A moment is enough for a person to face a high probability of danger to his life. Qualified medical care is only on the way, and blood loss from the wound from a ruptured artery can be fatal. Blood leaves the injured body in a rapid stream, and there is nothing at hand that could help in providing emergency assistance, and the hope for salvation is fading with every second.
An involuntary eyewitness to the incident leans over the victim, trying to assess the degree of the impending threat with anxiety in his eyes. But dirty scraps of clothing, mixed with bone fragments, blocked access to the fatal wound and made it impossible to see anything underneath. Finally, the person trying to help the victim assessed the extent of the dangerous situation.
Open bleeding from a wound requires immediate help, because delay threatens human life. He vigorously cleans the wound and squeezes the damaged artery with his fingers.
The blood continues to flow out, and the vessel between the fingers slips away and cannot be compressed effectively. The rescuer presses with all his might on the artery with the thumbs of both hands. Over time, his fingers go numb from incredible efforts. There is a need to change the method of clamping and apply hand coverage, pressing the ruptured artery with your thumb. There is still no help, and the hand squeezing the wound begins to experience pain. After about ten minutes, a cramp will cramp the limb, forcing you to change the method again. He will have to press the fist of his second hand on the finger pressing against the artery. While the exact source of bleeding is unknown, a decision is made to loosen the clamp and press on the wound itself with both palms and wait for the opportunity to apply a tight bandage to the wound. But if even after this the bleeding does not stop, and even worsens, then again you have to put pressure on the wound.
How to choose the right points
Knowing exactly where the main clamping points are located, you can squeeze the main arterial vessel, not in the wound, but slightly above it. This will significantly reduce blood flow and temporarily protect the injured body. The points are not chosen at random. It is necessary to take into account the direction of blood flow through the vessels, clamping the damaged artery on both sides. Only in this case a positive effect is possible. But if a bone is broken at the site of injury, then compression of the intended point is unacceptable!
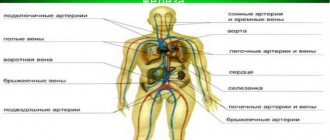
It is necessary to mark the exact places where the artery is being pressed. I would like to note that arteries are divided into the following:
- shoulder;
- femoral;
- sleepy;
- jaw;
- temporal;
- subclavian
If the brachial artery is affected, the closest point of pressure is between the muscles located on the shoulder. In this case, it is necessary to place the victim’s hand behind his head and take a place behind the victim, taking a comfortable position. You need to squeeze the artery with four fingers from the outside, feeling the depression between the shoulder muscles and pressing hard, pressing this place to the bone. There are cases when bleeding in the upper part of the shoulder is stopped by applying pressure with the fingers, pressing the vessel to the head of the humerus in the armpit.
In case of damage to the femoral artery, clamp a point in the groin area in the middle of the fold of skin. At this point the artery presses against the femur. Kneeling on the side of the injured leg, they press with all their weight on their outstretched arms for support, while clasping the victim’s thigh with all their fingers and only then pressing the point in the groin with their index fingers.
It is possible to stop bleeding of blood vessels from the head or if a vessel in the upper part of the neck is damaged:
- By acting on the carotid artery, the use of a tight, compressive bandage is eliminated, because the victim will not be able to breathe.
- The palm is placed on the back of the victim’s head, and pressure is applied with the thumb or placed behind and the wound is pinched with four fingers.
- Taking into account the direction of blood movement along the carotid artery, the point below the injury site is clamped.
- The location of this point is the middle of the anterior surface of the neck muscle.
- The wounded person's head is turned so that it is clearly visible. The artery is pressed against the spinous processes of the vertebrae.
If the head, shoulder joint or neck are injured, then instead of the carotid artery, the subclavian artery is pinched with the index finger and pressure is applied with all force to the fossa behind the collarbone.
The maxillary and temporal arteries are located in the zone of active blood supply to the face. Stopping heavy bleeding of the maxillary artery is achieved by pressing it to the lower jaw.
Stopping bleeding from the temporal artery occurs after pressing a point in front of the auricle.
In case of hand injuries, bleeding of blood vessels does not cause mortal danger. However, to reduce blood loss, finger pressure is applied at the moment when a tight bandage is prepared. Raising the limb with a circular grip of the hand, squeeze the point located in the middle third of the forearm.
Bleeding of the vessels of the foot is stopped by pressing the back of the foot.
Finger pressure on the artery during bleeding is temporary and is performed in case of emergency assistance to the victim until qualified specialists arrive.
What you need to know to carry out pressing
It is impossible to squeeze the vessel between your fingers because:
- it is not visible at all in a bleeding wound;
- At the same time, contaminated scraps of clothing and bone fragments may surround the site of the lesion.
Therefore, during arterial bleeding, the main afferent (main) vessel is compressed not in the wound, but above it - “along.” This reduces blood flow to the injury site. Not everyone knows anatomy well. The person providing assistance should only be familiar with the location of the main pressure points.
They are not chosen arbitrarily, but in accordance with the direction of the vessels and the nearest anatomical bone formations. For compression to be effective, the artery must be clamped on both sides.
The method is completely inapplicable when a bone is fractured at the point of supposed compression.
Since bleeding requires emergency care, the following rules should be followed:
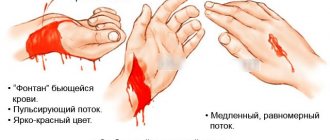
- delay is dangerous for the life of the victim, so the condition is assessed instantly (type of pulsating wound);
- if necessary, you can tear or cut part of the victim’s clothing, this will still have to be done to examine the wound;
- methods of compression are recommended either only with the thumbs, or by wrapping the hand so that the thumb is located at the desired point, however, after 10 minutes the rescuer may experience cramps and pain in the hands, so in practice one has to adapt and press with a fist;
- if the origin of the bleeding is unclear, then it is allowed to press with your palms on the wound itself until the location of the damage is determined (this is what you do when you are wounded in the stomach);
- It is necessary to maintain pressure until the pressure bandage is applied; if after this the bleeding intensifies, the pressure will have to be repeated.
Let's look at specific pressure points.
How to correctly diagnose internal bleeding
If it is not so difficult to determine the diagnosis with external bleeding, then with internal bleeding this is not the case. This will require certain knowledge, because the blood does not come out immediately, but after some time.
Thus, pulmonary hemorrhage is accompanied by hemoptysis, the flow of foaming blood from the nose/mouth. Esophageal or gastric bleeding is accompanied by vomiting blood (sometimes “coffee grounds”). If bleeding occurs in the stomach, duodenum, or biliary tract, this entails the appearance of tarry stools.
If bleeding occurs in the rectum/colon, this is accompanied by the appearance of raspberry, cherry, scarlet-colored blood in the stool. Kidney bleeding turns the victim's urine scarlet.
It is worth noting that with visible internal bleeding, bleeding may not appear immediately, but after some time. Accordingly, the use of general symptoms and certain diagnostic methods for internal bleeding is extremely necessary.
Diagnosis of hidden internal bleeding is definitely considered difficult. In this situation, local symptoms are divided into two main groups:
- Detection of bleeding.
- Some changes in the functions of certain organs that have been damaged.
To identify bleeding, you should pay attention to some signs:
- Bleeding in the pleural cavity:
- percussion sound is dull over a certain surface of the chest;
- breathing weakens;
- the mediastinum shifts;
- respiratory failure is observed.
- Bleeding in the abdominal cavity:
- the stomach is bloated;
- peristalsis weakens;
- percussion sound is dull in sloping areas of the abdomen;
- Sometimes symptoms of peritoneal irritation are observed.
- Bleeding in the cavity of a particular joint:
- the joint increases in volume;
- the appearance of sharp pain;
- violation of direct joint function.
- Hemorrhage/hematoma:
- swelling can be determined;
- pain symptom in acute form.
How to give first aid correctly
The procedure for providing first aid is directly related to the anatomy of the human body. Arteries are very elastic, so these blood vessels need to be pressed against the bone, otherwise they can get lost in the soft tissue, and the wound will continue to bleed. Therefore, ligation of the femoral artery is considered the most difficult.
In case of arterial bleeding, the artery should be pressed above the wound site to stop the flow of blood from the heart. However, this rule does not apply to neck and head injuries. In such a situation, pressure should be applied below the wound on the side of the heart.
Finger pressure on the artery
Pressure is the simplest and most effective method, but it is more suitable for short-term stopping of bleeding. The ruptured vessel is pressed against the bone formation above the injured area.
It can be compressed with the pads of the fingers (for example, subclavian, temporal, ulnar arteries) or with a fist (femoral artery, abdominal aorta).
If the vessels of the neck or head are damaged, then they should be clamped lower - closer to the heart.
Very important!
You can hold the vessel in a pinched state for no more than 10 minutes, otherwise irreversible changes will begin in tissues without oxygen.
First aid for bleeding
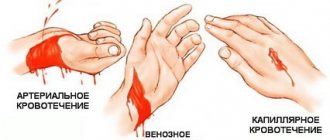
Depending on the type of bleeding (arterial, venous, capillary) and the means available to provide first aid, a temporary or permanent stop is carried out.
Temporary stopping of the most life-threatening external arterial bleeding is achieved by applying a tourniquet or twisting, fixing the limb in the position of maximum flexion, and pressing the artery above the site of injury with the fingers. The carotid artery is pressed below the wound. Finger pressure of the arteries is the most accessible and fastest way to temporarily stop arterial bleeding. The arteries are pressed in places where they pass near or above the bone (Table II, color insert).
Table II. Points of finger pressure of arteries
The temporal artery (1) is pressed with the thumb to the temporal bone in front of the auricle when bleeding from head wounds.
The mandibular artery (2) is pressed with the thumb to the corner of the lower jaw when bleeding from wounds located on the face.
The common carotid artery (3) is pressed against the vertebrae on the front surface of the neck to the side of the larynx. Then a pressure bandage is applied, under which a thick cushion of bandage, napkins or cotton wool is placed on the damaged artery.
How to apply pressure
It is impossible to compress an artery vessel by placing it between your fingers, because it cannot be seen in a bleeding wound. The affected area may be covered with dirty shreds of clothing and broken bones. In this regard, a large artery should be clamped to stop bleeding above the wound site.
Among non-specialists, the likelihood of meeting a person who knows anatomy well is vanishingly small. Therefore, a potential rescuer needs to know the location and points of digital pressure during arterial bleeding in order to temporarily stop the bleeding.
They are selected in accordance with the direction of blood flow in large arteries and adjacent bone formations. To effectively press the artery with your fingers, you need to squeeze the artery on both sides.
A table has been developed for digital compression of arteries during bleeding, according to which you can navigate which vessel to compress in which place to stop any bleeding.
Table of places of digital pressure on arteries during bleeding
The method cannot be used if the bone is broken at the point where blood flows from the artery of the recommended compression.
Carotid artery
Blocking blood flow is required if pulsating severe bleeding occurs from the arteries of the head, dorsal part of the neck and submandibular. The difficulty of manipulation lies in the inability to apply a pressure bandage to the neck without the risk of blocking the airways. Therefore, the carotid artery is pressed below the bleeding area with the thumb.
An alternative option for digital compression of the carotid artery is carried out using four fingers, located behind the injured person. The required point of digital pressure on the carotid artery in humans is located in the central part of the dorsal surface of the cervical muscle. The artery is pressed against the spinous crest of the vertebra.
Finger compression of the subclavian artery is performed for traumatic injuries of the head, neck and shoulder joint. With your thumb, press firmly from above into the clavicular fossa. The artery is pressed against the rib.