In medical practice, situations sometimes occur when pathology affects individual blood elements. In particular, red blood cells can change their shape and size, as a result of which their function is impaired. This deviation is called poikilocytosis. When it is detected in a blood test, we often talk about anemia. This is explained by the fact that red blood cells can no longer fully transport oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
Important Features
A notable feature of the pathology is that red blood cells, which were previously round in shape, lose their normal appearance. They develop unusual shapes: they become oblong, pear-shaped, sickle-like. But, in addition to changes in appearance, functional features also suffer. The main task they face is the transport of oxygen to the cells. It is gradually suppressed, which leads to anemia.
Poikilocytosis can only be detected using a microscope. For this purpose, the blood is sent for morphological examination. It is impossible to determine changes in the shape of red blood cells using an automatic analyzer. After conducting a qualitative analysis of the smear, the specialist makes a note about the presence of anisopoikilocytosis - another designation of pathology. The records also indicate the form that the red blood cells have acquired.
A feature of the disease is the percentage of red blood cells in a blood test. It is also practiced to designate it using pluses, points, and special terms. Poikilocytosis occurs:
- Unexpressed. This is when the smear contains 25-50% of red blood cells, the shape of which remains normal. This form is designated 1, or +;
- Moderate. In this case, the content of red blood cells is 50−70%. At this stage, red blood cells change their shape to a pathological one. The moderate variety is designated as 2, or ++;
- Expressed. There are 70−75% of red blood cells in such a smear. Their shape is not normal. This poikilocytosis is designated 3, or +++;
- Sharply expressed. Differences in shape can be observed in up to 100% of red blood cells. This anisopoikilocytosis is designated 4 or ++++.
In addition to all these designations, the doctor who noticed the presence of poikilocytosis must indicate what type of poikilocytosis we are talking about. There is an extensive classification, according to which ovalocytosis, anulocytosis, microspherocytosis, etc. are distinguished. It is important to record the shape of the cells , since this information is fundamental for the development of further treatment.
Prevention

A balanced diet is a good way to prevent macrocytosis
- Food must contain a sufficient amount of vitamins. However, you should not prescribe vitamin therapy yourself. An excess of vitamins and their incorrect combination lead to negative consequences, including macrocytosis.
- Smoking, in addition to intoxicating the body, poses a risk of developing macrocytosis due to the fact that cigarette smoke contains carbon monoxide. This component instantly combines with hemoglobin. As a result, hemoglobin molecules are no longer able to deliver oxygen to the tissues.
- Alcohol interferes with the absorption of microelements, including iron and vitamins, and also destroys hemoglobin molecules. Alcohol has a particularly negative effect on the liver, which leads to the accumulation of toxic substances in it and subsequent disruption of the kidneys, heart and brain.
- Active pastime in the fresh air will bring great benefits. This is the most effective way to saturate the body with oxygen.
Macrocytosis is not uncommon and is treatable in most cases. A healthy lifestyle and nutritious nutrition is a chance to forever get rid of the risk of a recurrence of pathology.
Biconcave shape
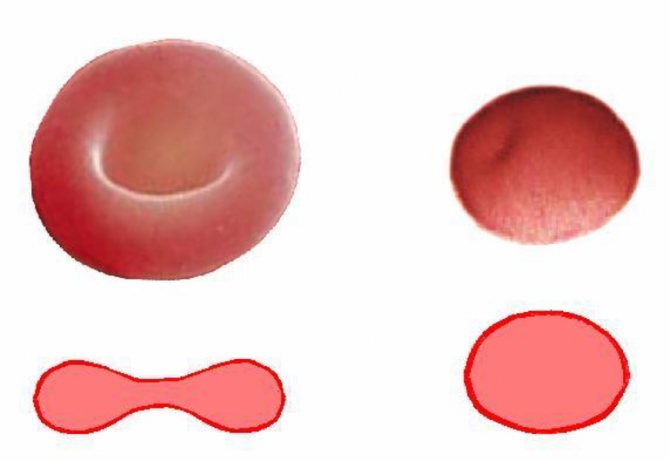
The normal shape of red blood cells, which in appearance resemble discs with light areas in the center. Hemoglobin provides them with their characteristic color. Such blood cells are responsible for the most important processes in hematopoiesis. But this is possible if they maintain their normal shape. It allows them to pass into the narrowest vessels and deliver oxygen to distant tissues and cells.
Impaired gas exchange can occur if the shape of the red blood cells becomes abnormal. This is an obstacle to their performance of their functions. This kind of internal disturbance affects a person’s well-being, and he begins to develop anemia.
With poikilocytosis, no single change occurs. Usually there are multiple changes in the configuration of red blood cells. Depending on the specific form, a certain type of poikilocytosis can be identified. The name of each of these varieties is directly related to the acquired form. For example:
- spherocytosis occurs when spherocytes are found;
- ovalocytosis - blood cells acquire an oval shape;
- schizocytosis - schizocytes are found in the blood smear;
- microspherocytosis - in the presence of microcytes and spherocytes in the smear.
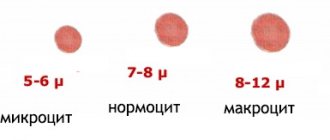
Healthy red blood cells are called normocytes.
Types of deformation
Depending on a particular pathology, blood cells can take on a certain shape. Sometimes certain types of deformation are detected:

- Anulocytes resemble a ring in shape. They are present in the bloodstream when iron levels are significantly reduced.
- Serocytes are characterized by a spherical shape. They have minimum sizes not exceeding 6 microns. Their peculiarity is the absence of a light area in the center. Red blood cells of this type can be found in disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, hemolytic anemia and other pathological conditions. Artificial heart valves can sometimes allow them to appear in the bloodstream.
- Ovalocytes are distinguished by their elliptical shape, which is why they are sometimes called elliptocytes. Usually their content in the blood is more than 10%. There are more of them with thalassemia and ovalocytosis.
- Planocytes are characterized by a flat shape. They occur in various types of hemoglobinopathies. These elements can also be detected in cases of iron deficiency anemia.
- Codocytes, otherwise called target cells, are characterized by an unusual appearance that resembles targets. For this reason they received their characteristic name. Such formed elements appear in iron deficiency anemia and alcohol intoxication.
There are a number of other forms that red blood cells take on in cases of poikilocytosis. For example, dacryocytes look like droplets. Their appearance in a blood smear usually indicates liver pathology or a significant decrease in hemoglobin content.
Other options
Acanthocytes have a jagged shape. Their appearance is caused by hemolytic anemia, liver damage, removal of the spleen, which entails a decrease in immunity, and hereditary forms of acanthosis. The variety of cells includes:
- Schizocytes. They are larger in size and resemble a helmet. But these inclusions are not full-fledged cells, but only their fragments formed as a result of the breakdown of red blood cells. Their detection indicates an advanced form of anemia, vasculitis. Sometimes the cause is a malignant course of hypertension.
- Sickle-shaped (drepanocytes). They are almost impossible to see, even if they are not present in large quantities in the smear. To see them, it is necessary to create an imitation of an artificial lack of oxygen. In such unfavorable conditions they perform well.
- Hydrocytes. The central part has the appearance of a curved line resembling a mouth. Such red blood cells are noted in the analysis after blood transfusion for cirrhosis of the liver.
- Stomatocytes are mature red blood cells whose cell membranes are damaged.
- Echinocytes. They look like balls covered with growths. Such cells are present in cases of damage to the liver parenchyma, hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
So wide is the variety of cells that indicate the presence of poikilocytosis. Each variety indicates a particular disease. At the same time, there are pathologies in which several types of cells are noted.
Poikilocytosis of erythrocytes: what it is, causes and degrees, symptoms, treatment and consequences
Violations of the basic functions of hematopoiesis occur in the practice of hematologists in a variety of forms and types. In most cases, these are quite dangerous disorders that, without treatment, lead to serious complications. Although in a situation where the body is able to compensate for the disorder, the patient does not even suspect the presence of any problem.
Poikilocytosis is a disorder of the normal synthesis of red blood cells by the body: formed cells become abnormal, taking on a strange, atypical shape.
They usually have the structure of a regular sphere. In the case of the development of a pathological process, we are talking about pear-shaped, sickle-shaped, ruptured fragmentary forms (schizocytes) and other options. It is clear that such abnormal cells completely or partially lose their own functions.
Symptoms appear when the damage is sufficiently severe or when the disorder turns into decompensation, when the patient’s body is not able to independently correct the deviation.
Treatment is required in all cases, since without therapy it is impossible to talk about the prospects for recovery. Gradually the condition will worsen.
Mechanism of development of the disorder
The formation of the disorder is based on a group of pathogenetic factors. There are three of them in total. They are basic, although there are additional ones that are less common.
- Congenital or acquired bone marrow diseases. Deviations appear immediately from the moment of diagnosis. There can be a great variety of process options. Up to malignant diseases.
Diagnosis almost always requires puncture and biopsy, morphological assessment of the condition of bone marrow cells. If detected in a timely manner, there is every chance of high-quality restoration.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins B9, B12 or iron. They provoke various forms of anemia. Megaloblastic and iron deficiency, respectively. A similar pathological process as the cause of the disorder occurs most often.
In this case, poor nutrition is not necessarily to blame; we can talk about problems with the absorption of beneficial compounds in the gastrointestinal tract. In any case, recovery requires specific treatment of the underlying diagnosis.
- Pathologies of the liver and digestive tract. Less often. Lead to generalized biochemical disorders and disorders. The deviation also affects hematopoiesis. It is necessary to start treatment as early as possible.
A change in the shape of red blood cells does not occur immediately; the development of the pathological process may take more than one month. It all depends on the cause of the disorder and the aggressiveness of its course.
Description in UAC
Poikilocytosis is accompanied by a pronounced disturbance in the shape of blood cells; this condition is clarified in a general analysis using microscopy. First of all, the structure and type of red blood cell are determined.
Depending on this point, doctors describe the following possible options for poikilocytes:
- Ovalocytosis. Occurs in hereditary diseases. A change in shape like an ellipse is observed.
- Microspherocytosis. Spherical variety. Despite the relative normality, the sizes are significantly less than adequate.
- Anulocytosis. Lack of a dense middle of the cell. The structures have the shape of a ring.
There are also sickle-shaped, teardrop-shaped, target-shaped red blood cells and others. There are many options, the most common ones are named.
When assessing and interpreting the condition of red blood cells, the number of changed cells is also described.
Depending on this criterion, there are 4 degrees of the pathological process:
- Initial phase or mild poikilocytosis. Accompanied by a concentration of abnormal cells of 25-50% of the total. Not characterized by any symptoms. The violation is noticeable only by the results of laboratory analysis.
- Moderate or moderate disorder. From 50 to 70%. There is a mild clinic, there are no deviations yet.
- Pronounced variety. Characterized by a large number of altered cells. More than 70%.
- Critical phase. About 100% of abnormal red blood cells. It is relatively rare. For hereditary pathologies, congenital problems, malignant tumors of the hematopoietic system, etc.
Poikilocytosis in a general blood test can be expressed as a percentage (described above), numerically in points (1, 2, 3, 4), verbally expressed, or indicated using pluses (+). For clarity, the data is shown in the table:
Degree of poikilocytosisPoints (+)
| Lightweight | 1 | + |
| Moderate | 2 | ++ |
| Expressed | 3 | +++ |
| Critical | 4 | ++++ |
Despite the general disorder and tendency to worsen, symptoms vary among patients. Even the 4th degree of the disorder does not always cause deadly complications. It all depends on the characteristics of the body and its adaptive capabilities.
Causes
The factors in the formation of the pathological process are diverse.
Among them:
- Liver lesions. First of all, we are talking about diseases such as hepatitis. Inflammatory phenomena of an infectious, less often other nature. Accompanied by problems with the biochemical component. Which leads to a chain reaction. Impaired liver function, cirrhosis (tissue death) causes critical disorders in hematopoiesis. In addition to poikilocytosis, hypocoagulation is observed - insufficient coagulation.
- Toxic processes. Poisoning of the body with certain compounds. Including when using a number of medications. Antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal, steroid medications. The same is possible after the active use of chemotherapy drugs.
- Deficiency of vitamins B9, B12. Megaloblastic anemia. Unlike other varieties, it is characterized by high danger. Hematopoiesis switches to the immature type, accompanied by a change in formed red blood cells. Recovery is urgently needed. Because without treatment, ischemic processes occur very quickly.
- Lack of sufficient iron or incomplete absorption. Leads to iron deficiency anemia.
- Hereditary pathologies. Genetic abnormalities. They are accompanied by critical symptoms almost immediately after the patient’s birth. Malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system are particularly common in this group of causes. Difficult to treat.
- Large area of burns. With extensive damage to the integrity of the skin, a temporary but significant increase in the concentration of abnormal blood cells is observed. This is a natural, but no less dangerous condition. Correction required.
- Platelet dysfunction. Not enough of them. It’s not easy to say where the cause is and where the effect is. As a rule, all disorders have a common etiology. For example, proliferative diseases of the bone marrow, oncology and other options.
- Cardiovascular system disorders. Including a recent myocardial infarction. The deviation can persist for up to several months; dynamic observation under the supervision of a cardiology specialist is necessary.
- Recent surgical treatment. Surgical interventions. Especially cavitary, extensive, traumatic.
The causes of poikilocytosis are due to diseases of the digestive tract, heart, and bone marrow. The influence of random episodic phenomena is also possible. Like a toxic component, ionizing radiation.
It is necessary to identify the etiological factor in order to react in time. Without determining the origin, therapy is impossible.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the stage of the pathological process and the individual adaptive capabilities of the body.
Typically, the manifestations are:
- Dizziness. It becomes the result of involvement of the extrapyramidal system, in particular the cerebellum, in the deviation. The episodes are regular and intense. The patient is forced to take a supine position to relieve the symptom.
- Neurological diseases. Focal disorders. The result of insufficient blood circulation in cerebral structures. Determined by a group of changes, depending on the location. Problems with hearing, vision, sensitivity, paresis, speech and articulation disorders and many other options.
- Heart rhythm disturbances. Like tachycardia, when heart rate increases. Fibrillations and the appearance of extrasystoles—extraordinary beats—are also possible.
All of these options initially pose a danger to health and even life. Restoring the normal functioning of the organ in the presence of symptoms is a priority task.
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system in general. Such problems are caused by insufficient nutrition of the myocardium and a decrease in the quality of blood circulation.
- Emotional and mental disorders. Irritability, aggressiveness. The most negative personality traits are emphasized.
- Weakness, asthenic syndrome. Inability to perform daily duties and work.
- Dry skin.
- Hair fragility.
- Fall in blood pressure. Usually minor.
- Fluctuations in body temperature. Up to 37-38 degrees Celsius. Rarely higher.
- Dyspnea. Especially under mechanical loads. Physical activity becomes at first extremely difficult, and then completely impossible.
Poikilocytosis manifests itself in the cardiovascular, central nervous systems, and other structures of the body. This is a generalized disorder.
There are two reasons for such a large list of symptoms. On the one hand, red blood cells are not capable of carrying oxygen due to their irregular shape. On the other hand, CO2 is transported from tissues as a waste product.
Additional examinations
Hematology specialists assess the condition of patients. Depending on the specific situation, other highly specialized doctors may be involved. Gastroenterologists and others.
The following special measures are prescribed as auxiliary diagnostic methods:
- Oral interview with the patient. To identify all possible health complaints. Assess symptoms and complex of manifestations.
- Anamnesis collection. Investigation of the probable origin of the process. Plays one of the key roles in diagnostics.
- Measuring body temperature. Also blood pressure levels.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. First of all, specialists are interested in the condition of the liver. To a lesser extent other structures.
- ECG, ECHO. Study of heart tissue.
As a last resort, it is necessary to perform a bone marrow puncture and histological evaluation of the biopsy (sample).
The list of diagnostic measures can be expanded.
Treatment methods
There is no specialized therapy. Poikilocytosis in a blood test is not an independent diagnosis, but a finding, a laboratory indicator. Therefore, it makes sense to eliminate the underlying disorder that caused the deviation.
Depending on the specific diagnosis, the following measures are prescribed:
- Surgery for tumors.
- The use of hormonal and steroid medications as part of the correction of thrombocytopathy and penia. Resection or complete removal of the spleen may also be prescribed. In approximately half of the cases with a disorder of this type, this has an effect.
- Changing your diet. Fortification. Increasing the amount of iron. To eliminate anemic disorders.
- If a malignant process is detected, radiation and chemotherapy are indicated. The appropriateness of such will be determined by the situation.
Physiotherapy may be performed according to indications. This question remains at the discretion of the hematologist, and then the specialized specialist.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=51n7O7Jpce8
Over the next years, the patient must give up alcohol and tobacco products. Intense mechanical loads and exposure to high temperatures on the body are also contraindicated.
Forecast
The prospects for recovery from poikilocytosis are unclear. Again they must be assessed in the context of the underlying disease.
As a rule, pathological processes such as vitamin or iron deficiency are eliminated easily and without a trace. That is why the forecasts are optimistic.
The situation is much more complicated in situations of the development of oncology, hepatitis, especially cirrhosis of the liver, since a high-quality complete cure is almost impossible. Although this is not a 100% calculation.
Survival is determined by diagnosis. Only the attending physician who is caring for the patient can clarify the issue of recovery prospects.
Reasons for appearance
Poikilocytosis is generally considered to be a laboratory manifestation of anemia. Sometimes it indicates other pathologies. This is not always a disease directly related to the circulatory system. The same person can experience both poikilocytosis and anisocytosis, a condition in which the red blood cells in the blood differ in size.
Lack of iron, as one of the most important microelements, is often explained by an inadequate diet. This is also facilitated by an increase in the need for microelements, for example, during pregnancy and breastfeeding. But there are dangerous iron deficiency conditions that require urgent action. They are characterized by the appearance of poikilocytosis.
Poikilocytosis sometimes indicates cancer, hemolytic anemia and other genetic pathologies. There are transient manifestations of this condition that occur in infectious diseases. An even more dangerous disease is hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Here anemia is combined with thrombocytopenia. At the same time, renal failure occurs. The causes of poikilocytosis in a general blood test in a child are the same as in adults.
“Faithful companion” - hypochromia
Unfavorable factors can cause red blood cells to change color and increase in size. They may retain their red color around the edges but become lighter in color on the inside. This phenomenon is called hypochromia. It is caused by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. There is a transition of red blood cells into codocytes, which resemble the target in appearance.
Hypochromia provokes hypochromic anemia. It is characterized by all the signs inherent in other varieties, accompanied by a change in the color of blood cells. These are iron deficiency, mixed forms, as well as anemia resulting from the redistribution of iron. All of them are accompanied by a similar set of symptoms:
- tachycardia;
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- irritability;
- lack of interest in what is happening.
If a person has several symptoms, he needs to take a general blood test.
What you need to know about poikilocytosis
So, you donated blood, and poikilocytosis was detected in it. Naturally, the question immediately arises for the simple ignorant layman: what is this poikilocytosis anyway?
Let's start from the very beginning. Nature always thinks everything through to the smallest detail. This rule does not bypass the structure of erythrocytes - blood cells, which are the most abundant in our blood fluid. They do an excellent job of transporting oxygen to tissues and organs. In this they are helped by their shape in the form of a disk, concave on both sides, and the hemoglobin content in it.
Only healthy cells can do their job perfectly. Now imagine that under the influence of negative factors, a progressive disease or an incipient illness, the red blood cell begins to deform, changing its size and shape. Can a “broken” cell perform its functions as before? Of course not. Then she tries to send signals of help through the blood.
It is not difficult to detect any pathology. It is enough to take a general blood test and wait for the results. If signs of erythrocyte pathology are detected in the blood, this can be either a symptom of anisocytosis or poikilocytosis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Anisocytosis in a general blood test: what is it?
- Anisocytosis of erythrocytes is increased: causes, norm
Do not confuse or combine two different medical phenomena. Anisocytosis is an indicator of the initial stage of anemia, in which the size of the red blood cell changes. Poikilocytosis is a more serious phenomenon, indicating anemia in the stage of rapid progression due to a change in the shape of the blood element.
The severity of the pathology is indicated by the level of modification of the appearance of the red blood cell. There are 4 of them in total:
| Designation in pluses | Severity of poikilocytosis |
| + | Changed red blood cells in the amount of 25%. Minor poikilocytosis |
| ++ | 50% of changed cells indicate a moderate degree of pathology |
| +++ | 75% of red blood cells are deformed. Pronounced degree of deviation |
| ++++ | All red cells are deformed and enlarged beyond the permissible norm. In this case, we are talking about the acute phase of poikilocytosis. |