How does a blood clot form?
The heart is a powerful motor for pumping blood along 100 thousand km (2.5 times the length of the Earth’s equator!) of large and small human blood vessels. This clot is a thrombus. It can grow and completely block the blood path to individual organs and tissues.
And sometimes it breaks off (thromboembolus) and begins its journey through the body. And this is already completely dangerous: at any moment it can clog an important vessel and lead to death.
Let's look at why blood clots form and how to avoid it.
Types and mechanisms of blood clot formation
The classification of blood clots depends on its purpose.
According to their structure, blood clots are:
- white (platelet) blood clots form slowly in capillaries and arteries when blood flows quickly;
- red (blood fibrin) blood clots quickly form mainly in the veins with slow blood flow and an increased level of blood clotting;
- mixed (layered), red and white thrombi, formed in the cavity of the aortic and cardiac aneurysm or in the veins;
- hyaline blood clots form in small vessels of various organs (gastrointestinal tract, urinary system, brain, lungs, etc.) usually due to the fact that there is more plasma in the capillaries than whole blood.
Blood clots are classified according to size and type:
- parietal thrombus - “smeared” along the wall of the vessel (usually in chronic heart failure - on the heart valves, in atherosclerosis - on large arteries, in inflammation - on veins, in aneurysms - in the heart and blood vessels) and covering no more than 50% of its diameter;
- clogging thrombus - blocking the lumen of blood vessels (usually in veins and small arteries, less often in the aorta and large arteries) over 50%, seriously interfering with blood flow, usually as a result of the proliferation of wall thrombi;
- progressive thrombus - a rapidly growing thrombus along the bloodstream, capturing the walls of the veins and reaching the collecting venous vessels;
- spherical thrombus - a growing thrombus of the left atrium with a high risk of breaking away from the inner wall of the heart;
- a dilated thrombus can form in the cavity of an aneurysm (the vessel wall is stretched more than 2 times), so it grows to a large size and can break off, completely blocking the blood flow.
The symptoms that should alert you are specific to the different locations of the blood clots.
If you suspect any blood clots, you should consult a doctor (general practitioner or phlebologist; if necessary, they will refer you to a surgeon or vascular surgeon).
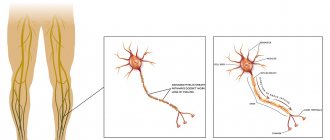
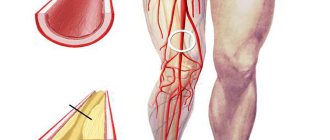
A blood clot has formed in the leg: symptoms and diagnosis
A blood clot in the leg is the most common phenomenon, the signs of which are:
- initially, swelling, mild pain, redness or blueness of the skin at the site of the clots;
- with the development of thrombosis, chills, surges in pressure and temperature, inflammation of the lymph nodes are added, pain increases, and it is difficult to walk;
- with thrombophlebitis of the legs, these symptoms are supplemented by bruising and peeling of the skin, trophic ulcers, and if left untreated, tissue necrosis begins, gangrene develops and there is a danger to life.
A blood clot that breaks off in the vessels of the leg can move:
- in the lobar branch of the pulmonary artery - pressure drops, pulse quickens, constant shortness of breath and pain in the chest appear;
- into the main trunk of the pulmonary artery (thromboembolism) - suffocation, acute pulmonary and heart failure, difficulty swallowing food, chest pain, urinary retention, and subsequently pulmonary necrosis and death appear.
If any symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for a more accurate diagnosis of the location, number, size and danger of blood clots.
Blood clot symptoms
Symptoms of a blood clot will vary depending on the type of vessel in which it formed.
Arterial thrombosis
leads to development
- myocardial infarction,
- stroke,
- gangrene of the limbs,
- intestinal necrosis.
Characteristic manifestations of arterial thrombosis
depending on the organ affected are
- pain in the heart area during a heart attack,
- neurological disorders due to stroke,
- pain, numbness, coldness and discoloration of the limb, as well as
- intestinal obstruction and abdominal pain.
Diseases associated with venous thrombosis
also vary depending on location:
- thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities,
- hepatic portal vein thrombosis,
- thrombosis of the jugular vein and cerebral venous sinus.
Symptoms
venous
thrombosis
are:
- Swelling, pain, redness of the affected area of the leg;
- Abdominal pain, manifestations of pancreatitis, liver cirrhosis;
- Neck pain, blurred vision.
Vein thrombosis is also dangerous because microorganisms quickly multiply in them, which leads to inflammation first of the surrounding tissues, and then of the entire body (sepsis).
Therefore, with a blood clot the symptoms
may be different, but always very serious.
Other locations of blood clots
Symptoms of blood clots elsewhere in the body are usually less severe than with thrombosis in the legs.
Blood clots in the blood vessels of the lungs are the most dangerous; about a third of all sudden deaths occur precisely because of unexpected blockage of the pulmonary artery.
Pulmonary blood clots are in 3rd place as a cause of death after cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
Most often, such a clot forms in the vessels of the lower extremities or the right side of the heart. Breaking off, it passes through an ever-narrowing vessel into the lungs and, having reached an artery of comparable size, clogs it.
The disease develops very rapidly, so it is important to consult a doctor in time if you feel the following symptoms:
These symptoms may be accompanied by uncontrollable hiccups, convulsions, hemoptysis, fainting, and fever. Emergency medical attention can save your life.
A blood clot broke off in the head
Thrombosis of cerebral vessels most often occurs in people over 40 years of age due to one or more reasons: vascular spasms during hypertensive crises, atherosclerotic plaques, anerisms.
In young people, clots in the brain are usually associated with a malformation (congenital abnormal connection) of blood vessels in the brain.
Blood clots reduce blood supply to the brain and cause attacks of severe headaches, temporary states of paralysis in the limbs of the other side of the body, difficulties with speech and memory, oculomotor disorders and other neurological disorders.
The more often such attacks, the closer the cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke).
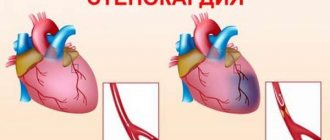
Blood clots in the heart form on valve leaflets or the inner walls of chambers, usually as a result of atherosclerotic lesions, endocarditis (various inflammations), artificial valves and other disorders that lead to the formation of blood clots that degenerate into thrombi.
In the case of atherosclerosis, thrombosis of the coronary vessels leads to the development of IHD (coronary heart disease).
The initial symptoms of incomplete filling of the artery lumen with a thrombus are shortness of breath, angina pectoris with pain in the heart.
As soon as the blood clot grows and blocks the artery, a heart attack occurs.
What causes blood clots? The blood thickens, coagulates and sticks to the wall of the vessel or travels freely through it.
Read also: Treatment of varicose veins on the legs with laser Kaliningrad
Reasons for the formation of blood clots in human vessels:
- damage to the walls of blood vessels as a result of injuries and inflammatory processes;
- violation of blood composition (primarily coagulation);
- a change in the speed of blood flow, causing stasis (slowing or stopping the flow of blood in the capillaries) or turbulence (disturbance in the direction of blood flow due to increased speed).
The truth about varicose veins: symptoms, causes, home methods of prevention and treatment
Varicose veins are an excessive enlargement of superficial veins, accompanied by their expansion with characteristic lengthening, kinks and the development of symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency.
Contents: 1. Symptoms of dilated veins 2. Provoking causes of varicose veins 3. Home treatment and prevention 4. When an emergency visit to a doctor is required
Blood clots in the veins - phlebology, pose a danger through pulmonary embolism.
Varicose veins appear mainly in the lower extremities (veins are the lowest blood vessels and furthest from the heart). Varicose veins also occur on the shoulders, arms, on the walls of the esophagus, rectum (hemorrhoids), bladder, uterus, vagina and spermatic cord. Varicose veins affect more women than men, and their incidence increases with age.
Varicose veins provoke inflammation of the veins, which harden and become inflamed due to the formation of aneurysm-like local expansions (nodes). This process leads to a slowdown in blood circulation and the formation of blood clots. A blood clot that ruptures can be fatal if it enters and blocks a pulmonary artery.
Symptoms of varicose veins
- The feeling of heaviness and fatigue in the legs increases in the evening and at night;
- Swelling of the ankles, accompanied by pain;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Periodic attacks of leg muscle cramps;
- The appearance of so-called “spiders” - a subcutaneous network of veins with a characteristic bluish color;
- Trophic transformation of the skin, formation of calluses, ulcers.
- The occurrence of eczema;
- Itching and burning of the extremities;
- The desire at the subconscious level to constantly change the position of the body;
Provoking causes of varicose veins
- A sedentary lifestyle has a negative impact on the circulatory system due to a lack of muscle activity, as a result of which blood is pumped more slowly from top to bottom.
- Age-related transformations - the walls of the veins cease to be elastic and plastic. They dilate, which leads to dysfunction of the venous valves that control blood flow to the heart, and this, in turn, causes blood to flow from the heart to the legs, which leads to venous stagnation and then = widening of the vein walls, and finally to varicose veins dilation of veins.
- Long-term stay in a sitting position associated with the performance of professional duties.
- Predisposition at the genetic level (up to 17% of the population).
- Pregnancy - a significant increase in abdominal volume and a decrease in physical activity interfere with venous blood flow; hormones relax the veins and soft tissues, which do not inhibit the development of the fetus.
- Previous phlebitis and thrombosis - blockage of the veins leads to increased venous pressure in the legs and damage to the valves.
- Use of hormonal drugs.
- Increased cholesterol levels in the body.
- Flat feet and other postural defects.
- Alcohol in excessive quantities.
- Smoking - nicotine promotes the deposition of calcium on the walls of blood vessels and narrowing of the veins.
- An incorrect diet leads to two factors that provoke varicose veins: obesity and constipation (low-fiber menu).
- Sauna abuse.
- Addiction to taking hot baths.
- Lifting weights.
- Excessive tanning.
- Tight, ill-fitting clothing that impedes blood circulation in the lower extremities.
Home treatment for varicose veins and prevention of varicose veins
Prevention of varicose veins should include an integrated approach in order to exclude recurrences of the leg disease. Foot massage and various creams (tinctures), physical activity and exercises, proper nutrition and diet, special compression garments, giving up bad habits.
Raising the feet above the level of the hips facilitates the functioning of the veins in the legs. This uses gravity. Recommended for mild pain in the legs. While lying down or sitting, place some elevation under your feet. For example, a pillow.
Preventive compression stockings for varicose veins of the leg.
Compression therapy. Anti-varicose stockings, elastic stockings (only up to the knees) or a special bandage do not allow blood to stagnate in the small blood vessels of the lower extremities. However, a poorly chosen (or incorrectly applied) bandage can lead to the opposite effect, like any tight clothing - creating an obstruction to the flow of blood from the legs to the heart. Contraindications to the use of this method are vein thrombosis and atherosclerosis.
Raising legs in anti-varicose stockings. The exercise combines two methods. It must be performed periodically several times a day. Put on compression stockings, lie on your back, rest your feet against the wall at a right angle, and hold in this position for at least 2 minutes. This exercise ensures the outflow of blood from the veins to the heart.
The combination of diaphragmatic breathing and leg elevation is an effective combination for relieving varicose veins. As in the previous exercise, you should lie on your back, rest your feet on the wall at right angles and breathe slowly and evenly from your diaphragm. Gravity will force the blood to drain from the legs, and deep and even breathing will create the correct negative pressure in the chest, which will greatly facilitate the flow of blood from the entire body, including the congested blood vessels in the legs to the venous vessels of the chest.
Modifying the bed by raising the rear legs. Before changing the horizontal position of the bed, you should consult your doctor. This method is contraindicated if you suffer from heart disease or have difficulty breathing.
When staying in a “sitting” or “standing” position for a long time, it is necessary to shift your body weight from one leg to the other (or with your toes to the heel and vice versa) as often as possible, regularly change your position, periodically move your feet, if possible, take short walks, perform squats and avoid the leg-over-leg position.
Avoid overheating your legs to prevent varicose veins. Heat dilates the veins, so it is necessary to avoid saunas, long hot baths, hot waxing, prolonged sunbathing, and staying in rooms with heated floors.
Cool shower. Low temperature hardens blood vessels and improves blood circulation. A cool, but not icy, shower is recommended, with a 10-second session for each leg, starting from the foot.
Physical activity is highly desirable as it improves blood circulation. Even a simple walk activates the leg muscles, which prevents blood from stagnating in the veins of the lower extremities. Cycling, jogging, swimming, dancing or climbing stairs are recommended - any physical exercise will gently stimulate the muscles of the lower extremities, but heavy lifting is strictly prohibited.
The optimal diet involves eliminating foods that are high in fat and cause constipation. The menu should include plenty of fruits, vegetables (for example, vegetable juices), an infusion of linden and birch leaves. You should limit your intake of salt, which retains water in the body, and simple sugar. Food should be rich in fiber, rutin, silicon, vitamins C, B, and E. Effective and natural regulation of the digestive system is ensured by the composition of Indian herbs “Triphala”.
Obesity contributes to the formation of varicose veins, impeding the flow of blood in the legs. It is necessary to get rid of excess weight. The main method is a healthy diet.
A foot massage is done morning and evening from the toes to the groin, preferably using a rough sponge and always towards the heart.
Use foot baths with infusions of calendula, horse chestnut, St. John's wort, horsetail, and a solution of sea salt (or kitchen salt). This relaxing procedure should last 20-30 minutes.
Use anti-varicose medications that help strengthen the walls of blood vessels. They can be in the form of ointments, creams, gels, tablets or bath salts. The most effective of them are those that contain troxerutin or chestnut seed extracts. The therapeutic effect can be enhanced by a combination of ointments and tablets used simultaneously.
Aromatherapy. The use of certain essential oils relieves pain from varicose veins. These include lavender, rosemary, juniper and lemon.
Don't wear tight clothes. Any clothing that compresses the body at the waist or groin area can impede blood circulation in the lower extremities.
High-heeled or high-top shoes should not be worn. Such shoes create additional stress on the lower limbs. The calf muscles do not activate and pump blood from the legs to the heart. The maximum heel is 3-4 cm. The foot in the shoe should be optimally positioned. Uncomfortable shoes should be corrected with appropriate inserts.
Birth control pills cause hormonal imbalances, which can cause varicose veins. Therefore, if there is a temporary connection between the first signs of varicose veins and the start of taking oral contraceptives, you should consult a doctor (or abandon hormonal contraception).
Regular gynecological monitoring is necessary for women suffering from varicose veins, as this disease can be accompanied by chronic gynecological diseases, in particular inflammatory processes, or cancer.
Smoking is one of the main reasons for the formation of varicose veins. Nicotine promotes the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the veins, reducing their capacity. Alcohol, especially pure vodka, has a bad effect on the circulatory system.
Analgesics can relieve leg pain that accompanies varicose veins. But their use is not recommended, since varicose veins in the legs, which cause pain, require medical consultation.
An emergency visit to a doctor is required in two cases:
- If a palpable or visible blood clot causes pain when pressed. If a blood clot in a vein is visible as a red nodule and does not disappear when the leg is raised.
- When a varicose vein ruptures in the ankle area. This situation leads to blood loss. In this case, you must apply a tight bandage or tourniquet and consult a doctor immediately.
Regular visits to a phlebologist should become the norm for a person suffering from varicose veins. The first consultation should take place immediately after the onset of early symptoms of the disease, which will help slow or stop its development. A phlebologist may prescribe immediate surgery or less invasive, but no less effective sclerotherapy, or an injection method of treatment.
Why is a blood clot dangerous?
Gradually, thrombotic masses adhere to each clot, as a result it slowly increases in size. Pressure builds up in the blood vessel and the clot can break off.
If there are a lot of blood clots (thrombosis), then they gradually clog the vessels and thromboembolism begins (reduction or cessation of blood supply and hypoxia of some organs or tissues).
In the future, even with recanalization (resorption) of blood clots, the valves of the veins are destroyed and post-thrombophlebitis disease (PTSD) develops and there will no longer be a complete recovery.
Who is most susceptible to blood clots?
What causes blood clots in humans? First of all, from a violation of a healthy lifestyle.
But there are other factors that bring a person into a high-risk area.
- Injuries . Blood clots protect us from blood loss. Any cut, scratch, hematoma, surgical operations on the legs, abdomen, chest, pelvic organs cause the formation of blood clots, but they quickly resolve as soon as the wound heals. However, with repeated injuries or an unfortunate combination of circumstances, they do not disappear, but become attached to the walls of blood vessels and lead to the onset of thrombosis.
- Medicines . Some medications (for example, antitumor drugs, some oral contraceptives, etc.) increase blood clotting, as a result, it “thickens” and generates blood clots.
- Pregnancy and illness . In a number of diseases (obesity, liver damage, cancer, heart failure, diabetes mellitus), after vein surgery (especially in the pelvic area), with insufficient mobility during pregnancy and the postpartum period, the body’s production of natural anticoagulants (for example, proteins C) is disrupted and S) and the speed of blood movement through the vessels, which leads to thrombosis.
- Life style . If you are in a stationary position for a long time (on an airplane, driving or at a computer), blood clots form within 45-60 minutes in 1 out of 50 people, after 2 hours - in every fifth person, after 6 hours - in 99% of people. They dissolve quickly if you regularly exercise and walk.
- Diet . Scientists have not fully established the role of nutrition in the development of thrombosis, but some facts suggest that there is a direct connection between elevated cholesterol levels and the appearance of blood clots.
Participates in the formation of a blood clot
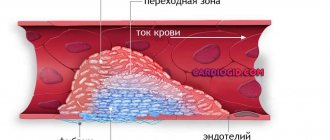
The mechanism of thrombus formation was created by nature itself to “repair” damaged vessels. The process of blood clot formation is called thrombosis . The meaning of this process is to carry out irreversible denaturation of proteins and blood cells (platelets and red blood cells) in order to hermetically seal the site of damage. A distinctive feature of blood clots is the fact that they are attached to the wall of a blood vessel and have a layered, crumbly structure and a rough surface. The entire design of the thrombus is designed to maintain blood flow, and its strong adhesion to the vessel under normal conditions does not provide for its separation.
Read also: I'm afraid that a blood clot will come off
The mechanism of thrombus formation.
When a blood vessel is damaged, substances begin to be released from its wall that inhibit antiaggregation processes (that is, processes that prevent blood clotting) in this place of the bloodstream. At the same time, platelets begin to change and disintegrate, and procoagulants (thrombin and thromboplastin) are released into the blood - substances that promote blood clotting. Under the influence of thrombin, febrinogen (a protein that affects the erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is converted into fibrin, which in the form of a mesh of threads forms the basis of a blood clot. Blood cells collect in the cells of this network: aggregated platelets, leukocytes and erythrocytes. The structure becomes denser over time. The process of thrombosis is completed and the “leakage” of blood is eliminated.
The causes of thrombosis can be varied.
- Physical damage to the walls of blood vessels - mechanical trauma, electrical trauma;
- Chemical damage to vascular walls;
- Exposure to endotoxins from microorganisms;
- Large-scale surgical interventions;
- Childbirth;
- Physiological disorders - atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, allergies;
- Epinephrine surges inhibit prostaglandin synthesis (prostaglandin slows down blood clotting), thereby promoting thrombus formation;
- Disorders of the system that inhibits blood coagulation, as well as disorders of the system that catalyzes blood clotting;
- Taking hormonal medications (for example, contraceptives);
- Smoking promotes the formation of thromboxane, a powerful blood clotting regulator, under the influence of nicotine;
- The process of the occurrence of neoplasms (the development of benign and malignant tumors) promotes thrombus formation;
- A sedentary lifestyle contributes to poor circulation and can cause pulmonary embolism or venous thrombosis.
Consequences of thrombosis.
The uncontrolled process of thrombus formation causes the development of many diseases:
Factors contributing to the detachment of a blood clot from the vessel wall.
Violation of the elastic properties of blood vessels leads to the development of their fragility, which means that the vessel wall will not be able to hold the blood clot tightly enough. The integrity of the vascular wall may occur at the site of attachment of the blood clot.
Since the thrombus is constantly washed by the blood and, being held on the wall of the vessel, experiences continuous resistance to the blood flow, the qualitative characteristics of the blood that put pressure on the thrombus - the fluidity and viscosity of the blood - are of particular importance. The higher the fluidity of the blood, the easier it is for it to wash the blood clot, going around it. The higher the viscosity of the blood, the more difficult it is for the clot to withstand the blood pressure in the vessel.
There is such a thing as a “floating” blood clot . Such a thrombus is connected to the wall of the vessel pointwise and constantly sways in the blood flow. Any sudden movement: coughing, deep breath, laughter, muscle tension when lifting weights can tear it from its place and throw it into the bloodstream. There are special hardware research methods to determine which of the blood clots can be dangerous - coagulogram , ultrasound angiology, sonoelastography.
The result of a blood clot detaching from a vessel is an embolism - blockage of the lumen of the vessel. If a small vessel is blocked, then in the worst case it will end in gangrene of the limb, in the blood vessel of which a thromboembolism , but if a blood vessel that supplies blood to the heart or brain is blocked, then the end result will be necrosis and death of the entire organism.
Hemostasis is a set of physiological processes aimed at preventing and stopping bleeding, as well as maintaining the fluid state of the blood.
Blood is a very important component of the body, because with the participation of this liquid medium all metabolic processes of its life occur. The amount of blood in adults is about 5 liters in men and 3.5 liters in women. No one is immune from various injuries and cuts, in which the integrity of the circulatory system is disrupted and its contents (blood) flow outside the body. Since a person does not have that much blood, with such a “puncture” all the blood can flow out in a fairly short time and the person will die, because his body will lose the main transport artery that feeds the entire body.
Read also: Brachial vein thrombosis treatment
But, fortunately, nature provided for this nuance and created a blood coagulation system. This is an amazing and very complex system that allows blood to remain in a liquid state inside the vascular bed, but when it is disrupted, it triggers special mechanisms that clog the resulting “hole” in the vessels and prevent blood from flowing out.
The coagulation system consists of three components:
- coagulation system - responsible for the processes of blood clotting (coagulation);
anticoagulation system - responsible for processes that prevent blood clotting (anticoagulation);
In a normal state, all these three systems are in a state of balance, allowing blood to circulate freely through the vascular bed. Violation of such an equilibrium system (hemostasis) gives a “skew” in one direction or another - pathological thrombus formation, or increased bleeding, begins in the body.
Impaired hemostasis is observed in many diseases of internal organs: coronary heart disease, rheumatism, diabetes mellitus, liver diseases, malignant neoplasms, acute and chronic lung diseases, etc.
Blood clotting is a vital physiological adaptation. The formation of a blood clot when the integrity of a vessel is violated is a protective reaction of the body aimed at preventing blood loss. The mechanisms of formation of a hemostatic thrombus and a pathological thrombus (clogging a blood vessel supplying internal organs) are very similar. The entire process of blood coagulation can be represented as a chain of interconnected reactions, each of which involves the activation of substances necessary for the next stage.
The process of blood clotting is under the control of the nervous and humoral systems, and directly depends on the coordinated interaction of at least 12 special factors (blood proteins).
Prevention of thrombosis
Where does a blood clot come from?
First of all, from poor nutrition and insufficient exercise.
Anyone at risk should consider all such factors carefully.
- What to eat to prevent blood clots ? No special diets are needed. However, vegetables, fruits, oatmeal, and bran are required in the diet and it is better if this is the predominant food. You should eat fish at least a couple of times a week and take fish oil regularly. It is better to limit the amount of dairy products, and it is better to exclude fatty meat from the diet. If there is not enough magnesium, potassium and calcium in food, they need to be taken in medications.
- How much do you need to move to avoid blood clots ? Minimum physical activity: 20 minutes daily. charging + 20 min. walk, or daily 3-5 times a day for 2-5 minutes. exercises + 2 times a week walks for 1.5 hours. If you have blood clots in your legs after walking and putting stress on your legs, you should definitely lie down, raising your legs 15-20 cm above body level;
- Means for prevention are primarily aspirin in small doses. You can also use traditional medicine recipes, but you should not rely on them alone, and preventive courses should be agreed upon with your doctor.
Treatment for blood clots
What to do? How to treat?
Only under the supervision of a doctor and following all his recommendations, including taking medications, healthy eating and physical activity.
Main areas of treatment:
- bed rest - depending on the severity of the disease and the location of the blood clot, 3 to 15 days are required in the hospital or parental home;
- drug treatment (thrombolytic therapy) - direct and indirect anticoagulants, thrombolytics, which can be taken in the form of tablets, and in emergency cases (for example, in case of danger of blockage of the arteries of the lungs) - intravenously;
- non-surgical implantation of vena cava filters - to prevent damage to the pulmonary artery by a detached thrombus;
- surgical intervention - for a large area of damage and in critical situations;
- non-drug therapy - the use of elastic bandages, compression hosiery;
- maintenance therapy - for many types of thrombosis (on the vessels of the brain, heart), special procedures are added to the direct treatment of blood clots to improve the health of the relevant organs.
It should also be remembered that blood clots in the legs are more common in women, but relapses of blood clots after treatment occur more often in men.
Types of thrombosis
Thrombosis is classified depending on its structure. Highlight:
- Hyaline - formed in small vessels;
- Red ones are characterized by formation in the veins;
- Whites are diagnosed in the arteries;
- Mixed ones occur in the aorta and veins.
The blood clots themselves are divided into:
- Occlusion, formed due to an enlarged wall thrombus. They cause serious disruption of blood flow. The vessel is often half closed;
- Parietal. Blood clots “smear” along the edges of the vessels. Diagnosed in large arteries, veins, heart;
- Progressive is characterized by rapid movement with blood flow;
- Dilatational ones are the most dangerous. They are found in the aneurysm and are large in size. They are characterized by rapid rupture and blockage of the vessel.
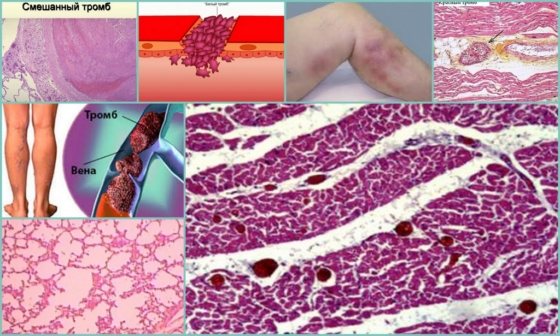
A blood clot can form in different types of vessels. According to this principle, pathology is divided into:
- Arterial thrombosis - formed due to the inflammatory process and injuries. A blood clot in the artery is accompanied by intense pain, swelling, redness of the skin, and a local increase in temperature. If one vein is blocked, it is manifested by swelling and minor pain. The general condition does not change. A blood clot formed in the superficial veins is determined by palpation. This indicates the development of thrombophlebitis;
- Venous – formed in individuals with hormonal imbalance, metabolism, or excess body weight. Venous thrombosis causes circulatory problems in the lower extremities. Next, blood flow in the lungs is disrupted. There is a threat of pulmonary embolism.
Read also: Venarus or phlebaven, which is better for varicose veins
Why does a blood clot break off and why is it dangerous?
The movement of a blood clot within the cardiovascular system is possible with the blood flow.
This requires two basic conditions
.
- The thrombus must be non-occlusive, i.e. freely placed inside the vessel. Typically, such blood clots form in the veins of the legs and heart cavity.
- The blood speed must be sufficient to break off the clot.
The danger of migrating blood clots is that they can travel considerable distances, fragment and lead to blockage of a large number of vessels.
The most common example of blood clot rupture is pulmonary embolism.
from the veins of the lower extremities. It would seem that not the most serious disease (varicose veins and thrombophlebitis) can lead to sudden death.
No one can say why a blood clot breaks off
exactly at the moment when you least expect it. For example, a patient is already recovering after surgery and is preparing for discharge. He gets up and begins to pack his things, but suddenly begins to choke and loses consciousness. This is usually how pulmonary embolism develops. In this regard, timely prevention and effective treatment of blood clots are urgently needed.
Causes of pathology
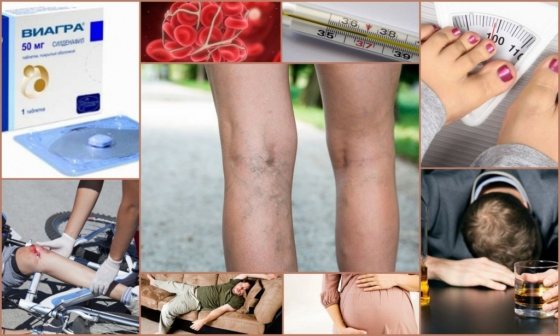
The basic reasons for the formation of blood clots in the vessels of the legs are combined into Virchow’s triad:
- Increased blood clotting. Such thrombosis is not associated with genetic predisposition. The disease occurs against the background of chronic pathologies accompanied by elevated body temperature, as well as as a result of alcohol abuse and diets that lead to dehydration of the body. Uncontrolled intake of medications with diuretic effects, oral contraceptives, hormonal drugs, and Viagra contributes to the occurrence of thrombosis. An increase in blood clotting has been noticed during frequent stress, with an active release of adrenaline, which provokes the release of aggressive substances into the blood that cause thrombosis;
- Slow blood flow. This is a problem for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, who suffer from excess body weight, have a history of cardiovascular failure, and varicose veins. Blood clots also appear due to impaired functioning of the valves during pregnancy, varicose veins;
- Injury to the blood vessels of internal tissues is another reason why blood clots form. This occurs after surgery, intravenous injections or injuries.
The development of thrombosis is recorded against the background of oncological processes, inflammatory diseases, poisoning with toxic substances, smoking, poor nutrition, when the formation of atherosclerotic plaques occurs, which is explained by high cholesterol.
How to recognize
- swelling of the legs;
- venous networks;
- causeless dry cough, or with blood;
- heart rhythm is disturbed;
- chest pain;
- redness with changes in body temperature in this place;
- fatigue.
Blood clots in blood vessels are dangerous because they may not show signs, so death occurs suddenly and quickly, so that doctors do not have time to intervene. But if you have a predisposition, then timely examination will help save your life.
Mechanism of thrombus formation
Many patients have a question about how a blood clot forms. Its formation goes through a number of stages:
- Stage of platelet agglutination. Damage to the walls of blood vessels occurs. Platelets stick together. Attached to the damaged area. At this time, the active substances are released;
- At the next stage, fibrin is formed. Platelets become the basis for further formation of a blood clot in the veins. The protein contents become denser;
- Red blood cells and leukocytes are captured by the thrombus;
- Precipitation stage. At this time, blood protein settles on the formed clot and becomes denser.
Blood clots attach to the damaged area. But a fragment of a blood clot can break off at any time. It enters the bloodstream, causing circulatory problems. Thromboembolism is dangerous because of a heart attack that develops against the background of a blocked vessel. A blood clot can break off as a result of various factors:
- Fast speed of blood movement through the veins;
- Large size of the formed blood clot;
- With progressive vascular diseases;
- Inflammatory process of veins;
- Excessive physical activity.
Risk group
Any person is susceptible to blood clots. But there is a risk group for this disease, which includes:
- Cancer patients;
- People who drink little fluid;
- Persons who make frequent and long flights;
- Patients who frequently undergo surgery;
- Women protected by hormonal contraceptives;
- Athletes taking anabolic steroids;
- Patients who have suffered spinal injuries;
- Disabled people who are bedridden;
- Obese patients.

The prognosis for thrombosis of the lower extremities can be favorable or unfavorable. It will be favorable when the blood clot resolves and blood flow in the vein is restored. There are known cases of blood clot canalization. Provided the blood clot has a loose structure and high pressure in the vessel, the blood makes a channel in the vein. Complete or partial restoration of blood flow occurs.
With an unfavorable prognosis, the following occurs:
- Thrombus tissue growth. It attaches tightly to the walls of the veins, disrupting blood circulation;
- Transformation of a thrombus into an embolus as a result of separation;
- Infection of a blood clot with pus, which causes the microorganisms to spread throughout the body;
- The formation of thrombosis in multiple microvessels, causing hemorrhage of the veins.
Causes of the disease
Like other types of thrombotic diseases, ileofemoral develops due to the presence of stagnation in the vascular network, as well as deterioration of blood clotting. Another reason is damage to the walls of the veins.
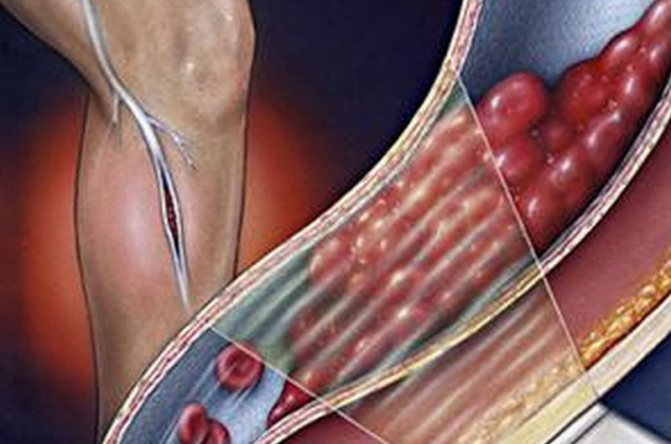
Thrombosis of this type occurs due to one or many factors, which include:
- A person remains in a lying position for a long time: for example, during illness or in the postoperative period.
- Traumatic effects on the veins of the lower extremities.
- The presence of bacterial invasions in the body.
- The use of hormonal drugs (for example, the use of contraceptives)
- Postpartum period in women. Pathology can also manifest itself during pregnancy: thrombotic changes occur in the veins compressed by the uterus in the pelvic area.
- The appearance of cysts in the knee area.
- Iatrogenic venous lesions.
It is important to know that the main factor triggering this pathology is disturbances in the functioning of the venous valves . This, in turn, leads to blood stagnation. The second important factor is problems with blood clotting.
Prevention of thrombosis
You can avoid blood clots by following these simple recommendations:
- Physical inactivity leads to stagnation of blood in the veins and worsens metabolic processes. Staying in one position for a long time should not be allowed. When working sedentarily, you should take regular breaks and do some exercise;
- It is important to drink more water, at least 1.5 liters. in a day. Water is an excellent blood thinner;
Recommended reading:
- You should protect yourself from injuries, increase your immunity;
- Avoid alcohol abuse, quit smoking;
- Control your weight;
- Avoid stress if possible;
- Stick to proper nutrition.
Knowing why blood clots form, you can avoid the development of thrombosis and its complications, which without adequate timely treatment can lead to death.
Classification by morphology
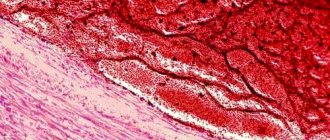
If we consider blood clots from the point of view of appearance and composition, then the classification will consist of four varieties: white, red, mixed (the most common) and hyaline. Depending on the components of the clot, the effect of medicinal substances may vary, therefore, during the diagnosis, the attending physician determines the type.
White clots
White blood clots are also called gray, agglutination or conglutination. They are formed by platelets - colorless and nuclear-free blood platelets of irregular shape, formed in the red bone marrow. They are directly involved in the coagulation process, and also control blood viscosity, protect vessel walls from damage and promote the dissolution of formed blood clots in healthy people. In some cases, the white clot may be formed by leukocytes (white blood cells) and fibrin (a protein made from fibrinogen synthesized in the liver).
As a rule, this type of clot forms in vessels with good blood flow, mainly in the arteries and cavities of the heart. White blood clots form slowly, perpendicular to the direction of movement of rapidly circulating blood; gradually the growth becomes voluminous and resembles coral. In appearance it is a light gray or white substance, and its surface is embossed. The structure of the clot is crumbling, that is, if it separates from the wall of the vessel, it will disintegrate into small particles.
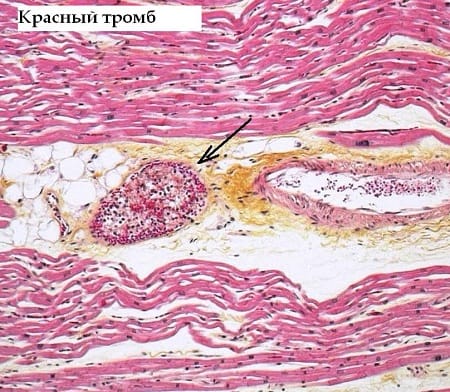
Red clots
Red blood clots (coagulation) are formed for exactly the opposite reasons - in vessels with slow blood circulation, which at the same time has a high degree of coagulation. The color of clots is determined by the high content of red blood cells, of which in most cases they are composed.
Read also: Is it possible to take birth control pills if you have varicose veins?
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) are disc-shaped biconcave cells that are saturated with oxygen in the lungs and then carry it to all cells of the body. The red color of these elements is due to the fact that their cytoplasm contains large quantities of hemoglobin, a pigment containing an iron atom. It not only determines the red color of the entire cell, but is also directly involved in the delivery of oxygen, since it is able to bind it.
In appearance, a thrombus of this type is in most cases smooth, but there may also be raised areas. The clot is usually loosely connected to the wall of the vessel, and, unlike white blood clots, it does not form large coral-like formations. Most often, red blood clots affect the veins.
Mixed clots
Mixed blood clots are formed by the fusion of white and red blood clots, so we can say that they are mainly composed of platelets and red blood cells. In this case, such a clot can form in an artery, a vein, or in the cavity of the heart. Mixed thrombi differ in structure from white and red ones; they have three anatomical parts - a conical or flat head, a body (directly mixed thrombus) and a tail. In this case, the head, which is a white blood clot, is attached to the wall of the vessel, and the tail, which is a red blood clot, is freely located in the lumen of the vein or artery and has a loose structure.
Since the head of a mixed thrombus is attached to the vessel wall, the tail poses the greatest danger. It is always localized against the blood circulation, so it can easily come off, clogging the vessel, this process is called thromboembolism.
In rare cases, when the tail reaches a significant size, it can provoke the detachment of the entire blood clot, which can even lead to death if the clot blocks the lumen of vital organs.
It happens that different parts of a mixed thrombus are located in different veins, for example, the head is in the femoral vein, the body is in the external iliac vein, and the tail is in the inferior vena cava.
Hyaline clots
Hyaline blood clots are currently considered the most mysterious by the nature of their occurrence, since researchers do not have a consensus on the mechanism of their formation. They appear predominantly in small vessels of the microcirculatory system and are mostly multiple in nature. Hyaline clots can occur after shocks, burns, disseminated intravascular coagulation (blood clotting disorders due to the release of thromboplastic substances from tissues), electric shocks, extensive skin injuries, etc.
Hyaline blood clots mostly consist of red blood cells, white blood cells, and precipitated plasma proteins glued together or destroyed. Also, the clot may contain a small amount of fibrin protein, but it is not constant, and sometimes the component may disappear completely. The prerequisite for the formation of a hyaline thrombus is often a significant slowdown or complete cessation of blood flow in the vessel.
Treatment of blood clots
Treatment for blood clots primarily depends on where the blood clot is located.
In case of arterial thrombosis, it is necessary to restore blood flow in the affected vessel as quickly as possible. If the catastrophe happened in the brain, then the doctor takes no more than 2-3 hours to treat blood clots, if in the heart it takes no more than 6 hours. The tissues of the limbs and intestines were the most resistant to malnutrition. There are two main ways to eliminate a blood clot.
A surgical method that includes
- shunting,
- stenting and
- mechanical removal of a blood clot.
During bypass surgery, the surgeon creates an additional blood supply that bypasses the affected vessel. This is an open operation and is performed under general anesthesia. A more modern way of troubleshooting is stenting. This method involves placing a stent (a hollow cylinder similar to a spring) in the area of narrowing of the vessel. It is performed through a puncture in the artery and does not require anesthesia. Before stenting, the clot is sometimes removed by suction with a special syringe.
Therapeutic method
It consists of dissolving a blood clot with the help of special medications (thrombolytics) administered intravenously.
A slightly different treatment tactic for venous thrombosis. Here everything is determined by how high the danger of its separation from the wall of the vessel is.
In case of floating blood clots (freely moving in the lumen of the vessel), the vein is ligated or a special trap for blood clots is installed - a vena cava filter. To stabilize a blood clot, heparin or its analogues (fraxiparine, clexane) can be used.
When the lumen of the vein is completely closed, medications can be used that will destroy the blood clot and, in some cases, will lead to the restoration of blood flow through the damaged vessel. These include heparin and warfarin. In rare cases, surgical removal of a blood clot from a vein is used to treat a blood clot.
Classification by localization in the vessel
In addition to the fact that thrombosis can occur in any part of the human circulatory system, that is, in the area of any internal organ, blood clots also differ in that they can be located differently in the vessel itself. This applies to blood clots of any structure and appearance.
Parietal variety
Parietal clots are quite common; they partially cover the lumen of the vessel. The parietal variety is characteristic of large vessels, as well as elements of the heart - chambers and valves. Often the parietal variety occurs as a result of inflammatory processes, for example thrombophlebitis, which is one of the complications of the last stages of varicose veins.
At first, such clots are not dangerous, since they block the blood flow only partially, but they have the characteristic feature of layering on each other, forming group accumulations. If therapeutic measures are not taken, the formed blood clot will subsequently completely block the blood vessel, which can be fatal.
Obstructive variety
Obstructing, or, in other words, clogging blood clots prevent blood circulation across the entire width of the affected vessel. Moreover, such clots, as opposed to parietal clots, are formed mainly in small blood vessels. The greatest diagnostic difficulty in this case is mixed thrombi, since it becomes difficult to determine where they begin and attach to the vascular wall, and where their tail ends.
Despite the fact that occlusive clots affect small blood vessels, they pose a significant threat to human health and life. If such a phenomenon occurs in the vessel of the spleen, there will be an increase in its size and a partial loss of efficiency; location in the renal branch of the circulatory network will lead to renal infarction, and in the intestine - to gangrene. When an occlusive thrombus is localized in a heart vessel, death is inevitable.
Axial variety
Axial thrombi can be called a kind of middle type between parietal and occlusive. Such clots are attached to the vascular wall in only one anatomical area - the head or part of the body, partially obstructing blood flow. Moreover, if a blood clot comes off, under the influence of blood circulation it can still remain in a suspended state for some time, “collapsing” into a spherical shape.
Causes of blood clots in blood vessels
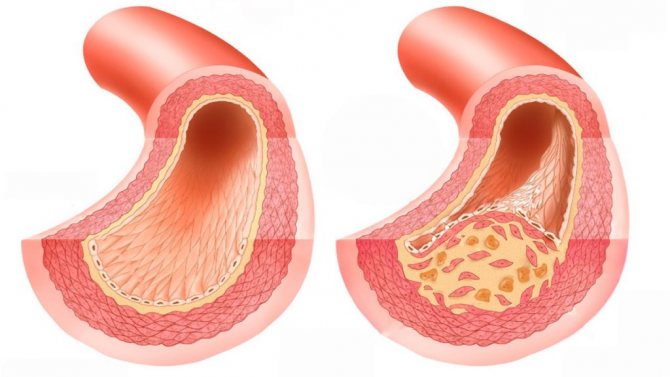
A blood clot forms in humans under different circumstances. The main cause of the disorder lies in slow blood circulation and high blood viscosity. Pathological syndromes develop if the patient's upper vascular layer is damaged. Thrombosis can be localized in the heart in cases where there is protrusion of the arterial wall. Formations in large arteries are considered to be the result of progression of atherosclerosis. When a patient experiences an inflammatory reaction in the body, venous thrombosis is likely.
The greatest danger to the health and life of the patient is an occluding thrombus.
Destructive processes inside the vascular wall
The reasons for the development of thrombosis often lie in atherosclerotic changes occurring in the lining of the vessel. Cholesterol plaques gradually become overgrown with calcium, as a result of which the vessels become less elastic, become thinner and become covered with ulcers. Thrombosis of the inner layer of the vessel is observed, due to which the blood flow is partially blocked. Clots may occur after surgery or anticoagulant therapy. Blood clots can form due to uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives or other medications. Vascular thrombosis can manifest with different symptoms, depending on its location.
What is the effect of slowing blood flow?

Blood clots often form in blood vessels in patients who do not move enough throughout the day. Such patients are more likely to develop varicose veins than others. A person who has constantly elevated blood pressure is also at risk of thrombosis. Clots in the veins are a consequence of improper flow of blood fluid, congestion, and increased venous turbulence.
Excessive viscosity
Thrombosis is highly likely to develop in the case of intravascular fluid viscosity. Patients prone to developing disorders are those who have the following conditions and abnormalities:
- autoimmune diseases;
- cancerous tumors;
- genetically impaired blood clotting system;
- lack of fluid in the body.
Other types
In addition to the main classifications of blood clots, there are several separate types that are specific to certain groups of patients. These varieties include the following types:
- Mirantic. It occurs in weakened elderly people with long-term dehydration. The thrombus is localized mainly in the superficial veins.
- Tumorous. Formed as a result of metastasis, that is, the formation of secondary foci of a malignant tumor. Often such a clot gradually grows towards the right lobes of the heart.
- Septic. Occurs as a result of a local inflammatory process caused by infection. Localized in the veins and on the valve flaps of the heart.
Thus, there are several types of blood clots, each of which will require a specific approach during treatment. The type of blood clot is determined by the doctor during diagnosis.
Sources:
//trombanet.ru/prichiny-obrazovaniya-trombov-v-sosudax-simptomy-profilaktika-i-lechenie/ //nogivnorme.ru/bolezni/tromboz-i-tromboflebit/o-tromboze/ot-chego-obrazuyutsya-tromby. html //flebdoc.ru/tromb/vidyi-2.html