Atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation (AF), is a heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular contractions of the atria and ventricles, which in many people is paroxysmal in nature. Such patients often feel the development of paroxysm (attack). In this case, it will be useful for them and their relatives to know how to provide first aid for atrial fibrillation.
It is quite difficult to independently recognize the development of the first attack of atrial fibrillation in your life. However, for most paroxysmal rhythm disturbances, the principles of first aid are the same. Therefore, our article will be useful to read for all people suffering from paroxysmal heart rhythm disturbances (supraventricular or ventricular tachycardia).
The danger of atrial fibrillation attacks for the heart
The danger of attacks directly depends on the form of atrial fibrillation. If the attacks can be stopped, that is, they can be eliminated, this must be done. Of course, it is better to choose a treatment so that paroxysms occur as rarely as possible. However, gradually, in most cases, the paroxysmal (attack-like) form of atrial fibrillation becomes permanent. In this case, another treatment is necessary - aimed at slowing down the pulse and preventing blood clots.
When an attack (paroxysm) of atrial fibrillation develops, the patient has an increased likelihood of thromboembolic complications, primarily stroke, as well as myocardial infarction.
How to determine low heart rate
To understand what your pulse is, just count it. At home, use a stopwatch and count the number of pulsations in the wrist vein in one minute. In the hospital, such an event is carried out with greater accuracy thanks to a procedure such as an ECG.
Electrocardiography can determine the reasons for the decrease in heart rate. In addition to the ECG, you will need to donate blood for bioanalysis to determine the amount of hormones.
There are many methods and formulas with which you can calculate the pulse for a specific person without averaged forms. Although these calculations are accurate, they do not take into account all factors, so the calculation error is 12%. The most famous formula is the Karvonen method, which determines the maximum possible heart rate in a person.
Another formula is considered more accurate: 205.8 - (0.685 * age). The result obtained is the upper heart rate bar. There are several pulse zones that affect many body processes. During training, to achieve the best results, you should try to keep your heart rate within the desired zone.
Functional arrhythmia occurs for many reasons: emotional stress, overload, sports, drinking coffee and alcoholic beverages. What is the maximum permissible heart rate for a person with arrhythmia? Doctors indicate 90 beats per minute as the maximum value. If the heart rate exceeds this figure, then negative changes begin to occur in the body. An increased pulse due to arrhythmia is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Increased breathing.
- Dizziness.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Unreasonable anxiety and fear.
Forms of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) can occur in several variants (forms):
- paroxysmal form: usually the patient has a normal sinus rhythm, but periodically it “breaks down” and an attack of irregular heartbeat develops, usually rapid;
- persistent form: the patient’s usual rhythm is atrial fibrillation, but sometimes due to unknown reasons, his normal heartbeat is restored for some time;
- permanent form: only an irregular heartbeat is recorded, sinus rhythm is not restored.
And also, depending on the average pulse frequency, tachysystolic, normo- and bradysystolic forms of atrial fibrillation are distinguished.
Tachysystolic form - an increase in the average heart rate of more than 100 per minute.
Normosystolic form with heart rate from 60 to 100 beats,
Bradysystolic form is a decrease in heart rate of less than 50 - 60 per minute.
In the paroxysmal course of MA, attacks usually have a high heart rate.
Treatment
Many factors can influence your heart rate. Anxiety, stress, physical activity, and various diseases can increase heart rate values. To obtain an adequate result, it is important to take these factors into account. In order to know what your maximum heart rate is and prevent tachycardia, it is important to measure your heart rate from time to time.
There are several ways to do this. You can measure your pulse either using instruments or simply by pressing the artery with your finger. The heart rate is best felt on the inner bend of the elbow, on the neck and on the wrist. By placing your finger on one of these places, you can easily count your pulse rate.
A heart rate monitor in the form of a watch or bracelet measures heart rate more accurately. The use of heart rate monitors is possible when necessary or on an ongoing basis. Many companies produce these devices in the form of watches or bracelets that read indicators around the clock. This way you receive data about your health over a long period of time.
But the easiest way to measure your pulse is simply by touching it - this method does not require special equipment. The most common way to measure the number of heartbeats is at the wrist. To get an accurate result, you need to sit on a chair and put your hand on the table, completely relaxing it. Then count your pulse for 60 seconds, having previously set a timer.
General rules for first aid
The rules for providing first aid for the treatment of paroxysm of atrial fibrillation are carried out differently depending on several characteristics of the attack:
- blood pressure level;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- duration of the attack;
- heart rate;
- primary or repeated paroxysm.
Depending on this, emergency doctors either try to restore sinus rhythm or reduce the heart rate, while simultaneously preventing the formation of blood clots. For this purpose, medications are used, and, if necessary and conditions exist, electropulse therapy is used.
What you can and cannot do at home during an attack
If an attack of irregular heartbeat develops, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Before the medical team arrives, you can:
- give the patient a semi-sitting position;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
- invite the patient to breathe with his stomach, wipe his face with a handkerchief dipped in cold water;
- give 20 - 30 drops of Corvalol in half a glass of water;
- prepare for the arrival of the team: organize its meeting, prepare medical documents, previous ECGs, think about transporting the patient to the ambulance (such a need may arise, but the duties of the ambulance personnel do not include carrying the patient);
- reassure the patient, tell him to call the doctors.
When detecting an attack of MA before the arrival of the ambulance, you cannot:
- give the patient medications before the ambulance arrives, including nitroglycerin;
- massage the eyeballs or the area of the carotid arteries;
- waste time measuring blood pressure without preparing for the arrival of medical personnel;
- collect things for hospitalization (this will be the time while the doctor examines the patient, relieves the attack, etc.; hospitalization is not always required);
- worry and panic.
How to stop an attack of MA on your own (a pill in your pocket)
Some patients whose diagnosis of “paroxysmal atrial fibrillation” has been established for a long time, and attacks occur less than once a month, can learn to independently stop such paroxysms. This tactic is called “pill in the pocket.”
It is used in intellectually intact patients who can adequately assess their condition. The “pill in your pocket” strategy should not be used if the next attack of arrhythmia caused any new symptoms:
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- facial asymmetry and so on.
In such cases, you should not stop the paroxysm on your own, since these symptoms may be a sign of the development of a heart attack or stroke.
If paroxysmal fibrillation proceeds as usual, the patient can take the drug propanorm at a dosage of 450–600 mg.
The patient should consult his cardiologist in advance about in what cases and in what dose to take this medicine. It is better if the first dose of propanorm is taken in a hospital, under the supervision of medical professionals.
Rapid pulse: causes, symptoms, treatment (what to do at home)
A rapid pulse is a symptom that in some cases may indicate the development of serious pathologies. Sometimes this phenomenon is observed under certain physiological conditions. Therefore, treatment for increased heart rate is not always necessary. Whether therapy is needed is determined after a series of diagnostic examinations.
Set heart rate rate
The pulse is assessed using several indicators. Frequency is the number of times the heart beats per minute. When a person sits or lies, the indicators may change.
Therefore, during the measurement process you should be in one position. Increased heart rate may be observed towards the end of the day. If the tapping is 10 units higher in the evening or in the morning, this is a variant of the norm.
Heart rate is also taken into account - this is the period of time between beats. If it is different, it means that the patient is developing an arrhythmia.
People of different ages have different heart rates. It is considered normal for children if the heart beats rapidly.
In newborns, it can reach 170 beats per minute, and this is not considered a deviation.
Over the years, the norms decrease. Therefore, in adults, the heart rate should be between 60-80 beats per minute. Exceeding the norm is called tachycardia, and lower levels are called bradycardia. In some situations, being rejected should not be a concern.
When there is a constant increase in heart rate, it is necessary to undergo examination and treatment.
What causes the problem
An increase in heart rate can be caused by physiological and pathological factors. In the first case, it is considered normal if the heart begins to beat faster:
- during physical activity;
- in the morning after waking up;
- as a result of a sudden change in body position;
- under the influence of strong positive or negative emotions;
- after eating, which is associated with the need to increase blood circulation in the organs of the digestive system.
Most people don't even notice when their heart rate increases. It should not lead to chest pain, weakness, shortness of breath and other unpleasant symptoms. If there is no discomfort, the problem does not pose a health hazard.
A rapid pulse is observed in children and adolescents. If the baby feels good, then everything is fine.
Idiopathic forms of tachycardia are also observed, in which increased heart rate is associated with the characteristics of the human body. Deviations in such cases are insignificant and do not exceed 15 beats per minute. This condition does not require treatment.
Also, due to the increased load on the body, tachycardia is observed in women in the last stages of pregnancy.
There are certain factors that cause the heart to beat faster. It happens:
- with insomnia or if a person has a nightmare at night;
- as a result of the use of narcotic substances and aphrodisiacs;
- during treatment with antidepressants or drugs to stimulate sexual activity;
- with constant stress and overwork;
- if a person abuses alcoholic beverages;
- with excessive body weight;
- with high blood pressure;
- for acute respiratory viral infections.
A rapid pulse can also have pathological causes. Tachycardia is observed:
- In feverish states. According to research, if your body temperature rises by one degree, your heart rate increases by 10 beats.
- For disorders of the nervous system.
- In pathological endocrine processes.
- If poisoning with alcohol or toxins occurs.
- For oncology.
- If a person suffers from cachexia or anemia.
- For illnesses of infectious origin.
- With myocardial damage.
If the heart beats quickly when a person is in a calm state, this indicates a pathological process in the body. Therefore, an examination is necessary.
Possible pathologies with increased heart rate in combination with other symptoms
In addition to strong pulsation, the patient may suffer from other manifestations of the disease. It all depends on the main reason that caused this violation. Tachycardia is a symptom of many diseases. Most often it manifests itself in heart defects, dysfunctions of nervous regulation and endocrine disorders.
Tachycardia with defects
In this situation, a rapid pulse causes attacks that have clear boundaries. The patient can know exactly the time of the onset and end of the attack. The heartbeat increases in a calm state or during stress and physical activity.
At the same time, the vital organ contracts with a frequency of more than two hundred beats. The person also suffers from other symptoms. Patients usually:
- dizzy;
- fainting conditions are observed;
- noise in the ears;
- the heart feels like it’s going to jump out of the chest or there’s a pressing sensation in the chest;
- sweating increases;
- in some cases nausea appears.
Also read: How to reduce heart palpitations using folk remedies
Paroxysms are quite dangerous to health, as they can cause flutter or ventricular fibrillation. During an attack, the likelihood of developing cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest increases.
This condition requires immediate treatment, which often involves surgery.
Disturbances in nervous regulation
Various types of dystonia are accompanied by an increase in contraction frequency.
In people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia, the pulse rises to 140 beats. In this case, the heart reacts poorly to physical activity. In some cases, the health deteriorates so much that the patient finds it difficult to climb stairs or walk.
Neurocirculatory dystonia is also characterized by an increase in pulse, which can be a constant concern or occurs in attacks.
If the patient has VSD, then in addition to strong heartbeat:
- often feel dizzy and have ringing in the ears;
- worried about constant weakness and excessive fatigue;
- sweating increases;
- feeling worse in stuffy rooms;
- there is constant anxiety and suspiciousness;
- I want to sleep all the time;
- mood changes suddenly;
- hot and cold flashes bother you;
- sometimes panic attacks and obsessive states are observed.
In the case of pronounced symptoms, dystonia is difficult to distinguish from neurosis or psychosis.
Various manifestations indicate that neurocirculatory dystonia is developing:
- hands and feet are constantly cold;
- the skin turns pale;
- a person gets tired quickly;
- headache and dizziness;
- pressure in the arteries increases or decreases.
These pathologies are eliminated depending on the manifestations. The patient's condition should be monitored by a neurologist and cardiologist.
Endocrine disorders
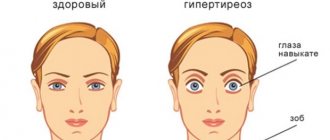
Rapid pulse and heartbeat always accompany hyperthyroidism. In this condition, the thyroid gland produces more hormones than it should. In this case, tachycardia becomes permanent. The pulse reaches 120 beats. The heart rate does not slow down even when the person is sleeping. The pathological condition is recognized by:
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland;
- large difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area;
- increased appetite due to sudden weight loss;
- increased sweating;
- irritability and fatigue;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle, breast enlargement, potency problems in men;
- increased blood sugar;
- increase in liver size.
An endocrinologist should treat such problems.
In rare cases, a persistent increase in heart rate occurs with hypothyroidism.
Methods for lowering heart rate
You can get rid of an attack of increased heartbeat by coughing, pinching, or blowing your nose. It is also useful to wash your face with cold water. There are other methods to solve the problem:
- Take a deep breath and hold your breath for a few seconds, then exhale slowly.
- You can easily massage the carotid artery.
- Some medications help. In such situations, Valocordin or Corvalol. 20-30 drops are enough.
Medical assistance for a rapid pulse is necessary if these methods do not help improve the condition and the patient’s well-being quickly deteriorates.
Diagnostics in the clinic
To identify the cause of pulse deviation from the norm, doctors prescribe a series of diagnostic examinations. If you have an elevated pulse and other unpleasant symptoms, you should visit a medical facility. After an external examination and medical history, the doctor will conduct the necessary studies.
To determine what caused the development of tachycardia they resort to:
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography;
- Holter monitoring;
- ultrasound examination of the heart, liver, thyroid gland;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- urine examination.
After studying the examination results, the doctor will determine the cause of the deviation and select the appropriate option to eliminate the problem. Only if the influence of the provoking factor is eliminated can normalization of heart function be achieved.
Treatment Options
An increased heart rate is a treatable problem. Methods for eliminating the disorder depend on the underlying disease. Conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
Depending on the problem, heart disease can be treated using:
- statins;
- antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants;
- nitrates;
- beta blockers;
- immunomodulators;
- antifungal, antiviral or antibacterial agents;
- cardiac glycosides;
- B vitamins;
- multivitamin complexes.
If a person is diagnosed with a heart defect, they resort to surgical treatment. For arrhythmias, radiofrequency ablation is used. The operation option is selected taking into account the disease, the patient’s age, and the individual characteristics of the body.
To avoid such violations, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid the negative influence of provoking factors, undergo timely treatment for pathologies of internal organs, and regularly undergo preventive examinations.
Source: https://KardioPuls.ru/bolezni/ritm/uchashchennyy-puls/
Algorithm of emergency care for atrial fibrillation
Emergency care during an attack of atrial fibrillation (AF) is provided by a linear ambulance team, or less often by a cardiac team. In any case, it is first recommended to administer a “blood thinning” drug, for example, heparin, then the algorithm of actions will depend on the general state of health and the severity of the attack.
After assessing the patient’s condition, ambulance doctors can apply one of three treatment tactics:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs
- Cardiac glycosides
- Electropulse therapy
Antiarrhythmic drugs (cautious tactics)
Normalizing the pulse rate without stopping the attack is a “cautious tactic” that is used when the patient’s condition is unstable – low blood pressure, the duration of the attack is more than 48 hours, the first episode of atrial fibrillation, shortness of breath at rest, fever. Depending on the heart rate, the patient is given antiarrhythmic drugs and, if necessary, antishock drugs, and hospitalization is suggested. If the pulse rate is from 60 to 100, the patient may not be hospitalized; in this case, on the same or the next day he is visited by a local therapist (he is called by the ambulance team).
Cardiac glycosides (drug treatment)
For drug relief of an attack, cardiac glycosides are used, as well as one of 2 antiarrhythmic drugs, primarily these:
- Cordarone;
- Sotalol.
It is also advisable to administer sedatives and sedatives. Novocainamide is now rarely used to relieve an attack of atrial fibrillation due to its side effects. If the paroxysm is stopped, the patient usually remains at home.
Electropulse therapy (emergency care)
Electrical pulse therapy for paroxysmal AF is a type of emergency treatment used by emergency cardiac teams for urgent indications, for example, arrhythmic shock. In this condition, due to a sudden rhythm disturbance, the contractility of the heart sharply decreases, which leads to a significant decrease in pressure and oxygen starvation of the brain. In this condition, transporting the patient to the hospital is life-threatening, so doctors use electropulse therapy. The method involves applying one or more electrical discharges to the heart area, restoring normal heart rhythm. Before this, the patient is given intravenous painkillers and sedatives.
Pathological factors
There are not many of them. It is possible to distinguish a pathogenic process from a relatively harmless condition through diagnosis.
If no organic pathologies are identified, it makes sense to work through the problem with a neurologist and psychotherapist.
Interesting:
You can try to distinguish one from the other based on the clinical picture: with physiological deviations there are almost no symptoms, and if there are, they are short-lived.
What are we talking about:
- A stressful situation that develops over a long period. For example, the moment before an exam or a public speaking. The body mobilizes and produces more specific hormones: catecholamines and corticosteroids. Hence tachycardia and increased blood pressure, as well as other autonomic symptoms. No treatment is required, everything returns to normal after the stressful situation ends.
- Psychological overload, nervous breakdown or shock. It develops like a snowball; the body simply cannot stand it. The pressure jumps sharply, the heart rate rises to significant levels, up to 110-150 beats per minute, the patient falls into a stupor or completely loses consciousness for a short period. Autonomic manifestations are obvious, clearly visible even to a person without medical education: tachycardia, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, pallor of the skin, sweating, affective manifestations (laughter, tears, inhibition of thinking, anger or irritability). Therapy is carried out with sedatives or tranquilizers until the condition stabilizes.
- Too much tonic. This can be either harmless coffee or cocaine with heroin, which also cause persistent tachycardia. The difference is in the duration of the effect: when consuming the first, the heartbeat continues for 2-4 hours, while drugs cause persistent deviation for 12-24 or more hours, and we are not talking about the effect of opiates, but as a result of the influence of harmful impurities of homemade street psychoactive substances . Treatment in the second case is urgent, with detoxification and neutralization of the harmful effects.
- Moving to a damp or humid climate. At the same time, it is not necessary to move anywhere; unfavorable weather conditions can come on their own. This is especially noticeable in the summer months in regions with a harsh continental climate. The entire central zone of Russia is like this. Heavy weather is difficult to bear, you need to move less, drink more and better not go outside.
- Nightmares. They differ from other processes in their short duration. Autonomic symptoms cease to exist as quickly as they appeared. Within 2-5 minutes. No specialized medical care is required.
In 30% of cases, a pulse of 110 means that there are physiological deviations as a result of the subjective controlled actions of the patient himself or the influence of external stimuli. Correction is almost never required.
They occur much more often. Possible diseases include:
- Diabetes. Systemic endocrine condition. Requires lifelong therapy. In the early stages, it is difficult to identify; there is often a latent course: the patient can walk with the problem for years; it is discovered by chance or when it is too late for a total correction. You need to pay attention to the following manifestations: sudden attacks of hunger, tremors (shaking hands), pallor, weakness in the legs, fainting. Objectively, glucose does not always increase; you need to examine the sugar curve throughout the day. The heart and blood vessels suffer “for company”, diabetes affects all organs and systems.
- Problems with blood circulation in the brain. The result of osteochondrosis and compression of the arteries feeding the cerebral structures. The normal regulation of cardiac activity at the level of the central nervous system is disrupted. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist.
- Hyperthyroidism. Excessive production of thyroid hormones as a result of poor nutrition, natural factors, and the development of tumors. Accompanied by increased body temperature, headaches, shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, inability to sleep, bulging eyeballs, changes in the relief of the neck (goiter), and mental disorders of a depressive-affective nature. Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
- Hypercorticism. Another pathology of the same profile. The concentration of adrenal hormones, primarily cortisol, only increases. Secondary Itsenko-Kushang disease occurs with sudden weight gain, uneven fat deposition, destruction of the spine and entire skeleton, and mental problems. Often results from a tumor of the adrenal gland or pituitary gland. Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist and neurosurgeon.
- Violations from the heart itself. As a result of irritation of the third reflex zone of the organ, the heart rate accelerates. The assessment is carried out by a cardiologist. Despite the variety of diseases, their symptoms are almost the same: chest pain of a pressing nature, radiating to the arms and back, shortness of breath even at rest, especially after physical activity, sweating, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, pallor of the dermal integument, fatigue, arrhythmias ( not only by type of tachycardia). Mandatory electrocardiography is carried out, and, if possible, stress tests.
- Vascular diseases. First of all, atherosclerosis, with narrowing or blockage of the lumen by cholesterol plaque. Lipid deposits grow radially, along the entire diameter of the blood supply structure, making it more difficult for blood to overcome resistance. That's why the heart speeds up. This is the only visible symptom. Another, less obvious one is increased blood pressure.
- Panic attack, affective disorders. Psychotherapeutic problems.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Bones of the facial skull - SKULL BONES - SKELETAL SYSTEM - MUSROMOTOR SYSTEM - ATLAS OF HUMAN ANATOMY
A pulse of 107-112 beats per minute is the result of hemodynamic and endocrine pathologies. Often in the system. Therefore, treatment is carried out under the supervision of a group of doctors of different profiles.
Pulse life-threatening
If the pulse exceeds the maximum values, the person’s heart may simply stop. Even at 120 beats/minute, most people no longer feel very good, what can we say about values of 190-200. Despite the fact that heart rate indicators are individual, there are certain values that are considered critical.
Most often, the pulse goes through the roof in athletes. In the midst of training, not many people pay attention to this and end up with serious injuries. The record for the maximum heart rate in a person was 220 beats per minute. This is almost twice the normal rate, and with such a pulse, you urgently need to stop the activity and get the necessary help.
Causes of tachycardia
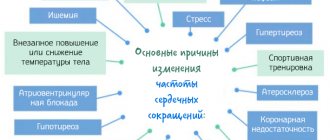
The causes of increased heart rate (tachycardia) can be physiological and pathological. Physiological tachycardia is a normal circulatory response that is caused by the following conditions:
- Physical exercise;
- Increased mental activity;
- Allergic reactions;
- Psycho-emotional agitation, fear, panic, stress;
- Increased body temperature in infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- Drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- Intoxication, including drugs;
- Dehydration – loss of fluid;
- Heatstroke – overheating of the body;
- Pregnancy.
In these cases, after eliminating the causative factor, the pulse returns to normal. Pathological tachycardia is a symptom of diseases:
- Circulatory organs (heart failure, valve defects, atherosclerosis, hypertension),
- Lungs (pneumonia, asthma, chronic bronchitis);
- Brain with a violation of the heart regulation centers (tumors, stroke, traumatic brain injury);
- Endocrine organs involved in the regulation of blood circulation (diabetes, thyroid disease, adrenal gland);
- Kidney failure;
- Anemia of various origins.
Headache with tachycardia
Headaches are a common symptom of tachycardia. The reason is the development of oxygen starvation of the brain - hypoxia. This can be due to nervous and physical fatigue, stress, acute illnesses with increased body temperature, and various intoxications.
In parallel with the pain, a decrease in hearing and visual acuity may occur.
There are many pathological causes - diseases of the circulatory system, endocrine organs, kidneys. If the cause of the condition is known, you need to take all measures to eliminate it, normalize sleep, rest, nutrition, and get rid of bad habits. If headaches and tachycardia are persistent and little dependent on external factors, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
What to do if your heart rhythm is abnormal
Physiological arrhythmias do not require a course of therapy. It is enough to avoid the causative factor. Pathological forms are treated by eliminating or stopping the underlying cause. Regardless of the type of failure, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist for an examination, the results of which will make a diagnosis.
If you have bradycardia, you will need to take medications that stimulate your heart. It is advisable to combine them with folk remedies based on medicinal herbs. You can increase your heart rate during an attack through light physical activity, caffeine, Zelenin drops and tablets based on belladonna extract.
Rest in a well-ventilated area will help reduce the frequency and intensity of your heartbeat. Before doing this, it is advisable to wash your face with cold water and remove clothes that are constricting the neck area. Additionally, you can do breathing exercises and take valerian tincture.
In both cases, nutritional correction, exercise and walks in the fresh air are recommended. If the attack cannot be stopped and the symptoms increase, then you need to call an ambulance. Visiting specialists must be told about the measures taken to alleviate the condition.
All people who want to avoid diseases of the cardiovascular system should know the normal heart rate by age. Deviations from acceptable limits may be physiological or pathological. In the first case, treatment is not prescribed. It is enough for the patient to learn about methods of stopping attacks. The course of treatment for a pathological abnormality in the heartbeat is aimed at eliminating the causative factor.
Usually, with psycho-emotional and physical stress, the heart rate increases. This phenomenon is considered normal in such cases and goes away on its own. But sometimes an increased heart rate indicates problems with a person’s health, primarily with his cardiovascular system.
Maximum allowable heart rate during sports
A high heart rate is considered to be more than 100 heart beats per minute at rest. What is the maximum heart rate for a person who plays sports? This figure can be found by calculating your heart rate using one of the formulas given above. It is best not to exceed this indicator under any circumstances.
Why is heart rate so important during sports? Heart rate affects the performance of exercises. If you follow a diet, go to the gym regularly, but do not see any changes, then you should pay attention to your pulse. Many exercise machines have special heart rate monitors that read information and display it on the screen. The program adjusts your heart rate to your target and warns you if you go beyond the heart rate zone.
A person’s maximum heart rate during physical activity can also be determined by smart bracelets and watches. They are fixed on the wrist and read the number of beats per minute. They can also be used in everyday life to monitor your health. Many reasons can prompt a person to monitor their heart rate.
Both during sports and in everyday life, it is important not to exceed the maximum values. The current record for the maximum heart rate in humans is 220 beats per minute. A too fast heartbeat wears out the heart muscle and can lead to various pathologies, including death. Therefore, it is important not to reach such values.
Pulse before death of a sick and healthy person
The functioning of the cardiovascular system directly affects a person’s overall well-being. Increased or decreased heart rate can be a harbinger of various diseases and lead to a critical condition. Therefore, it is necessary to know what the pulse is at death.