and kidney diseases, stomach ulcers.
This type of stroke requires stopping bleeding in the brain, eliminating swelling of the organ and normalizing blood pressure. For these purposes, doctors prescribe ganglion blockers and angioprotectors.
For any form of stroke, ischemic or hemorrhagic, the patient must take drugs that improve brain function - neuroprotectors. The drugs are used during the rehabilitation period to prevent damage to brain structures in order to improve the transmission of nerve signals.
Doctors prescribe restorative drugs that have proven themselves in Europe.
Nootropics
- a drug used in the treatment of diarrhea – Imodium;
- antidepressant drug – Valium;
- anesthetic agent – Codeine;
- trouble blockers.