General information about cholesterol and lipoproteins
Cholesterol (in chemistry - cholesterol) is distinguished by origin:
- Endogenous, that is, internal, is synthesized by hepatocytes (liver cells). It is the basis and makes up 80% of the total.
- Exogenous - these are animal lipids (fats) that enter the digestive system as part of consumed dishes and products.
Lipophilic alcohol is vital for the normal functioning of the entire body. It is the basis of elastic tissue that separates and protects the cell from the external environment. On the basis of cholesterol, sex and steroid hormones are produced, as well as bile acids and neurotransmitters, through which nerve impulses are transmitted. Without cholesterol, it is impossible to absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, etc.
Cholesterol homeostasis (internal constancy) is the result of a balance of three processes:
- intake and production of cholesterol;
- its correct use by the body;
- timely removal of excess.
Fatty alcohol molecules cannot easily move inside the body until they meet proteins (conducting proteins). Through the walls of the small intestine, cholesterol is absorbed into the blood, where it combines with proteins. During lipid-protein interaction, lipoproteins are formed that can freely “travel” through the bloodstream.
Lipoproteins are classified by density:
- low-density (LDL);
- high-density (HDL);
- very low density (VLDL).
Density is determined by the ratio of proteins and fats. The smaller the protein part and the more fat, the lower the density.
What is cholesterol
Cholesterol, also known as cholesterol, is a fat produced in the liver and is responsible for many functions in the human body. Each cell of our tissues is enveloped in a layer of cholesterol, which plays the role of a metabolic regulator and hormone producer.
Therefore, this substance is extremely important for the normal functioning of our body, and its low and high levels indicate the presence of any diseases.
What functions does cholesterol perform?
- forms and protects cell walls;
- participates in the production of female and male sex hormones;
- helps produce bile;
- produces vitamin D;
- Helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins;
- serves as a protective sheath for nerve fibers.
If you think that the body should not contain cholesterol at all, then you are deeply mistaken. Without it, it is impossible to maintain health and beauty. The indicator is considered high if its content in mmol per 1 liter is more than 6.2.
Lipidogram and blood biochemistry
A detailed biochemical analysis and lipid profile includes a decoding of indicators responsible for the protein-fat balance of the body:
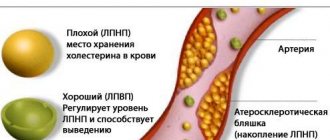
- low and very low density lipoproteins (the so-called bad cholesterol) are the main suppliers of endogenous fat from the liver to the body cells to ensure the functions of cholesterol;
- high-density lipoproteins (“good” cholesterol) ensure that excess LDL and VLDL are returned to the liver for processing and excretion;
- triglycerides – fats that represent a lipid resource (the body stores them “in reserve” to maintain energy tone);
- total cholesterol (TC) – a set of lipoprotein fractions;
- the index or atherogenic coefficient (AC) reflects the risk of developing vascular atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (calculated using a special formula).
Indicators, the determination of which is carried out according to the special prescription of a doctor, are apoproteins and chylomicrons. They are not included in an extended biochemical study, but have diagnostic value in case of questionable test results:
- apoproteins – proteins directly involved in the formation of lipoproteins;
- chylomicrons (CM) are lipoproteins with the function of delivering exogenous fat from the intestine to the liver through the bloodstream (synthesized by the intestine from exogenous cholesterol).
Percentage
| HM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
| apoproteins | 2 | 10 | 25 | 50 |
| triglycerides | 90 | 60 | 10 | 5 |
| cholesterol | 5 | 15 | 55 | 20 |
| other lipids | 3 | 15 | 10 | 25 |
Norms of indicators for women and men
Before you try to decipher the indicators, it is worth taking into account that there are several types of tests that laboratories offer.
General analysis
This test checks the amount of HDL and LDL. If the total cholesterol level is exceeded, the specialist judges the degree of risk of atherosclerosis. For people of different ages and gender, the norms are different. For example, cholesterol levels increase with age. Also, the content of lipoproteins also depends on estrogen, which is much higher in men. Indicators are measured in mmol/l. The norm for total cholesterol is indicated in the range of 1 – 1.5 mmol/l.
Blood chemistry
Biochemistry determines not only the levels of LDL and HDL, but also:
- Atherogenic index,
- Triglycerides.
For women, the HDL level is considered normal in the range of 1 - 1.9 mmol/l, slightly increased 2 - 3.6 mmol/l, and increased with high-density lipoprotein levels up to 4.2 mmol/l.
HDL level more than 4.2 mmol/l, or less than 1 mmol/l is considered dangerous. There is a risk of cardiovascular pathologies.
For men, respectively, the normal level of HDL is from 1.7 to 2.6 mmol/l, moderate – 2.7 to 4.1 mmol/l, and elevated – from 4.2 to 5.1 mmol/l. Results above and below acceptable values are considered isolated values and a prerequisite for examining other organs - liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system.
Triglycerides are not cholesterol, but the content of fats that are present in the body. Experts have defined “normal levels” as 200 to 400 mg/dL.
An important criterion for assessing the condition of the body is the atherogenic index. The coefficient is deciphered as an indicator of the relevance of HDL to LDL and is calculated using the formula:
Atherogenic index = (Total cholesterol - LDL)/HDL.
The index reports the risk of developing atherosclerosis. Moreover, the norm for this coefficient is relevant for people of all ages and is 3. That is, the content of “bad” cholesterol to “good” cholesterol should normally be 1:3.
Detailed analysis
The scientific name of the study is lipid profile. The difference from biochemistry is that in addition to measuring the levels of HDL, LDL, triglycerides and the atherogenicity index, the lipidogram also considers fraction indicators.

In the lipid profile, HDL is designated α-cholesterol, and LDL is designated β-cholesterol. When conducting such an analysis, the norm indicators are qualitatively different. Thus, the norm for HDL does not exceed 0.9 mmol/l, and for LDL – 2.5 mmol/l. The atherogenicity index should also be within 3. The cost of a lipid profile is on average 900 rubles.
Espress - diagnostics
Express tests are firmly established in the lives of people who are prescribed to monitor certain blood parameters constantly. For example, hand-held glucose meters are used by people with diabetes. For those who monitor their blood cholesterol levels throughout their lives, home analyzers and test strips have also been developed.
When using the express method, the recommendations prescribed for blood collection in laboratories are preserved. Taking the home test is easy:
You need to prick and place your finger on the test strip, or in a special window if we are talking about an analyzer. If your cholesterol level is alarming, the test strip will turn a certain color. Unfortunately, the exact amount of the indicator will not be written. But information about the deviation is enough for analysis in the laboratory.
Indications for donating blood for cholesterol
A conventional biochemical blood test determines the concentration of TC. The study is carried out as part of a routine medical examination and perinatal screening, when visiting a doctor with symptomatic complaints, as a control of the therapy.
An assessment of all cholesterol indicators (lipid profile) is prescribed:
- with increased TC in the results of preliminary biochemistry;
- after heart attacks and strokes;
- for diabetes mellitus, chronic cardiac pathologies, diseases of the hepatobiliary system (liver, gall bladder), hypertension;
- obese patients.
The analysis must be carried out before planned surgery and after surgery. It is recommended to regularly donate blood for TC and lipoprotein levels:
- women in menopause;
- men aged 40+;
- patients with nicotine addiction;
- people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Blood for cholesterol should be regularly checked in the presence of unfavorable heredity (hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, vascular pathologies in close relatives).
High cholesterol - what to do?
If the results of blood tests for cholesterol showed a total amount of more than 5.0 mmol/l, and there is more “bad” cholesterol than “good” cholesterol, it is customary to talk about hypercholesterolemia. It is important to get tested regularly, because at the initial stage the disease does not manifest itself in any way.
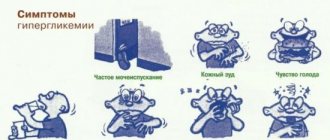
Over time, symptoms appear that indicate progression of the disease:
- dyspnea;
- chest pain;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- temporary loss of vision;
- memory losses;
- lameness;
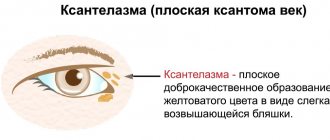
- yellow spots on the skin.
If your blood test shows elevated cholesterol, it is important to rethink your lifestyle and change your diet.
Prohibited products:
- fatty meat products;
- chicken egg yolk;
- high fat milk;
- margarine;
- mayonnaise;
- offal;
- salo;
- fast food;
- confectionery;
- crackers, chips.
You need to focus on the content of saturated fats in foods, and not on cholesterol, since the human liver synthesizes “bad” cholesterol from them.
To reduce cholesterol, it is recommended to regularly consume:
- greenery;
- legumes;
- garlic;
- red fruits and vegetables;
- olive oil;
- seafood.
Laboratory notations
The accepted unit of measurement is the number of millimoles of dissolved substance in one liter of blood (mmol/l). The following designations are used in biochemistry and lipid profile forms:
- Cho (Cholesterol) or TC – total cholesterol;
- TRIG or TG – triglycerides;
- HDL – HDL;
- LDL – LDL;
- VLDL – VLDL;
- IA – atherogenicity index.
A high concentration of TC in the blood is called hypercholesterolemia, a low content of TC is hypocholesterolemia. An imbalance of lipoproteins of different densities is called dyslipidemia. A form with the results of a laboratory test conducted in a regular clinic is sent to the attending physician. You can take a blood test for cholesterol yourself at paid clinical diagnostic centers Helix, Invitro, etc.
How to submit?
UAC and biochemistry
The OAC gives general information about the body. General analysis is the most common method of determination. When conducting this type of examination, biomaterial is taken from a finger. Preparation is necessary before donating blood: it is advised to sit down for 15 minutes and calm down. This is especially important if the patient has previously walked or climbed stairs quickly.
In addition, this method of examination helps to check the functioning of internal organs. Then a tourniquet is tied above the elbow so that the vein appears on it. Afterwards they give an injection, untie your hand and draw up liquid (2-5 milliliters) with a syringe. To determine the amount of cholesterol in the body, a photometric or colorimetric biochemical analysis is performed, based on the effect of reagents on a biomaterial sample.
How to donate blood for cholesterol? The main objective of this examination is to determine the risk of cholesterol plaques appearing in blood vessels. Also, this analysis, along with other types of examinations, allows you to get a correct idea of the condition of the liver and its work. Thanks to this analysis, lipid metabolism disorders can be detected.
And even if a person does not have all of the above diseases, the doctor prescribes a blood test for cholesterol if he has an addiction to smoking or is overweight.
One of the main reasons for prescribing a test is when the patient reaches a certain age. For men it is 40 years, for women - 50. The risk of increasing the level of low-density cholesterol in the blood is always present in people who lead a passive lifestyle and eat foods high in fat and cholesterol. Fried food lovers are also at risk.
Your doctor will tell you how to take a cholesterol test correctly. Blood sampling is carried out in a laboratory. To conduct the study, venous blood is taken from the patient, so the patient must immediately take care of clothing that freely gives access to the bend of the elbow joint, from where the blood will be drawn.
Preliminary preparation for analysis
To obtain the most informative and accurate results, you need to prepare for donating blood for cholesterol. Key preparation conditions relate to diet correction. For 2-3 days before blood sampling, do not consume foods and dishes rich in animal fats, and also exclude alcoholic beverages (of any strength) from the menu.
3 days before the analysis, interrupt drug therapy (with the exception of vital drugs). The evening before the procedure, limit your sugar intake, give up processed meats and fast food. Fast for at least 8 hours before blood collection (ideally 12 hours). Blood for biochemistry and lipid profile is taken strictly on an empty stomach.
Important! Before taking the test, it is strictly forbidden to take coagulant drugs that thin the blood (Aspirin, Thrombo ACC, Heparin, Warfarin, etc.).
The day before donating blood, it is recommended to reduce the intensity of sports training (reduce other physical activities).
How to take a cholesterol test correctly
To determine the amount of cholesterol, venous blood is examined. You need to donate 5 ml from a vein. The procedure takes a few seconds, and the result is ready the next day or a couple of days later. At this time, the blood is examined using a special apparatus. The test is taken on an empty stomach , usually in the morning from 8 to 10 o'clock. But before it, preparation is necessary . There are certain rules that must be followed for the result to be reliable.
It is not recommended to donate blood after surgery, a heart attack, an exacerbation of a chronic pathology, or an acute illness. It is recommended to wait at least 6 weeks for your health condition to stabilize.
Diet before donating blood
The patient should know what not to eat or drink before donating blood for cholesterol. Since blood is tested on an empty stomach, you need to fast for 12-14 hours. In the evening at 7-8 o'clock, have a light dinner and eat nothing else. You can drink water, but all other drinks and foods can affect test results.
It is recommended to follow a diet a few days before donating blood. It is necessary to exclude fatty foods and fried foods from the diet. Limit the consumption of sweets, confectionery, spicy seasonings - that is, those foods that can affect lipid metabolism and liver function.
Preparing for analysis
In order for the results to be accurate, you need to know how to properly prepare for donating blood for cholesterol. It is advisable to do this in advance. If medications were prescribed to reduce its level, you need to stop taking them 2 weeks before the test. The doctor should also be warned about other medications you are taking, as many of them may affect the results. You should try to avoid, if possible, the use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs, diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, multivitamins and dietary supplements.
It is also important to prepare properly on the day of the test. It is better to follow these recommendations :
- avoid physical activity, sit quietly for 15 minutes before donating blood;
- try not to be nervous;
- do not smoke on the day of the test;
- You can drink water, even immediately before donating blood, as it does not affect cholesterol levels.
It is recommended to donate blood while sitting; if the patient stands, the cholesterol level will increase, and if the patient is lying down, it will decrease.
Blood collection procedure
You can also read: Normal cholesterol levels in human blood
To properly donate blood, the patient is advised to arrive at the medical facility 15 minutes before the procedure. This will help stabilize your pulse and blood pressure.
The concentration of cholesterol and lipoprotein components is determined in serum or plasma of venous blood. To provide the medical staff with comfortable access to the vein, you need to work with the fist of the hand from which the blood is taken.
Depending on the equipment of the laboratory, biomaterial for analysis can be taken using a disposable spitz or using a modern sterile vacutainer. A qualified laboratory technician takes 2-3 minutes to draw blood from a vein. After the procedure, a piece of cotton wool soaked in an alcohol solution is applied to the puncture site. You need to press it and bend your arm at the elbow joint.
The key rule is to hold the cotton swab until the bleeding stops completely. Otherwise, the blood that has not had time to coagulate is poured under the skin. This causes a bruise to form. To prevent hematoma, you should not put any strain on the arm from which the blood was taken for several hours (lift and carry heavy objects, perform physical exercises, etc.).
Preparing and conducting tests for cholesterol levels
It is believed that the main enemy of the cardiovascular system is cholesterol. Based on this, many people think that the less of this substance is detected in the blood during analysis, the better for health. This is not entirely true. Cholesterol is necessary for fat metabolism, so in small quantities it is beneficial for the human body. This substance is needed for the synthesis of bile acids in the liver; without it, the process of building cell membranes is impossible; it is involved in the formation of sex hormones. This means you don’t need to completely get rid of cholesterol, it’s important to just monitor its amount in the blood.
When to conduct research?
You should donate blood for cholesterol under the following circumstances:
- to make a risk forecast or diagnose atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease;
- pathologies in the activity of the endocrine system;
- kidney or liver diseases;
- conducting dyslipidemia screenings;
- testing the effectiveness of treatment with statins and other lipid-lowering drugs.
It is important to know that the normal level of cholesterol in the blood is not a constant value; it changes with age, so the older the person, the higher the indicator. There are also differences due to gender: before 50 years of age, normal rates are higher among the male population, after 50 - among the female population.
How to prepare for the analysis?
There are a number of factors that affect blood cholesterol levels. Therefore, you must adhere to the following rules in order to obtain reliable analysis results:
- You need to donate blood on an empty stomach, which means you should abstain from eating for at least 12 hours before visiting the laboratory. But you shouldn’t get carried away with fasting; a maximum person is allowed not to eat for 16 hours on the eve of the procedure.
- 2-3 days before the study you need to refrain from eating fatty foods.
- It is not recommended to drink alcohol 24 hours before the examination.
- Another bad habit that you should give up at least an hour before the test is smoking.
- On the eve of the test, you are allowed to drink clean water; under no circumstances should it be sweetened.
- Non-alcoholic drinks such as tea, coffee, juice can be drunk 6 hours before donating blood.
- Before the analysis, a person is recommended to spend 15 minutes at rest, in a sitting or lying position. This is especially true if he walked quickly or climbed stairs.
- X-rays, rectal examinations, or physical therapy procedures should be performed after blood collection.
- During the menstrual cycle, women should not refuse the test, since this condition does not affect cholesterol levels in any way.
- In the case of constant medication use, the patient must inform the doctor, who will refer him for examination. There are a number of medications that affect blood cholesterol levels. These include antibiotics, diuretics, hormonal drugs, vitamins, etc.
Norms and interpretation of analysis
The study analyzes several types of cholesterol. Once in the human body, this substance combines with proteins responsible for its transportation. As a result, lipoprotein particles appear with different densities. It can be high, intermediate, low and very low. High-density particles contain good cholesterol, which protects blood vessels from the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. The remaining three types of particles are characterized by the content of bad cholesterol, which is deposited on the walls of blood vessels.
For the interpretation of the analysis to be reliable, only a general blood test for cholesterol is not enough. The study calculates not only the level of total cholesterol, but also the amount of its fractions: triglycerides, low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). As a result, the atherogenicity index is calculated, which makes it possible to identify the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
It is possible that on the form with the analysis results the indicators are presented in the form of an English abbreviation. How to deal with them and understand what they mean?
Deciphering such results will be quite simple if you know that:
- total cholesterol is designated Chol or TC;
- HDL - HDL;
- LDL - LDL;
- triglycerides - TG;
- atherogenic coefficient, which is also called the index, IA.
The normal limits for cholesterol in a blood test for a healthy person are the following: from 3.1 to 5 mmol/l. The normal level of triglycerides is from 0.14 to 1.82 mmol/l. As for deciphering HDL indicators, their amount should be more than 1 mmol/l. More specifically, the norm for high and low density lipoproteins is:
- for women: LDL level - from 1.9 to 4.5 mmol/l, HDL - 1.42 mmol/l;
- for men: LDL level - from 2.2 to 4.8 mmol/l, HDL - from 1.68 mmol/l.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
If the values deviate from the norm, this may be a signal of the presence of pathological changes in the body, for example, metabolic disorders. Decoding the analysis result allows you to calculate the atherogenicity coefficient, that is, an indicator that makes it possible to assess the degree of risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. How is this index calculated? The amount of HDL is subtracted from the total cholesterol level, after which the resulting value must be divided by the amount of HDL. The resulting index can be interpreted as follows:
- a value greater than 5 indicates the beginning of the development of atherosclerotic changes;
- a coefficient that ranges from 3 to 4 indicates a possible risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease;
- coefficient below 3 - the chances of developing atherosclerosis are insignificant.
The atherogenic index depends on many indicators: gender, age group, body weight of the patient. So, in infants its value is no more than one. In healthy men and women under 30 years of age, it is 2.2 and 2.5, respectively. For men aged 40–60 years, the coefficient is 3–3.5.
An excess of triglyceride content (more than 2.29 mmol/l) indicates that coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis have already developed; such a deviation from the norm may also indicate the presence of diabetes mellitus. If the concentration of triglycerides is between 1.9 and 2.2 mmol/l, this is a sign of the onset of cardiovascular disorders and atherosclerosis.
However, such knowledge does not provide sufficient grounds for independently deciphering indicators and making a diagnosis. It is important to understand that only a doctor can correctly decipher the test results and say what is a deviation from the norm and what needs to be done in each specific case.
Finding the nearest clinic Find the clinic closest to your home in your city
Top
asosudy.ru
Reference values for lipid profile
Cholesterol and lipoprotein standards are classified by gender and age. Children's values are lower than the values accepted for adult patients. This is explained by the imperfection of the child’s hormonal system and the lower need for exogenous lipids. With age, the content of Cholesterol increases in proportion to the growth and development of the body.
Norm for children
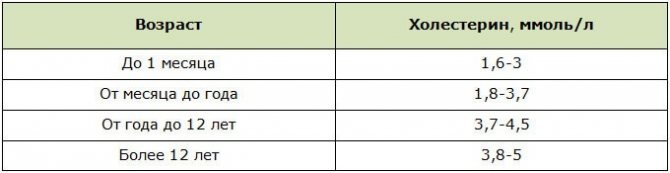
Children with hereditary hypercholesterolemia and a predisposition to diabetes are recommended to have their blood tested annually for cholesterol and sugar. Women's lipoprotein standards are slightly higher than men's. This is due to the activity of lipophilic alcohol in the process of producing sex hormones and the ability of a woman’s body to accumulate lipids “for future use” to maintain pregnancy.
Normal lipid profile
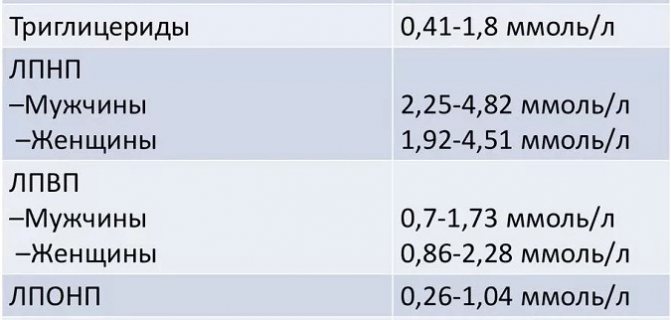
In the second and third trimester of the perinatal period, the synthesis of progesterone (the sex hormone responsible for preserving the fetus) increases in the female body; accordingly, the level of cholesterol involved in the production of progesterone increases.
In addition, cholesterol is a fat base for the cells of the provisional organ (placenta). Providing two organisms forces the liver to synthesize it in increased volumes. Separate standards for lipoproteins and TC have been developed for pregnant women.
Norms of basic lipid profile indicators by trimester
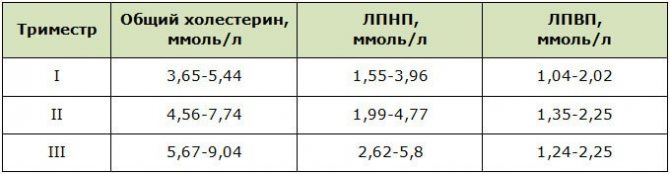
After delivery, the indicators, as a rule, decrease on their own. A deviation from the norm of 1-2 mmol/l is not considered a pathology in women during menopause. During menopause, instead of the lost estradiol (sex hormone), estrone begins to be synthesized, the basis of which is fat cells. With hormonal deficiency, it is much more difficult for the body to control metabolic processes and regulate cholesterol production.
Female reference values during premenopause and menopause
| Age | Normal TC values (in mmol/l) |
| 45+ | 3,94-6,85 |
| 50+ | 4,20-7,37 |
| 55+ | 4,45-7,76 |
The concentration of HDL in the blood in elderly patients is increased by an average of 2 mmol/l. This is due to a decrease in physical activity and the natural processes of aging of the body (fading of reproductive function, slowdown of metabolism, etc.). The average reference values of TC have no gender differences.
Average Cholesterol Values for Adults
Atherogenic coefficient
KA is a marker indicating atherosclerotic changes in the arteries. To calculate the coefficient in hematology, a formula is adopted that takes into account the values of lipoproteins and TC.
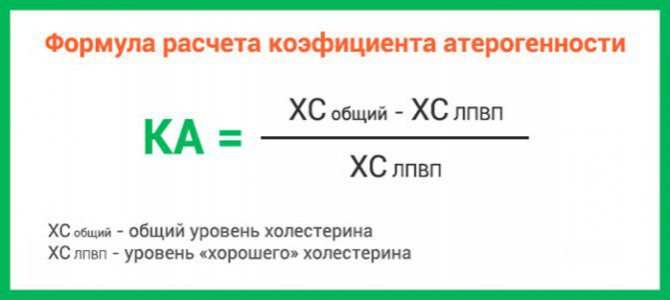
Decoding the values of the atherogenic index
| Index | Normal | Maximum allowed | Overpriced |
| Result | 2-2,5 | 3-4 | >4 |
| Preliminary diagnosis | Proper fat metabolism | Risk of atherosclerotic changes in arteries | Progressive atherosclerosis, threat of heart attack, stroke |
The second version of the formula, which can be used to independently determine the index: KA = (XO - HDL) ÷ HDL.
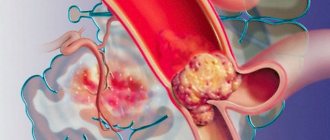
Important! The content of TC and lipoproteins in the blood is one of the indicators of the condition of the arteries of the heart, brain, kidneys, and lower extremities. Hypercholesterolemia is the main cause of atherosclerosis - circulatory disorders due to the growth of cholesterol growths on the inner wall of blood vessels.
Indications for testing
A blood test for cholesterol is important not only for those who suffer from certain pathologies, but also for those who care about their health and want to adjust their lifestyle and diet in a timely manner. Diagnosis of atherosclerosis and coronary diseases is impossible without donating blood for analysis. In addition, the following diseases will be indications for identifying HDL and LDL:
- Kidney and liver,
- Diabetes,
- obesity,
- Tuberculosis,
- Infectious,
- Thyroid gland,
- Heart failure.
Those people who are observed by a therapist and are forced to take statins and other cholesterol drugs for life should monitor the dynamics of indicators after completing the course.
There are a number of methods for conducting cholesterol tests that can tell us about existing abnormalities in the human body.
Briefly about the reasons for the development of atherosclerosis
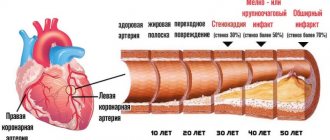
Atherosclerotic changes are the result of the influence of two factors that are closely related to each other:
- microdamage to the inner lining of the vascular walls (endothelium, otherwise intima);
- dyslipidemia caused by chronically elevated levels of TC due to an increase in the concentration of LDL and VLDL and a compensatory decrease in the content of HDL.
During hemodynamics, excess LDL and VLDL “get stuck” in the microcracks of the intima. The settled molecules form a cholesterol spot, which grows over time and transforms into a plaque that partially blocks the natural blood flow. Depending on the location of the affected arteries, the blood supply to the brain, myocardium, legs, and kidneys is disrupted.
| Causes of cholesterol metabolism failure | Causes of intimal microcracks |
| Long-term nervous overload, unhealthy addiction to sweet and fatty foods, physical inactivity, chronic diseases of the hepatobiliary system (gallbladder, liver) and endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism), digestive system (malabsorption) | Destructive effects of nicotine and alcohol, some aggressive pharmacological drugs, changes in blood composition in hematological, endocrine, oncological diseases, arterial hypertension |
Increased fragility of vascular walls can be the result of hypovitaminosis of ascorbic acid, vitamins D, E, group B.
Results
A test for total cholesterol is carried out as part of a biochemical blood test. Average normal values range from 3.2 to 5.2 mmol/L. To determine all indicators of fat metabolism (lipoproteins and triglycerides), a lipid profile is prescribed. It is recommended to monitor TC levels annually.
The following need to be checked more frequently:
- patients with chronic pathologies of the cardiovascular, endocrine and hepatobiliary systems,
- smokers;
- people who abuse alcohol.
Increased attention to the indicators of TC, LDL and HDL should be shown in the presence of hereditary hypercholesterolemia and a predisposition to diabetes mellitus.
The normal level of cholesterol in the blood
In the blood serum, the analysis determines cholesterol and three indicators - LDL, HDL, VLDL.
Total cholesterol is the total number of the listed indicators. Its level is measured in mg/dL or mol/L. Indicators of no more than 5.2 mmol/l are considered normal. Further, with data up to 6.5 mmol/l, moderate hypercholesterolemia is diagnosed.
With indicators up to 7.8, the condition is classified as severe hypercholesterolemia. If the level exceeds 7.85 mmol/l - very high hypercholesterolemia.
- Total cholesterol - General rules for preparing for testing
Laboratory tests are considered the most reliable method that allows you to determine the condition and, if necessary, begin therapy.
To obtain reliable data, the patient must follow the rules for preparing for testing. This will provide an accurate clinical picture. How to properly prepare for donating blood for cholesterol?
The list of requirements for blood tests is as follows:
- Donate blood only on an empty stomach. All indicators tend to change during the day. The morning analysis most accurately reflects the picture. All laboratory standards are established specifically for these indicators.
- In the morning before the test, avoid drinking any drinks - juices, tea, coffee. Only water is allowed as it does not affect the results.
- The time between laboratory testing and food intake is at least 12 hours.
- Avoid drinking alcohol for a day or two.
- For a few days you should not change your usual daily routine, and you should give up physical activity.
- Do not smoke for two hours before the procedure.
- They do not take tests during menstruation.
- All blood tests are carried out before fluorography/radiography and ultrasound diagnostics; a few days before, exclude all physical procedures, visits to the solarium and cosmetic procedures.
- When taking medications, the patient informs the laboratory technician.
- Half an hour before the procedure, you need to sit down and relax; immediately after arriving at the laboratory, you should not immediately take the test.