Globulins and total blood protein
Proteins in the body play the role of a very important building material of all tissues and cells. Most of the organs, enzymes and hormones that regulate many processes in the body are formed from them.
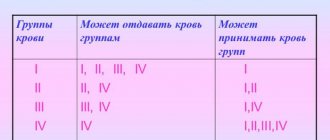
The proteins present in blood plasma are called total protein, which is divided into 3 main classes: albumin, globulin and fibrinogen. Based on the proteinogram, which allows for electrophoretic separation of proteins, globulins are divided into several types: alpha-1-globulin, alpha-2-globulin, beta-globulin and gamma-globulin.
Globulins are part of the total protein in the blood along with the remaining protein fraction, that is, albumin and fibrinogen. The ratio of globulins to albumin is measured by calculating the values obtained by directly testing the total protein and the albumin fraction; in most cases, albumin makes up about 56-65% of the total protein.
Human gammaglobulin: instructions for use, functions, indications, reviews
Modern medicine is based on the introduction of new forms of treatment and prevention of diseases and the improvement of old ones.
What human gamma globulin is, instructions for use, indications and contraindications, functions and reviews is known to the doctor who prescribes this drug.
This is the most important point in the prevention of many diseases, a proven and effective method of combating various pathologies and their consequences.
What is gamma globulin
Gamma globulin is a class of blood plasma proteins that has high mobility when separated by electrophoresis. It is produced by completely purifying the plasma, leaving only the necessary elements that will be included in the product.
It is also the name of a medicinal product containing antiviral antibodies, which are used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes for a number of diseases.
Most often, prevention is represented by immunization with antibodies of a special protein fraction, which has three main types of gamma globulins, the structure of which may vary depending on the specific disease.
There are four types of human immunoglobulin:
- A class - contained in the blood and secretions, take part in the immune system, creating a barrier to the penetration of infections and toxins;
- E class - take part in the neutralization of toxins, bacteriolysis and other processes; during infectious diseases their content in the blood increases sharply;
- D class - localized in the plasma cell membrane, presumably involved in autoimmune processes;
- G class - the most important immunoglobulins, provide protection to the body from most infections, bind toxins, fight viruses and bacteria, and through the placenta transfer passive immunity to the newborn when he is separated from the umbilical cord and begins to live separately.
Gamma globulin is used as a means for immunoprophylaxis; it creates passive immunity for a certain period, when the rate of onset of viruses and bacteria is maximum.
Release form, composition and indications
The drug human gamma globulin is available in the form of a solution for intramuscular administration in 1.5 ml ampoules. Cardboard or plastic packages contain 5 or 10 ampoules of the drug. Depending on the dosage of the active substance, the doctor prescribes a different number of capsules for the course; the patient’s age also matters. Registration No. Р N001544/01 dated 07/08/08 for an indefinite period.
An immunoglobulin preparation is a concentrated solution of an immunologically active protein fraction, which is isolated at temperatures below 0°C from donor blood plasma by fractionation with ethyl alcohol. To submit the material, it is checked for the absence of HIV, hepatitis B, antibodies to the hepatitis C virus and other diseases that are carried in blood plasma.
Human gamma globulin is recommended for the following indications:
- prevention of hepatitis A, whooping cough, measles, meningococcal infection, influenza and polio;
- increasing the body's resistance during infectious diseases;
- treatment of hypobulinemia.
Pharmacokinetics of antibodies is achieved 1-2 days after administration, elimination lasts 3-4 weeks. Pharmacodynamics - excreted through the kidneys after an increase in antibody levels.
Dosage and instructions for use
The drug is administered intramuscularly into the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle or into the thigh, the outer surface.
When administered, the operating rules are always followed: if the ampoule was stored in the refrigerator, it must be kept at room temperature for 2 hours.
When opening, it is necessary to strictly follow all antiseptic rules, and in order to avoid the formation of foam, it must be collected with a needle with a wide bore.
A previously opened and unused ampoule must be disposed of, and a drug with a changed color, sediment or expired expiration date must also be disposed of. The dosage of gamma globulin depends on the doctor's prescription.
Prevention of hepatitis A:
- children 1-6 years old – 0.75 ml;
- up to 10 years – 1.5 ml;
- from 10 years and adults – 3 ml.
Prevention and treatment of influenza:
- children under 2 years old – 1.5 ml;
- from 2 to 7 years – 3 ml;
- from 7 years and adults – 4.5-6 ml.
Prevention of measles:
- once from 3 months, not sick and not vaccinated;
- no later than 6 days after contact with the patient;
- dosage 1.5 - 3 ml.
Prevention of whooping cough:
- once with an interval of 24 hours, 3 ml for children who have not been sick and have not been vaccinated;
- no later than 3 days after contact with the patient;
- dosage 1.5 - 3 ml.
Prevention of polio:
- once 3-6 ml for unvaccinated children and after contact with a sick person.
On a note!
It is strictly forbidden to administer the drug intravenously. It is administered only as directed by a doctor and is not used together with calcium gluconate.
The administration of the drug is recorded in special accounting forms, which indicate the batch number, date, expiration date and the name of the manufacturer, dose and nature of the reaction.
Contraindications for use
Before prescribing, the doctor will definitely check the patient for the presence of various diseases that may appear when plasma protein is administered:
- allergic reactions;
- systemic immunopathological blood diseases;
- nephritis.
After administration, in order to avoid a reaction to the immunoglobulin drug, you need to take any antihistamine and continue taking it for 2-3 days. This will help eliminate allergies.
If the patient has various immunopathological diseases already diagnosed by the doctor, in this case the drug is administered against the background of appropriate therapy.
Its interaction with other drugs has not yet been studied and there is no data or incompatibility.
special instructions
Preparations based on human gammaglobulin are used only as prescribed by a doctor. After administration of the medicine, vaccinations against measles and mumps are carried out no earlier than 3 months later.
Also, after vaccination, it is administered no earlier than 2 weeks, and if it is necessary to use the drug earlier than this period, vaccination is repeated.
All other vaccinations can be done at any time, regardless of the date of administration of the serum.
Side effects
Over the more than 25-year history of using the drug, doctors have made thousands of injections, and this amount is enough to obtain an objective assessment of its effect on the human body.
During this time, allergic reactions and the development of anaphylactic shock were not recorded.
Therefore, the indications about the danger of allergies in the instructions for the drug are purely informative and do not correspond to reality.
The reason for the absence of allergies after the use of gamma globulins is the same structure of constant fragments of immunoglobulins in different people and the presence of an antidiotypic network - a system of antibodies against antibodies. Therefore, drugs are successfully used to treat allergies.
Important!
Class G antibodies in the drug block substances that cause atopic reactions, therefore they help in the treatment of allergies and dermatitis.
The myth that as a result of the administration of gamma globulin preparations a person can become infected with microorganisms has not been confirmed. It arose due to ignorance of the composition of the drug, which does not contain foreign components. When isolating immunoglobulins from serum, processes are used that reduce the entry of viral particles by 100%.
Gamma globulins - division and significance
Gamma globulins (γ-globulins) form mainly immunoglobulins, which are antibodies that play an important role in the body's defense response against viruses, bacteria, parasites and, to a lesser extent, also fungi.
Immunoglobulins are divided into 5 classes: IgG (conditional immunity), IgA (present in secretions), IgD (B-cell surface receptors), IgM (first activated during disease), IgE (their number increases during an allergic reaction and during parasitic infection).
Gamma globulins include C-reactive protein, which is an acute phase protein, meaning it is activated in response to inflammation. Gamma globulins should make up 11-22% of the total protein.
IMMUNOGLOBULIN: instructions, reviews, analogues, price in pharmacies
Immunoglobulin is a concentrated solution of an immunologically active protein fraction isolated by fractionation with ethyl alcohol at temperatures below 0°C from the blood plasma of healthy donors.
To produce a series of immunoglobulins, plasma obtained from at least 1000 healthy donors is used, individually tested for the absence of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg), antibodies to the hepatitis C virus and the human immunodeficiency viruses HIV-1 and HIV-2.
The protein concentration in immunoglobulin ranges from 9.5 to 10.5%. The stabilizer is glycine at a concentration of (2.25±0.75)%. The drug does not contain preservatives or antibiotics. The active principle is immunoglobulins, which have the activity of antibodies of various specificities.
The drug also has nonspecific activity, increasing the body's resistance.
Pharmacokinetics
Cmax of antibodies in the blood is achieved after 24-48 hours, T1/2 of antibodies from the body is 3-4 weeks.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of the drug Immunoglobulin are: - prevention of hepatitis A, measles, whooping cough, meningococcal infection, polio, influenza; - treatment of hypo- and agammaglobulinemia; - to increase the body's resistance during the period of convalescence of infectious diseases.
Mode of application
Immunoglobulin is injected intramuscularly into the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle or the outer surface of the thigh. The drug should not be administered intravenously. Before injection, ampoules with the drug are kept for 2 hours at room temperature.
The opening of the ampoules and the administration procedure are carried out in strict compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. To avoid the formation of foam, the drug is drawn into a syringe with a wide-bore needle. The drug cannot be stored in an opened ampoule.
The drug is unsuitable for use in ampoules with damaged integrity or labeling, if there is a change in physical properties (change in color, clouding of the solution, the presence of flakes that do not break), if the expiration date has expired and storage conditions are not observed.
The dose of immunoglobulin and the frequency of its administration depend on the indications for use.
Prevention of hepatitis A.
The drug is administered once in doses: children from 1 to 6 years old - 0.75 ml, up to 10 years old - 1.5 ml, over 10 years old and adults - 3 ml. Repeated administration of immunoglobulin if necessary to prevent hepatitis A is indicated no earlier than after 2 months. Prevention of measles The drug is administered once from the age of 3 months to persons who have not had measles and are not vaccinated against the infection, no later than 6 days after contact with the patient. The dose of the drug for children (1.5 or 3 ml) is determined depending on the state of health and the time that has passed since contact. For adults, as well as children in contact with mixed infections, the drug is administered in a dose of 3 ml.
Prevention and treatment of influenza
The drug is administered once in doses: children under 2 years old - 1.5 ml, from 2 to 7 years old - 3 ml, over 7 years old and adults - 4.5-6 ml. When treating severe forms of influenza, repeated (after 24-48 hours) administration of immunoglobulin in the same dose is indicated.
Prevention of whooping cough
The drug is administered twice with an interval of 24 hours in a single dose of 3 ml to children who have not had whooping cough and have not been vaccinated (not fully vaccinated) against whooping cough, as early as possible after contact with the patient, but not later than 3 days.
Prevention of meningococcal infection.
The drug is administered once to children aged 6 months to 7 years no later than 7 days after contact with a patient with a generalized form of meningococcal infection in doses of 1.5 ml (children under 3 years old) and 3 ml (children over 3 years old).
Prevention of polio
The drug is administered once in doses of 3-6 ml to unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated children with polio vaccine as early as possible after contact with a patient with polio.
Treatment of hypo- and agammaglobulinemia
The drug is administered in a dose of 1 ml per 1 kg of body weight, the calculated dose can be administered in 2-3 doses with an interval of 24 hours. Subsequent administrations of immunoglobulin are carried out according to indications no earlier than after 1 month.
Increasing the body's resistance during the period of convalescence of acute infectious diseases with a protracted course and in chronic pneumonia. The drug is administered in a single dose of 0.15-0.2 ml per 1 kg of body weight.
The frequency of administration (up to 4 injections) is determined by the doctor; the intervals between injections are 2-3 days.
Contraindications
Immunoglobulin is contraindicated in case of a history of severe allergic reactions to the administration of human blood products.
For persons suffering from allergic diseases or with a history of severe allergic reactions, antihistamines are recommended on the day of immunoglobulin administration and for the next 3 days.
Persons suffering from systemic immunopathological diseases (blood diseases, connective tissue diseases, nephritis, etc.) should be administered immunoglobulin against the background of appropriate therapy.
Pregnancy
Immunoglobulin with caution during pregnancy and lactation.
Interaction with other drugs
Immunoglobulin therapy can be combined with other drugs, in particular antibiotics. The administration of immunoglobulins can weaken (for 1.5-3 months).
) the effect of live vaccines against viral diseases such as measles, rubella, mumps and chickenpox (vaccinations with these vaccines should be carried out no earlier than 3 months later).
After the administration of large doses of immunoglobulin, its effect can last in some cases up to one year. Do not use simultaneously with calcium gluconate in infants.
Overdose
Cases of overdose of the drug Immunoglobulin have not been described.
Storage conditions
Storage and transportation in accordance with SP 3.3.2.1248-03 at a temperature of 2 to 8°C out of the reach of children. Freezing is not allowed. Shelf life - 2 years. A drug that has expired cannot be used.
Release form
Immunoglobulin – solution for intramuscular administration 1.5 ml/1 dose: amp. 5, 10 or 20 pcs.
Compound
Immunoglobulin contains the active substance: human normal immunoglobulin.
Additionally
It is possible to use Immunoglobulin in children according to indications. In infants, do not use it together with calcium gluconate. Immunoglobulin is used only as prescribed by a doctor. The administration of immunoglobulin is registered in the established accounting forms, indicating the batch number, release date, expiration date, manufacturer, date of administration, dose, nature of the reaction to the administration of the drug. After the administration of immunoglobulin, vaccinations against measles and mumps are carried out no earlier than 3 months later . After vaccination against these infections, immunoglobulin should be administered no earlier than 2 weeks later; If it is necessary to use immunoglobulin earlier than this period, vaccination against measles or mumps should be repeated. Vaccinations against other infections can be carried out at any time before or after the administration of immunoglobulin.
Source: https://www.medcentre.com.ua/medicamenty/immunoglobulin.html
What are beta globulins
Beta globulins are proteins that are part of the blood plasma protein and act as a transporter. Among them are transferrin, hemopexin, beta-lipoprotein, beta2-microglobulin, blood coagulation factors, enzymes (cholinesterase, phosphatase, protease), bradykinin, angiotensin and isoagglutinins.
Beta-glubulin has many functions, including transporting iron, as well as transporting fatty acids and steroid hormones. In healthy people, beta globulins should make up 8-15% of total protein.
The role of alpha1-globulins and alpha2-globulins
Alpha1-globulins and alpha2-globulins are the smallest groups of proteins, accounting for 2-5% and 7-13% of the total protein, respectively.
Alpha1-globulins form alpha1-antitrypsin, alpha1-acid glycoprotein, alpha-lipoprotein and thyroxine-binding globulin. Among the many functions of alpha1-globulin, one can highlight participation in the body’s defense processes, especially in inflammatory diseases.
Alpha2-globulins form alpha2-macroglobulin, ceruloplasmin and haptoglobin. Alpha2-globulins play the role of markers of pancreatitis, transport copper, support the transport of iron, protect the kidneys from the harmful effects of hemoglobin, and are also activated during inflammatory diseases and tissue damage.
Elevated levels of globulin in the blood
The concentration of some types of globulins increases due to microbial infection, as well as inflammation in the body, due to which it is able to fight the disease. Elevated levels of some types of globulins can be a sign of many serious diseases.
An increase in beta globulin levels above 13% may indicate multiple myeloma, cancer, nephrotic syndrome, liver disease, Waldenström's disease, amyloidosis, and may also be a natural condition in women in the third trimester of pregnancy. An increased level of globulin along with a simultaneous increase in total protein in the blood often indicates dehydration.
The concentration of alpha-1-antitrypsin , produced in the lungs and liver, increases during inflammatory processes in the body, as does the level of alpha-2-globulin.
According to doctors, the concentration of individual gamma globulins increases during autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus. Elevated levels of gamma globulin may indicate chronic bacterial inflammation, collagenosis, sarcoidosis, bronchiectasis, as well as chronic parasitic infection.
What provokes an increase in indicators
As a rule, when a pathological process occurs, an increase in one or two antibodies occurs, and the ratio of the rest remains unchanged.
Based on the nature of changes in the gamma globulin composition of antibodies, the development of certain diseases can be assumed:
- Rheumatoid lesions and systemic diseases, chronic processes in the liver or oncological processes, tuberculosis - all these ailments will provoke an increase in the number of IgA antibodies.
- Chronic hepatitis, HIV, kidney disease or cancer in the lymphatic system, as well as multiple sclerosis will cause an increase in IgG levels. And also a large amount of this group of antibodies can be caused by drug addiction or eating a large amount of foods high in chemical preservatives. This is also possible when working in hazardous industries.
- Infection with various invasions, mononucleosis, various fungi and the presence of cancer cells in the tissues of the body - all this will provoke an increase in IgM antibodies.
- Atopic dermatitis, non-infectious asthma and many other types of allergic processes will increase the IgE level. They may also increase during long-term parasitic processes.
- The mechanism of work of IgD antibodies has not yet been sufficiently studied, but an increase in their number, even with normal levels of other gamma globulin antibodies, serves as an indirect indicator of the beginning of pathology in the abdominal region or in the chest organs.
Of course, it is impossible to determine the cause of the disease using only one analysis. But increasing levels of certain types of antibodies will help the doctor most fully determine the examination plan and determine the cause of the disease.